Permanent grassland on peaty and eroded soils [Estonia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Endla Reintam
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Püsirohumaa turvas- ja erodeeritud muldadel
technologies_3113 - Estonia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
Selge Are
Hummuli Agro
Estonia
researcher:
Penu Priit
Agricultural Research Centre
Estonia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
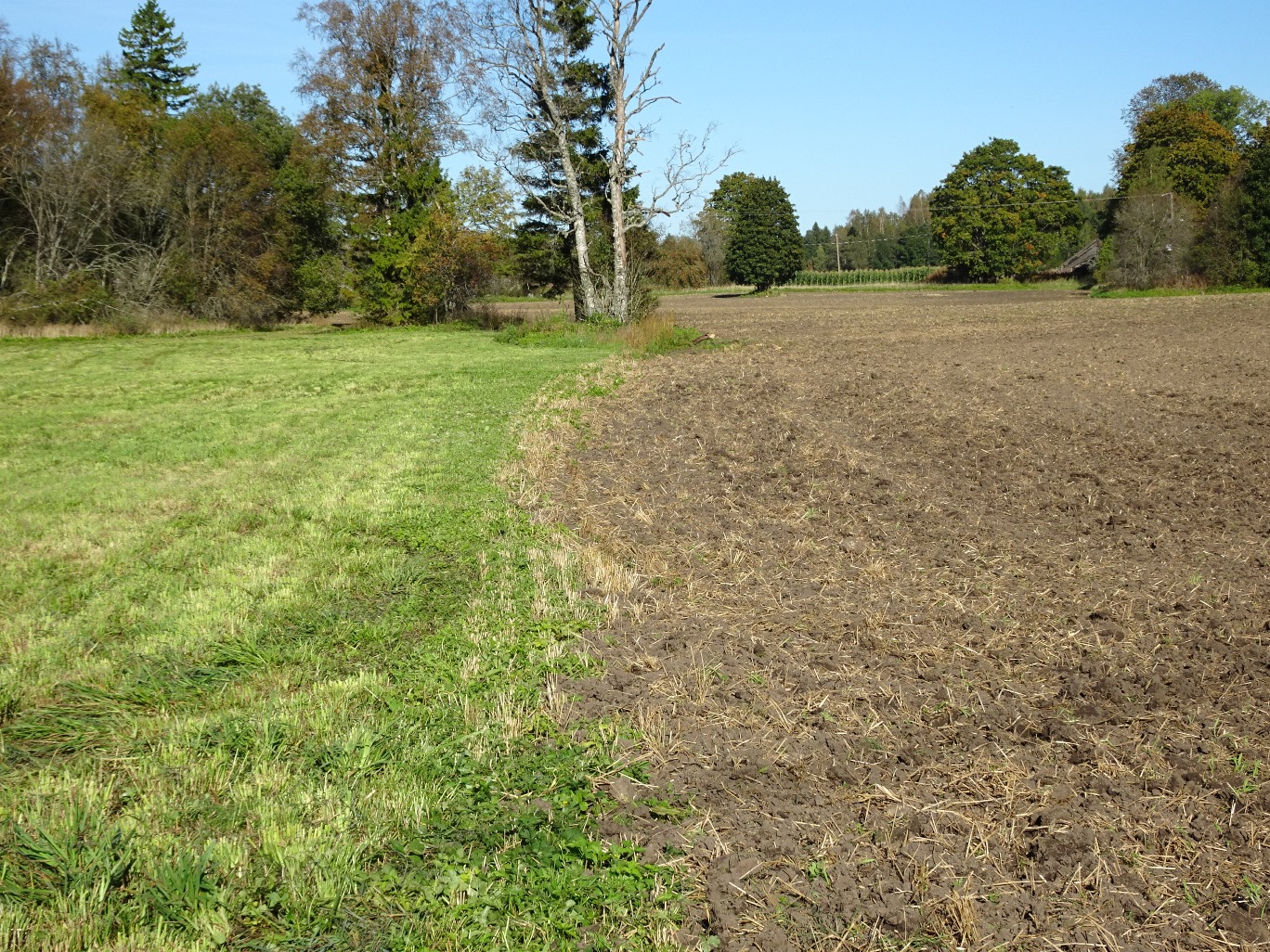
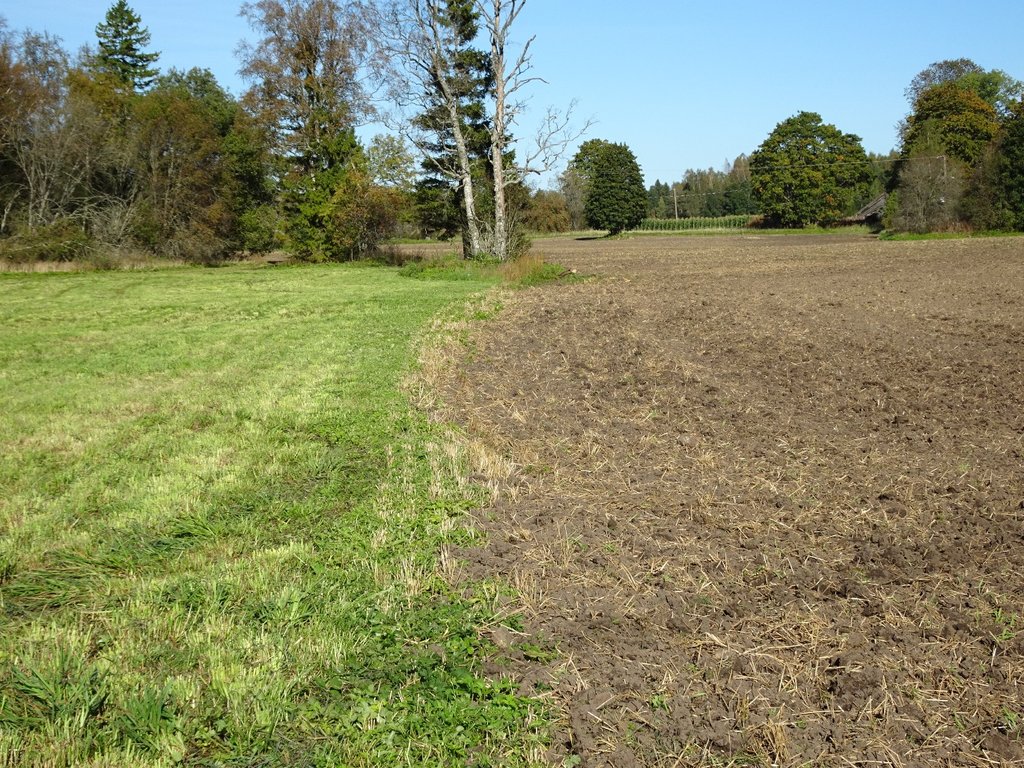
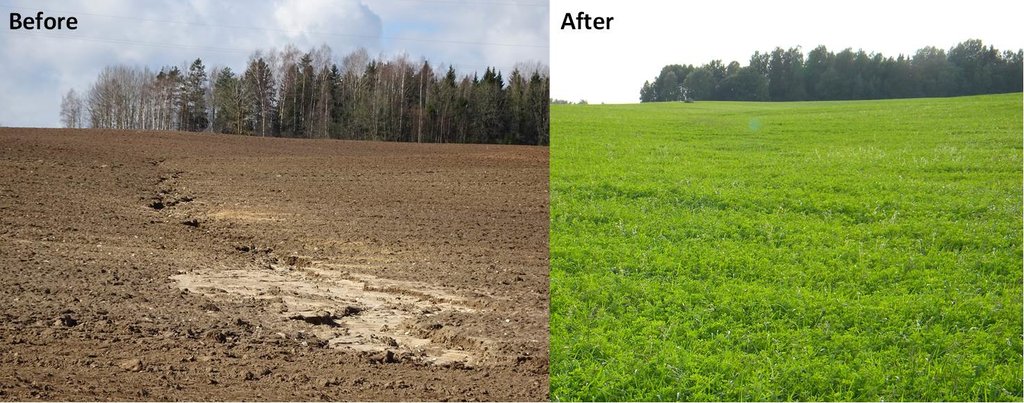
A permanent plant cover is maintained or established to protect soil against erosion or peat decomposition.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
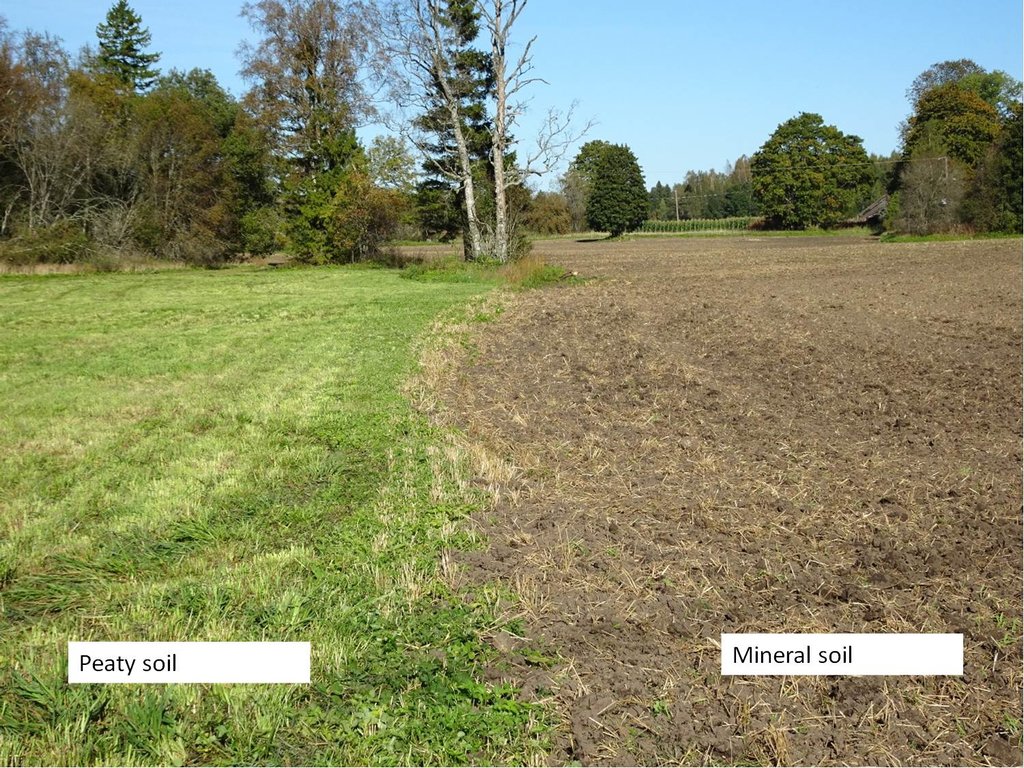
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat to slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) inthe north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. The peat cover of peatlands varies from 0.3 m to more than 10 m from well decomposed to poorly decomposed peat. On hilly areas the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater in near the surface in peatlands and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity of these areas is medium. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 1000 ha).
In the agricultural land the area will be excluded from intensive tillage by establishing a permanent plant cover, mainly with grass. The aim is to protect the slopes over 10% against erosion and peaty soils from further intensive decomposition of organic matter and with that the reduction of CO2 emission. The farmers should maintain permanent plant cover in the areas mentioned, or establish permanent plant cover. Renewing of the grassland is allowed from the top (without ploughing) once in a 5 year period. Government pays support of 50 EUR/ha if the area is bigger than 0.3 ha. The technology reduces intensively tilled area and thus the possibility to grow cash crops and/or reduces the yield from grassland. On the other hand it allows to still use wet areas for agriculture (i.e. fodder production).
The rules of the technology are fixed with the Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014-2020 under activity "Support for regional soil protection" (https://www.agri.ee/et/eesmargid-tegevused/eesti-maaelu-arengukava-mak-2014-2020) related to the reguation of the European Parliment and of the Council 1305/2013, article 28. The regulation is relevant more to the South-Estonia in case to reduce erosion, as the landscape is more hilly there. The exclusion of peatlands from agricultural use is relevant more in West-Estonia where the share of peatlands of the total area is the highest. However, it can be applied in whole Estonia if the area of peatland is bigger than 0.3 ha.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Estonia
Region/ State/ Province:
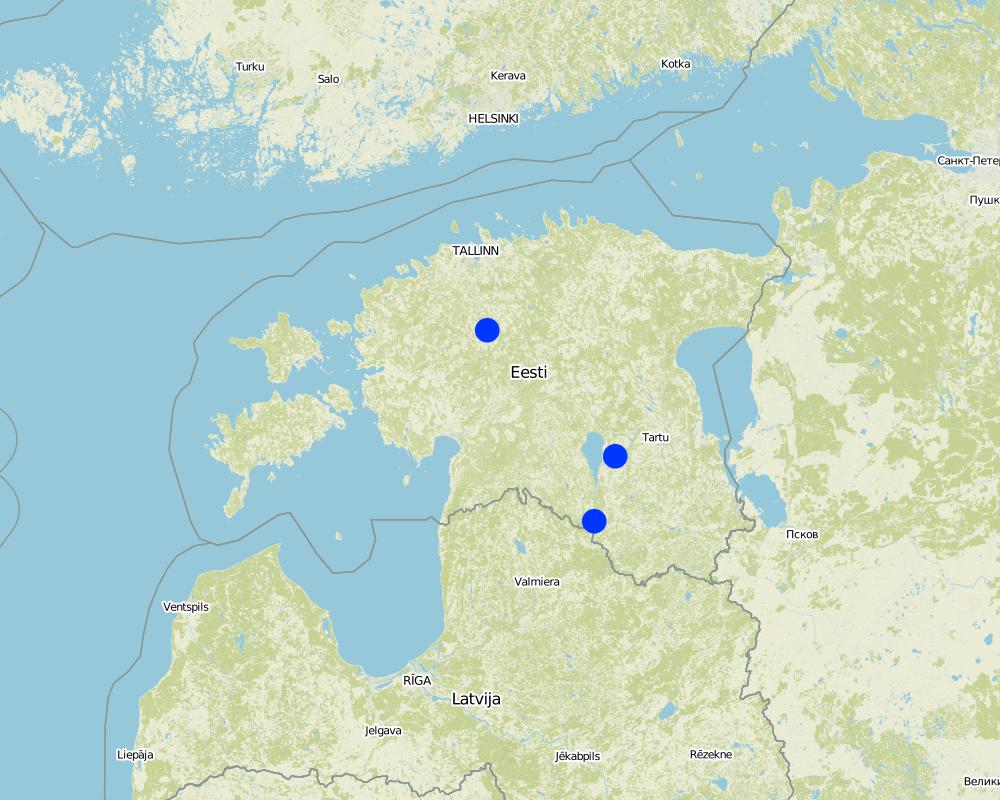
One site at Rapla, second at Tartu, third at Valga (erosion)
Further specification of location:
One site: Rapla county, Pae; second site Tartu county, Annikoru, third site Valga county, Hummuli
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
To get the governmental support the area should be larger than 0.3 ha. Othervise the size is not important, depending on the area covered by hilly area or wet soils in the landscape.
In 2016 it was 10554 ha Histosols and only 40 ha of eroded soils covered with this technology in Estonia. This area excludes grasslands on another soil types. On specific sites: in Rapla county in Pae the size of the field is ca 3.2 ha, at Tartu county, Annikoru 2.8 ha.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
- Governmental tool
Comments (type of project, etc.):
The tool is a part of Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020 for soil fertility.
The survey was done by the Soil Survey Bureau of the Estonian Agricultural Research Centre (http://pmk.agri.ee/). The results presented here are partly from this survey and from the work done by the project iSQAPER.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- cereals - oats
- cereals - rye
- legumes and pulses - beans
- legumes and pulses - peas
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- vegetables - root vegetables (carrots, onions, beet, other)
- wheat
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
For the cereals one harvest per year, for grasslands 1-4 cuts per year. For hay 1 cut, for silage 2-4 cuts depending on the year

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Ranching
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Improved pastures
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- cattle - non-dairy beef
- sheep
Products and services:
- meat
- milk
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Cropland
Comments:
Usually before the implementation of the technology the land was intensively tilled and used for annual crop plantation. After implementation the grasslands can be used for cutting and grazing.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
On Histosols the groundwater is close to the surface.
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- minimal soil disturbance
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A3: Soil surface treatment

vegetative measures
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
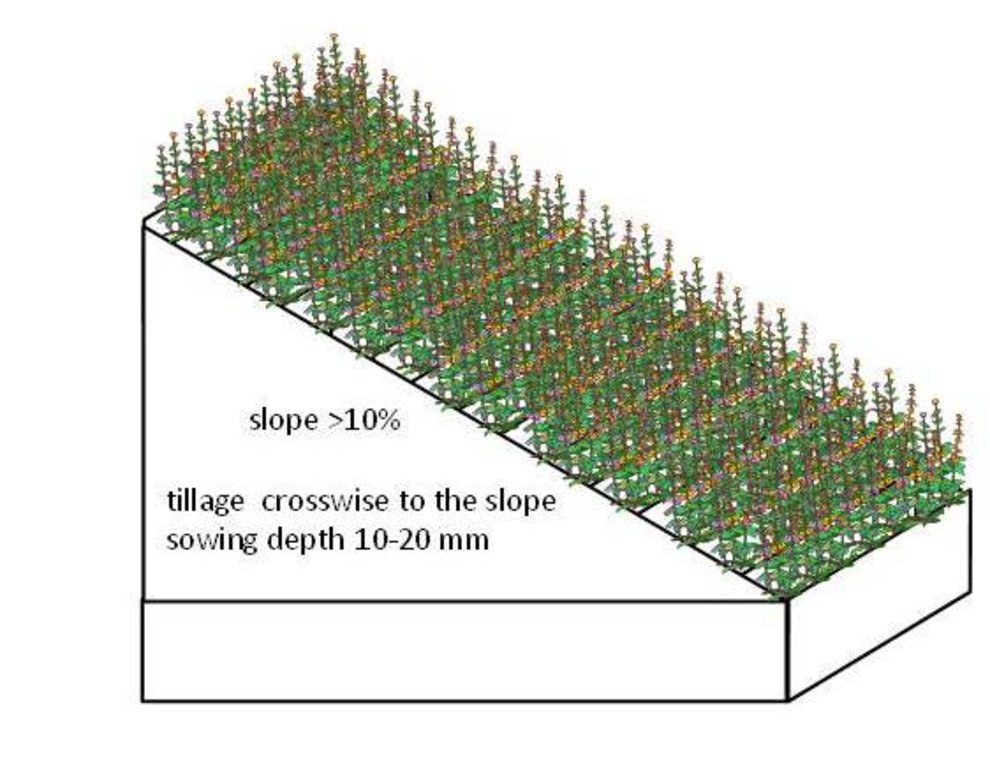
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
The requirements to create a permanent grassland depends on soil type.
Species mixture suitable for the permanent grassland on wet soils (Histosols): Bromus sitchensis 30%, Phalaris arundinacea 45%, Phleum pratense 20%, Poa pratensis 5%. Sowing rate 20 kg/ha.
For the drier areas (eroded soils) the next mixture is suitable: Dactylis glomerata 65%, Phleum pratense 26%, Poa pratensis 9%. Sowing rate 23 kg/ha.
Author:
Endla Reintam
Date:
14/08/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
per hectar
other/ national currency (specify):
EUR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1.18
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage (ploughing, cultivation) | in spring |
| 2. | Collecting stones, slip (by demand) | in spring |
| 3. | Fertilization | in spring complex fertilizer |
| 4. | Sowing | in spring |
| 5. | Rolling | in spring |
| 6. | Cutting the weeds | during growth (summer) |
| 7. | Fertilization during growth period | after every cut of grass, if cutted grassland, N-fertilizer |
Comments:
If renewing the grassland, there will be no ploughing, collecting the stones and sliping. Only chisel plowing and/or sowing with fertilization. If the grassland will be use for grazing, no need for fertilization during growth period.
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Driver (machinery work) | person day | 0.5 | 36.0 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Equipment (machinery) cost on establishment year | year | 1.0 | 207.0 | 207.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Seeds | kg | 22.0 | 2.47 | 54.34 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Complex fertilizer | kg | 500.0 | 0.42 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 100.0 | 0.33 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 522.34 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 442.66 | |||||
Comments:
For tillage and other operations it is calculated 14-18 EUR/ha.
If to hire equipment the labour costs should be included to the machinery costs - for cutted grassland 225 EUR/ha, for grazed grassland 162 EUR/ha
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting or grazing the grass | 1-4 times per vegetation period |
| 2. | Fertilization | in spring in the beginning of season and after every cut N-fertilizer, after each second year complex fertilizer |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Grasslands for cutting - machinery costs | year | 1.0 | 141.0 | 141.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 200.0 | 0.33 | 66.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Complex fertilizer | kg | 200.0 | 0.42 | 84.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Materials for hay making | year | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 306.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 259.32 | |||||
Comments:
The governmental support to establish and to maintain the grassland is 50 EUR/ha.
If to use the land for the grazing, the machinery cost per year is 38 EUR/ha.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Fuel price.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
696.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Tartu Tõravere
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- convex situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Eutric Histosol, well decomposed peat, drained area.N 2.32%; C32.89%; C/N14.20%; P2,62 mg/100g; K 13.73 mg/100g; Ca 1762.32 mg/100g; Mg 166.98mg/100g
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Histosols biodiversity depends on the base saturation and level of groundwater (degree of drainage). Diversity is higher at higher pH and better drainage.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
- cooperative
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
- elderly
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
Comments:
There are also small-scale and medium-scale farms applying the technology. At Pae, the farm have 4900 ha of land, from which 1800 are grasslands, at Annikoru the farm have 2320 ha of land from which 390.5 ha are grasslands.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
- individual/open access
Comments:
Groundwater belongs to the state. Smaller water bodies can be in individual use, larger are usually open access
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
The area will be excluded from crop production and it means no cash crops can be cultivated on this area. Instead of crops hay or silage is possible to sell.
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
As it is not allowed to renew these grasslands intensively, the quantity of grass will drop. For short term clover+grasses mixture the average yield is 16 tons/ha per year, for long-term grass mixtures 5.2 tons/ha per year.
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
Due to the change of species in the mixture, the protein level will drop. Instead of red clover grasses will be used in the mixture of long-term grasslands.
animal production
Comments/ specify:
Due to the changes in silage/hay quality (protein) there can be reduction of milk and meat production if the differences will not be covered with other fodder.
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
In case of crop orientation, there are new products to sell - grass, hay, silage, or grasslands to rent.
land management
Comments/ specify:
Depending on the farm it can be simplified or hindered. If focus was on crops, then new machinery is needed to manage grasslands (for cutting, hay or silage making).
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
As renewing of grassland is after every 5 years, there is no need to buy seeds every year, as well as pesticides and to till the soil.
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Due to the reduction of the inputs costs, the income my increase. Also the government pays support 50 EUR/ha for the land under these measures.
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
Next to the yield (grass, silage, hay) the support from the government (50 EUR/ha)
workload
Comments/ specify:
It may decrease due to no need of every year tillage and sowing and due to the change from 2 year short-term grasslands to the permanent grasslands. However, if not managed grasslands earlier it may increase the workload as cutting and collecting the grass is needed.
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
More land under grasslands than under crops. Grasses are suitable for animals feeding, not for human direct consumption.
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Comments/ specify:
In case of erosion, no soil will be washed down to the hill as plant cover protects soil surface and increases infiltration. In case of peatlands, grass cover creates better structure and increases water infiltration thus decreases surface runoff during heavy rainfall.
excess water drainage
Comments/ specify:
Grass creates protection to the soil surface and raindrops can't destroy the soil structure any more. Also grass roots create better porosity and structure in the soil leading to better water drainage.
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
The difference in soil moisture between mineral and organic soils under cereals and under grassland was ca 5% and 25%, respectively, in favour to the grasslands in autumn 2016.
soil cover
Quantity before SLM:
40%
Quantity after SLM:
100%
Comments/ specify:
Under spring cereals soil is covered only 4-5 months per year, under grasses soil is covered 100% of the year.
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
On the slopes depending o the crop and the amount of precipitations, the loss varied from 3 to 60 tons/ha, under permanent grass cover it is less than 0.05 tons/ha per year. Without every year tillage there is no intensive decomposition of the peat, as well as no wind erosion.
soil accumulation
Comments/ specify:
Under grasses we can increase the soil organic matter content by 0.35 t/ha in 5 year period in peatlands. In eroded soils we can increase 0.02% per year.
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
As plants protect soil surface, raindrops can't destroy the soil structure and there will be no crust formation
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
Under the grasslands the bulk density was lower by 0.1-0.2 g/cm3 compared to tilled soil.
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Comments/ specify:
As the intensive decomposition of the peat stops or there will not be any leaching by water, more nutrients remain in the soil. Also the permanent plant cover during the whole year stops nutrient leaching.
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
Under permanent grasslands the Corg increases by 0.35 t/ha per 5 year period.
acidity
Comments/ specify:
Without periodic liming the acidity of peatlands starts to increase. If no CaCO3 in mineral part, also pH of previously eroded soils starts to decrease slowly, as organic acids form during decomposition process.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
Thanks to the permanent plant cover there is no period of the year without vegetation.
biomass/ above ground C
Comments/ specify:
If previously the plant residues were mixed with the soil by tillage, now there will always some extent of plant mass be left above ground (5-10 cm), even if the most is removed for hay or silage.
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
Long-term grassland includes at least 4 species in the mixture, short-term mixtures 2-3 species. However, compared with the cereals, the annual weeds will disappear and the diversity may decline.
animal diversity
Comments/ specify:
There are more spiders, ants, beets.
beneficial species
Quantity before SLM:
2 species of earthworms
Quantity after SLM:
3-4 species of earthworms
Comments/ specify:
Under grasslands were 1-2 more earthworm species than under tilled management. More spiders and ground beetles were found there compared to the tilled soil.
habitat diversity
Comments/ specify:
Grasslands create untilled patterns to the landscape.
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
Grasses surpress many soil born crops diseases and pests, also annual and perennial weeds.
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
Comments/ specify:
Grass roots go to the deeper soil and they are not so sensitive to the drought.
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
fire risk
Comments/ specify:
If the grass will not be cutted before winter, the dry grass has the risk of higher landscape fires in the spring.
micro-climate
Comments/ specify:
The changes of soil temperature as well as moisture content are smaller under permanent grass cover than under tillage.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
buffering/ filtering capacity
Comments/ specify:
All year plant cover helps to bind nutrients and stop their leaching from the soil. Higher amount of organic matter in the soil increases water holding capacity.
wind transported sediments
Comments/ specify:
Organic peat particles are light and are easy subject of wind erosion in dry conditions by tillage. Permanent plant cover stops such kind of erosion
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
On hilly landscape no extra soil is flushed to neighbours fields. In case of peatlands no dust is carried around.
damage on public/ private infrastructure
Comments/ specify:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | winter | increase | moderately |
| seasonal temperature | spring | increase | moderately |
| annual rainfall | increase | not known | |
| seasonal rainfall | winter | increase | not known |
| seasonal rainfall | autumn | increase | not known |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local thunderstorm | not known |
| local hailstorm | not known |
| local snowstorm | moderately |
| local windstorm | not known |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| cold wave | not known |
| extreme winter conditions | moderately |
| drought | moderately |
| land fire | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | moderately |
| storm surge/ coastal flood | moderately |
| landslide | well |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
In 2016 two hundred four households got the governmental support, in total 10554 ha
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
Comments:
Anyway, the use of Histosols and Gleysols is limited due to their properties and regular use of these soils is for grazing or grass cutting.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Better soil protection |
| Possibility to earn money in unsuitable soil conditions. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Reduces soil erosion on hilly landscape |
| Reduces the decomposition of peat on Histosol |
| Reduces CO2 emission from agricultural land. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Loss of income | Governmental support (50 EUR/ha) |
| Problems with the grass (farms without animals) | Cooperation with neighbours, selling the hay for energy production |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Farmers don't want to use the technology | More effective lobbying |
| Wrong declaration of the land under the technology | Better advisory system and improvement of electronic databases |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
5 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- interviews with land users
10 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
8
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
04/06/2017
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Bender, A. (koostaja) 2006. Eritüübiliste rohumaade rajamine ja kasutamine. I. ja II. osa. Jõgeva
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Bender, A. 2010. Heintaimede sordiaretus ja seemnekasvatus. Jõgeva Sordiaretuse Instituut
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Older, H. 2011. Kohalikud söödad. Eesti Rohumaade Ühing.
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020
URL:
https://www.agri.ee/en/objectives-activities/estonian-rural-development-plan-erdp-2014-2020
Title/ description:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
Title/ description:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
Title/ description:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2007-2013 2. telje ning Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi püsihindamiseks 2016. aastal läbiviidud uuringute aruanne. Põllumajandusuuringute keskus. Saku 2016.
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/09/aruanne_uuringud_2015.pdf
Title/ description:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules