Wooden check dams [Slovakia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Zuzana Studvova
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Drevené prehrádzky (Slovak language)
technologies_1664 - Slovakia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Slovak University of Technology (Slovak University of Technology) - Slovakia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river … [Slovakia]
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
- Compiler: Zuzana Studvova
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
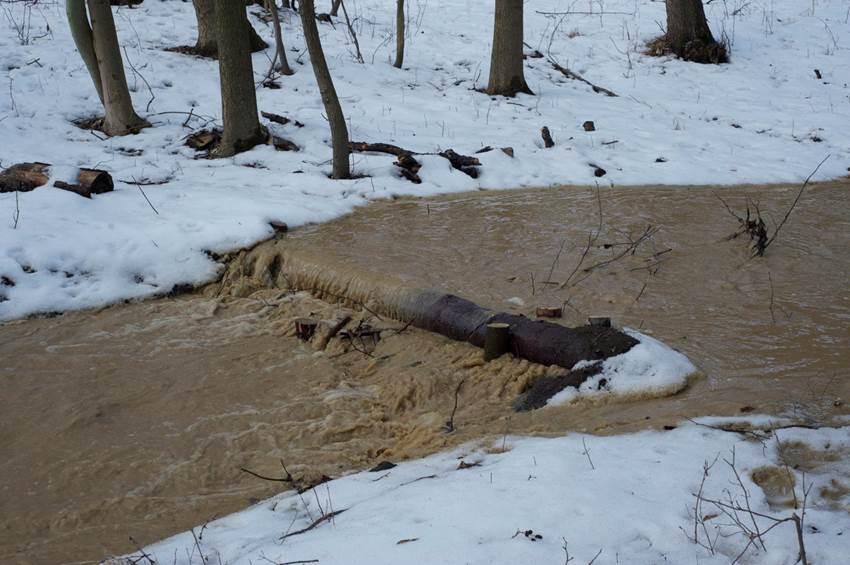
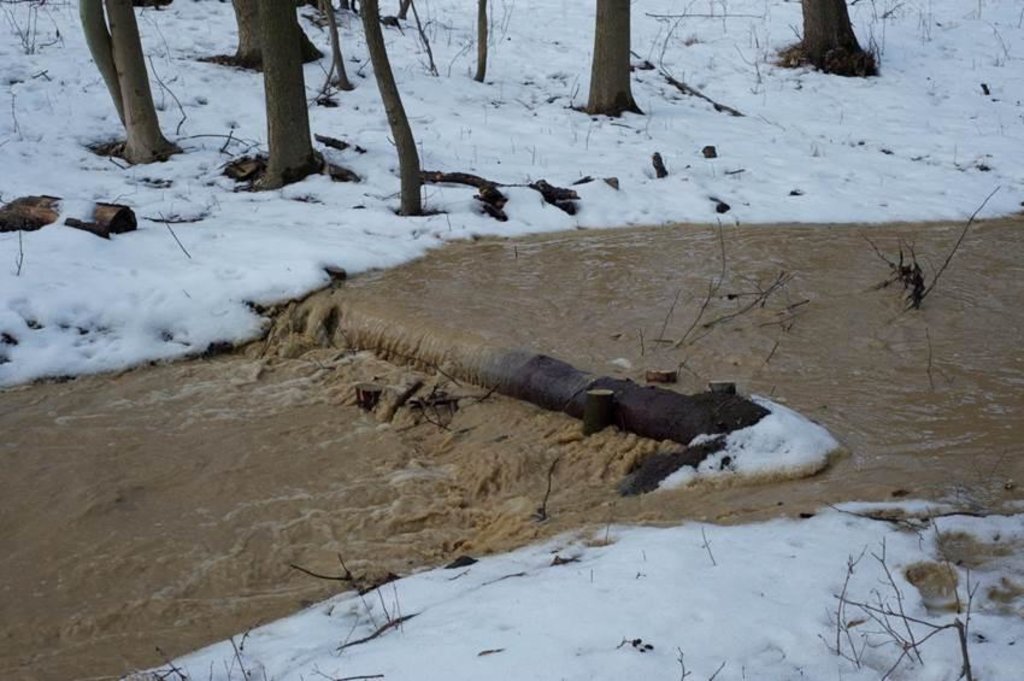
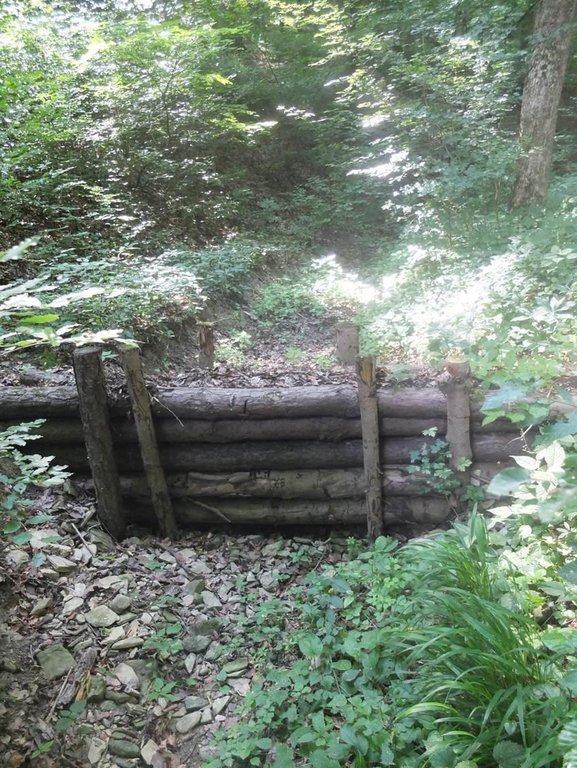
Small wooden check dams built in erosion rills, grooves or gorges to reduce flood risk.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
The terrain is considerably sloping with deep "V" cuts in steep terrain. In that area small check dems, made of wooden logs, were realized..
Purpose of the Technology: The aim was to reduce flood risk mitigation by torrential rains and local flooding.
Natural / human environment: The area is situated in a valley at the foot of the Carpathians, which are part of the outer Carpathian Belt formed by flysch. Relatively large differences in elevation of the country cause excessive concentration of surface runoff. Substantial part of the tributaries are formed by concentrating runoff in ravines, erosion grooves, rills. Most of the country consists of agricultural production of crops, less by forests and grasslands.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Slovakia
Region/ State/ Province:
Slovakia / Myjava
Further specification of location:
Myjava
Comments:
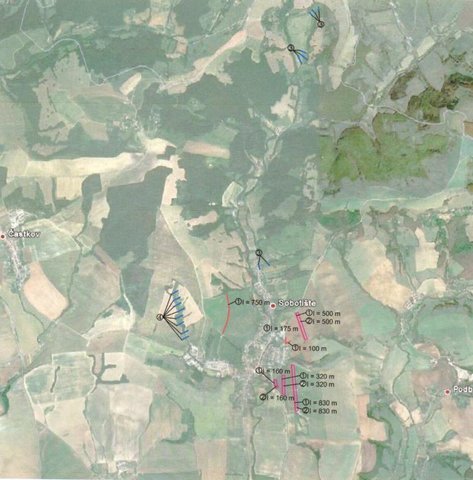
The area of the one small check dam is few squared meters. The technology was used on different places in the area. The area of the city is 4854 ha.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
- wheat
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April to october

Forest/ woodlands
- (Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- Selective felling
Products and services:
- Timber
- Fuelwood
- Nature conservation/ protection
- Recreation/ tourism
- Protection against natural hazards
Comments:
Major cash crop: Oil-seed rape (Brassica napus)
Major food crop: Wheat
Other crops: Maize / corn (Zea mays)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main land use problem is steep terrain. During heavy rains runoff forms and floods in the lower part of the area.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Steep terrain with influence of heavy mechanisms forms gullies in the forest and causes demages by floods and mud floods.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Unknown
Forest products and services: Primary: Timber, fuelwood, secondary: Recreation / tourism third: protection against natural hazardsnature conservation / protection,
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S5: Dams, pans, ponds
Comments:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy forest mechanisms (The use of the heavy mechanisms that make cuts (rills) by its wheels in the ground, especially during or after rain. Runoff that forms, flows in rills and deepen those rills.)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): -
Spacing between structures (m): -
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): -
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1 to 5 m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): -
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 m
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): -
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): -
Construction material (wood): Wooden round logs (rough strains)(150-180 mm in diameter; 100-500 cm long), wooden stakes.
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 20.53 to 94.09, together 374m3
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.89
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wooden structure instalation | november, december |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | Dam | 1.0 | 238.0 | 238.0 | |
| Equipment | Tools | Dam | 1.0 | 182.0 | 182.0 | |
| Construction material | Wood | Dam | 1.0 | 626.0 | 626.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 1046.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1175.28 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: chainsaw, handsaw, heavy hammer, shovels, spades, hoes, pickaxes, ax
The costs are calculated (averaged) for one dam. Together 6 wooden dams were built on the study area - 90 ha. The costs were valid for the year 2011. The prices were calculated with the 20% VAT.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Material and labour price.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
93 -100 rainy days/year,
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
- arid
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Topsoil organic matter is unknown
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is unknown
5.4 Water availability and quality
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Ground water table is unknown
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water (ground water)
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- commercial/ market
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative; 4%
Off-farm income specification: Unknown
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
1-2 ha: 1036 ha of forest. Population is 11740. Number of households is unknown.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- leased
Water use rights:
- leased
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Other socio-economic impacts
Damage
Comments/ specify:
Less demage on properties because of flooding and mud floods.
Ecological impacts
Other ecological impacts
Speed of runoff
Comments/ specify:
Retard/slow down runoff
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very negative
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very negative
Comments:
The life of the structur, as it is made of wood is not very long. It is sedimated signifitantly afterheavy rains.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The technology is easy to built and maintain. |
| Simple tools and equipment needed. |
| Low number of labour. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Relative short duration. | |
| Maintanance needed. | |
| Ineffective during extremly high storms and it can be damaged. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
http://www.hospodarskyklub.sk/docs/katalog2.pdf
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river … [Slovakia]
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
- Compiler: Zuzana Studvova
Modules
No modules