Technologies
New SLM Technology [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: MIZROBSHO AMIRBEKOV
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_3695 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all
Completeness: 69%
1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
{'additional_translations': {}, 'value': 'Mizrob Amirbekov', 'user_id': '2000', 'unknown_user': False, 'template': 'raw'}
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Tajikistan {'additional_translations': {}, 'value': 898, 'label': 'Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)', 'text': 'Committee for Environment Protection of Tajikistan (Committee for Environment Protection of Tajikistan) - Tajikistan', 'template': 'raw'} {'additional_translations': {}, 'value': 898, 'label': 'Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)', 'text': 'Committee for Environment Protection of Tajikistan (Committee for Environment Protection of Tajikistan) - Tajikistan', 'template': 'raw'}1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
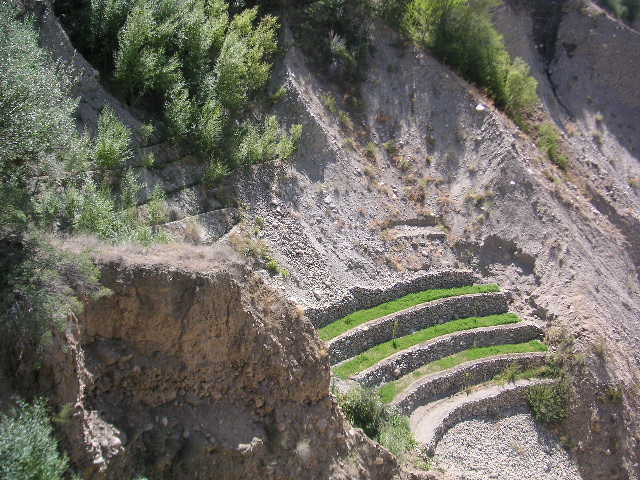
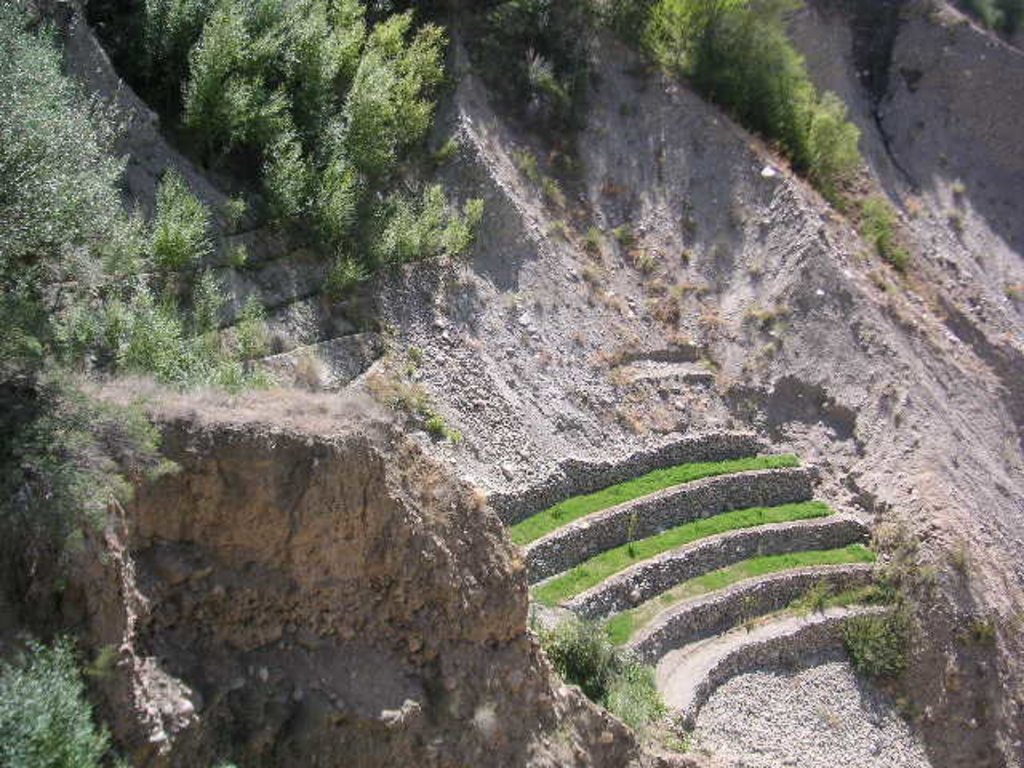
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- cross-slope measure
- ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
- A3: Soil surface treatment

vegetative measures
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
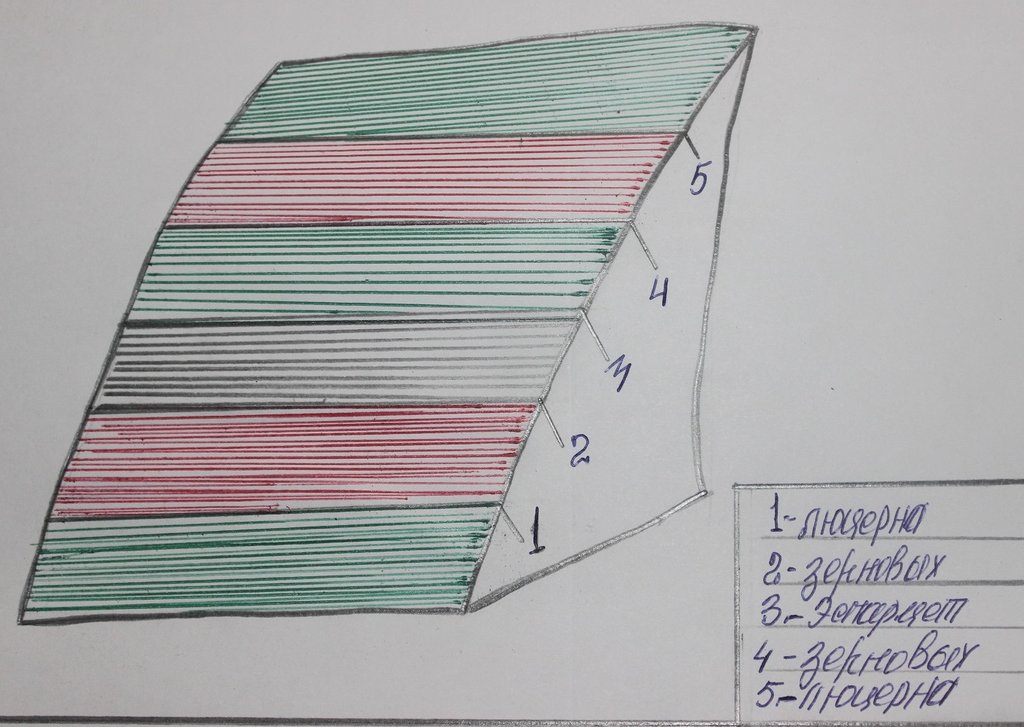
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
{'additional_translations': {}, 'content_type': 'image/jpeg', 'preview_image': '/media/70/0/7004e884-b239-46e2-a6e6-9b8e96309a14.jpg', 'key': 'Technical drawing', 'value': '/media/90/9/909107af-49a1-4b1d-8e67-278fc47a6caf.jpg', 'template': 'raw'}
Date:
10/03/2008
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.94
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 1.0 | 22.4 | 22.4 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 220.0 | 0.56 | 123.2 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 18.0 | 2.8 | 50.4 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 250.0 | 0.45 | 112.5 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 150.0 | 0.45 | 67.5 | 100.0 |
| Other | None | None | 1.0 | 460.0 | 460.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 853.8 | |||||
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| Other | None | None | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 200.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
decreased
crop quality
decreased
fodder quality
decreased
animal production
decreased
Socio-cultural impacts
health situation
worsened
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil cover
reduced
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
decreased
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
increased
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local hailstorm | well |
| local sandstorm/ duststorm | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| landslide | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
slightly negative
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
09/08/2009
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules