Trouaison [Togo]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Laura Ebneter
Pon daw (en Kabyè, deuxième langue nationale)
technologies_998 - Togo
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Dogo Madawè
+2289892825
pameyoyo@yahoo.fr
Ecole Supérieure d'Agronomie, Université de Lomé (ESA UL)
Lomé
Togo
SLM specialist:
Sokame Bonoukpoè Mawuko
+2289913490
mawuko86@yahoo.fr
Ecole Supérieure d'Agronomie, Université de Lomé (ESA UL)
Lomé
Togo
SLM specialist:
Hounkpati Kwevitoukoui
+2289181954
khoun75@yahoo.fr
Ecole Supérieure d'Agronomie, Université de Lomé (ESA UL)
Lomé
Togo
SLM specialist:
Ayeva Tchatchaibara
+2289011334
Institut Togolais de Recherche Agronomique
Kara
Togo
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ecole Supérieure d'Agronomie, Université de Lomé (ESA) - TogoName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Institut Togolais de Recherche Agronomique (ITRA) - Togo1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
16/08/2007
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
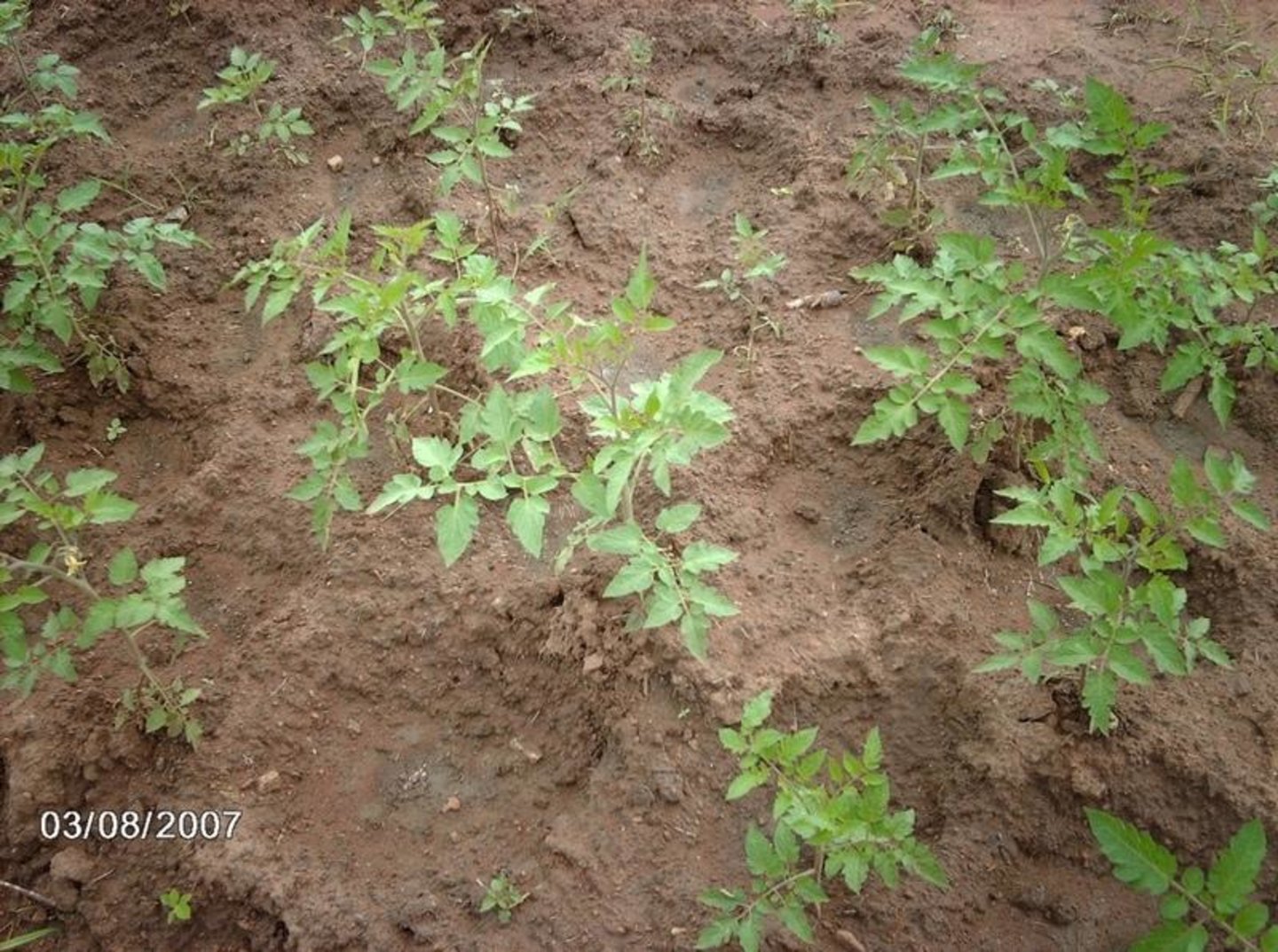
La technique de trouaison consiste à creuser de petits trous circulaires entre les plants pour l'économie de l'eau surtout en saison sèche et la retention des fertilisants à proximité des plants.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
La confection des trous s'effectue sur des planches de cultures maraichères. Il s'agit de petits trous ouverts à l'aide d'une binette ou d'une petite houe entre les jeunes plants de légumes (tomates, piments,chou, etc.). Ces trous ont un diamètre d'environ 22 cm et une profondeur de 10 cm en moyenne.Les trous sont faits suivant les lignes de semis. L'eau d'arrosage reste stagnée dans ces trous et est progressivement utilisée par les cultures. Il en est de même pour les fertilisants (engrais minéraux) apportés .Le curage hebdomadaire de ces trous est nécessaire pour éviter leur envasement.
Objectif: Rétention et utilisation rationnelle de l'eau et des fertilisants.
Activités de construction / d'entretien et intrant: * confectionnement des trous à l'aide des binettes entre les plantes
* curage hebdomadaire de ces trous de poquets
Environnement naturel / humain: Cette technique s'applique sur les perimètres maraichers, le long des cours d'eau et dans les bas-fonds de préférence en saison sèche.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Togo
Region/ State/ Province:
Kara
Further specification of location:
Lassa
Map
×3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Comments:
les problèmes majeurs d’utilisation des terres (du point de vue du compilateur): lessivage des fertilisants, sécheresse des planches et ralentissement de la croissance des jeunes plants
les problèmes majeurs d’utilisation des terres (du point de vue de l’exploitant): drainage de l'engrais dans les sillons
3.3 Further information about land use
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Saison de culture: durée en jours 180, du mai - oct
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Comments:
Superficie totale de la zone de la Technologie de GDT 0.55 ha.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A3: Soil surface treatment
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
problème de dégradation des terres majeur: aridification
problème de dégradation des terres secondaire: baisse de la fertilité du sol et du niveau de matière organique
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Author:
Idrissou BOURAIMA, Carto/FLESH, UL; Lomé-Togo
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Dessin d'illustration de la technologie de trouaison
Lieu: Lassa Badjo. Préfecture de la Kozah
Date: 25/08/2007
le niveau de connaissances techniques requis pour le personnel de terrain: faible
le niveau de connaissances techniques requis pour l'exploitant: moyen
Objectif principal: augmentation / maintien de la rétention d'eau dans le sol
Objectif secondaire: augmentation de l'infiltration, augmentation de la fertilité du sol
pratiques agronomiques: engrais minéraux
matériel / espèces: NPK (15-15-15)
quantité / densité: 1bol/12 pl
remarque: épandage au pied des plants
Surface du sol: trouaison
Remarque: 49500 trous par hectare en alignement
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1 ha
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5.56
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Main d'œuvre | ha | 1.0 | 84.0 | 84.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Outils | ha | 1.0 | 62.0 | 62.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Compost/Fumier | 1.0 | 121.0 | 121.0 | 100.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Engrais (kg) | 1.0 | 162.0 | 162.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 429.0 | |||||
Comments:
Duréé de mise an place: 12 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | défrichement | Agronomic | début de saison sèche / chaque saison de culture |
| 2. | remuer le sol | Agronomic | début de saison sèche / chaque saison de culture |
| 3. | repiquage | Agronomic | début de saison sèche / chaque saison de culture |
| 4. | trouaison | Agronomic | saison sèche / chaque saison de culture |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Main d'œuvre | ha | 1.0 | 217.0 | 217.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Outils | 1.0 | 278.0 | 278.0 | 100.0 | |
| Other | arrosages | ha | 1.0 | 105.0 | 105.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | eau (m3) | 1.0 | 11112.0 | 11112.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 11712.0 | |||||
Comments:
outils: 3 binettes, 4 houes, tuyaux, arrosoirs, motopompe, ces coûts ont été calculés par hectare de terre traitée
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
- rich
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
70% d'exploitants sont riches et détiennent 90% of the land (niveau de vie élevé).
30% sont moyens et détiennent 10% of the land (autosuffisance).
en saison morte, ils s'adonnent à l'artisanat et aux petits commerces
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- leased
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
en période sèche
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
disponibilité des ressources agricoles pour l'achat des intrants (engrais) pour la campagne suivante
economic disparities
Comments/ specify:
la confection et l'entretien de poquets demandent plus de travail
workload
Comments/ specify:
la confection et l'entretien de poquets demandent plus de travail
Socio-cultural impacts
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
entendement entre les populations
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
bonne maitrise de la conservation de l'humidité dans le sol
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
67
Quantity after SLM:
13
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
la retention de l'eau favorise son infiltration dans le sol
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
7
Quantity after SLM:
4
Other ecological impacts
réduction du ruissellement de surface
Quantity before SLM:
67
Quantity after SLM:
13
augmentation de la fertilité du sol
Comments/ specify:
réduction de lessivage de l'engrais minéral
amélioration de la biodiversité
Comments/ specify:
maintien des planches
saturation en eau des sols
Comments/ specify:
lexiviation (perte des éléments nutritifs) en profondeur
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
Comments/ specify:
réduction des quatités d'eau ruissellant vers l'aval
groundwater/ river pollution
Comments/ specify:
réduction des débris organiques transportés par l'eau ruissellante
wind transported sediments
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
100% de familles exploitantes ont appliqué la technologie de GDT sans assistance materiélle externe
98 nombre de familles exploitantes avec 13% de la superficie de la zone du à l'augmentation du rendement
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
retention d'humidité dans le s Comment peuvent-ils être maintenus / renforcés? paillage des planches surtout en saison sèche |
|
bon développement de la plante Comment peuvent-ils être maintenus / renforcés? apport d'engrais minéral |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
maintien ou réhabilitation de la fertilité du sol Comment peuvent-ils être maintenus / renforcés? apport du fumier ou engrais minéral |
|
augmentation du rendement agricole Comment peuvent-ils être maintenus / renforcés? entretien des trous et semis des plants (traitements phytosanitaires) |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| forte humidité du sol surtout en saison pluvieuse | pas de trouaison en saison des pluies |
| jaunissement des plantes en cas d'excès d'eau dans le sol | pas de trouaison en saison des pluies |
| lexiviation (perte d'éléments minéraux en profondeur) surtout en cas de grade de pluie | pas de trouaison en saison des pluies |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| travail fastidieux | mécanisation du travail |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Rapport, Etude de l'amenagement participatif du bassin versant de Lassa Badjo; 2ème phase, Direction Régionale de l'Agriculture, de l'Elevage et de la Pêche (DRAEP) Kara. 2004.
Available from where? Costs?
ESA UL
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Mémoire, Système d'érosion et cartographie de la dynamique de l'environnement du site urbain de Sokodé, BOURAIMA I.. 2004.
Available from where? Costs?
Université de Lomé, FLESH, Département de Géographie
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules