Community grazing management [Namibia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Ibo Zimmermann
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Omarisiro wovinamuinjo motjimbumba
approaches_3050 - Namibia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
land user:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Southern African Science Service Centre for climate change and Adaptive Land management (SASSCAL)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Conservation Agriculture Namibia (Conservation Agriculture Namibia) - NamibiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Zakumuka Producers Co-operative (Zakumuka Producers Co-operative) - Namibia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies
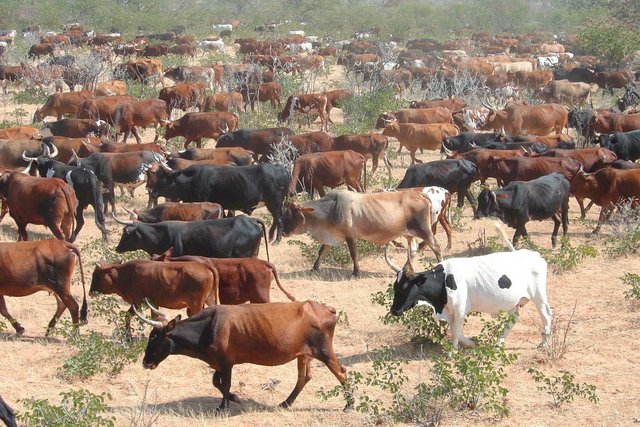

Combined herding for planned grazing [Namibia]
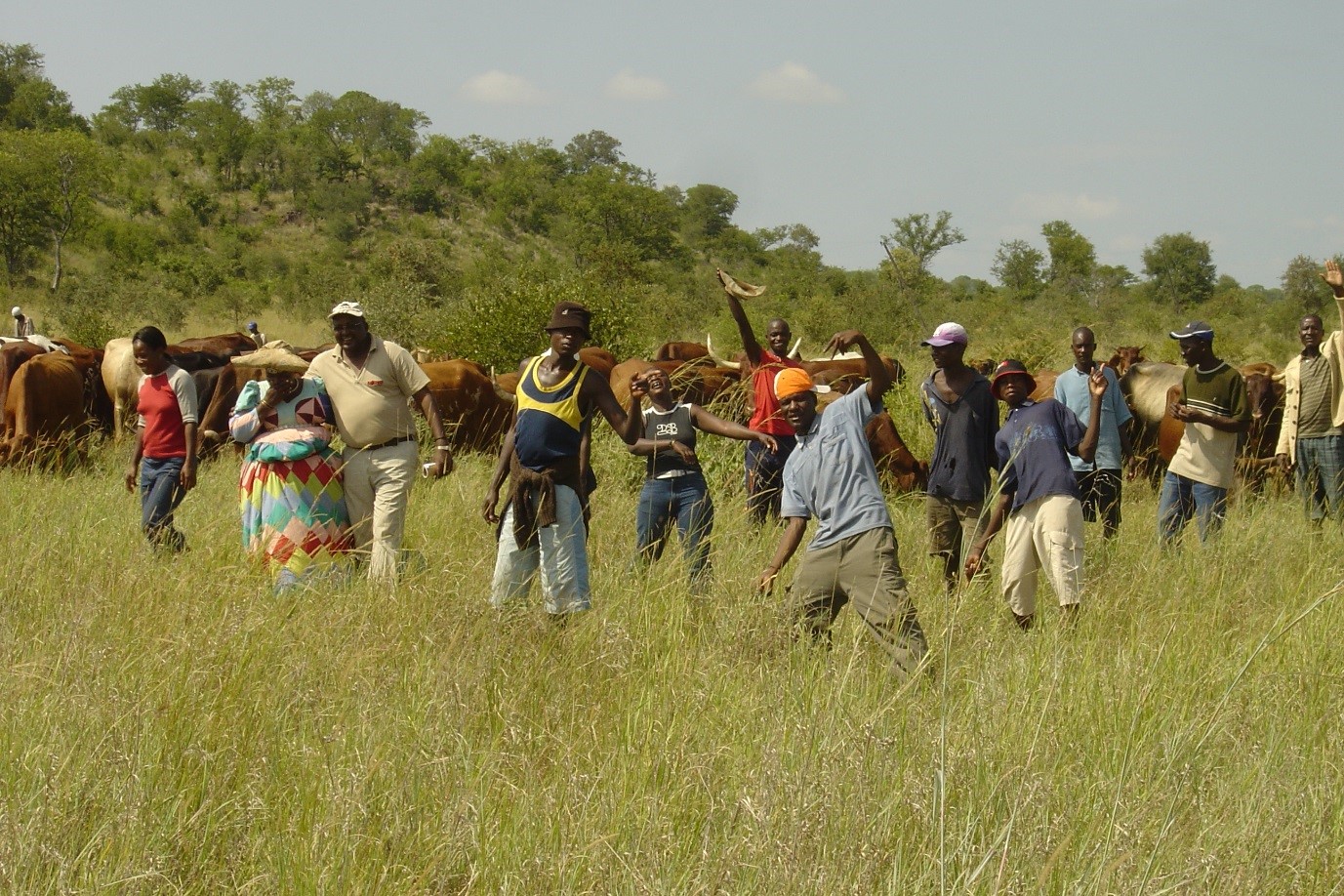
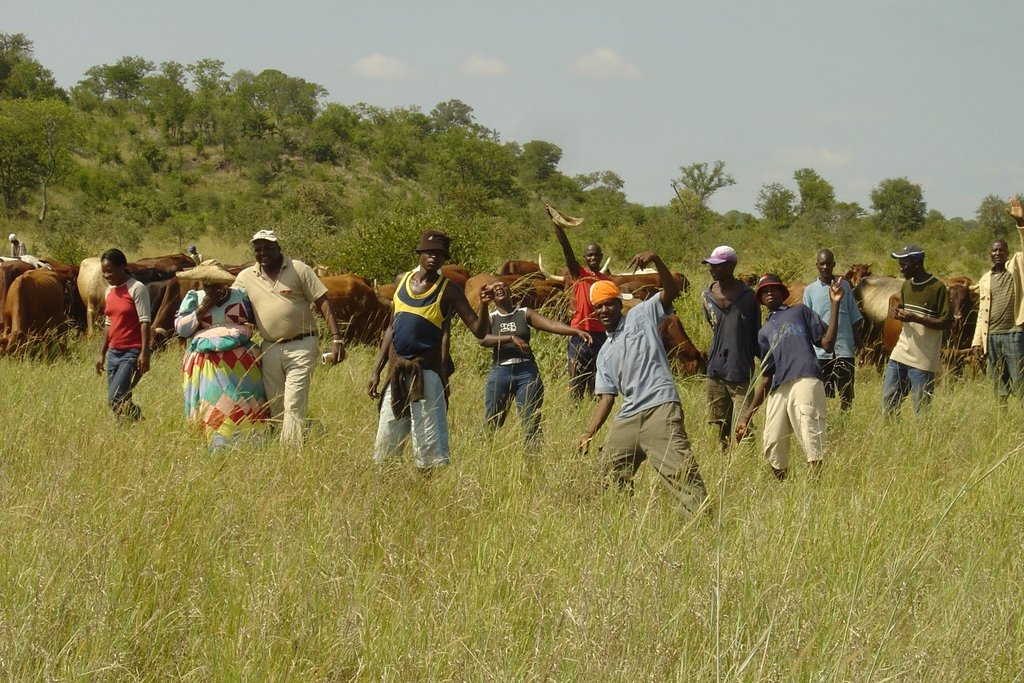
Daily combining of livestock from all households into a single herd to be driven to different designated portions of the communal grazing area. Grass can then recover by replenishing its reserves before being re-grazed some months later.
- Compiler: Ibo Zimmermann
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
Agreement among community members to jointly manage their communal grazing area by combining their livestock into a single herd. The herd is managed and moved according to an agreed growing season plan that provides sufficient recovery for perennial grasses, and a non-growing season plan to graze in a way that prepares soil and plants for the next season. Regenerating rangeland productivity and well-being is the goal.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
The approach is a partnership between an NGO, Ministry of Land Reform (MLR), Ministry of Agriculture , Water and Forestry (MAWF), the National Farmers Union (NNFU), traditional authorities, and regional and local government. The NGO raises awareness among the community about the damage caused to the rangeland by individual herds of livestock grazing continuously – and to appreciate the benefits of planned grazing. Livestock owners invite facilitators to compare the current state of their land with that of the past. The reasons for the decline are investigated. Once livestock owners understand that perennial grasses need recovery, they soon conclude that their management caused the loss of perennial grass and the increase in bare ground. At this point, the aim of the approach can be pursued. This is to regenerate rangeland productivity in the communal grazing area and thereby support higher livestock production. This in turn supports livelihoods.
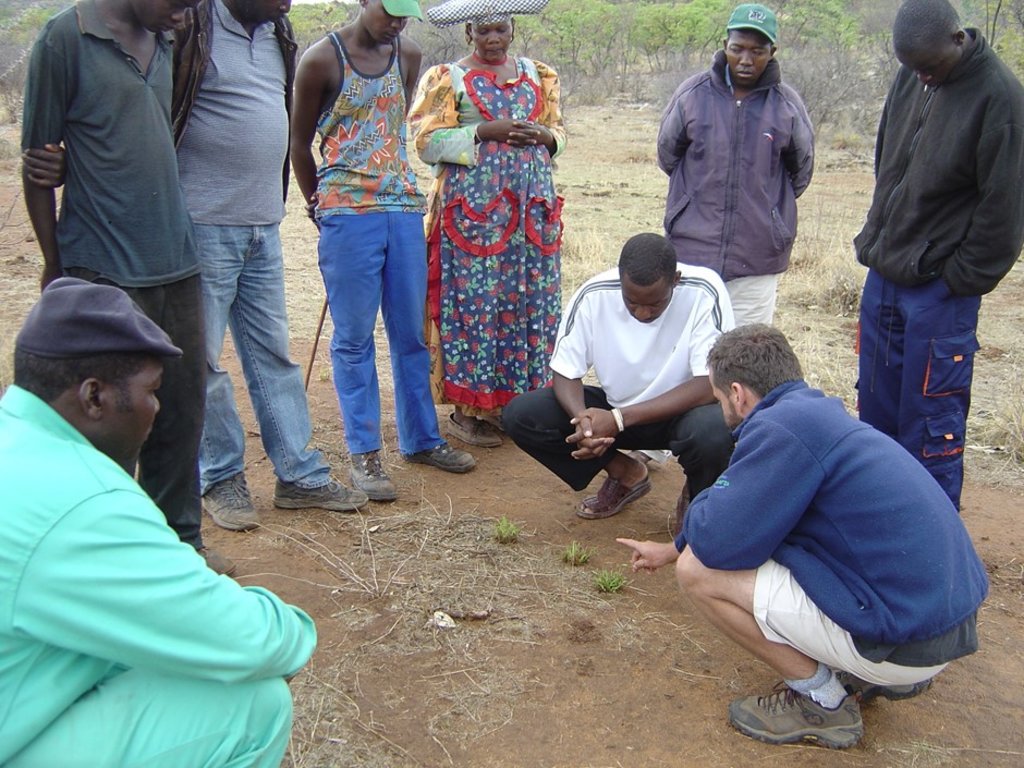
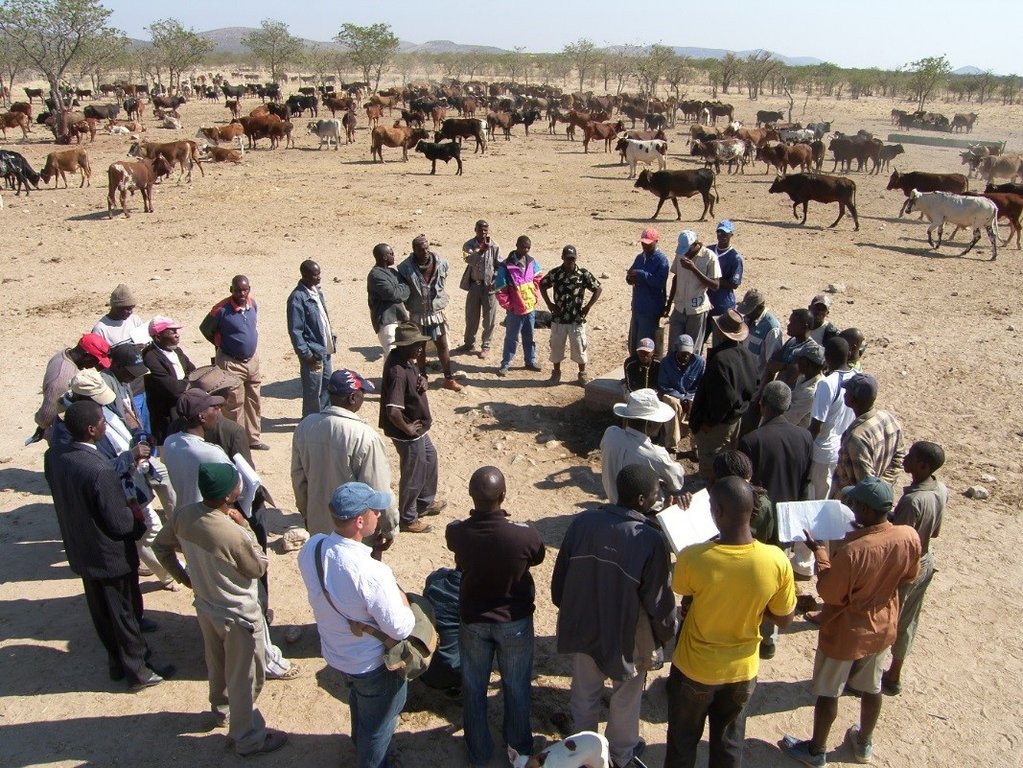
If motivation to apply planned grazing exists among the community members, then their right to claim common property ownership needs to be established. In pioneering communities this requires at least 10 village level livestock owner meetings to decide on modalities of planned grazing. These meetings continue after planned grazing has started to deal with ongoing planning, animal production and marketing. Exposure visits to areas with successful grazing management help. On return frequent follow-up meetings, facilitated by the NGO and the MAWF, can resolve local issues, including traditional taboos, such as combining animals in one kraal, and whose bulls should be kept and managed.
Boundaries with neighbouring communities need to be mapped, recognised and respected by all. In case of grass poaching, the offenders must to be swiftly dealt with, preferably through customary law. A grazing plan needs to be agreed by all livestock owners, and endorsed by the local Traditional Authority. The grazing area (GA) is then mapped, while six herders, one of whom is their manager, are appointed from among the community though common agreement. Each livestock owner pays a portion of the herding and management cost pro-rata based on the number of his livestock. At night the cattle are separated and kraaled near the homesteads of their owners. In the morning, the herders collect cattle from the kraals. Different portions of the grazing area are grazed daily and only returned to when the grass has replenished its root reserves - some months later.
The process started at Erora in 2004, facilitated by the NGO, Integrated Rural Development and Nature Conservation (IRDNC). Implementation began in 2006, combining approximately 1200 cattle from 12 households. Livestock owners noticed a higher density of annual grasses after the first season; dramatic improvement in soil cover after three years with emergence of grass seedlings where none had grown for decades. Then after another three years, perennial grasses returned with increased biodiversity in many parts. However, when the extended drought started in 2011, planned grazing was interrupted and gullies expanded, down which rainwater flowed, dehydrating the rangelands. The drought lasted for five years, and the planned grazing was temporarily discontinued in 2013. During this period, rehabilitation work included constructing bush filters along key gullies: facilitation was taken over by another NGO, Conservation Agriculture Namibia (CAN). After successive years of severe drought, cattle became too weak to be rounded up, and in 2014 the community members decided to revert to keeping cattle near their homesteads. This was intended to be temporary but cattle only gained sufficient strength in 2017. The communal grazing management approach was extended to other villages in 2012, despite the drought. New boreholes were drilled and installed to facilitate improved planned grazing.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.4 Videos of the Approach
Comments, short description:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=xNyFkDUH6MQ
This video is from a DVD created by the Integrated Rural Development and Nature Conservation (IRDNC), a Namibian NGO and co-sponsored by the Namibian Ministry of Agriculture and the Namibian National Farmers Union. The video documents the development of a rangeland program focused on Holistic Management, spearheaded by Colin Nott, a Holistic Management educator.
Date:
2007
Location:
Erora, Namibia
Name of videographer:
Andrew Botelle
Comments, short description:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Ey5v40KtkI
Combined herding to manage communal grazing with the use of stress-free handling of cattle,
Date:
2007
Location:
Erora, Namibia
Name of videographer:
Andrew Botelle
Comments, short description:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=6C4V_Cib8ts
Managing water flow to repair gully erosion
Date:
2015
Location:
Namibia
Name of videographer:
Andrew Botelle
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Namibia
Region/ State/ Province:
Kunene Region
Further specification of location:
Erora village, 18.32637 South, 14.05912 East
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2004
Comments:
Combined herding was discontinued at Erora in 2013 due to extreme drought, which ended in 2016/2017 rainy season, and land users are planning to use reserved grazing, whereby cattle are taken out each day by herders and left there to return on their own to water points. In the meantime, combined herding has already resumed at the Outokotorua grazing area.
2.7 Type of Approach
- Science informs the traditional practice
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
To regenerate rangeland productivity for supporting livelihoods and improved quality of life.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
social/ cultural/ religious norms and values
- enabling
Herding is customary, and the task is now shared among families
- hindering
Herding no longer carries the high social status that it had previously.
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- enabling
No bought inputs are required, and fewer herders needed than with many small herds. Also fewer losses from stock theft and predators
institutional setting
- enabling
A grazing area committee was established with support of livestock owners
- hindering
The grazing area committee is not legally recognised
collaboration/ coordination of actors
- enabling
Partnership approach with MLR, Ministry of Agriculture, Water and Forestry (MAWF) the NNFU, traditional authorities and regional and local government.
- hindering
Resolution of local issues to apply grazing plans needs to be resolved
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- enabling
National Policy and strategy is in place which supports sound management principles
- hindering
Grass poaching by neighbouring communities is not adequately dealt with by the law
policies
- enabling
The approach is based upon the Namibia National Rangeland Management Policy and Strategy
- hindering
Common property rights are insufficiently promoted
land governance (decision-making, implementation and enforcement)
- hindering
Lack of integration of different scales of management between conservancies at large scales and grazing areas at smaller scale is required
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- enabling
The awareness exists among participating livestock owners and stakeholders
markets (to purchase inputs, sell products) and prices
- enabling
The Namibia National Farmers Union is busy addressing markets north of the veterinary cordon fence, which maintains a zone free of foot-and-mouth disease to the south from where farmers are able to access the lucrative EU market
- hindering
During drought the drop in prices from sudden increase in supply, results in inability of farmers to sell livestock when sudden shortage of forage occurs
workload, availability of manpower
- enabling
Fewer herders are required for one large herd than for many small herds
- hindering
The role of herders as rangeland managers lacks status and is not adequately appreciated, resulting in high turnover of trained herders and their manager.
other
- hindering
One large livestock owner at a given place can hinder efforts of the majority to improve rangeland management
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
Communities of Erora, Outokotorua and Nsindi
To organise, plan and implement
- community-based organizations
Grazing Committee
Oversee day to day implementation
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
Integrated Rural Development and Nature Conservation (IRDNC), then Conservation Agriculture Namibia (CAN) and Namibia National Farmers Union (NNFU)
To facilitate adoption and upscaling of the approach
- researchers
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)
To assess rangeland condition changes
- NGO
First IRDNC, then CAN
To facilitate the approach
- private sector
Zakumuka Producers Cooperative
To organise auctions for sale of livestock
- local government
Traditional authorities
To support and enable agreed rules
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
Namibian Ministries of Lands & Agriculture
Assist with facilitation and support
- Farmers union
Namibia National Farmers Union
Enabling policy and legislation
If several stakeholders were involved, indicate lead agency:
Integrated Rural Development and Nature Conservation (IRDNC), taken over in 2014 by Conservation Agriculture Namibia (CAN)
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | The community, with focus on livestock owners, youth, women and herders, under facilitation by NGO by conducting exchange visits to neighbouring countries |
| planning | interactive | Feedback was given to communities by participants of exchange visits, grazing committees appointed to contextualise and re-plan for the way forward under guidance of NGO, Ministry of Agriculture, Water and Forestry (MAWF) and Namibia National Farmers Union (NNFU) |
| implementation | interactive | The grazing committee, livestock owners and herders carry out the grazing plan with support of NGO, MAWF and NNFU |
| monitoring/ evaluation | interactive | The grazing committee and livestock owners constantly plan and replan and evaluate results on livestock performance and rangeland and daily check where livestock have grazed and where they will graze next and feed results into re-planning. Annual assessments of forage in May, to determine stocking rate. |
| external assessment of data | external support | External assessment by researchers of data gathered by USDA through Innovations for Poverty Action (IPA) |
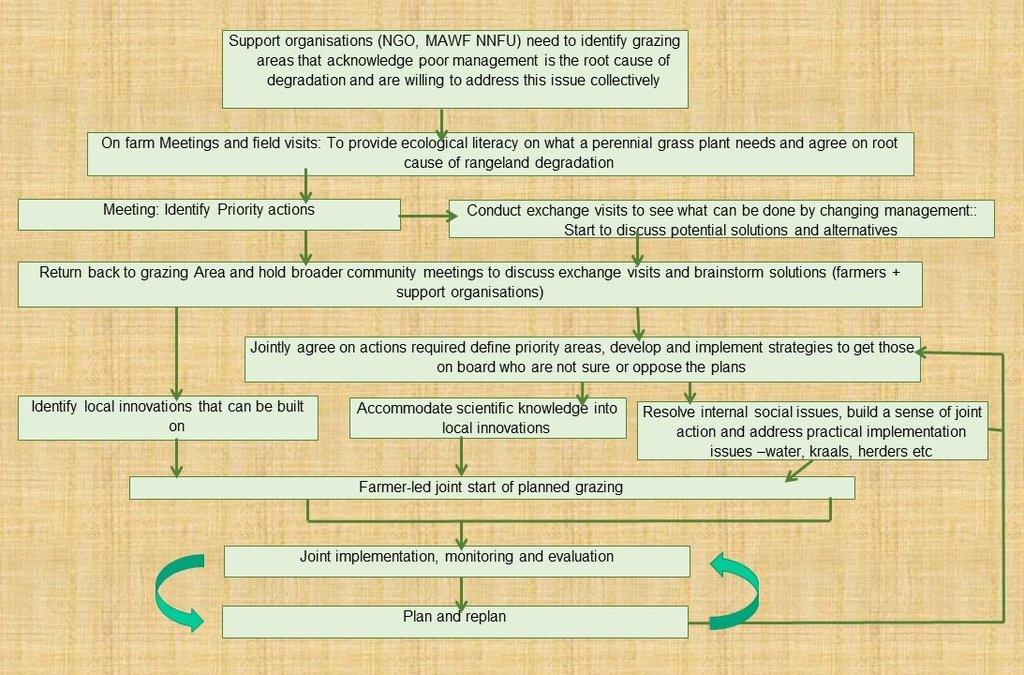
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
Description:
Flow chart of the process to facilitate community grazing management.
Author:
Colin Nott
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
Explain:
After exposure to sound management techniques and on farm identification and agreement on the root cause of the degradation – the farmers themselves decide if they will continue or not.
Specify on what basis decisions were made:
- evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
- personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
Specify who was trained:
- land users
- field staff/ advisers
- Ministry of Agriculture, Namibia National Farmers Union.
If relevant, specify gender, age, status, ethnicity, etc.
Inclusion of youth, women and herders.
Form of training:
- on-the-job
- farmer-to-farmer
- public meetings
Subjects covered:
On farm(s) exploration of root cause of degradation based on how it was in the past and how it looks now and why this change has happened.
Comments:
A number of issues including: Rangeland management, focussing on the needs of grass plants and soil. Needs of herders, people and stakeholders and how these various needs can be met. Institutional support for grazing committee, focussing on budgeting and financial management.
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
- Visits to successful farmers
Describe/ comments:
Mostly through exchange visits, community meetings, on farm excursions and on-the-job training.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, greatly
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
- regional
Describe institution, roles and responsibilities, members, etc.
Grazing Committee guides and implements the grazing plans and support organisations including Ministry of Agriculture, Namibia National Farmers Union and NGOs provide support and advice.
Specify type of support:
- capacity building/ training
- equipment
Give further details:
Exchange visits, facilitation of meetings and on-the-job training. Drilling and equipping of boreholes. Redesign of water supply for livestock and combined kraaling system.
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
Comments:
To support decision making
If yes, is this documentation intended to be used for monitoring and evaluation?
No
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Yes
Specify topics:
- sociology
- economics / marketing
- ecology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
USDA/IPA came to evaluate rangelands and consult key stakeholders
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
Indicate the annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach in US$:
10000.00
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- 10,000-100,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Major donor to initiate the project was Enagelica Entwikelins Diens (EED), through IRDNC and later funding came from the Millenium Challenge Account (MCA), the EU and now the Finnish Embassy through CAN. Cost is per grazing area for local level field facilitation.
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify type(s) of support, conditions, and provider(s):
Upgrades of boreholes, drilling and equipping of new boreholes that are elephant-proof and construction of lion-proof kraaling was funded through the NGO.
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- labour
| To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|
| partly financed | Part payment to herders 2004-2007 in Erora only |
- other
| Other (specify) | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| Boreholes and kraals | partly financed | Erora upgrade USD 10 000, second solar borehole half funded by community USD 10 000. Lion proof kraal funded by Africat – USD 2 000 |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- paid in cash
Comments:
Only for first four years at one of the villages to enable proof of concept to be established.
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
5.5 Other incentives or instruments
Were other incentives or instruments used to promote implementation of SLM Technologies?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach empower local land users, improve stakeholder participation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Through the whole approach.
Did the Approach enable evidence-based decision-making?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Through observations by herders and livestock owners.
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Combined herding through planned grazing.
Did the Approach improve coordination and cost-effective implementation of SLM?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Key stakeholders are all involved.
Did the Approach mobilize/ improve access to financial resources for SLM implementation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Did the Approach improve knowledge and capacities of land users to implement SLM?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Training provided the skills to self organise and implement activities based upon identification of root cause of land degradation.
Did the Approach improve knowledge and capacities of other stakeholders?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Ministries of Agriculture and Lands.
Did the Approach build/ strengthen institutions, collaboration between stakeholders?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Key stakeholders are all collaborating, since the solution to rangelands cuts across various sectors.
Did the Approach mitigate conflicts?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Reinstated sense of community
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Women-headed households now have their livestock herded communally.
Did the Approach improve gender equality and empower women and girls?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Women-headed households now have their livestock herded communally.
Did the Approach encourage young people/ the next generation of land users to engage in SLM?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Herders are mainly youth and young livestock owners, who appreciate improved rangeland and are now willing to remain.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The willingness to address appropriate land rights may initiate resolution of land issues.
Did the Approach lead to improved food security/ improved nutrition?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Much during good rains and little during drought.
Did the Approach improve access to markets?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Did the Approach lead to improved access to water and sanitation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Access to borehole water was provided.
Did the Approach lead to more sustainable use/ sources of energy?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Solar installations were installed or replaced diesel where possible for pumping of water.
Did the Approach improve the capacity of the land users to adapt to climate changes/ extremes and mitigate climate related disasters?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Improved grass growth in good rain years and improved survival in drought.
Did the Approach lead to employment, income opportunities?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Herders and managers were appointed.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- increased production
Increased grass, higher calving and reduced mortalities.
- increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
Increased grass, higher calving and reduced mortalities.
- reduced land degradation
Changing unsustainable practices for improved resource base.
- reduced workload
Fewer herders needed.
- prestige, social pressure/ social cohesion
Social cohesion to implement joint management.
- environmental consciousness
To support the future of livestock in their area.
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- yes
If yes, describe how:
They mobilise themselves, appoint herders, do the implementation, do the planning jointly and, and only asking for some technical support.
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| By caring for the rangeland, farmers will have grass all year round and minimise effects of drought. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| It has proven to improve the resource base if applied properly. |
| It is viable and upscalable. |
| It has diverse benefits for the land user, including economic, social and environmental. |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| If a new water point needs to be developed, then funds will be required | Convince land users that by selling one or a few cattle to invest in a new water point, they will realise the returns from increased productivity within a few years. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The herding is hard work, the status of herders is perceived to be low and they are poorly compensated. |
Convince livestock owners that they can adequately afford to compensate the herders. Start national and regional vocational training in herding, grazing management, low-stress handling, animal health, rangeland management, water management and financial and farm management. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Global case studies of grazing in nature’s image, Jim Howell, 2008, 1-4392-1610-X
Available from where? Costs?
www.booksuge.com
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Community based rangeland and livestock management
URL:
https://rmportal.net/groups/cbrlm/cbrlm-for-review/namibia-community-based-rangeland-livestock-management-cbrlm-2nd-edition/view
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Combined herding for planned grazing [Namibia]
Daily combining of livestock from all households into a single herd to be driven to different designated portions of the communal grazing area. Grass can then recover by replenishing its reserves before being re-grazed some months later.
- Compiler: Ibo Zimmermann
Modules
No modules