Calcareous soils management [Egypt]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Daniel Danano Dale
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_716 - Egypt
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Calcareous soils management: March 18, 2019 (public)
- Calcareous soils management: April 26, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 23, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 19, 2017 (inactive)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
This technology serves many purposes but particularly tackles problem of land degradation due to soil fertility decline, waterlogging and soil surface crust
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Managing calcareous soils through combined structural measures and chemical amendments methods for improving soil productivity and reduce land degradation
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
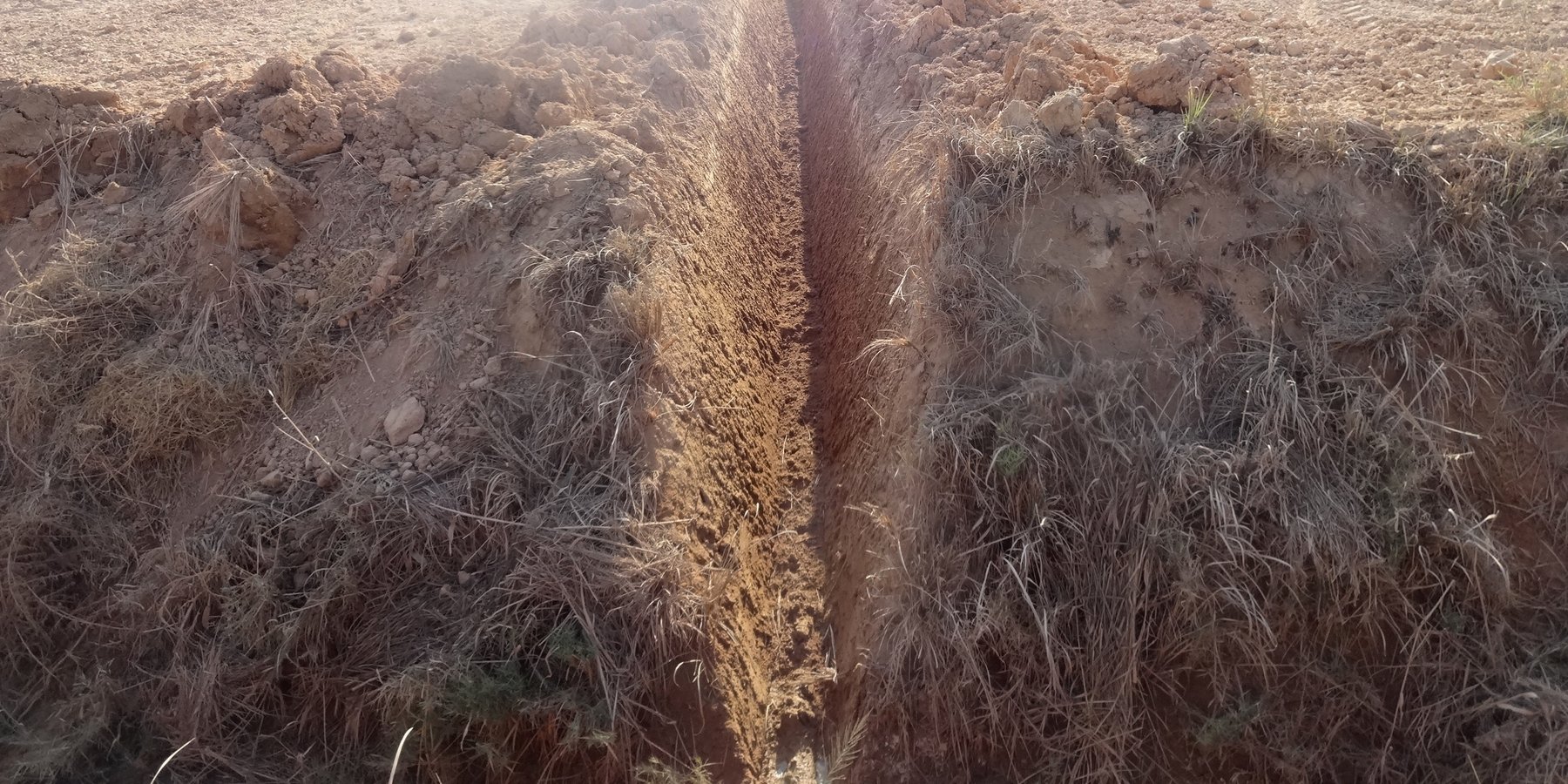
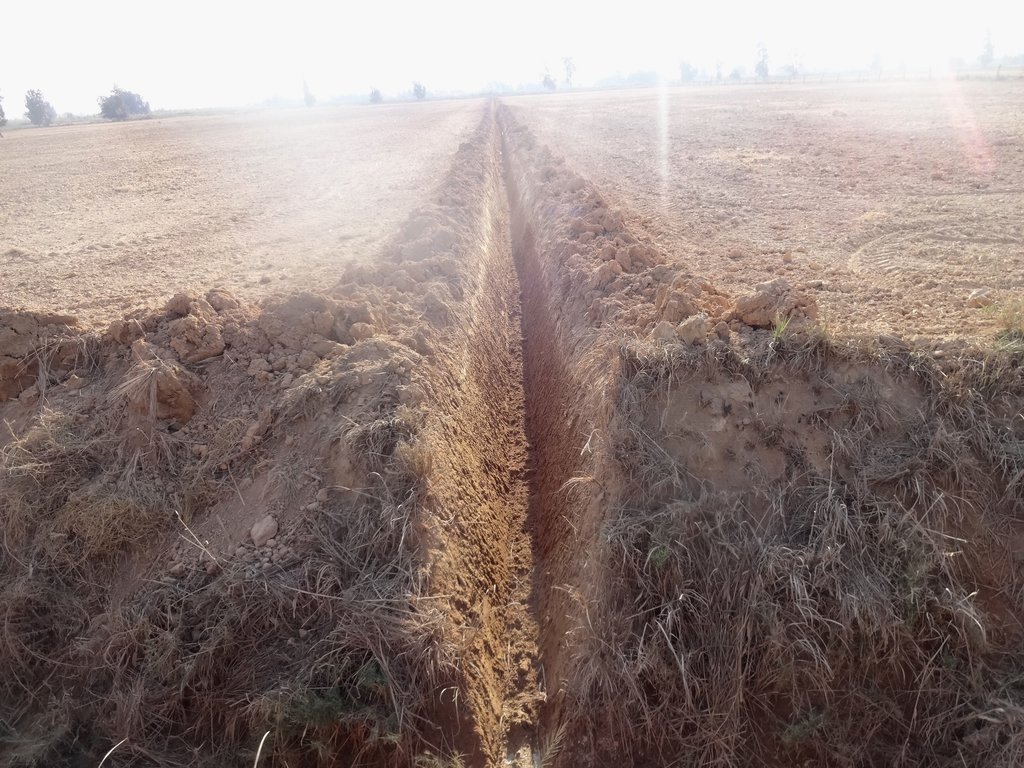
The technology is applied to facilitate drainage in calcareous soils (high calcium carbonate soils) that in addition suffer water logging. The technology is tested in research plots and then demonstrated on farmers field. The research and piloting is carried out by the Soil and Water Research Institute of Egypt. The technology is applied in agricultural fields where variety of cereal crops and vegetables and livestock feed is grown. These fields have been continuously farmed (soil nutrients mining) and have been exposed to varying land uses. The technology area is dominantly owned by smallholder farmers, who are forced to use the land for growing crops for their livelihoods (consumption and market). the fields could be under cultivation for two or more cropping annually and are exposed for varying degradation risks.
farm fields that are degraded by water logging and high calcium carbonate content (increase in the pH) are treated first in constructing surface drains that are laid out at sloping gradients towards the outlet, so that excess water is safely drained from the field. Ammonia gas 82% is ingested in the soil after seedbed preparation to lower the pH content of the soils. Excess water after irrigation is drained by the drains placed in the field at intervals.
The soils that degrade from water logging and high pH are treated by the combination of measures that are part of the technology. Water is drained by the drains and alkalinity treated by soil amendments in injecting ammonia.
Benefits of the Technology are reduced soil degradation, improved soil quality and health, and productivity increase (crop and fodder).
Land users liked the technology as it helped them increase crop and fodder production. water logged crop fields are safely drained becuse of the drains that remove excess water from the field to safe outlets
2.3 Photos of the Technology
General remarks regarding photos:
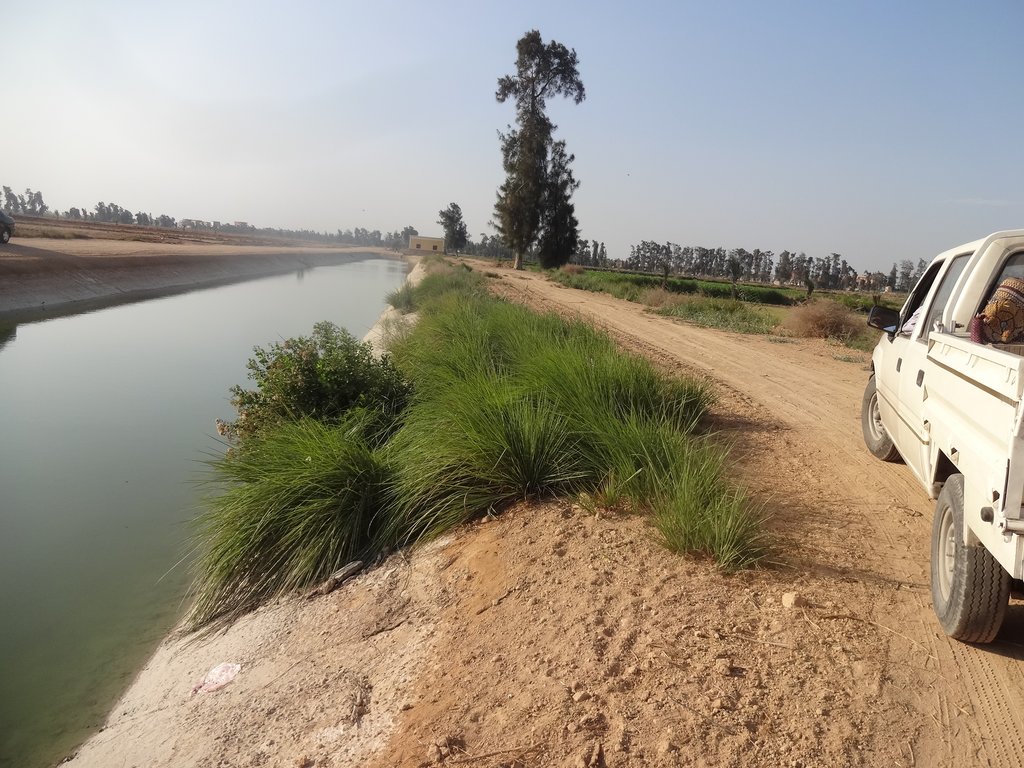
Farmers' field where the technology is implemented: Photo by Daniel Danano , Nile Delta, ElNubaria
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Egypt
Region/ State/ Province:
El Nubaria
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
The technology is being applied in many farmers' fields particularly in the newly reclaimed lands of El Nubaria and others
Research and farmers fields demonstration
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- vegetables - other
- wheat, rice
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Minimum 2 or 3 in most cases

Grazing land
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing
- Improved pastures
Animal type:
- buffalo
- cattle
Comments:
In the area, land management is the most indispensable investment, without which livestock and crop productions becomes virtually impossible.
Livestock density: Livestock are mostly stallfed and sometimes let to seasonal grazing after harvest
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Comments:
Land use could change in such a way that some years the land is used for cropping and on the other used to grow fodder for animals (cultivated - pasture- cultivation)
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
2-3 crops could be irrigated in a year depending on the type of crop
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated crop-livestock management
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- water diversion and drainage
- sustainable soils management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
- A3: Soil surface treatment

vegetative measures
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants

structural measures
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
- S11: Others

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level
Comments:
Soil conditioners such as ammonia hydroxide for reducing the pH of soils.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cs: salinization/ alkalinization

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
- Pw: waterlogging

water degradation
- Hg: change in groundwater/aquifer level
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- adapt to land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
The dimensions of the drains vary from (0.5 m - 1.5 m wide) depending on the spacing of the drains. In the case of narrow spacing's of the drains the width is smaller and when the spacing is larger then the width of the drains gets larger as well (7 - 20m). The depth of the drains is normal bigger near the outlets it could range from 0.3 m at the beginning and could be as deep as 1 meters near the outlet
Author:
-
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
18.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
80 LE (Egyptian Pound)
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | land preparation / seed bed preparation | October -November |
| 2. | constructing drainage ditches | November |
| 3. | injecting soil conditioners | November |
| 4. | stabilizing drainage banks | November |
| 5. | planting | Nov - Dec |
| 6. | weeding and cultivation | Dec-Jan |
| 7. | harvest | April |
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | land tilling | 2-3 times a year |
| 2. | cultivation and weeding | 2 times |
| 3. | repair in channel and ditch breaches | ones a year |
| 4. | removing silt from main drains | ones in a year or ones in 2 years |
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Rainfall is less than 25 mm per annum. Desert lands predominate outside the Nile Delta, which are under reclamation in the Nubaria area; few kilometers along the two sides of the Nile River
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Yes
Specify:
Due to sea water entrusion along the mediterranian coast and in areas where there is no adequate irrigation water
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users could be of both gender. It could be used by all age groups but more dominant users are the middle aged as they have the labor that is needed to do all kinds of farm operation or the land could be contracted out to companies or cooperatives.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- company
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Without the technology no production of either crop or livestock fodder is possible
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
Land productivity decreased very much and in certain cases it reached to a level where crop farming was impossible because of waterlogging
fodder quality
animal production
Comments/ specify:
animal feed growth has been increased as the soil conditions to support fodder crops ahs been substantially improved because of the technology
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
farm income
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
excess water drainage
groundwater table/ aquifer
Soil
soil organic matter/ below ground C
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Yes
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- labour availability (e.g. due to migration)
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The technology has the advantages primarily of reclaiming water logged farm fields to more crop friendly environment. It is not very costly because the drains could be easily made by farm implements the land users have or could be easily rented from cooperatives or companies that provide the service. The amendments used are also within the reach of land users to purchase them and are available in the near vicinities |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Require frequent maintenances. Take away substantial segment of the farm out of cropping interfere in farm operations (pose difficulties for farm machineries and tools to be easily maneuvered as they restrict free turning of machinery and the tractors pulling them. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
08/11/2016
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules