Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed [China]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Intergraded development of a small watershed
technologies_971 - China
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed [China]
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve land production and farmers' income.
- Compiler: Unknown User

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [China]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- Compiler: zhangsheng LIU
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve integrated production.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
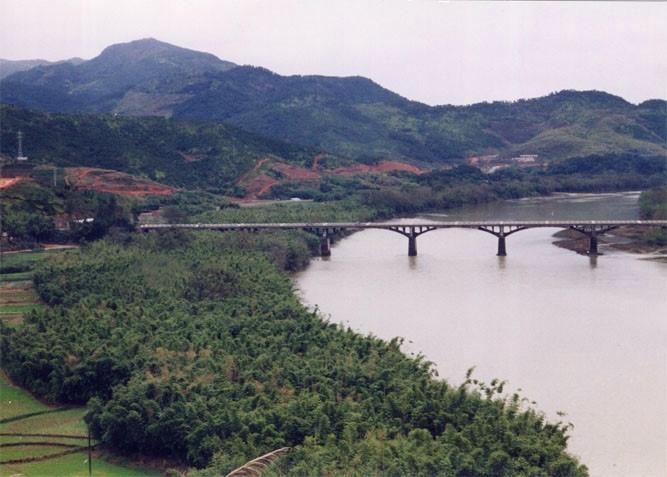
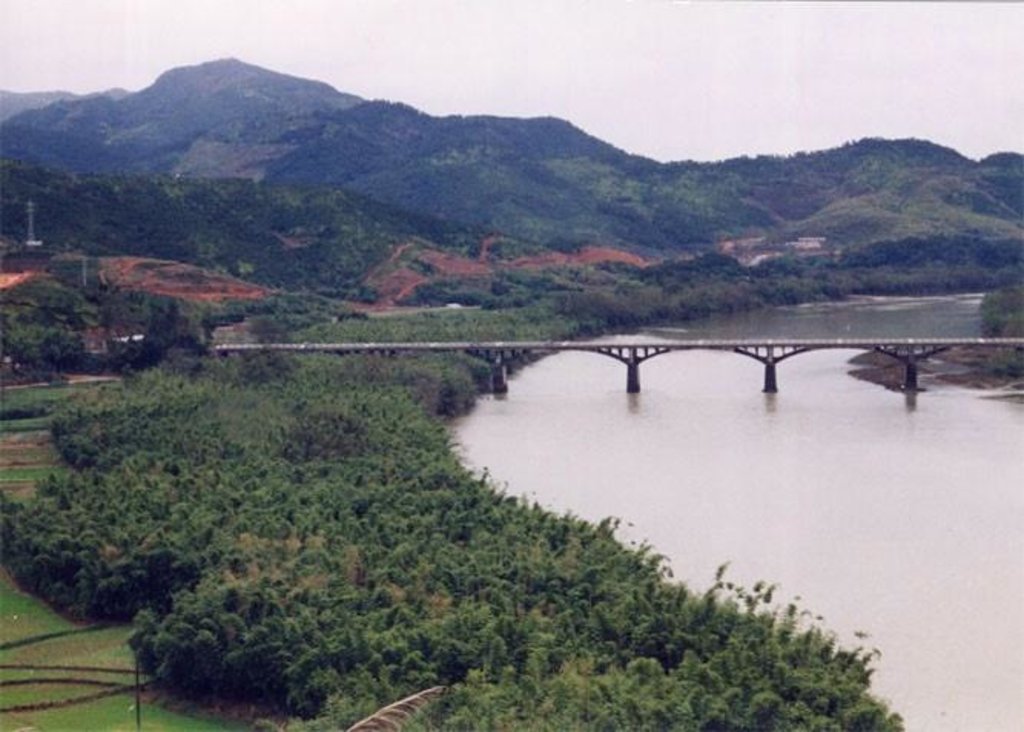
Based on the national conditions and soil and water loss in the area, the corresponding SWC measures were adopted to pursue the targets including: 1. Closing the hilly and mountain area of 224ha for the timber forest and grass growing as well as preventing soil and water loss; 2. Adjusting the land use structure so as to strengthen the comprehensive development of the hilly land as well as crop land irrigation; 3. Changing the area of W & S loss to economic vegetation land; 4. Constructing reservoirs and roads.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
China
Region/ State/ Province:
Fujian Province
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
5.93
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5.93 km2.
Xinxili small watershed is located in southern Zhenghe county. It belongs to administration of Jiefang village of Xiongshan town including three villages. The area of the watershed is about 606 ha. The weather in the region is sub-tropical monsoon climate with artificial vegetation. The soil type is red soil.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Based on the long term experiences of the mass's practice in SWC, the SWC specialists innovated through guidance, design and implementation of local water & soil conservation.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-silvopastoralism

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
- rice
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- grapes
- tea
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: Jan - Dec
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes

Grazing land
Animal type:
- poultry

Forest/ woodlands
Type of tree:
- Abies species (fir)
- Bamboo bamboo
- Pinus species
Products and services:
- Timber
- Grazing/ browsing
- Nature conservation/ protection
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The layout of vegetation is not rational. The traffic is not convenient.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of new species and SWC technique. Hopefully more funds could be supported from government.
Grazingland comments: Reclaiming fish pools area of 5.6 ha, stall breeding chicken, duck etc.
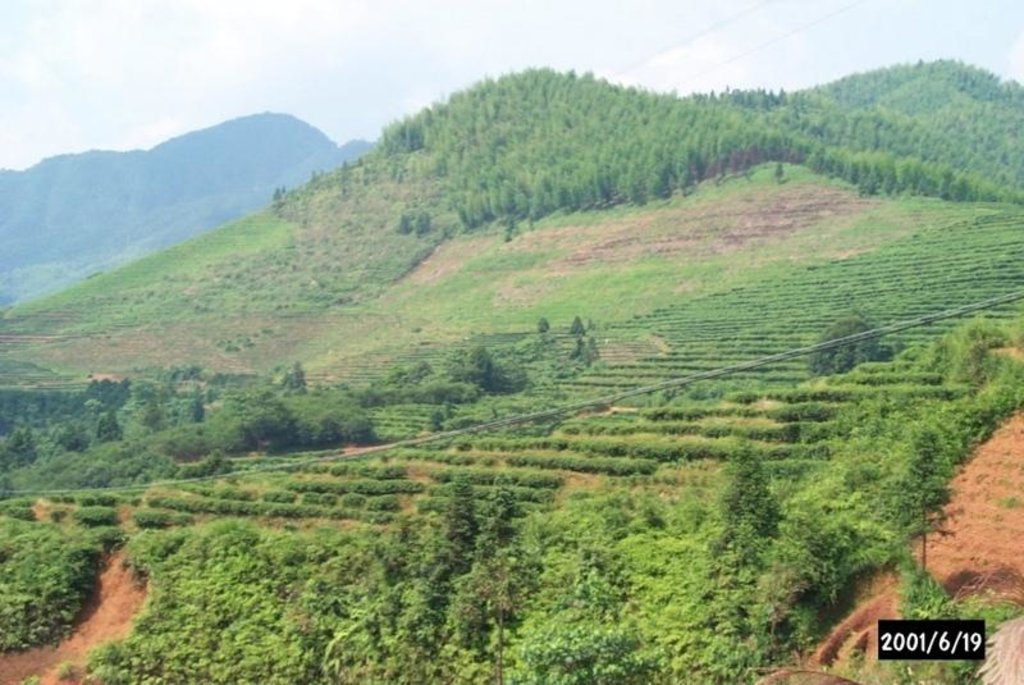
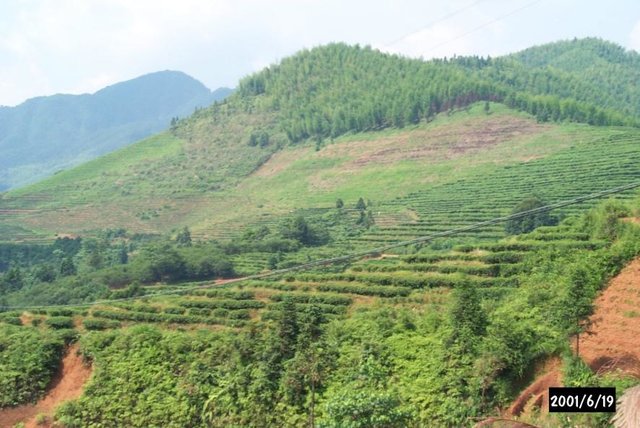
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Planting young bamboo in the sparse woodland (about 135 ha) in the western watershed and planting lotus after deforesting the woodland (36.7 ha) in the southwestern watershed as well as changing the adult tea gardens to afforest in the northeast watershed.
Forest products and services: timber, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection
Type of grazing system comments: Reclaiming fish pools area of 5.6 ha, stall breeding chicken, duck etc.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply also mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

structural measures
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, minimum tillage, contour tillage
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (population increasing and lack of fuel), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial: Low living standard of the local people and lack of funds.)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (neglecting ecological benefit, overfelling forest), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sandy and loose red soil.)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, Improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Remarks: Intercropping/mixed cropping
Mulching
Material/ species: Straw
Quantity/ density: all crop a
Remarks: strips
Trees/ shrubs species: fir, bamboo, horsetail pine,
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pear, loquat, peach, greengage
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 20.00%
Construction material (earth): With some stone
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 25.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 60.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10.00
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
1.44
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | closing mountain to afforest | 1990 |
| 2. | planting bamboo | 1990 |
| 3. | bamboo forest cultivated | 1990 |
| 4. | changing farmland to forest | 1990 |
| 5. | planting fruit trees | 1990 |
| 6. | Building sluice dams | 1990 |
| 7. | road constructing | 1990 |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 72 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | fertilizing | 1990-1999 /3 |
| 2. | cleaning out ruderal | 1990-1999 /2 |
| 3. | Preventing and curing illness and insect pests | 1990-1999 /3 |
| 4. | Broadening road | 1995/timely |
| 5. | highway maintenance | 1995/timely |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Size of the variable structural measures and areas of grass planting.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Because mechanic machines are not available, more labor forces are needed costing much. In addition, the expense for seeding, fertilizer, flagstone used in building dams take most of the total fees.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1609.00
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
soil texture: granite and fiber rock
Soil fertility: medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
and own 2% of the land.
and own 2% of the land.
and own 72% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
and own 8% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The benefit of SWC implementation is about 1.03 million US dollars. Among them, 257,289 US Dollars from the agricultural production, 145,301 USD from the forest industry and 286,746 USD from others.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
40
Quantity after SLM:
30
Soil
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
25
Quantity after SLM:
5
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
510 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
Comments:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
410 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even without fund support, rich land users could gain added income from the implementation of SWC technique.
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed [China]
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve land production and farmers' income.
- Compiler: Unknown User

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [China]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- Compiler: zhangsheng LIU
Modules
No modules