Maize strip tillage [Switzerland]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
Streifenfrässaat
technologies_1010 - Switzerland
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
24/09/2008
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
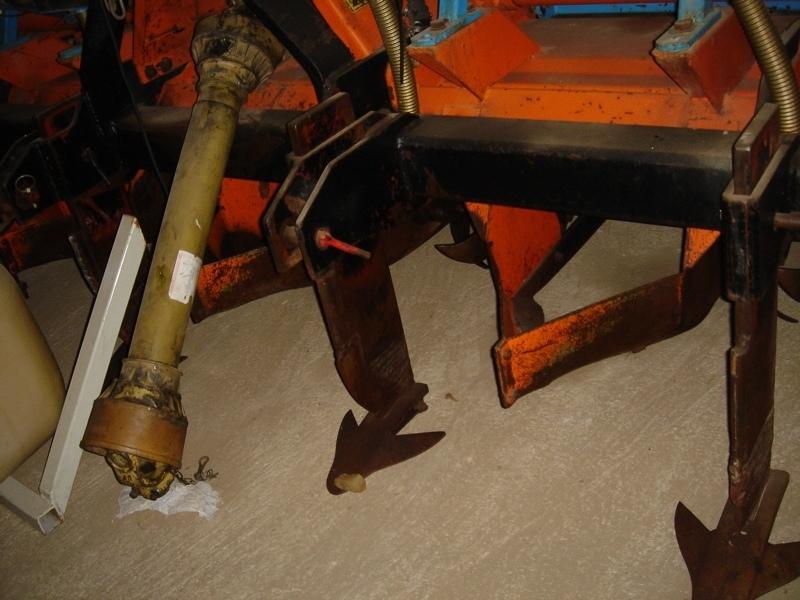
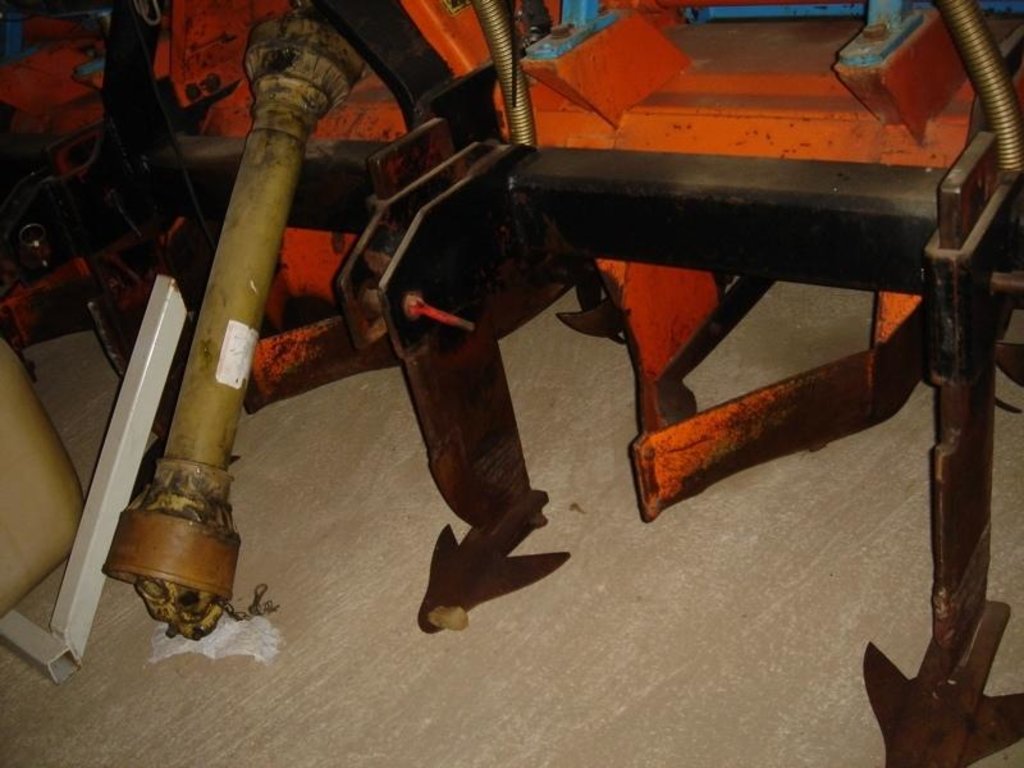
Maize strip tillage is a conservating method for corn production.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Maize strip tillage is a soil-conserving method used in crop production. First of all the grass in the area needs to be prepared by splattering round-up about 3-10 days prior to sowing.
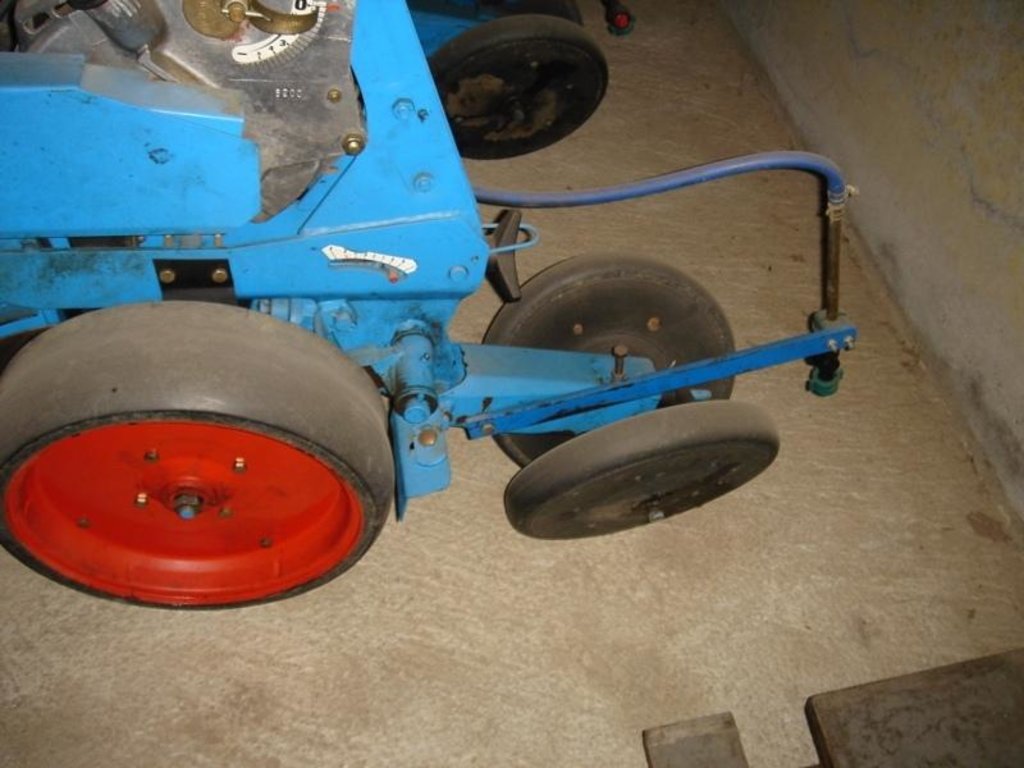
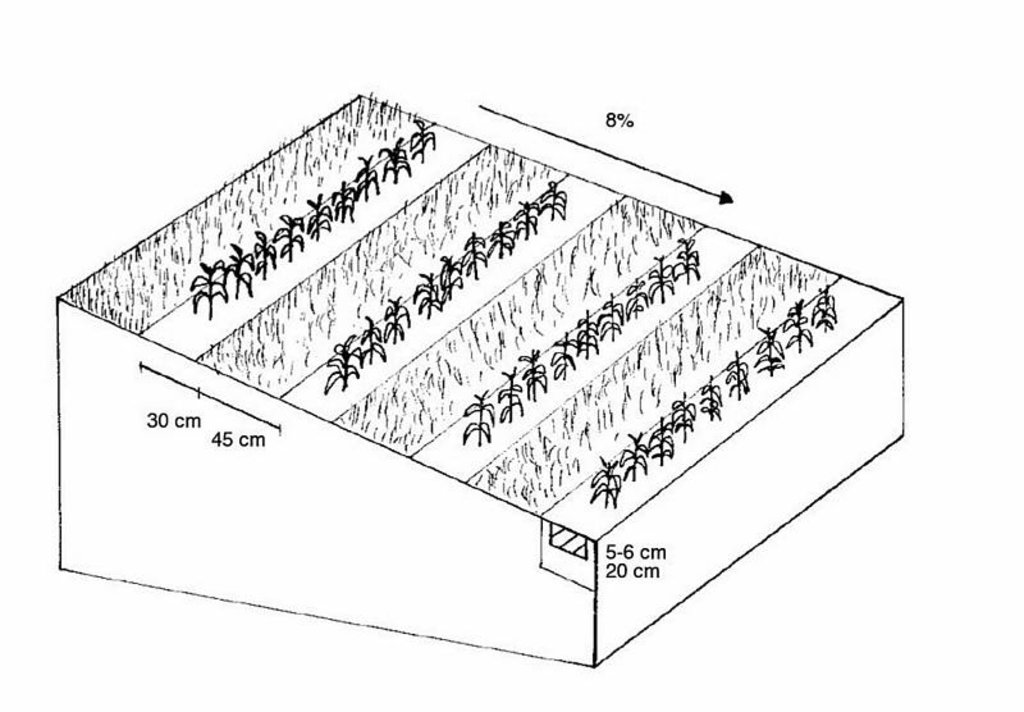
If the weather conditions are dry enough, a special grubber ('Flügelschargrupper') slacks the soil (20cm), the fertilizer is added in the stripes and afterwards the seed is added. Then the actual maize strip tillage machine carves a stripe and the seed are inserted within this strip of 30 cm. At the same time fertilizer is added on these cultivated stripes. Between those cultivated stripes the mulch-grass stripes (45cm) are unmechanised and protect the soil by increasing its stability. At the end a herbicide is applied on the cultivated strip. All working steps can be done at the same time compared to the traditional technique whereas the farmer needs to drive for each working step separately.
There are some clear economic advantages using this technology. It is less time consuming and the costs for diesel are also lower. On the other hand, by applying maize strip tillage the timing of the cultivation is very important and if the conditions are too wet, it is very likely that a farmer needs more herbicide in order to guarantee an optimal growth period.
However, like in a minimum tillage system there are some ecological advantages like enhancing soil stability. Another advantage is the better soil structure due to the mulch stripes. Due to these mulch-stripes the matrix of the soil is more complex and therefore the stability is better especially during the harvest in September. Soil compaction would occur less and the possibility of soil erosion is decreasing. Especially in hilly areas, as there are many in Switzerland, the technology is suitable since soil erosion is a problem in hilly areas when using a plough.
The interviewed farmer said that the farmers need a sound knowledge about the natural environment. Compared to the traditional technology, the farmers need to observe the corn plants carefully in order to ensure their growth period. Frthermore he said that the farmers need to get used to the sensitivity of this technology. If they are not applying the right amount of herbicide, the probability of getting a smaller harvest is increasing. If springtime is humid, the farmers should be able to use the traditional technology cause this SLM technology is only useful if the conditions are not too humid.
The interviewed farmer said that the economic advantages would be very beneficial to most of the farmers. Although the establishment costs for the machines needed for this technology seem to be high. The farmer can also hire a contractor like him and then he only needs to pay the labour but not the equipment itself. If a farmer wants to apply this technology, the canton of Bern provides them with subsidies during the initial 5 years.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Switzerland
Region/ State/ Province:
Bern
Further specification of location:
Thunstetten
Comments:
The farmer owns 35 km2 but is applying the technology on 100 km2 in the surrounding area
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
A decade ago a farmer invented the machine for maize strip tillage and the departmenet for soil conservation promoted this technology afterwards.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): If a plough is used when having a hillside situation the soil may easily erode.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The danger of erosion and soil compaction is accelareted when using a plough in a hillside area.
3.3 Further information about land use
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- minimal soil disturbance
- cross-slope measure
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 m2.
The farmer owns 35 km2 but is applying the technology on 100 km2 in the surrounding area
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (using the plough on hillside areas can increase soil erosion)
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Minimum tillage
Remarks: only where the crop seeds are inserted
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Swiss Franc
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
1.08
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
194.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying machine for stripe mill cropping | Agronomic |
Comments:
Life span of the product: 15 years
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Applying Round-up herbicide on the area | Agronomic | 1 once before corn cultivation |
| 2. | Using of the machine for maize strip tillage, seeding and fertilizing within one workstep | Agronomic | 1 |
| 3. | Appliance for herbicide (Glyphosat) | Agronomic | 1-2 |
| 4. | Harvest of the corn | Agronomic | 1 |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Establishment costs are estimated for the contractor. Labour costs indicated above are the costs which the contractor is demanding for if he is hired. Additionally, those farmers who adapt this technology can get subsidies from the Canton if the farmer commits to apply soil conservation measures during 5 years, in Bern it is 450 CHF per ha.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour costs might seem high for a farmer if he delegates the establishment to a contractor. In comparison to the traditional cultivation system the contractor would ask about $240 for ploughing , $185 for harrowing , $92 for seeding, $70 for biocide and $46 for fertilizer per ha. Therefore using maize strip tillage is almost a third less expensive than the traditional cultivation. Most of the farmers that hire the contractor are applying the biocides themselves when using maize strip tillage, which makes the costs even lower.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Average:
850-900 mm for the last 3 years
1200 mm some 10 years ago
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil texture is coarse/light (sandy) or medium (loamy, silty) (medium till light soils, depending on the area. On heavy soils technology is not applied).
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Ground water table: 5-50 m (depending on the area)
Water quality (untreted): Good drinking water (depending on the region)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- very rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Usually the women are responsible for the administration and household and the men for the actual work on the fields, assuming that the decision to implement a new technology is made by both.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
(His contract company is relatively large.).
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
Comments:
The area around the farmer house is individually owned but the surrounding agricutlural land is leased.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | well |
| local windstorm | not known |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not known |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not well |
Comments:
With the grass stripes between the corn, the water can infiltrate faster and the soil is more stable and protected. The technology can be more tolerant towards intensive rainfalls but only to a certain moment. The technology is more sensitive towards humid conditions in spring and problems can accure when trying to apply the stripe mill cropping.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: If farmers have good experiences more than 80% are maintaining this technology even without external subsidies of the Canton.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The subsidies from the Canton are very supportive for farmers to implement the new technology
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules