Participatory action research on drip irrigation
(Nepal)
Descripción
Conducting participatory action research with farmers and line agencies for demonstrating, disseminating and scaling up drip irrigation.
Most farming in the uplands of Nepal's midhills is rainfed with many fi elds remaining fallow during the dry season due to lack of irrigation water. The People and Resource Dynamics Project (PARDYP) water demand and supply survey identified scarcity of irrigation water as a major issue in Nepal's midhills. To assess the potential of drip irrigation to address this problem, the University of British Columbia (UBC) in 2000/2001, in collaboration with PARDYP, tested a low cost irrigation drip set and a more costly set in the Jhikhu Khola watershed; and PARDYP and Tribhuvan University's Institute of Engineering (Nepal) tested the low cost set with farmers at another site at Kubinde village, Kavre.
PARDYP started research on drip irrigation at an agricultural research station (the Spices Crop Development Centre at Tamaghat, Kabhrepalanchok) and brought different stakeholders, principally farmers, to the station to learn. After seeing the trials some farmers, especially those living near the research station, started testing drip irrigation on their farms. From 2001 to 2004, PARDYP subsidised 50% of the cost of the drip sets to most adopting farmers. PARDYP organised several farm visits for stakeholders to the research station and farmers’ fi elds. The number of interested farmers increased and many started testing and demonstrating the technology on their farms. PARDYP provided technical support during installation, advice about water application, and trouble shooting training to user farmers. Soon, many farmers started using drip irrigation with little or no technical support from PARDYP. Some collected quantitative and qualitative information on the performance of their systems. Results and experiences were shared regularly after cropping seasons through interaction meetings. Users’ experiences convinced many others to adopt the technology.
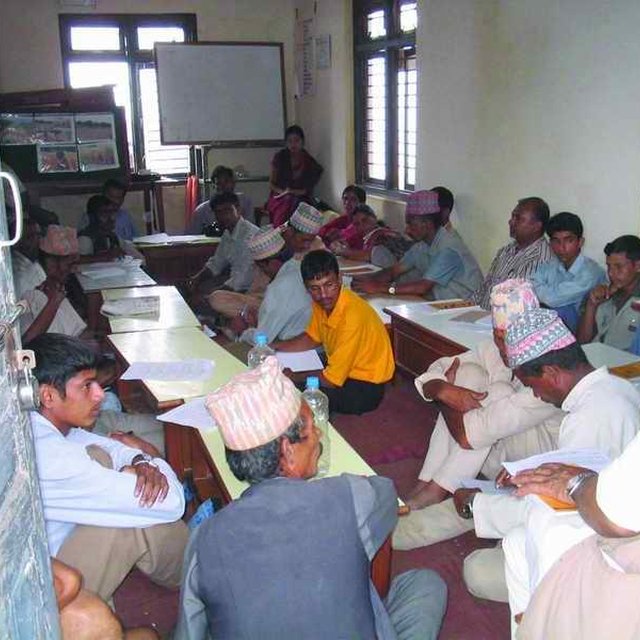
Interaction meetings were organised to communicate farmers’ feedback to the organisation and businesses involved in making the drip sets. Farmers from the watershed were taken to the drip set manufacturers to establish a direct link between them and to allow the project to phase out its support.
This approach emphasised on-station to on-farm research and demonstration to facilitate ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the performance of locally made drip sets.
Lugar
Lugar: Kavrepalanchowk/ Jhikhu Khola watershed, Nepal
Georreferencia de sitios seleccionados
Dato de inicio: n.d.
Año de conclusión: 2005
Tipo de Enfoque
-
tradicional/ local
-
iniciativa local reciente/ innovadora
-
proyecto/ basado en un programa

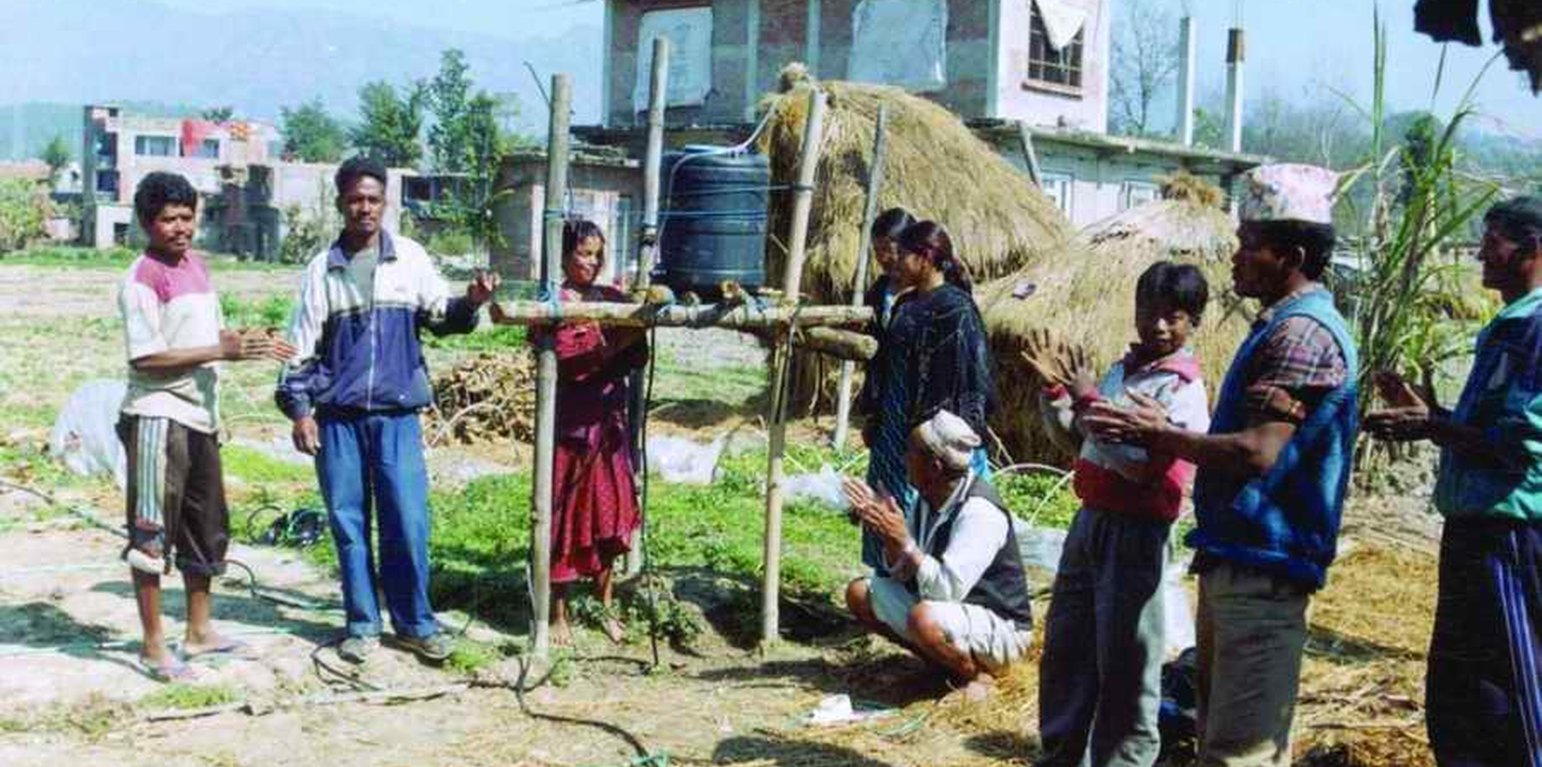
Farmer interaction programme: results and experiences were shared regularly. through interaction meetings where drip users and non-users discussed the technology. (Madhav Dhakal)
Metas del Enfoque y entorno facilitador
Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (income generating activities, vegetable farming with micro irrigation system)
To test, demonstrate, and evaluate drip irrigation systems under local conditions with multiple stakeholders. To share results and experiences with communities to scale up the technology
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of systematic on-farm research on drip irrigation. - Weak institutional collaboration for developing, disseminating and scaling up drip technology. - Inadequate water available for agriculture alongside strong seasonality and poor irrigation facilities
Condiciones que facilitan la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
-
Marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Because of private land owners there were no conflicts on land to implement the technology and for it's dissemination. and scaling up.
Condiciones que impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
-
Disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros : Insufficient government incentives
Treatment through the SLM Approach: A Cost-effective technology and implementing approach
-
Entorno institucional: Weak institutional collaboration among line agencies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Participatory action research with several institutions - universities, local research centres, and farmers
-
Conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico: Promotion of micro irrigation was not a priority of line agencies in the study area
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Technology implemented with multiple stakeholders' participation
-
Otros: Lack of awareness on potential water-saving options
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Community-based training, discussions and field visits
Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
| ¿Qué partes interesadas/ entidades implementadoras estuvieron involucradas en el Enfoque? |
Especifique las partes interesadas |
Describa los roles de las partes interesadas |
| usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales |
|
On farm research and demonstration
men and women worked equally |
| organizaciones comunitarias |
|
existing groups of land users; community forest user group and terrace improvement committee |
| especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas |
Field technicians |
|
| ONG |
|
On station research
|
| gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades) |
|
On station research |
| organización internacional |
|
On station research |
Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
ninguno
pasivo
apoyo externo
interactivo
auto-movilización
iniciación/ motivación
A water demand and supply survey identified problem of lack of water in the dry season for irrigating crops. The concept of drip irrigation was shared at public meetings and a demonstration plot established at a local agricultural research centre. Several farmer visits organised to the research cent
planificación
Public meetings; farmers showed interest in drip irrigation. The project supported them by transporting drip sets to the nearest roadhead and subsidising the purchase costs
implementación
Farmers implemented the technology and the project provided technical support
monitoreo y evaluación
Mainly: measurements/observations, public meetings; partly: reporting; Farmers monitored the technology with project support. Evaluation was usually done at meetings and exchange visits.
Research
On-farm; The technology was tested at the local research centre during the first few years followed by on-farm research with farmers. Farmers collected and analysed quantitative and qualitative information themselves.
Flujograma
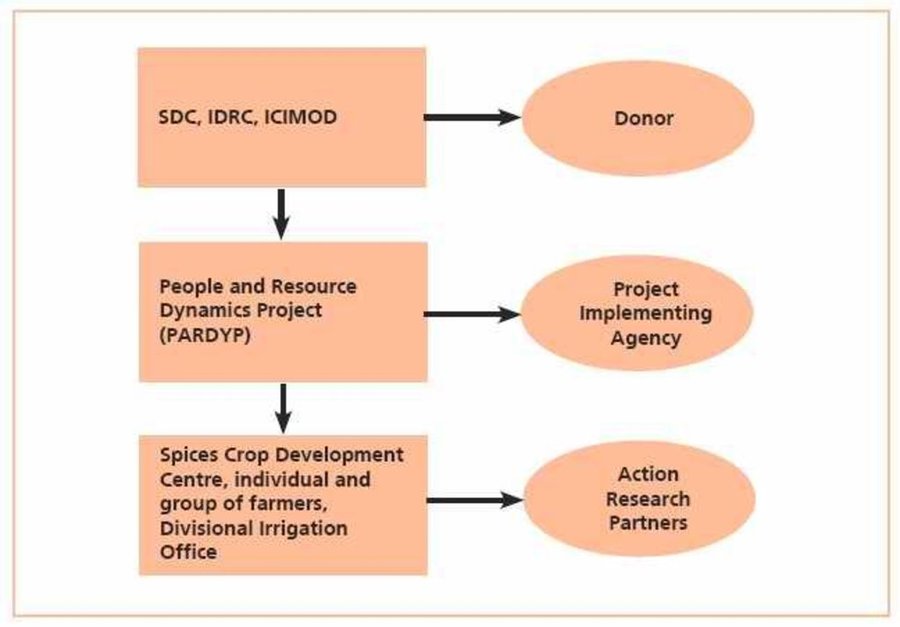
PARDYP project donors and implementing partners: SDC (Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation); IDRC (International Development Research Centre); ICIMOD
La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología MST
Las decisiones fueron tomadas por
-
solamente usuarios de tierras (autoiniciativa)
-
principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
-
todos los actores relevantes, como parte de un enfoque participativo
-
principalmente por especialistas MST en consulta con usuarios de tierras
-
solo por especialistas MST
-
por políticos/ líderes
La toma de decisiones se basa en
-
la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
-
hallazgos de investigaciones
-
la experiencia personal y opiniones (no documentadas)
Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
Las siguientes actividades o servicios fueron parte del enfoque
-
Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
-
Servicio de asesoría
-
Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
-
Monitoreo y evaluación
-
Investigación
Construcción de capacidades/ capacitación
Se proporcionó capacitación a las siguientes partes interesadas
-
usuarios de tierras
-
personal de campo/ consejeros
-
extensionists/trainers
Forma de capacitación
-
en el contexto de trabajo
-
de agricultor a agricultor
-
áreas de demostración
-
reuniones públicas
-
cursos
Temas avanzados
Training programmes were organised on how to install and maintain the drip systems. Likewise farmers were trained on record keeping for water application, production, and cost-benefit analysis.
Servicio de asesoría
Se proporcionó servicio de asesoría
-
en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
-
en centros permanentes
Name of method used for advisory service: Farmer to farmer dissemination; Key elements: Interactive meeting, on-station and on-farm visits, workshops; 1) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: non-governmental agency; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users, technicians/SLM specialists; Activities: interactive meeting, farm visits , workshops
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Government , NGOs and CBOs still continuing the activities.
Fortalecimiento institucional
Se fortalecieron/ establecieron instituciones
-
no
-
sí, un poco
-
sí, moderadamente
-
sí, mucho
Describa la institución, los roles y las responsabilidades, miembros, etc.
Tipo de apoyo
-
financiero
-
construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
-
equipo
Detalles adicionales
On-site training during drip installation provided to a local NGO (Ranipani Gram Sewa Kendra) with vegetable seedling support.
Monitoreo y evaluación
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land use change, crop rotation, soil surveys
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: water requirements
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: socioeconomic surveys
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: cost-benefit production
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: area under drip irrigation
land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: number of drip users
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The subsidy system was withdrawn and work with groups rather than single households was started. In addition, interaction programmes were organised at different locations in the watershed.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation.
Investigación
La investigación trató los siguientes temas
-
sociología
-
economía/ marketing
-
ecología
-
tecnología
Action research was carried out to compare the water requirements, the cost-benefit, and the advantages and disadvantages of traditional and drip irrigation.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
Presupuesto anual en dólares americanos para el componente MST
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.d.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour): 50.0%
Los siguientes servicios o incentivos fueron proporcionados a los usuarios de las tierras
-
Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
-
Subsidios para insumos específicos
-
Crédito
-
Otros incentivos o instrumentos
Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
El trabajo de los usuarios de las tierras fue
-
voluntario?
-
comida por trabajo?
-
pagado en efectivo?
-
recompensado con otro tipo de apoyo material?
Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
Impactos del Enfoque
No
Sí, un poco
Sí, moderadamente
Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
Land users started cropping land that was previously left fallow in the dry season and increased the area under cash crops - especially vegetables. Drip irrigation used only 60% of water compared to bucket irrigation.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
A few institutions and district level line agencies like Ranipani Gram Sewa Kendra, a local NGO, and the Divisional Irrigation Office Kabhrepalanchok started organising interactive meetings to discuss drip irrigation.
Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
-
producción incrementada
-
incremento de la renta(bilidad), proporción mejorada de costo-beneficio
-
reducción de la degradación del suelo
-
reducción del riesgo de desastres naturales
-
carga de trabajo reducida
-
pagos/ subsidios
-
reglas y reglamentos (multas)/ aplicación
-
prestigio, presión social/ cohesión social
-
afiliación al movimiento/ proyecto/ grupo/ redes
-
conciencia medioambiental
-
costumbres y creencias, moral
-
conocimiento y capacidades mejorados de MST
-
mejoramiento estético
-
mitigación de conflicto
Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
Most of the land users continue to use drip irrigation and are maintaining the sets. A few farmers, including women, abandoned drip after using it for some time. The women who abandoned it said they did so because of 'lack of technical knowledge', 'not enough labour' and 'too far to get water'
Conclusiones y lecciones aprendidas
Fortalezas: perspectiva del usuario de tierras
-
Regular interaction meetings provided land users with a platform to share ideas and for non-adopters to learn about drip from users. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters)
-
Farmer-to-farmer visits were helpful to build confi dence of farmers by seeing on-site results (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters)
-
On-site training on drip installation and maintenance helped build confi dence in using drip sets (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters)
Fortalezas: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clave
-
This approach emphasises the participation of multiple stakeholders in researching, disseminating, and scaling up the use of the technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Identify and involve new interested stakeholders.)
-
On-station and on-farm research was important to get results from different locations and under different conditions. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue research to acquire in-depth knowledge on performance of drip irrigation under different conditions.)
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: perspectiva del usuario de tierrascómo sobreponerse
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clavecómo sobreponerse
-
Women drip farmers' constraints were not sufficiently addressed.
Women's priorities and constraints must be better understood and addressed by programmes and projects on drip irrigation.
-
Many local land users remain unaware about the potential of drip irrigation technology.
Make more funds available to further promote the technology.
Referencias
Fecha de la implementación: 16 de enero de 2009
Últimas actualización: 28 de junio de 2017
Personas de referencia
-
Madhav Dhakal (mdhakal@icimod.org) - Especialista MST
-
Isabelle Providoli (isabelle.providoli@unibe.ch) - Especialista MST
Descripción completa en la base de datos de WOCAT
La documentación fue facilitada por
Institución
- CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal
Proyecto
Referencias claves
-
Shrestha-Malla, S. (2004). Adoption of Drip Technology and its Impact on Gender: a Case Study from Jhikhu Khola Watershed, Nepal. PARDYP/ICIMOD (unpublished): ICIMOD
-
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD: ICIMOD