Strip mine rehabilitation [South Africa]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Kirsten Mahood
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli
technologies_970 - South Africa
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
University of Stellenbosch (University of Stellenbosch) - South Africa1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
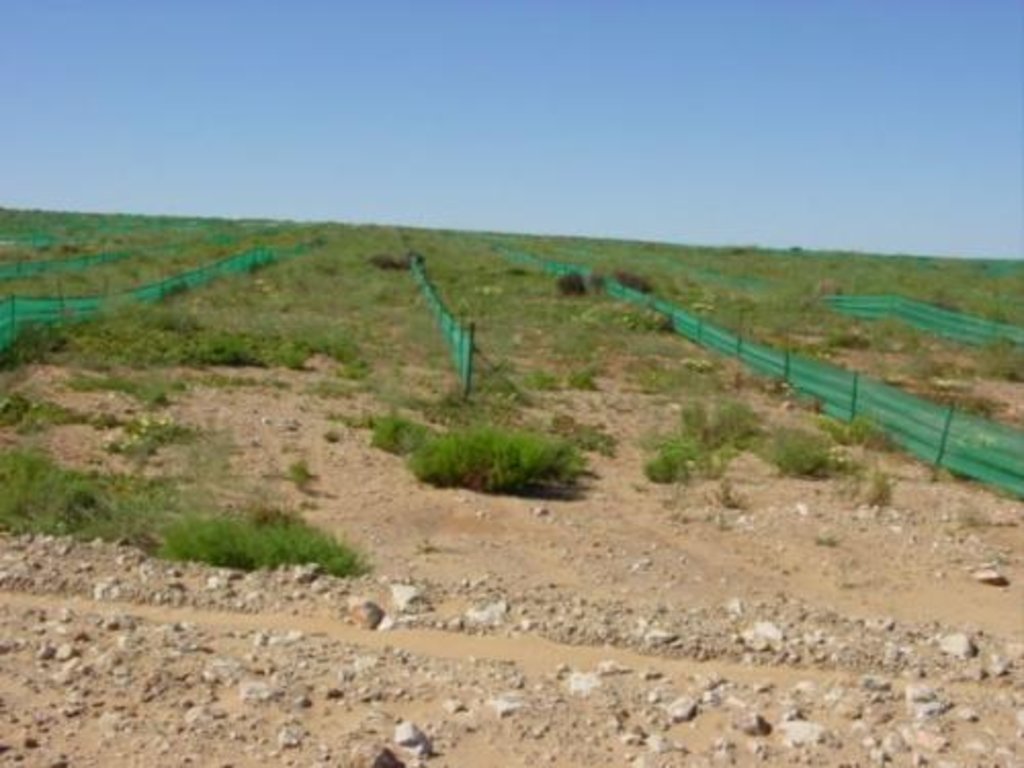
Rehabilitation of areas degraded by strip mining, through returning stockpiled topsoil and transplanting of indigenous species, to promote revegetation.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
In contrast to the land degradation commonly caused when ‘strip mining’ is carried out, a land rehabilitation technology, which was first developed experimentally, is now routinely applied by mining companies on the west coast of South Africa. Indeed it is now a legal requirement in South Africa for mining companies to rehabilitate mined areas to a condition and productivity equivalent to the pre-mining situation.
The primary purpose of the technology described here is to achieve this result – thus allowing the site to be used again for extensive grazing by sheep and wild animals. Revegetation also reduces wind erosion. The technology further contributes to increasing biodiversity, as particular attention is given to planting a range of locally endemic and other indigenous species.
The sequence of operations is as follows: during strip mining operations the topsoil is pushed to one side by bulldozer, and stockpiled. The substrata is then excavated mechanically, removed by tipper truck, and processed to extract the heavy metals. The tailings (waste materials) are returned by tipper truck to the area from which they were mined, and then levelled by bulldozer. The stockpiled topsoil is returned and spread by bulldozer over the levelled tailings. Indigenous succulents and other plant species are dug out by hand, with a spade, from either the surrounding areas of natural vegetation, or from the piles of topsoil (where plants may have naturally established) and transplanted manually into the newly spread topsoil. The planted areas are protected from wind erosion by erecting fine mesh nylon netting as windbreaks. These are 0.8 metre high and 5 metres apart. The nets are usually installed for a period of up to 2-3 years. Subsequently they are removed, once the vegetation has successfully become re-established, and they may be re-used at the next rehabilitation site. Maintenance activities continue for a few years – until the site is rehabilitated. An individual mine strip is usually about 1 km long and some 100 m wide.
This form of strip mine rehabilitation has been in operation since 1990, and costs on average just over US$ 200 per hectare, with all expenses met by the mining company. This particular approach was developed for the Anglo-American subsidiary – ‘Namaqua Sands’. A similar approach was adopted by ‘PBGypsum Mines’ located further inland, where rehabilitation is also conducted on several hundreds hectares of mined land. Not all mining companies use the same technology, however.
Purpose of the Technology: Establishment activities:
Mining activities (not part of technology)
1.Removal and stock piling of topsoil
2.Excavation, removal and processing of substrata to extract heavy minerals
3.Return and levelling of the mine tailings
4.Return and spreading of topsoil Technology activities
5.Collection/digging up of indigenous plants
6.Transplanting into returned topsoil
7.Erection of fine mesh nylon net windbreaks Activities 1-4 are a continuous process associated with the speed of mining activities and involve the use of heavy earth moving machinery (bulldozers, front end loaders, tipper trucks). Activities 5&6 take place immediately prior to the onset of the rainy season and involve hand labour for collection and transplanting and tractor and trailer for transporting collected plants. Activity 7 can take place at any time of the year involving hand labour for erection of the nets and tractor and trailer for transport.
Maintenance / recurrent activities per year:
Maintenance activities restricted to:
1.Ensuring the nylon nets remain upright
2.Supplementary watering during the winter months, when rainfall inadequate, to support plant growth
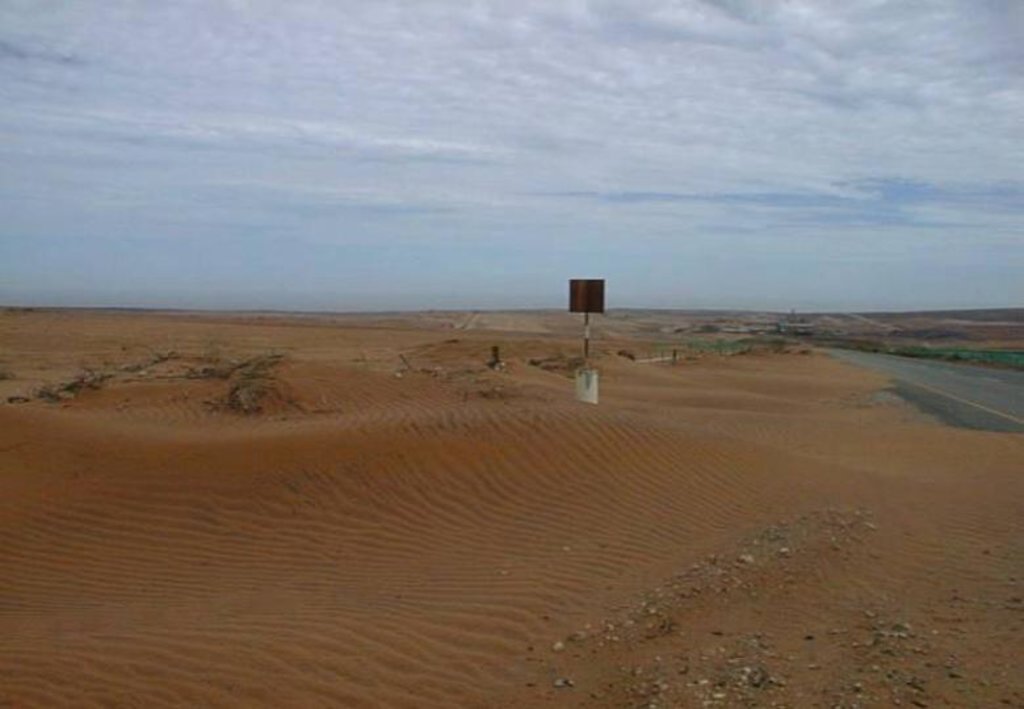
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
South Africa
Region/ State/ Province:
Western Cape
Further specification of location:
Brand-se-Baai, Western Cape
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Developed at University of Stellenbosch
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Ranching
Mines, extractive industries
Specify:
Stockpiling of topsoil; processing of subsoil
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Aridness and climate change. Erratic rainfall/climate. Frequent drought.
Ranching: Yes
Constraints of mines and extractive industries: Stockpiling of topsoil; processing of subsoil
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Aug
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A3: Soil surface treatment
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.1: No tillage

vegetative measures
- V5: Others

structural measures
- S11: Others
Comments:
Specification of other vegetative measures: translocation of indigenous plants
Specification of other structural measures: land levelling, artificial windbreaks
Type of agronomic measures: zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

physical soil deterioration
- Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 2000
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Other species: Succulent plants
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
Structural measure: silt fence
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Construction material (other): nylon net - small grid size
Silt fence: all 5m and height of 0.8m
Author:
Kirsten Mahood
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Rand
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
9.07
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
12.00
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of plants from natural vegetation | Pre-rainy season |
| 2. | Collection of plants from topsoil stockpiles | Pre-rainy season |
| 3. | Transport plants to rehabilitation area | Pre-rainy season |
| 4. | Plant all plants | Pre-rainy season |
| 5. | Insert droppers into net pockets | all year |
| 6. | Spread nets over topsoil areas | all year |
| 7. | Erect nets and hammer in droppers | all year |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | hectare | 1.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Machine use | machine hours | 0.5 | 134.0 | 67.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Construction material | Nylon net | ha | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 212.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 23.37 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topsoil pushed into stockpile | all seasons / continuous |
| 2. | Subsoil removed and processed | all seasons / continuous |
| 3. | Processed subsoil returned to mined area and levelled | all seasons / continuous |
| 4. | Stockpiled topsoil spread over processed subsoil | all seasons / continuous |
| 5. | Plants transplanted onto spread topsoil | just before rainy season / late autumn/winter |
| 6. | Ensure nets remain upright | all year/continuous |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 37.0 | 37.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 37.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 4.08 | |||||
Comments:
Per hectare
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour costs
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
soil fertility: very low, soil drainage / infiltration = low, soil water storage capacity = low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Most of income from mining
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
vegetation, establishment
animal production
Comments/ specify:
Land can be used again for extensive grazing after mining
Socio-cultural impacts
community institutions
national institutions
Comments/ specify:
improved conservation / erosion knowledge
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil cover
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
Comments/ specify:
restoration of bio-productive function
habitat diversity
Comments/ specify:
biodiversity enhancement
Climate and disaster risk reduction
wind velocity
Comments/ specify:
reduced wind velocity
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
wind transported sediments
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Low establishment costs and very low maintenance costs How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make use of whatever resources and potentials are naturally available (such as micro-catchments to trap rainwater and improve soil moisture conditions for plants) to lower establishment costs. |
|
Costs are met by the mining company – no costs are transferred to those who subsequently use the land for grazing How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular monitoring of soil and vegetation conditions. |
|
Land productivity is restored and biodiversity increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Seeding as well as transplanting. |
| Wind erosion minimized. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Rehabilitation is an extra cost for the mining company. | Ensure mining company meets the costs through enforcing legislation. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules