Mangroves as Buffer against Natural Hazards [Philippines]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Ursula Gaemperli
"Bakauan"
technologies_578 - Philippines
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
SLM specialist:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
philcatsecretariat@gmail.com
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Visayas Avenue corner Elliptical Road, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Gultiano Wilfredo
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Visayas Avenue corner Elliptical Road, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Abarro II Ace Wilfred
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Diliman, Quezon City
SLM specialist:
Lofranco Rufino
DENR-Community Environment and Natural Resources Talibon
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
10/08/2016
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
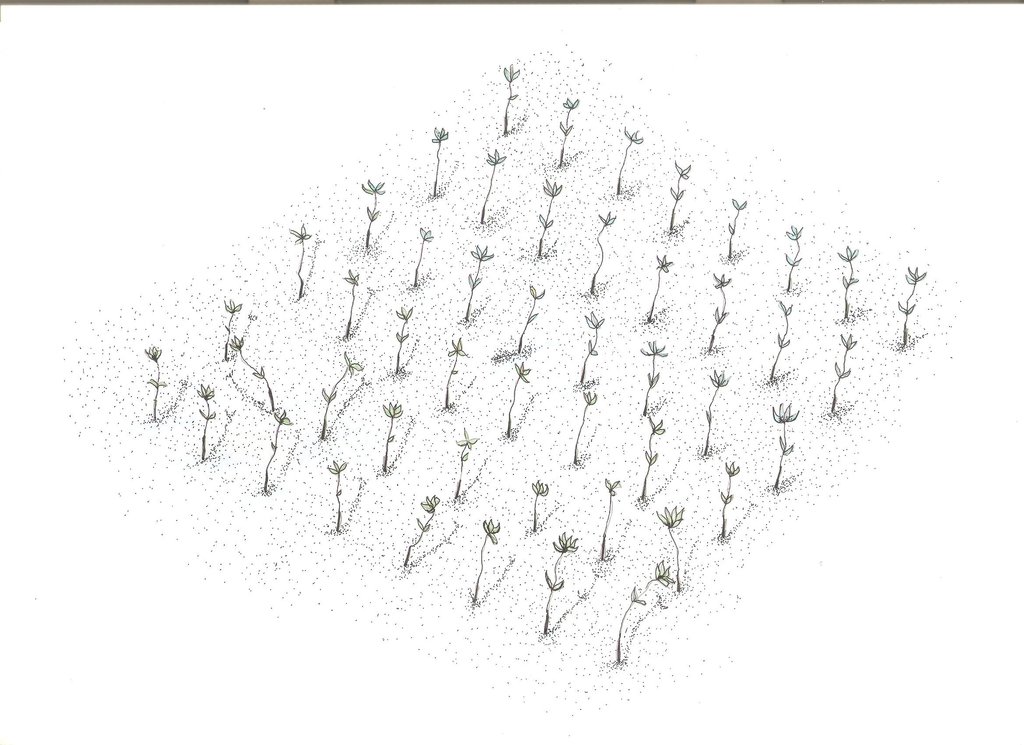
Mangroves "bakauan" are planted in the island coast to form barriers and as first line of defense during storm surges.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
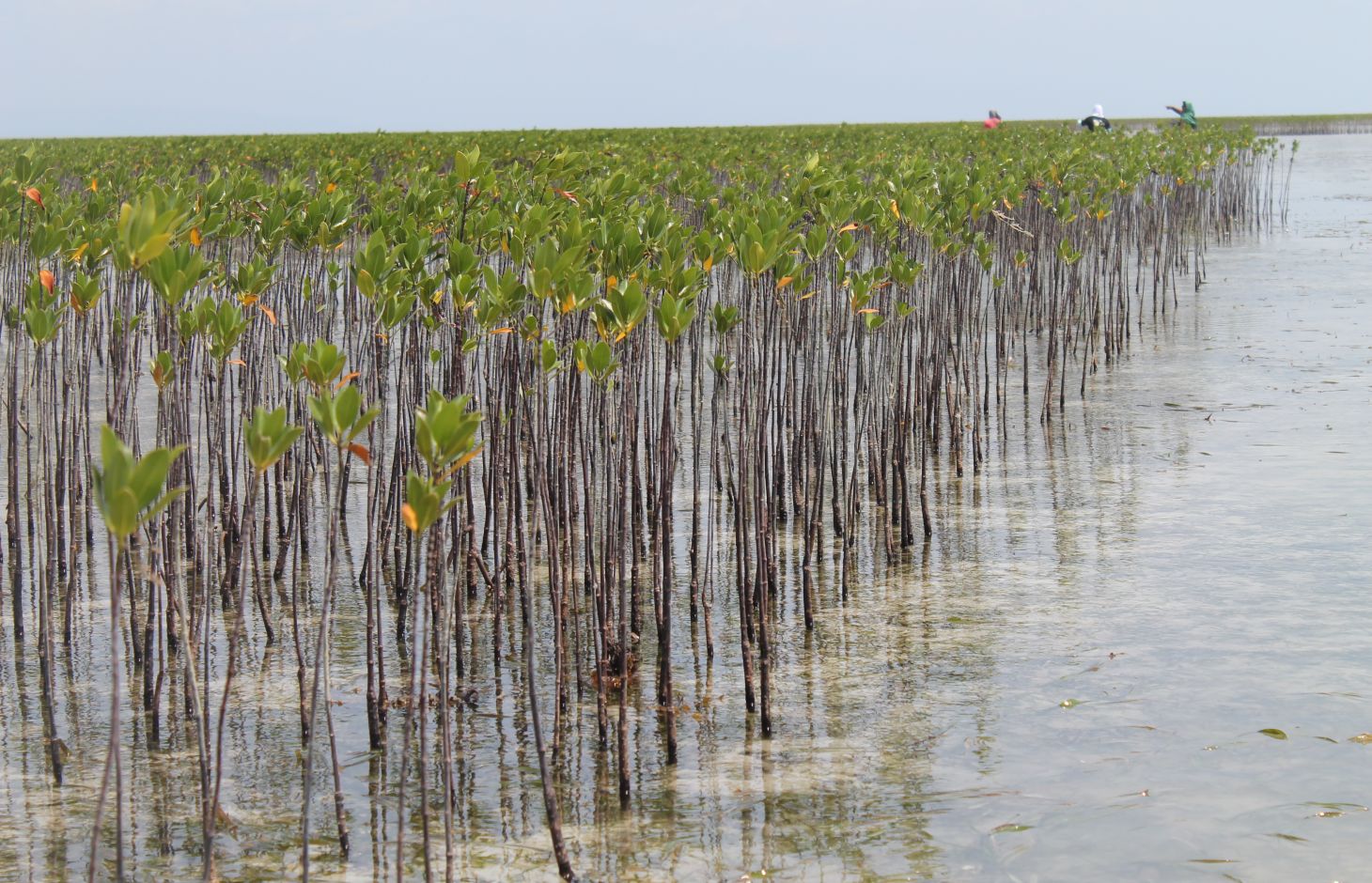
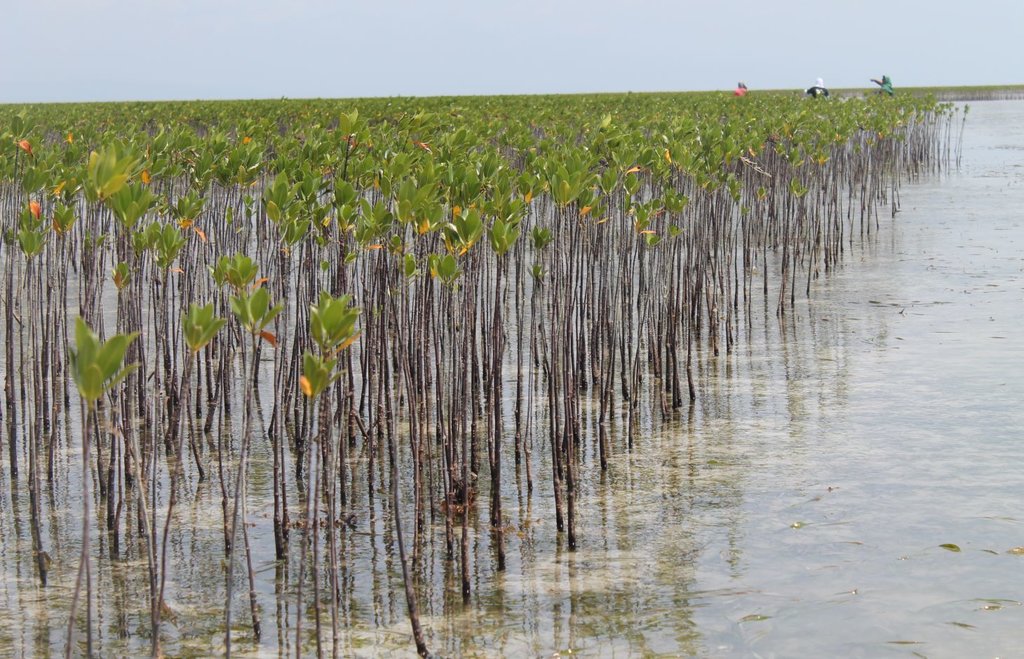
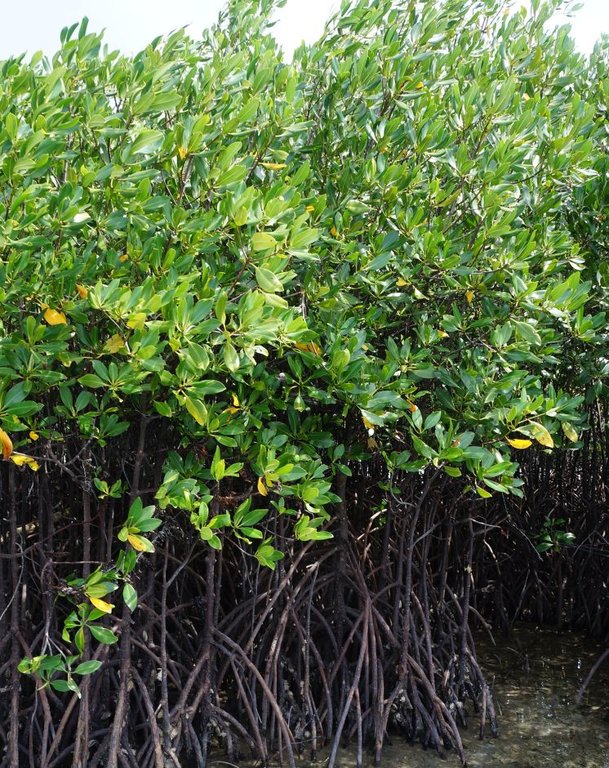
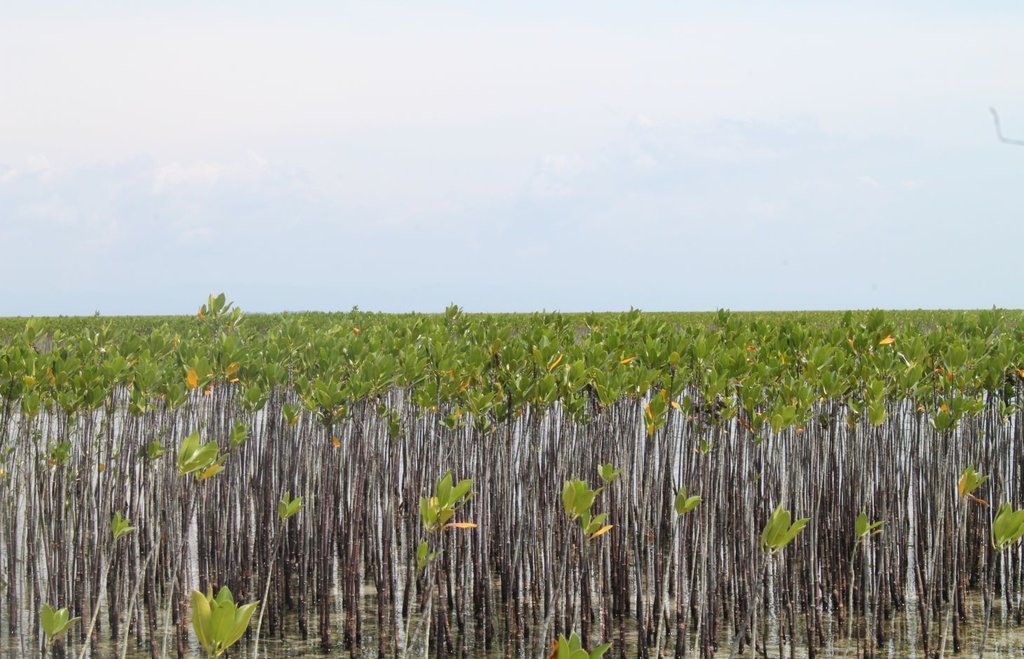
Mangrove plantation in the island of Banacon which is 10.91 kilometers away from the municipality of Getafe, Bohol in Central Visayas started in 1957.The most common specie grown is the “Bakauan” under the Rhizophoracea family.
Mangroves contribute in protecting the coast against natural hazards such as storms, tsunamis and coastal erosion. It weakens the impact of typhoons that bring strong winds, continuous high waves and storm surges. A dense cluster of bakauans obstruct the entry of winds and waves when passing through the mangroves minimizes the force of wind sand waves. According to the residents of the island, they were spared from total destruction of properties during onset of typhoons because of the presence of the bakauans. Mangroves were utilized also by the Banacon residents as source of poles for houses, fishpens and charcoals for cooking. The dense roots of the trees bind the soils thus preventing erosion. The tree roots serve as spawning ground for fishes and other variety of sea species that lead to an increase in harvest of sea foods in the area. The mangrove plantation was also developed into ecotourism site.
Site evaluation is the pre-requisite in the establishment of mangrove area. An ideal area is with sand dune during low tide. It is followed by site lay out using the planting design that is adopted, and direct planting of propagules in the soil. Planting materials used are the cigar-shaped mature propagules harvested from the Bacauan- Lalake specie of mangroves. The direct seeding planting is the ideal method of planting in establishing a mangroves plantation. Mangrove propagules must be planted after collection. It should not be exposed to direct sunlight to prevent moisture loss.
There are (3) planting designs used in the establishment of the mangroves. First, the high density planting of propagules with no lay out to be followed. This planting design can accommodate 30,000 pcs of propagules per hectare. Second, design has a spacing of 1 meter by 1 meter planted in rows and can hold 10,000 pieces of propagules per hectare. Third is the block/cluster design in which each cluster was planted with 750 pieces of propagules with a distance of 30 centimeters apart per propagules. The spacing between the blocks or cluster is 10 meters and can contain 5,000 pieces of propagules per hectare. Maintenance includes monitoring of the crop status, replanting of missing hills and weeding by removing sea weeds, barnacles and sea debris.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Philippines
Region/ State/ Province:
Bohol
Further specification of location:
Banacon Island, Getafe
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
This was started in the 1950's by Ernesto Pandi and supported by the DENR through programs such as National Greening Program, Community Based Forest Management
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- conserve ecosystem
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Forest/ woodlands
- Crustaceans breeding ground
Products and services:
- Nature conservation/ protection
- Recreation/ tourism
- Protection against natural hazards
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Specify:
Perennial trees
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- forest plantation management
- ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bh: loss of habitats
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
There are (3) planting designs used in the establishment of the mangroves. First, the high density planting of propagules with no lay out to be followed. This planting design can accommodate 30,000 pcs of propagules per hectare. Second, design has a spacing of 1 meter by 1 meter planted in rows and can hold 10,000 pieces of propagules per hectare. Third is the block/cluster design in which each cluster was planted with 750 pieces of propagules with a distance of 30 centimeters apart per propagules. The spacing between the blocks or cluster is 10 meters and can contain 5,000 pieces of propagules per hectare. Maintenance includes monitoring of the crop status, replanting of missing hills and weeding by removing sea weeds, barnacles and sea debris.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1 hectare
other/ national currency (specify):
Philippine peso
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
50.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
250
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting of matured propagules | Vegetative | During the month of June |
| 2. | Direct seeding of propagules | Vegetative | During low tide |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Person day/ hectare | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | ||
| Plant material | mangrove propagules | pieces | 5000.0 | 1.0 | 5000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 7500.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
The cost was funded by the government through the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replanting of propagules | Vegetative | monthly |
| 2. | Weeding and cleaning of site | Vegetative | monthly |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | labour | person day | 3.0 | 250.0 | 750.0 | |
| Plant material | propragules | pieces | 250.0 | 1.0 | 250.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
The cost was funded by the government through the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR)
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Water quality (untreated):
unusable
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Yes
Regularity:
frequently
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Frequent flooding as mangrove forests are a part of the coastal marine ecosystem region
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
forest/ woodland quality
non-wood forest production
Comments/ specify:
Mangrove forest are breeding grounds for various marine animal species such as fish, crabs and shrimps.
Socio-cultural impacts
recreational opportunities
Comments/ specify:
Establishment of beach forest
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Formation of Peoples Organization.
Ecological impacts
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
impacts of cyclones, rain storms
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
Mangrove forest in Banacon Island has potential in terms of carbon sink by reducing organic pollution.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| storm surge/ coastal flood | very well |
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
Most of the people in the community are involved in the mangrove forest program because of the support of the Department of Environment and Natural Resources.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Yes
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
Planting design was modified through clustering for a technology resilient to climate change
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Innovative planting design using clustering as climate change mitigation measure. Mangroves are planted in cluster to achieve strength. The community and the Peoples' Organization (POs) determine the size of cluster to allow space as passage for boats. Spacing design used is flexible to adjust to local conditions that include depressed grounds, and patches of vegetation. |
| It provides livelihood for the community since it supports fisheries production and aquaculture. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| It provides protection in the coastal communities from storm surges, waves, tides, and currents. Mangrove has buffering capacity to hold back sea waves and reduce wave forces because of its extensive and dense above ground roots. |
| Mangrove plantation has potentials for ecotourism development. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Mangrove pests and diseases have caused failure of mangrove forest development.Planted propagules that are submerged most of the time have a low mortality rate. | Proper site selection of plantation site |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Mangrove sites are threatened by urbanization, conversion to agriculture, cutting/overharvesting of mangrove trees for industrial uses such as timber and charcoal | Strict implementation of rules, policies related to the protection and conservation of coastal areas and mangrove forest sites. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
3
- interviews with land users
3
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules