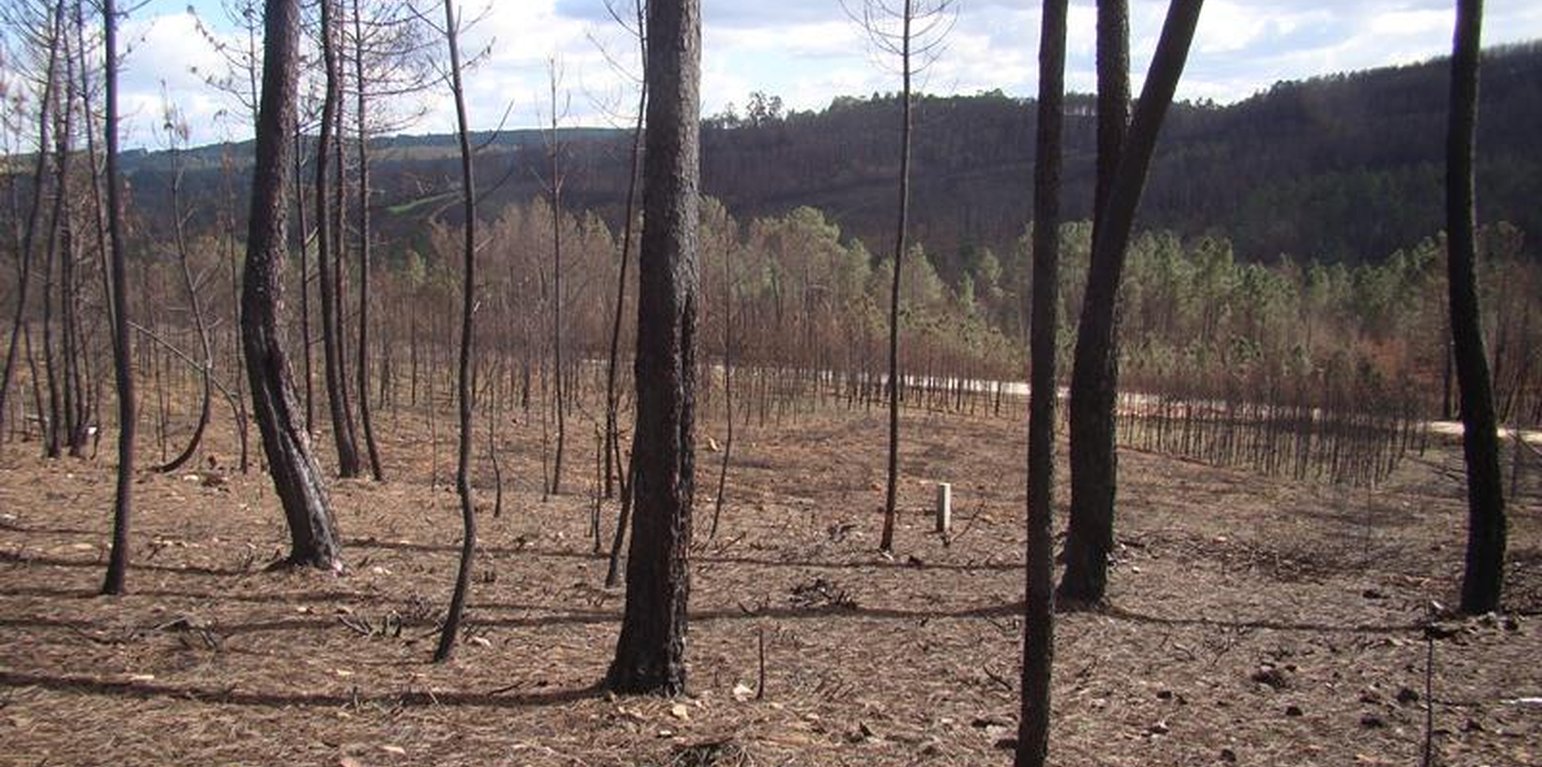




In the 2007 summer a wildfire affected the locality of Pessegueiro do Vouga, municipality of Sever do Vouga, north-central Portugal. The area was afforested with eucalypt and pine plantations. The research team of the University of Aveiro checked that in some burnt areas the crown damage was very small, despite the litter and underground vegetation were totally consumed by fire. The pine site presented a markedly lower fire severity, with the canopies only partially consumed by the fire, so it allow to study the effect of fire severity on soil erosion by comparison with adjacent slopes burned a high severity.
Purpose of the Technology: In a wildfire that affected a pine plantation in central Portugal in 2007, the research team of the University of Aveiro set up an experiment in order to test the effect of forest residue mulching as a soil erosion mitigation treatment. However, the low fire severity resulted in an elevated litter cover prior any technique was applied. The objective is to determine were “no action” in post-fire management will still result in low soil erosion values.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The high litter cover will decrease post-fire soil erosion by reducing raindrop impact over the ashes and the bare soil, and decrease the runoff amount by increasing water surface storage, decrease of runoff velocity, and increase infiltration. As the needle litter cover was natural, no action was needed. After a simple assessment of the remaining ground cover in the burnt area, the "no intervention" option should be selected if the soil is covered by litter, leaves or needles. The benefits of this are not only the mitigation of soil erosion (and associated soil fertility losses) immediately after forest fires, but also the long-term conservation of the soil resources without additional costs.
Natural / human environment: The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-)natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. Since the 1980´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, aided by a general warming and drying trend but driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
Lugar: Sever do Vouga, Pessegueiro de Vouga, Portugal, Aveiro, Portugal
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción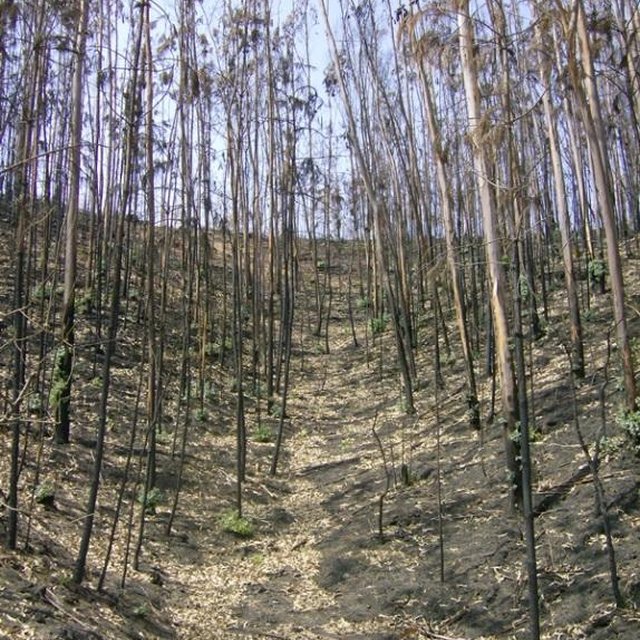




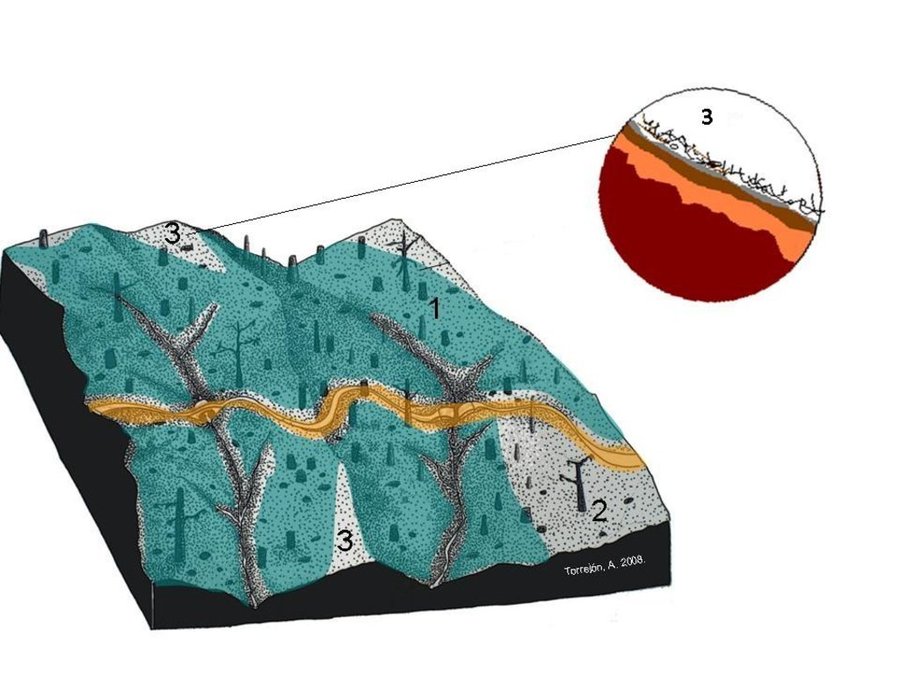
Some reduced wood production can be associated to the technique by carrying out selective felling.
Public awareness of the technology is very limited. It is necessary to show it to landowners and stakeholders and increase dissemination.