Drainage Ditches in Steep Sloping Cropland [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Erik Bühlmann
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1016 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SwitzerlandName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kyrgyzstan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
19/07/2005
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Drainage ditches are dug in steep cropland areas to reduce soil erosion by diverting excess rain water away.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
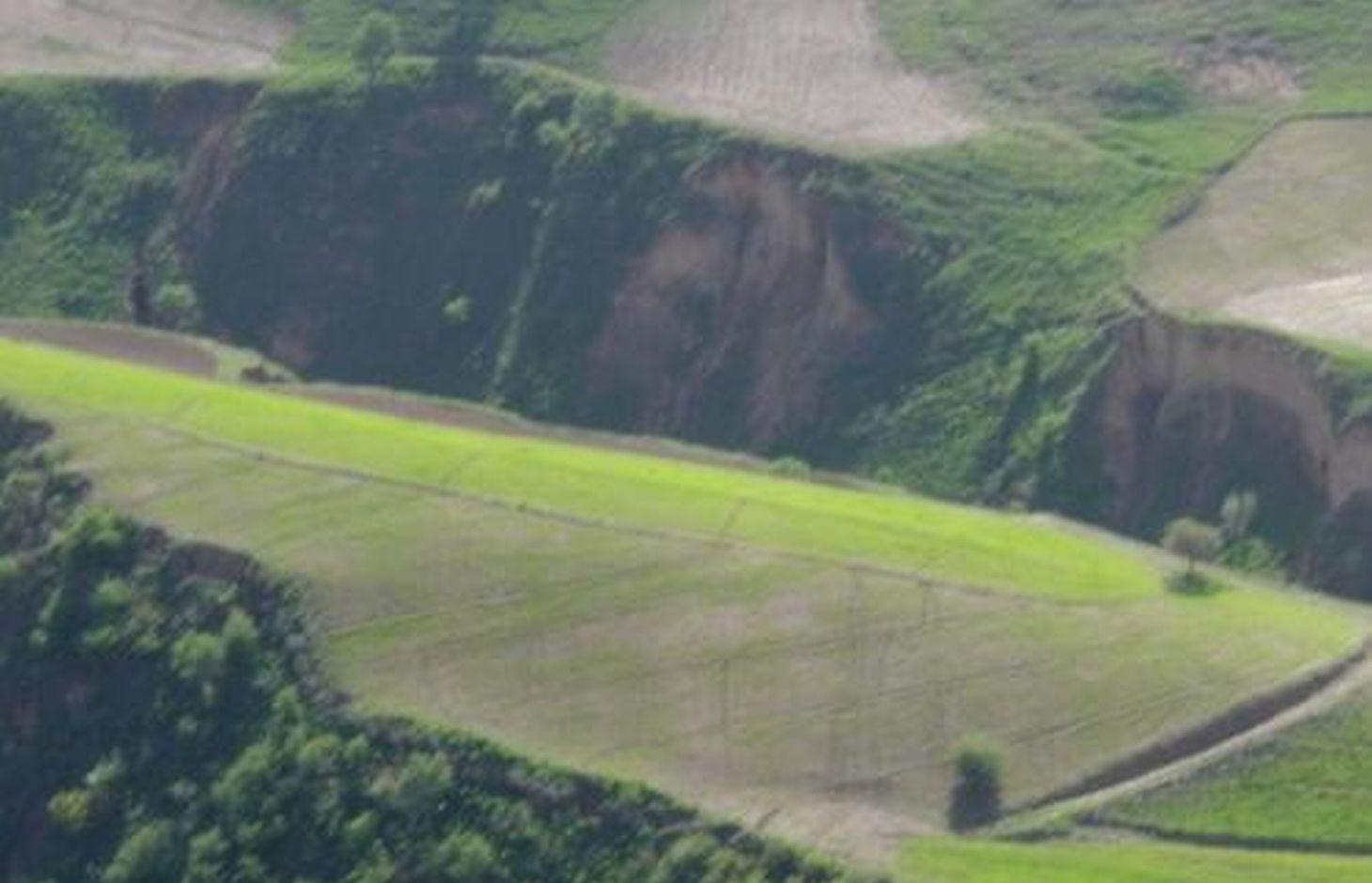
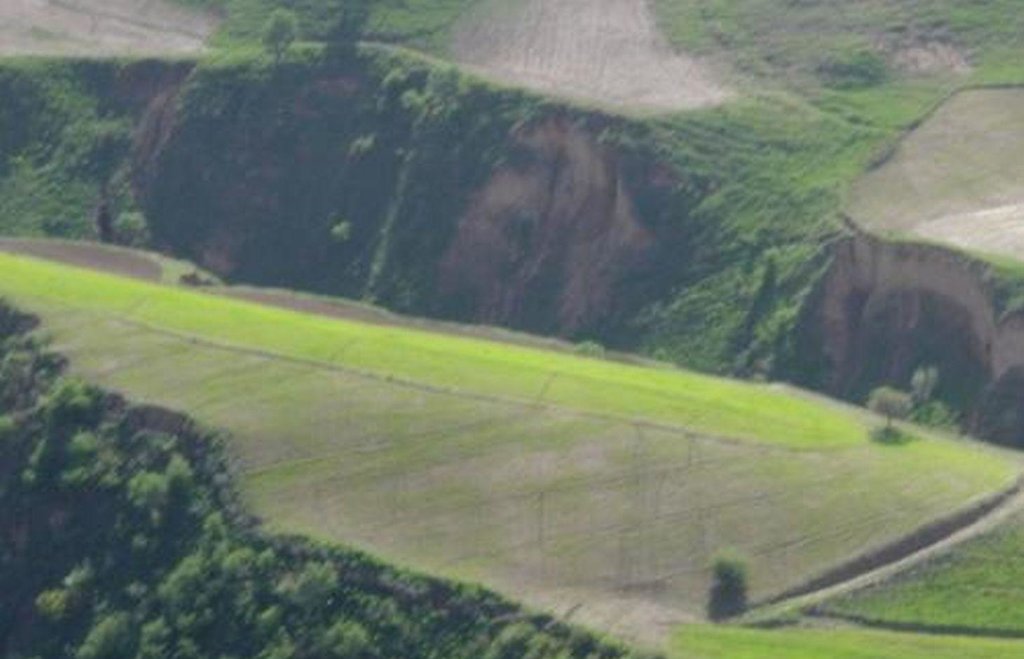
Description:
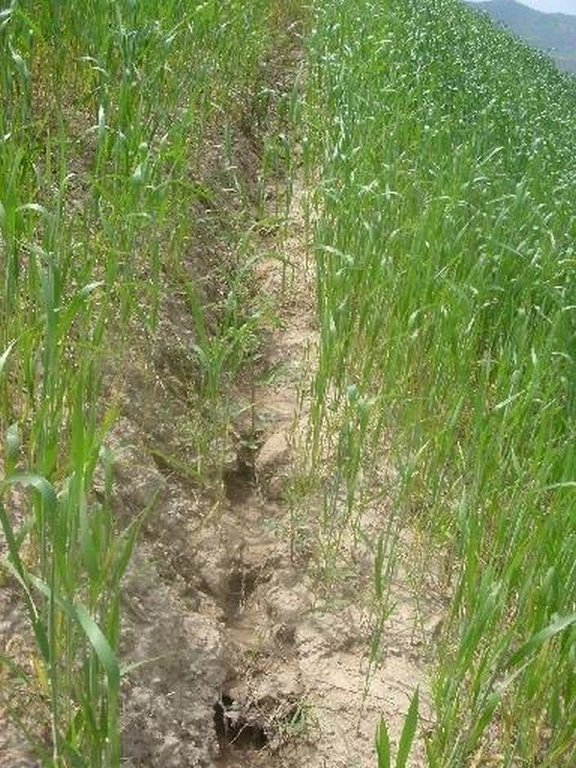
In steep wheat fields drainage ditches are dug at 5-10m intervals to help reduce soil erosion. The ditches are on average 15cm deep and 30cm wide, and are dug with a gradient of 10-20%, to facilitate the draining of excessive rain water. At the top of the field a 50x50cm cut-off drain prevents run-on onto the field.
The small drainage ditches in the field are dug each year after tillage and sowing activities. The earth removed from the diches is piled up below the ditch to decrease the risk them breaching. The cut-off drain at the top was established 5 years ago and is cleared regularly from washed in soil. Most farmers in Faizabad Rayon dig 1-3 drainage ditches in their sloping cropland. Drainage ditches and cut-off drains are often not constructed deep enough and are not well maintained. Construction of the technology is not time consuming or costly, however, drainage ditches and cut-off drains are completely ineffective if not maintained on a regular basis.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Labour input for this work does not exceed three person days per hectare.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
RRS
Further specification of location:
Faizabad Rayon
Map
×3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
major cash crop: vegetables
major food crop: wheat
other: chickpeas, flax
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): severe water erosion (gullies and rills) and subsequent fertility decline on cropland and overgrazed pastures
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): fertility decline, soil erosion and downslope washing of seeds before sprouting
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Winter wheat (and sometimes chickpeas) are sown in the autumn, all other crops are cultivated in the spring. Harvesting takes place in July and August.
3.3 Further information about land use
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March - August
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water diversion and drainage
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
Comments:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
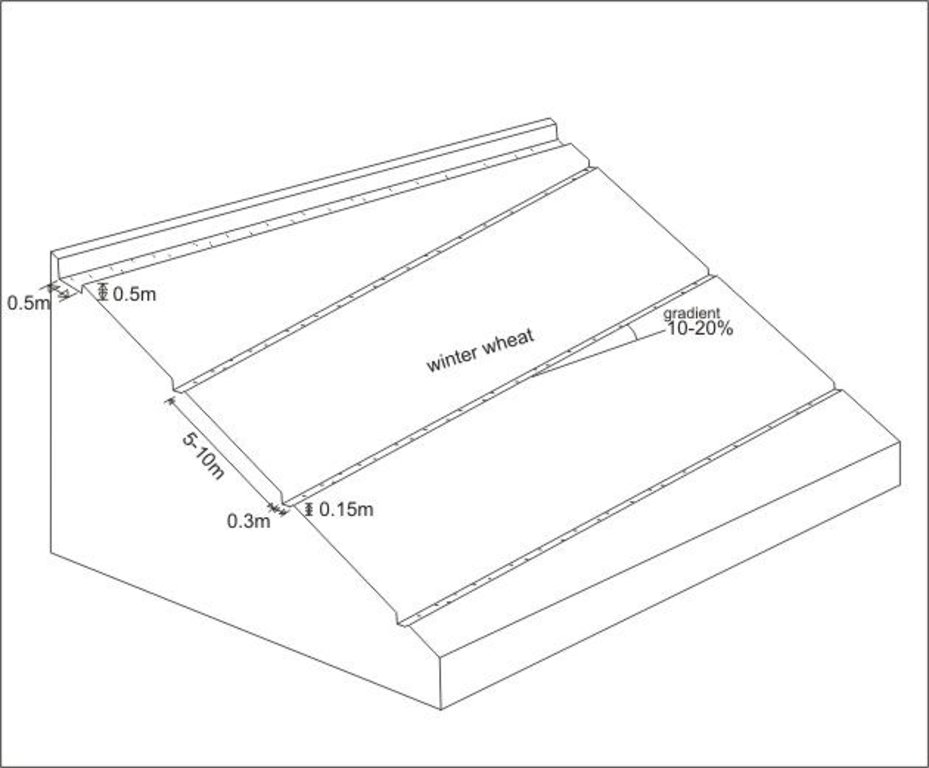
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Graded drainage ditches in steep sloping cropland, cut-off drain at top of field to prevent runon
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad Rayon, RRS
Date: 10.07.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Agronomic measure: drainage ditches
Remarks: depth: 0.15m, width: 0.3m, intervals: 5-10m, gradient: 10-20%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Construction material (earth): earth with spade removed
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 40%
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of cut-off drain | Structural | spring |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | digging of cut-off drain | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 8.0 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of drainage ditches | Agronomic | after sowing of crops / annually |
| 2. | deepening and clearing | Agronomic | rainy season / after every rainfall event |
| 3. | clearing of cut-off drain from washed in soil | Structural | rainy season/after heavy rainfall events |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | digging of drainage ditches | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | deepening and clearing | ha | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 21.0 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: tool: spade
Per hectare of cropland; maintainance activities for drainage ditches and cut-off drain after every heavy rainfall (twice a week over 3 months, based on an average of one hour of work per time)
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
- semi-arid
growing period between 180-210 days
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Altitudinal zone: Also 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also mountain slopes
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility: low - high
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium - good
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- very poor
- average
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In general, all farmers (including those applying SWC technologies) are highly dependent on off-farm income which in most cases is earned in Russia either by themselves or by their relatives.
Level of mechanization: ploughing is carried out by tractor whenever possible an therefore mechanized/ motorized is also existent in this area.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Subsistence, only surplus crops are sold
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology aslo: 0.5-1 ha
Furthermore: Households are depending on available working force, labour is limiting factor
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- leased
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
production area
land management
Socio-cultural impacts
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
excess water drainage
Soil
soil loss
Other ecological impacts
soil fertility
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
NA
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Increasingly, farmers have to cope with fertility decline of their cropland; one of the first measures they take is the establishment of drainage ditches. However, most farmers implement only a few drainage ditches without maintaining them in an appropriate way.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| reduces soil erosion |
| reduces fertility decline |
| low cost |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Require only a small cost for establishment and maintainance. |
| effectively prevents development of large rills and therefore reduces soil erosion |
| Has the potential to reduce the deline in fertility of the soil |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| requires regular checking | |
| cause a lot of damage, if they collapse |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| technology ineffective if not maintained on a regular basis | deepening and clearing after every rainfall event |
| does not prevent development of small rills and hence does not stop all erosion | small intervalls between drainage ditches reduce soil erosion more effectively. Combining this technology with other measures (grass strips, agroforestry etc.) is advisable |
| if the drainage ditches collapse, they cause a lot of damage to the cropland | appropriate management reduces the risk of braking |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules