Plantation Sylvo pastorales [Morocco]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Mohamed Yassin
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
تحسين المراعي الغابوية
technologies_1196 - Morocco
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Alaoui Ismaili Fatma zahra
CRF-Rabat
Morocco
SLM specialist:
Babaou Yamina
CRF-Rabat
Morocco
SLM specialist:
Rahine Nabil
DPEFLCD-BENSLEMANE
Morocco
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royaume du Maroc, Haut Commissariat aux Eaux et Forêts et à la Lutte Contre la Désertification (Royaume du Maroc) - MoroccoName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Centre de Recherche Forestière de Rabat (CRF-Rabat) - Morocco1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Plantation des terres de parcours
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
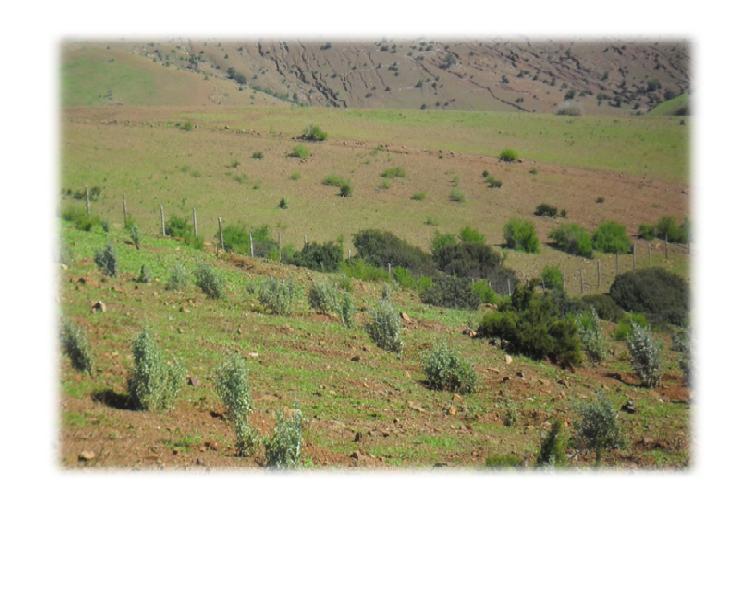
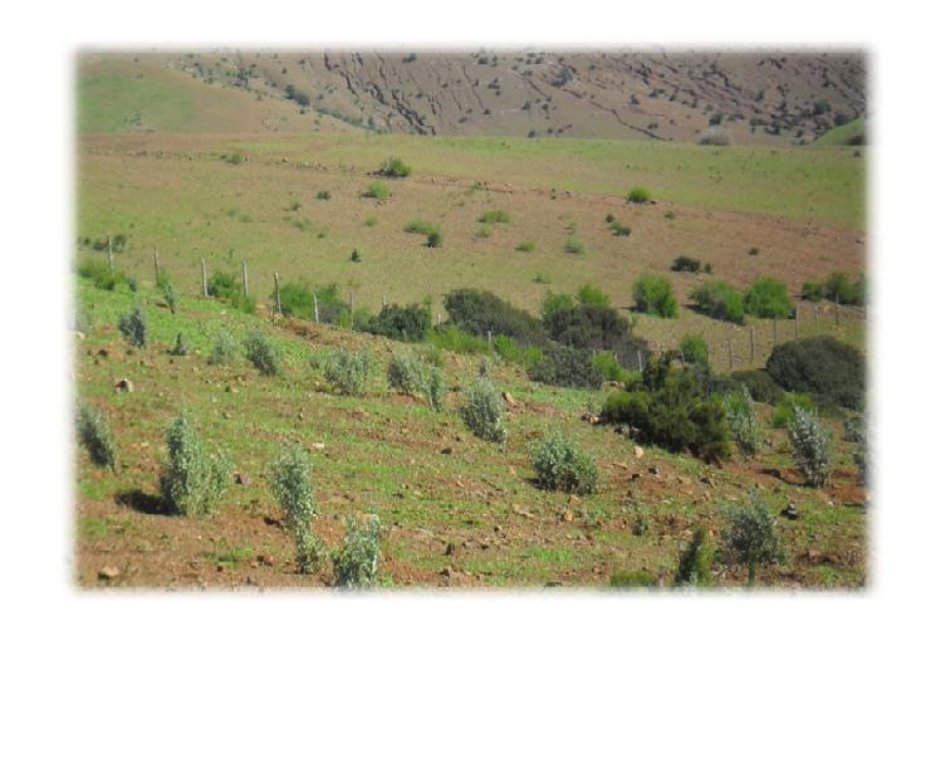
Il s'agit de plantation d'arbustes fourragères. La technologie consiste en l’intervention par des travaux de préparation du sol par ouverture de fossés continus à l’intérieur desquels sont ouverts des éléments de potets avec une densité totale de 516 ouvrages/Ha . L’opération de préparation du sol est suivie des travaux de rebouchage, plantation, et de désherbage et binage
L'augmentation du niveau de production fourragère des parcours, la lutte contre l'érosion éolienne, et la production de bois de feu pour les populations riveraines.
Il s'agit de l'ouverture de fossés continus de 0,40m X 0,40m sur une longueur de 16.000 ml. L'Ouverture d’éléments de potets de 0,50mX 0,50m X0,50m soit (36000)
L'opération de rebouchage d’ouvrage se fait avec confection d’impluviums de 0 ,60 m de rayon.
Il s'agit d'une forêt dégradée constituée principalement de lentisque.
La population est dispersée et exerçe une forte pression sur forêt par prélevement du bois de feu et pacage des animaux.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Morocco
Region/ State/ Province:
Benslimane
Further specification of location:
Chaouia Ourdigha
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- conserve ecosystem
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Grazing land
Extensive grazing land:
- Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism
Main animal species and products:
ovins, caprins et bovins

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agro-pastoralism
Main products/ services:
Culture alimentaire principale: Céreales
Comments:
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (avis du compilateur): dégradation du milieu naturel
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): Surpaturage et délits de parcours et de coupe de bois vif
Foresterie de plantation: Oui
Produits et services forestiers: bois d'oeuvre, bois de feu, pâturage / broutement, autres produits / utilisation des forêts (miel, pharmacopée, etc.), récréation / tourisme, protection contre les risques / catastrophes naturels
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Aussi pluviales-irriguées
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
La plus longue période de croissance en jours: 60; Période de croissance la plus longue de mois en mois: Novembre-decembre
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- windbreak/ shelterbelt
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comments:
La superficie totale couverte par la technologie GDT est de 0,8 km2.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits

management measures
- M7: Others
Comments:
Mesures secondaires: mesures structurelles, mesures de gestion
Spécification des autres mesures de gestion: mise en defense
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Principales causes de dégradation: surpâturage (une forte supplément d'animaux et délits de parcours), sécheresses (longue periode de secheresse et irrégularité des précipitations), pression de la population (collection de bois de feu et bois de chauffage)
Causes secondaires de dégradation: déforestation / disparition de la végétation naturelle (inclus les feux de forêts) (coupes illegales du bois), surexploitation de la végétation pour l’usage domestique (collecte de bois de feu), changement des précipitations saisonnières, pauvreté / santé (carbonisation et parcours), infrastructures et intrants (routes, marchés, répartition des points d’eau, autres)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Objectifs secondaires: prévention de la dégradation des sols, réhabilitation / remise en état des terres dénudées
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
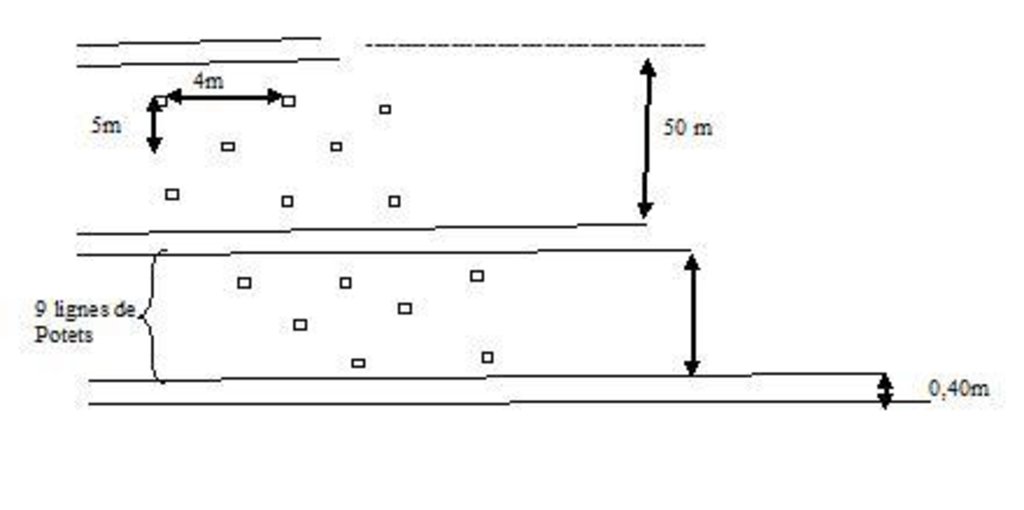
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Creusement des fossés continus séparés de 50 m entre ces fossés
Et ouverture de neuf lignes de potets
Emplacement: Périmètre oued Laatach. Benslimane
Date: Dec 2012
Connaissances techniques requises pour le personnel de terrain / conseillers: moyen
Connaissances techniques requises pour les utilisateurs fonciers: fort (le HCEFLCD délègue le marché de mise en oeuvre aux entreprises selon un cahier de charge).
Principales fonctions techniques: stabilisation du sol, augmentation de l'infiltration, augmentation de la biomasse (quantité), développement des espèces végétales et de la variété (qualité, ex : Fourrage appétent)
Fonctions techniques secondaires: contrôle du ruissellement en nappe: rétention / capture, contrôle du ruissellement en nappe: ralentissement / retard, contrôle du ruissellement en ravines: ralentissement / retardement, contrôle du ruissellement en ravines: drain / dérivation, amélioration de la couverture du sol , Amélioration de la structure de la couche arable du sol (tassement, compaction), augmentation de la matière organique, augmentation du niveau / recharge de la nappe phréatique, amélioration de la qualité de l'eau, eau filtrée / solution tampon
Aligné: -contour
Matériel végétatif: T: arbres / arbustes
Mesure végétale: aligné en quinconce
Matériel végétatif: T: arbres / arbustes
Nombre de plantes par (ha): 516
Intervalle vertical entre les rangées / bandes / blocs (m): 4
Espacement entre les rangées / bandes / blocs (m): 5
Intervalle vertical dans les rangées / bandes / blocs (m): 4
Largeur dans les rangées / bandes / blocs (m): 5
Mesure végétative: matière végétale: T: arbres / arbustes
Espèces d'arbres / arbustes: plantation d'Atriplex et cactus
Pente (qui détermine l'espacement indiqué ci-dessus): 15%
Retenue / infiltration fossé / puits, sédiment / sables
Intervalle vertical entre les structures (m): 4
Espacement entre les structures (m): 5
Profondeur des fossés / puits / barrages (m): 0,4
Largeur des fossés / puits / barrages (m): 0,4
Matériaux de construction (terre): terre
La végétation est utilisée pour la stabilisation des structures.
Changement de type d'utilisation du sol: Mise en défens pour une durée de 6 ans
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Dirham
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
100
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Préparation du sol: - Fossées contenus | Vegetative | |
| 2. | préparation du sol:- Potets | Vegetative | |
| 3. | Rebouchage | Vegetative | |
| 4. | Fourniture de plants et transport: | Vegetative | |
| 5. | transport des plants | Vegetative | |
| 6. | plantation: distribution et mise en terre | Vegetative | |
| 7. | Entretien:Desyrbage et binage | Vegetative | annuel |
| 8. | installation de cloture | Management | |
| 9. | gardiennage | Management |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Préparation du sol: - Potets | potets | 36000.0 | 3.0 | 108000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Rebouchage | ouvrage | 41333.0 | 0.94 | 38853.02 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Plantation: distribution et mise en terre | plant | 41333.0 | 1.42 | 58692.86 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Entretien: Desyrbage et binage | plant | 41333.0 | 1.07 | 44226.31 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Fourniture de plants et transport: | plant | 10333.0 | 3.4 | 35132.2 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Transport des plants | plant | 36000.0 | 0.54 | 19440.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Labour: Préparation du sol: - Fossées contenus | ml | 16000.0 | 5.5 | 88000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Labour: Installation de cloture | personnes/jour | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Labour: Gardiennage | personnes/jour | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 392524.39 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | preparation du sol | Vegetative | année 2012 |
| 2. | Rebouchage | Vegetative | |
| 3. | Transport | Vegetative | |
| 4. | plantation | Vegetative | |
| 5. | Desherbage et binage | Vegetative |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Preparation du sol | potets | 20000.0 | 3.8 | 76000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Rebouchage | potets | 20000.0 | 0.76 | 15200.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Transport | plants | 20000.0 | 0.38 | 7600.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Plantation | plants | 20000.0 | 1.14 | 22800.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Desherbage et binage | plant | 41333.0 | 0.56 | 23146.48 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 144746.48 | |||||
Comments:
Machines / outils: outils
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
L'eau; la topographie et les conditions climatiques de la zone et la main d'oeuve
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Pluies irrégulières en hivers
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Classe de climat thermique: tempéré
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Reliefs: Zones à faible pente (0-5%) s’étendent sur 53% de la superficie totale du bassin. Très accidentée et très encaissée (plus de 20%) n’occupent que 16 % de la superficie total du bassin et moyennement accidentée (5-20%) couvrant 30% se la surface du bassin ;
Zones altitudinales: L’altitude au niveau du bassin versant varie entre 0 et 962 mètres. 50 % du bassin a une altitude supérieure à 500 m et 15 % du bassin a une altitude inférieure 200 m.
Pentes moyennes:
la pente de 0-5% représente 53% du bassin versant e
la pente de 5-30% représente 39% du bassin versant
la pente de plus de 30% représente 7% du bassin versant
la pente de plus de 40% représente 3% du bassin versant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
La fertilité du sol est moyenne
Le drainage des sols / l'infiltration est bon
La capacité de stockage d'eau du sol est moyenne
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
excess
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- employee (company, government)
Level of mechanization:
- animal traction
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Les utilisateurs des terres qui appliquent la technologie sont principalement des utilisateurs de terres défavorisés
Différence dans la participation des femmes et des hommes: l'intégration de la femme dans le processus de développement rural est très limité. L'accès au crédit est fortement handicapé par le fait que le personnage est la propriété des hommes. Le mouvement associatif féminin est très en retard pour la révision aux aspérités locales.
Croissance annuelle de la population: 2% - 3%
98% des usagers de la terre sont pauvres et possèdent 100% du terrain (La petite exploitation domine l'étendue dans le milieu, sur le parc de l'exploitation des exploitations).
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
Aussi 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha et 2-5 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- individual, titled
- collectif
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Comments:
Le statut collectif est par la colonisation, comme fond potentiel de concession foncière sur des terres labourables de plaine, et moyen de mise sous tutelle des collectivités ethniques. Les terres collectives correspondent à des terres à usage tribal collectif historique qui sont restées en l'état, c'est-à-dire non transformées en un autre statut qui annulait en fait et/ou en droit l'usage collectif du terrain (melk ou domaine forestier essentiellement en montagne).
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
Perimètre mise en defens
animal production
wood production
product diversity
energy generation
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
diversity of income sources
economic disparities
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
community institutions
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
water quality
harvesting/ collection of water
surface runoff
excess water drainage
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
soil crusting/ sealing
soil compaction
nutrient cycling/ recharge
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
animal diversity
beneficial species
habitat diversity
pest/ disease control
Climate and disaster risk reduction
fire risk
Other ecological impacts
Risque pour les événements indésirables
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
wind transported sediments
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | not well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not well |
Comments:
La mise en defens permet de proteger les plants au debut pour les proteger contre le pacage abusif.
L'arrosage permet aussi de donner un coup de pousse pour augmanter les chances d'une croissance rapide des plants d'atriplex.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Amélioration de la production ligneuse et fourragère |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Disponibilité en Fourrage et en bois |
| Amélioration du couvert végétal |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Technique relativement coûteuse pour une période relativement longue (3 à 5 ans) | Proposer des alternatives aux populations usagères |
| Technique qui nécessite un apport en eau régulier | Prévoir des points d'eau |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Etude ttoba
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules