Banana intercropping in sloping land [Lao People's Democratic Republic]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Bounthanom Bouahom
- Editors: anousit namsena, Pasalath Khounsy, Bounthanom Bouahom, kang phanvongsa
- Reviewers: Nivong Sipaseuth, Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_2907 - Lao People's Democratic Republic
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Saylaveng Amyem
Village head
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - Lao People's Democratic Republic1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
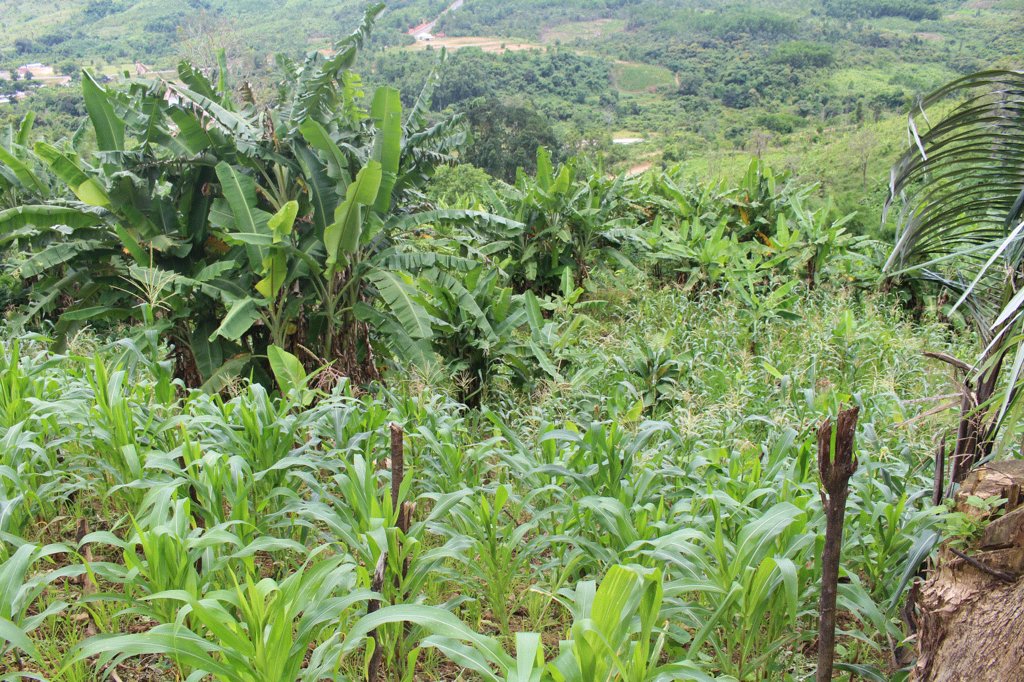
In mountain regions of Laos Banana cultivated with intercrops during the first year of plantation led to mutually better plant growth by higher availability of soil nutrients and subsequently produces better yield. It also prevents soil erosion, air pollution (reduction of slash and burn cultivation) and it mitigates climate related drought.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
The banana provides significant benefits for the households in the uplands of Lao PDR. It serves for own consumption and for selling to generate regular household income. Its leaves are wanted on the market as well and can therefore generate good income too. Besides its low maintenance cost and easy to grow, banana can retain soil moisture and complement with ecology and biodiversity, on condition that its cultivation sustainable. Currently, the banana consumption in the region is increasing and results in banana expansion in the upland areas of Lao PDR. By tradition during the first year of banana plantation the local land users of Samouy district, Saravan province, Lao PDR cultivated banana intercropped with other upland crops (potentially with upland rice and maize) . However, the farmers implemented this cultivation technique without exact planning, measurement, in unorganized rows, or inadequate size of the hole. Also the poor maintenance after planting led to low banana productivity. In 2010, a Project supported by IFAD encouraged local people to grow banana with provision of technical advice through training and implementation. Banana plantation method recommended by the Project is following:1. Site selection: the land area with slope between 10-20 percent and rich loamy soils.2. Spacing and digging of holes: farmers arrange banana plants in lines and rows with spacing of 3m x 3m. 3. Dimension of hole: 25cm x 25cm with a depth of 30cm.3.Soil amendments: If the fertility of soil is low, manure (3 – 5kg/hole) has to be added on the bottom of the holes.4. Intercrops during first year of planation: Between the banana’s rows upland crops can be seeded in regular rows. This helps to prevent soil erosion during the first year.5. Maintenance: Regular thinning and cutting of the banana branches are required after planting to get good yield. Thinning may also involve removal of excess banana suckers if there are more than 3-4 shoots per hole.6. Farmers are required to maintain banana plantation areas including regular weeding as well as soil amendment (animal manure) to promote successful banana production. Covering the soil constantly with banana leaves is one of the most important activities to maintain the soil’s fertility (prevent soil leaching), structure and moisture, to improve the soil life, to lessen the burden of weeding and to prevent soil erosion. Chemical pesticides and fungicides are not foreseen to be used in this practice.7. After harvest of the intercrops: After the first year, when the maize or upland rice has been harvested, banana suckers will be planted in the rows on the remaining space between the one year old banana trees.In summary, this method of banana planting in sloping areas is simple and with average of 3-4 million Kip per household per year it generates good and regular income for the households. Banana provides fruits all year round that can be sold throughout the year whilst demand is also increasing. Currently, the average of the banana plantation area is approximately 10 ha per household. In addition, banana is tolerant to drought. Banana leaves spread over the soil (mulching) keep the soil moist provide best nutrients for soil organisms. And supplement amendment in form of animal manure improves the nutrient recharge. The soil cover improved to some extent from the beginning by the improved intercrop method according to the criteria learned by the project. However, the workload increased due to improved maintenance of banana.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Region/ State/ Province:
Samouy district of Salavan province
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2010
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
ໂຄງການ ແຜນງານ ຄາໍ້ປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ ແລະ ໂພສະນາການ (IFAD)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rice (upland)
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Banana as perennial (noon-woody crop / upland rice and maize at first year of banana cultivation.
Comments:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Banana as perennial (noon-woody crop / upland rice and maize at first year of banana cultivation.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- rotational systems (crop rotation, fallows, shifting cultivation)
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
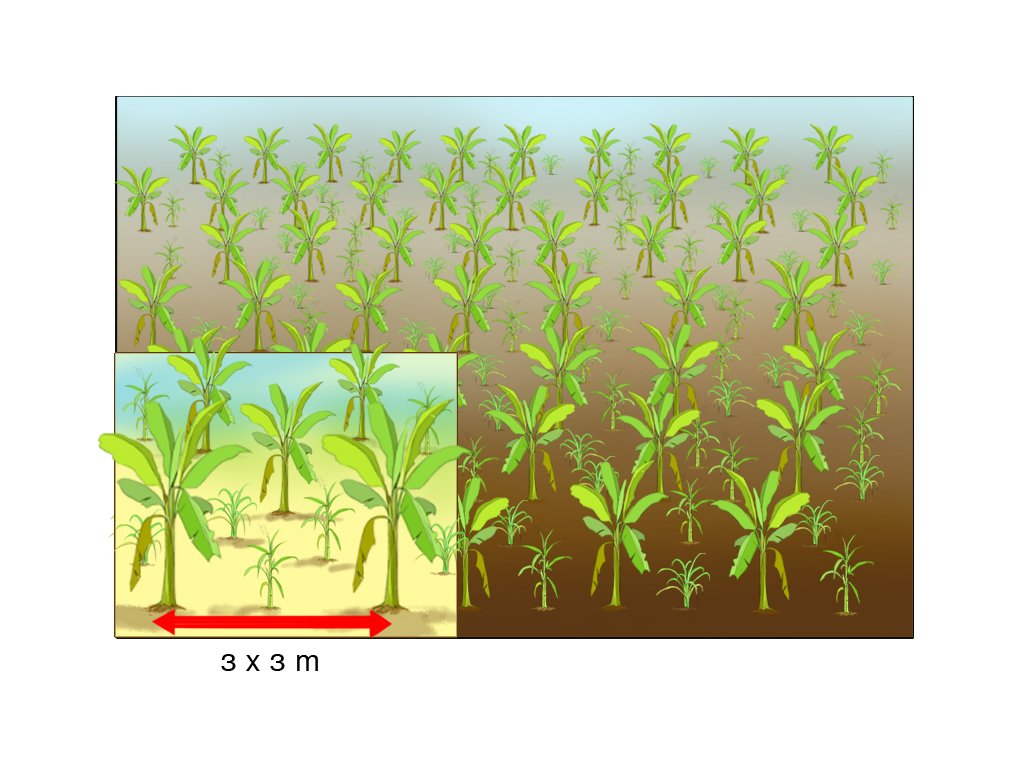
1. Site selection: land area with slope range between 10-20 percent and rich loamy soils; 2. Spacing and digging of holes: farmers arrange planting in lines and rows with spacing of 3m x 3m.; dimension of hole: 25cm x 25cm with a depth of 30cm. 3. Soil fertility: If the fertility of soil is low, manure (3 – 5kg/hole) has to be added on the bottom of the hole.4. Intercrops during first year of plantation: Between the banana rows upland intercrops can be seeded. This helps also to prevent soil erosion in the first year.5. Maintenance: Regular thinning and cutting of banana branches are required after planting to get good yield. Thinning may also involve removal of excess banana suckers, if there are more than 3-4 shoots per hole. The
young banana suckers that are removed can be planted in new areas.6. Farmers are required to maintain banana plantation areas including regular manual weeding as well as soil amendment (cow manure) to promote successful banana production. Covering the soil constantly with banana leaves is one of the most important activities to maintain the soil’s fertility (prevent soil leaching), structure and moisture, to improve the soil life, to lessen the burden of weeding and to prevent soil erosion. Chemical pesticides and fungicides are not foreseen to be used in this practice.7. Year after intercropping: After harvest of the crops such as maize or upland rice, banana sucker will be planted in rows on the remaining space between the 1 year old banana trees.
Author:
Anousith Namsena
Date:
06/07/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1ha
other/ national currency (specify):
LAK
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
30000
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slash and clearance vegetations | January to Febuary |
| 2. | Burning for land preparation | March |
| 3. | Digging the holes for the seedlings and planting | April (before rain) |
| 4. | Collecting the banana suckers from forest | May |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour for land preparation | person day | 70.0 | 30000.0 | 2100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Labour for planting | person day | 10.0 | 30000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Labour for collecting banana suckers | person day | 10.0 | 30000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Knief | piece | 4.0 | 30000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Shovel | piece | 4.0 | 20000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Banana sucker | sucker | 60.0 | 5000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Manure | kg | 240.0 | 1000.0 | 240000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3440000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 430.0 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | 2 times after planting |
| 2. | Cutting of banana "branches" | At different times when necessary |
| 3. | Banana harvest | After one year of planting |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour for weeding | person day | 20.0 | 30000.0 | 600000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Labour for cutting of banana "branches" | person day | 12.0 | 30000.0 | 360000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Labour for harvest | person day | 15.0 | 30000.0 | 450000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1410000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 176.25 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
The most important factors affecting the costs is labour for establishment and maintenance.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Meteorological Office in Samouy district of Salavan province
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
unusable
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Compared to the traditional cultivation practice the new technology introduced by the IFAD project bear far better banana yield.
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
The land users got bigger bananas and the productivity increased comapred to the former cultivation practice.
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Due to better yield all year round the income from banana selling increased.
workload
Comments/ specify:
Workload increased do to improved maintenance of the banana cultivation area (weeding, manuring, branch cutting etc).
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
Food security improved due to better banana production that provide enough income to meet other important household needs.
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Established and strengthened banana producer groups to negotiate with the traders.
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
The banana leaves on soil as mulch improved the soil moisture.
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
The soil cover is improved to some extent as both, banana and intercrop (maize and upland rice), are planted according to the criteria learned by the project. Futhermore, banana leaves scattered as mulching material cover the soil now.
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
Due to better soil cover.
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Comments/ specify:
Amendment in form of manure and the mulching by banana leaves improved the nutrient recharche.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
The banana plantation and its leaves on soil is good for increase in predators, earthworms, pollinators.
habitat diversity
Comments/ specify:
Increased micro organism (millipede, earth worn, centipede).
Climate and disaster risk reduction
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
Decreased emission of carbon and greenhouse gases from slash and burn shifting cultivation.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
The improved banana cultivation reduced the slash and burn practice and thus as well the emission of carbon and greenhouse gases.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| annual rainfall | increase | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | very well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
ສຳລັບ ການບຳລຸງຮັກສາ ມີພຽງແຕ່ ເສຍຫຍ້າ ຊື່ງບໍ່ໄດ້ສີ້ນເປືອງຫຼາຍ ເພາະໃຊ້ພຽງແຕ່ ແຮງງານພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
80 households out of 110 holds within the village hold such kind of banana plantations.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| The planting technique promoted by the project was not complicated to be implemented. |
| Banana plantation became the main source of household income. |
| Stabilized slash and burn shifting cultivation. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The land users can harvest bananas during the whole year, that ensure regular income. |
| The low investment costs for banana plantations. |
| The banana plantation can contribute to the climate change resilience and to reduce CO2 emission. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Weeding is a problem as it is labour intensive activity and family labour force is limited. | The land users have to pay more attention on weeding on time by hiring more labour for weeding activity. |
| Lack of experience and knowledge for which part of banana trees is the best to cut the banana branches to get the banana productive. | The land users require more specific training and field visiting to exchange with other land users who are experienced in good practices. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The land users have not enough experience by which means they can design the rows and lines exactly with regard to the sloping area before planting. | The land users can use plastic rope to measure the length from one hole to another hole. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1
- interviews with land users
1
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
1
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
04/07/2017
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules