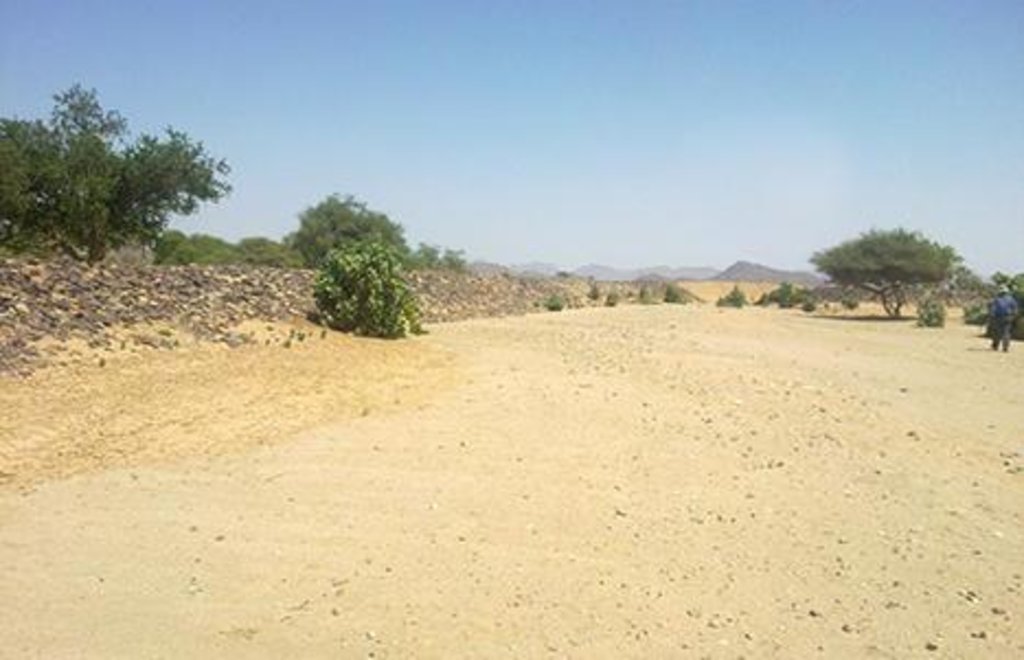
Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [Sudán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Abdalla Osman Eisa
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Sidud (Local Arabic) - Tarrit (Beja dialect) for earth dams
approaches_2543 - Sudán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Gaiballa Abdelaziz
gaiballa@gmail.com
Sudan University of Science and Technology
Sudán
Especialista MST:
Dabaloub Sayed
+249 912913623
dabaloub@gmail.com
SCLUWPA Dirctor (1986-1995), now the ECDP Centre
Port Sudan
Sudán
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Soil Conservation, Land Use and Water Adminstratio (Soil Conservation, Land Use and Water Adminstratio) - SudánNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
VU University Amsterdam (VU University Amsterdam) - Países BajosNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Sudan University of Science and Technology (SUST) - Sudán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
15/05/2012
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST
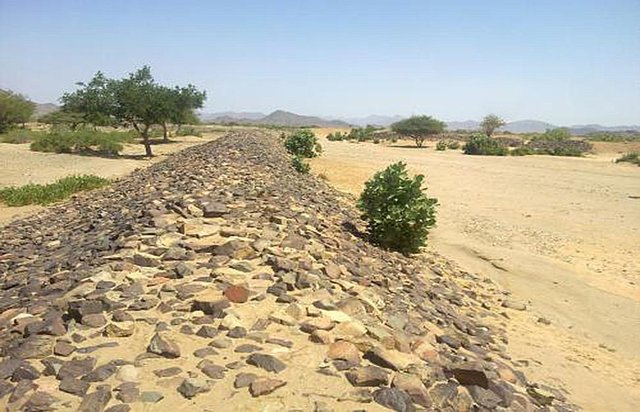

Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [Sudán]
Water Spreading (or Spate Irrigation system) conducted through the construction of earth dam structures at the khor cross section.
- Compilador: Abdalla Osman Eisa
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
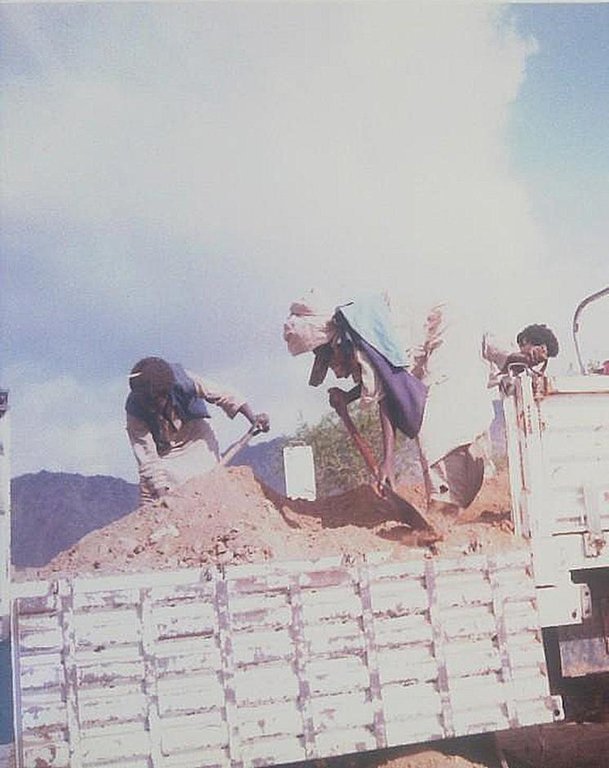
Construction of water spreading system on khor and wadi with machinery jointly government and farmers in dam compaction and pitching.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: The main objective of the approach is to enable domestic land users cultivating crops (sorghum mainly) on a flood plain through construction of an earthen, stone-pitched barrier across the bed of a khor (stream). This earth dam serves to divert floodwaters onto their fields downstream. The approach is fully subsidized as the government provide technician and machines for the construction. Only some voluntary contribution from the beneficiaries is needed (for stone pitching). However maintenance support by the government is not provided later on.
This case study is typical of all those in the State. All are demand-driven...In addition the government supports farmers in rural extension e.g. preparedness, awareness, organization and mobilization, and to establish farmers VDCs (Village Development Committee) to guide the community in public works. Training and capacity building sessions in cultural extension are hold to develop crop raising techniques. The aim behind this is mainly to fill the gap of people’s deficiency in storage of crops such as sorghum and millet to maintain food security in the region.
Methods: 1/ Earth dam and terraces construction for water diversion and spreading.
2/ Agronomic measures e.g. ploughing, levelling, furrowing etc. to raise the soil to its maximum capacity.
3/ Provision of certified seeds: Varieties of short mature period and of drought resistance.
4/ Provision of special hand tools for weeding to maintain soil moistures and sustain the growing of crops.
5/ Development of mixed crop systems by provision of cash crop to support the rural economy.
Stages of implementation: 1. Identify and prioritize the needs of local beneficiaries according to their land size, social and economic situation, the local soil types, the cultivated indigenous crops etc.
2. To reach mutual partnership between Government and local communities a certain number of beneficiaries of the community is dedicated to contribute to volunteer manual work.
3. Based on peoples previous natural environment experience the location of the dam is to be examined and an engineering map has to be set out. That means people’s involvement from the very beginning of the project for planning, design and implementation.
4. For construction the government provides necessary needed machines.
5. The local community should mainly ensure the maintenance and the clearing out of the land for smooth water flow.
Role of stakeholders: Division of labor between the stockholders so as to identify the role
1- Land owners: piece of land.
2- Farmers: farming activities.
3- Ministry of Agriculture (MoA): provide machinery and technical support.
4- SLM specialist: will give the technical advice.
Other important information: Floodwater now takes way to any lower area and creates a new water course.
After several years soil should be tilled by ploughing, planking and furrowing to increase water infiltration and percolation as over the years the accumulated silt turns the soils nearly impermeable.
Finally some types of soil in the Red Sea State become very fertile and rich and do not need chemical or organic fertilizers anymore.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Sudán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Red Sea State
Especifique más el lugar :
Sinkat Locality
Comentarios:
This covers the case study of Hashtribab water spreading scheme as documented in the associated QT though is an approach used all over the State. e.g. Erkawit.
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
1970
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Rehabilitation of natural resources and agriculture for improving soil conditions and fertility. )
To overcome the inability of poor farmers to invest in durable water harvesting schemes and (later; in the 1990s and onwards) to take over the implementational role from NGOs and donors. They could continue to invest but they should be stopped to be concernde with implementation as they were in the 1970s and 1980s
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of water to grow crops, lack of money for farmers to invest in infrastructure.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
normas y valores sociales/ culturales/ religiosos
- impiden
Lack of machinery and money to construct durable schemes
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Assistance from Government
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
1/Limited resources specially in the infrastructure of the concerned government departments
2/ Low capacity of the traditionally adopted technology as well as at farmers communities level.
3/ Limited financial resources especially of extension and capacity building and training at grass root level as well as at staff level
Treatment through the SLM Approach: 1/ Raise the capacity of the technology used
2/ intensive training of both cultural, and rural extension
3/ Training in water harvesting techniques for traditional farmers and in reclamation methods in water management
4/ Encourage farmers innovations and initiatives based on community based approaches for land use management
entorno institucional
- impiden
1/ At community level VDCs has low capacity in community organization
2/ Follow up and monitoring is very limited and at an adhoc bases where as carried on occasionally
3/ serious problem as related to water spreading and diversions usually vulnerable to breakage and washed out. The miss located sites of earth dam constriction is the main factor behind
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Raising the capacity of Gov. Dept. in extension techniques and the most develop water harvesting methods
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- impiden
Some conflicts on some areas arise
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Negotiation between parties / stakeholders under their traditional leadership (tribal)
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
Lack of technical training
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Fund for training should be available
carga de trabajo, disponibilidad de mano de obra
- impiden
partnership between different partners with less extent of homogeneity and commitment.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: strength the linkage between different partners in the targeted activities.
otros
- impiden
Wage differences between NGO staff and government employees
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Top-up payment to government employees
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Farmers with VDCs and individuals.
The adult (40 years) and youth (20 – 30 years). Rarely it has be taken by women
It can be said that the whole community is economically disadvantaged
Men predominant in meeting and negotiations. This were conducted through the VDC's and community elected community board.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
Extension agents
- ONG
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
Soil Conservation Department (SCLUWPA) (named differently in different parts of the country), Range and Pastures and Forestry Dirctorates
Community leaders (tribal), Localities assembly, VDCs, Community representatives and Ministers at State level
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | auto-movilización | Demand-driven |
| planificación | interactivo | Together with specialists |
| implementación | interactivo | Some subsidized labour and in some cases volonteer labours |
| monitoreo y evaluación | ninguno | None |
| Research | ninguno | Some information provided |
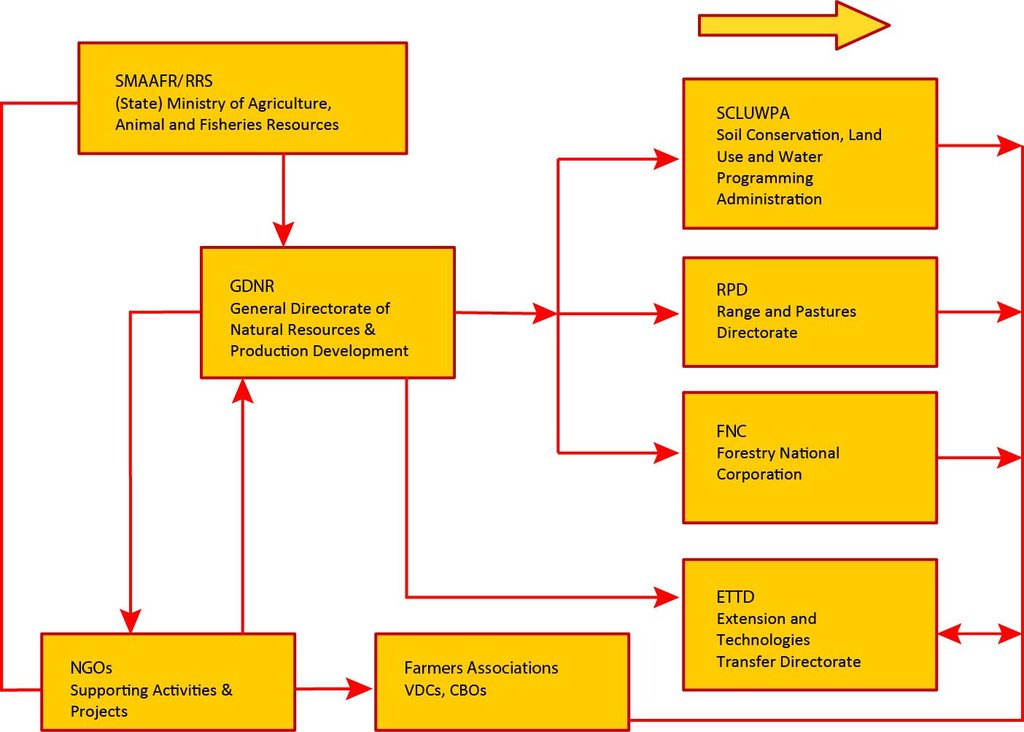
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
Descripción:
Institutional framework: Stakeholders and their roles: cross-disciplinary linkages between SMAAFR, collaborating institutions and farmers.
Autor:
Abdalla Osman Eisa (Soil Conservation and Land Use Admin. Red Sea State, Sudan)
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
Explique:
Most of the schemes (of which Hashatribab is a good example) began as a traditional water spreading schemes. Thus the Government built upon the traditionally adopted farmer's technology and developed it my means of improved soil and crop management knowledges and capacity bulding to farmers.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. The machinery necessary was in the hands of the Government and the specialists knew what was possible and how it could be done. But for all the land users were consulted.
To develop the traditionally adopted technology it is in the hand of the people themselves and need to be supported by the government. Such technology men are dealing with the natural resources, preventing tree cutting, moving regularly for grazing governance to recover ranges etc. and also they need hand tools awareness techniques.
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
- other related goverment Departments
Si fuese relevante, también especifique género, edad, estatus, etnicidad, etc.
on gender basis.
Forma de capacitación:
- de agricultor a agricultor
- reuniones públicas
Temas avanzados:
Rural extension as community organization, public work methods, extension and awareness services
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
Describa/ comentarios:
Conventional extension; Key elements: 1.Visits, 2.Training, 3.Practice and training by doing ; Cross visits are very important to improve the technical know how and to learn by experience. The practical training is very useful and effective rather to the theoretical one.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Yes, in terms of technical know how but not in terms of adequate resources
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, un poco
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
- man power
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
Because the local institution was involved in negotiations with the Government and also organizing communities; mobilization and awareness. SCLUWPA activities are mainly oriented to conserve soil and vegetation. They tend to clarify land according to the amount of Khor floods into land for agriculture and the land of forests and ranges. This practice is carried on down streams of seasonal rivers while is not specifically going in plains which in need to be reclaimed to reduce sand dunes formation and desert like conditions
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Not relevant as no monitoring took place. Only monitoring and evaluation is carried on by SCLUWPA for its activities in earth dams' construction and terraces to speed water. Usually this takes places after and within the period of flooding in addition to sea wall, effectively these devices functioned and finally to trace the impact and the outcome.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: as above. In purpose of to check what have done to do some amendments.
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Especifique los temas:
- ecología
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 2,000-10,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (Training, capacity building and assistance of equipment.): 30.0%; government (Technical staff, equipment and agricultural inputs.): 60.0%; local community / land user(s) (Volunteer man power): 10.0%
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
Sí
Si respondió sí, especifique el tipo o los tipos de apoyo, condiciones y proveedor(es) :
By Government either directly or from donor sources. SCLUWPA, Range and Pastures, UNDP and UNISCO supporting desertification.
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- equipo
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| herramientas | totalmente financiado | |
- agrícola
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| semillas | totalmente financiado | |
- construcción
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| piedra | parcialmente financiado | partial community contribution |
| madera | parcialmente financiado | partial community contribution |
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
see QT
Only machinery financed for construction period and maintenance.
Labour appears in all mentioned forms above. But voluntarely and food for work is most common.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
They were able to make the land directly more productive because of the extra water. Furthermore it helped land users in raising their technical know how.
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Yes, as the whole community was economically disadvantaged
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
no problems related to that issue of land rights and ownership and early can be recognized by tribal leadership. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. within the tribal system it can be solved any problems on land in cases of difficulties the leadership take decision to be used by all members.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Not relevant as it is a government driven system. The newly introduced technology is to improve before it can be adopted by other land users.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Yes, because of extra food supply – though not as dramatic as with irrigation By using simple technology e.g. the hand tools and ohter manually applicable implements can be used easily by land users.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
In terms of food security: but differs from season to season If support subsistence farmers to produce crop and animal herders to multiply animal numbers.
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
The primary motivation
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Also very important
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- no
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
The land users can continue to crop and to maintain structures within their ability, but no expansion would be possible or repairs to major breakages, unless the level of surplus production will be reached.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
1) Improve the socioeconomic situation. 2) Learning and improve their technical capacity. 3) Raising the community awareness and preparedness. 4) Encourage peoples to be involved in collective action. 5) Enhance their capacity of community effective. Management resources (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: -Building and strengthening the establishment of the community institutions i.e. from VDCs to local Community Base Organization CBos national NGos.) |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
1/ Demand driven response to people’s needs. 2/ Reducing the direct in-field role of NGOs. 3/ Progress to create a national Ngo's. 4/ Building the community institution. 5/ Raising the self help and self reliance for sustainable management. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: 1/ Continue to listen to the people 2/ By making sure the Government continues to play that role effectively 3/Increase funding . ) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
|
1) Weak economic base at rural areas. 2) Weak community innovation and involvement. 3) Illiteracy and isolated and knowledge of others experiences 4) Low level of the technology used by the people. 5) Poverty and high vulnerability to natural disasters. |
- to increase land productivity. - to develop crop mixing strategy to include cash crops. - enhance and encourage agroforestry approach. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
|
1/ Weak of funds. 2/ Weak of monitoring and evaluation. 3/ Low of documentation and knowledge sharing. 4) Lack of research involvement. It is better to say few or adequate research activity |
1/ More support. 2/ Introduce a clear, simple system. 3/ International community need to make more efforts to assist with these aspects. 4/ Both Government and NGOs need to recognise the potential role of researchers |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [Sudán]
Water Spreading (or Spate Irrigation system) conducted through the construction of earth dam structures at the khor cross section.
- Compilador: Abdalla Osman Eisa
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos