Enhancement of existing SLM technologies into demonstration sites [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Habib Kamolidinov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
ADB, GEF, GITEC, DMC. Rural Development Project
approaches_2634 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
GITEC/ADB/DMC Rural Development Project Land Management Institute - Tayikistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST
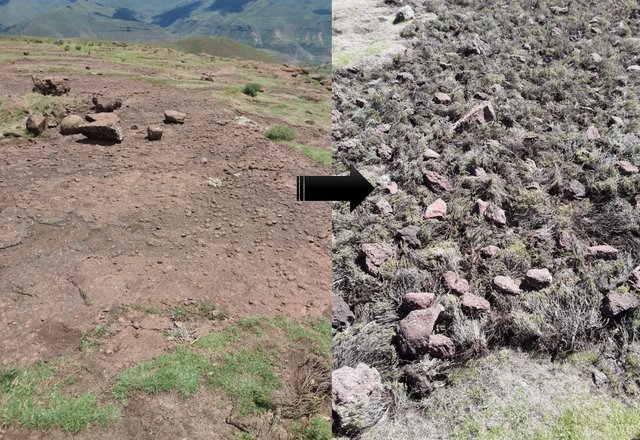

Brush Layering [Lesoto]
The technology requires removal of invaders as resources for layering. The technology enhances accumulation of silt and moisture storage in dry-lands due to increased organic matter content in the soil from the brush.
- Compilador: Matoka Moshoeshoe
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Enhancement of existing self developed SLM technologies into demonstration sites.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: The farmer clearly stated that his prime, initial aim in taking over this “ruined and abandoned land” was to improve and better assure the quality of his family’s lifestyle, through enhanced and assured food and fodder production. He also recognised the potential for future profit, through sale of his excess produce to market. Currently, the family has almost no need to buy food (and fodder) from nearby markets, apart from flour (for bread making). This is a large cost saving factor. In hindsight, the farmer sees that he has dramatically improved land quality within the enclosure through mitigating erosion and increasing year-round vegetation cover
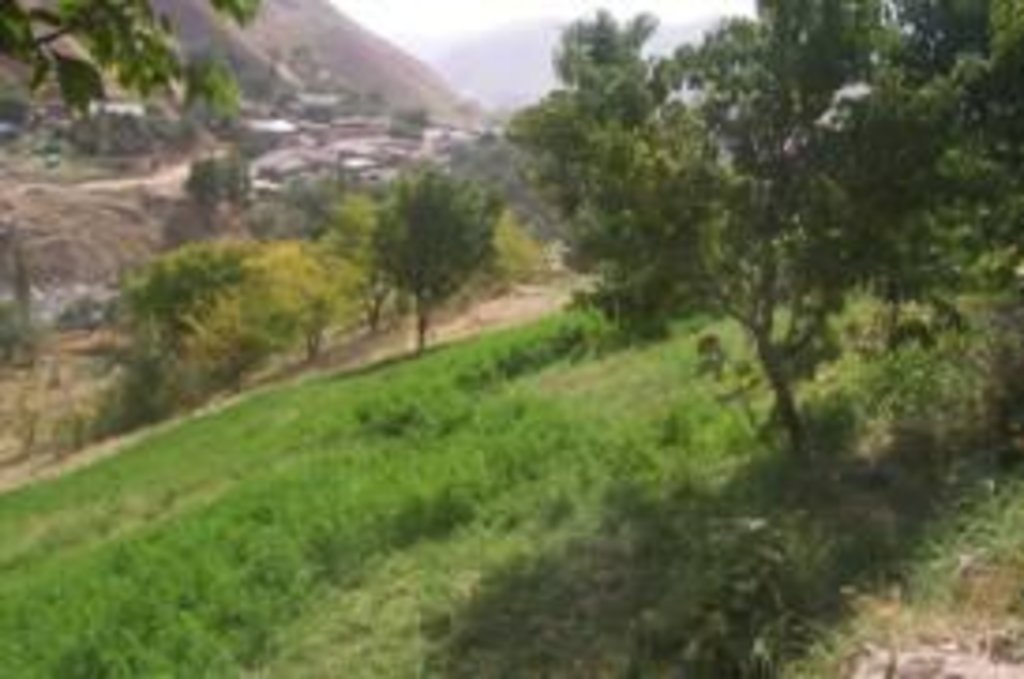
Methods: The success of the enclosure is the result of using several methods. The fence construction was critical to keep out both domestic animals (cattle, goats and sheep) and wild ones, (pigs and wolves) from what was to become a vegetation rich “island” amoungst the bare and degraded hillslopes. Stone clearing (by hand) of the whole area inside the enclosure greatly improved land quality due to enhanced soil depth and subsequent vegetative growth. Tree planting (apple, cherry, apricot, pear) was critical to provide family food. Lucerne planting provided food for the farmer’s animals (1 cow, 10 goats) that provide milk and meat. A small area of land near the homestead (approx. 20 x 20 metres) was levelled into several small terraces for vegetable production (potatoes, garlic, onion, peppers, tomatoes). Irrigation is conducted within the upper part of the enclosure; water being provided by a 20mm polythene pipe that brings water from 1.5 km away where there is a permanent spring.
Stages of implementation: The family (Enomali) first occupied this land in 1984. The first task was tree planting – the first orchard trees – on 0.1 ha of the current enclosure. This was fenced, then after nine family members left (to work in Dushanbe) he expanded the fence to the current 0.2 ha and continued to plant trees. Stone removal continued through the 1990s and even to today. The lucerne and vegetable gardens were initiated in the 1990s and continue to be enriched. The fodder, trees and vegetable production is an ongoing task, as is feeding the animals with the home-grown fodder. He continues to plant orchard trees every year and currently has more than 100. He gained a “certificate” of ownership” in 2008.
Role of stakeholders: All of the work within the enclosure has been conducted by family members. The main two are the husband and wife, though in the early stone clearing and fence construction days his 1st cousin assisted. His son and daughter in law have also assisted (though the son now works in Dushanbe) – even the young grandchildren help.
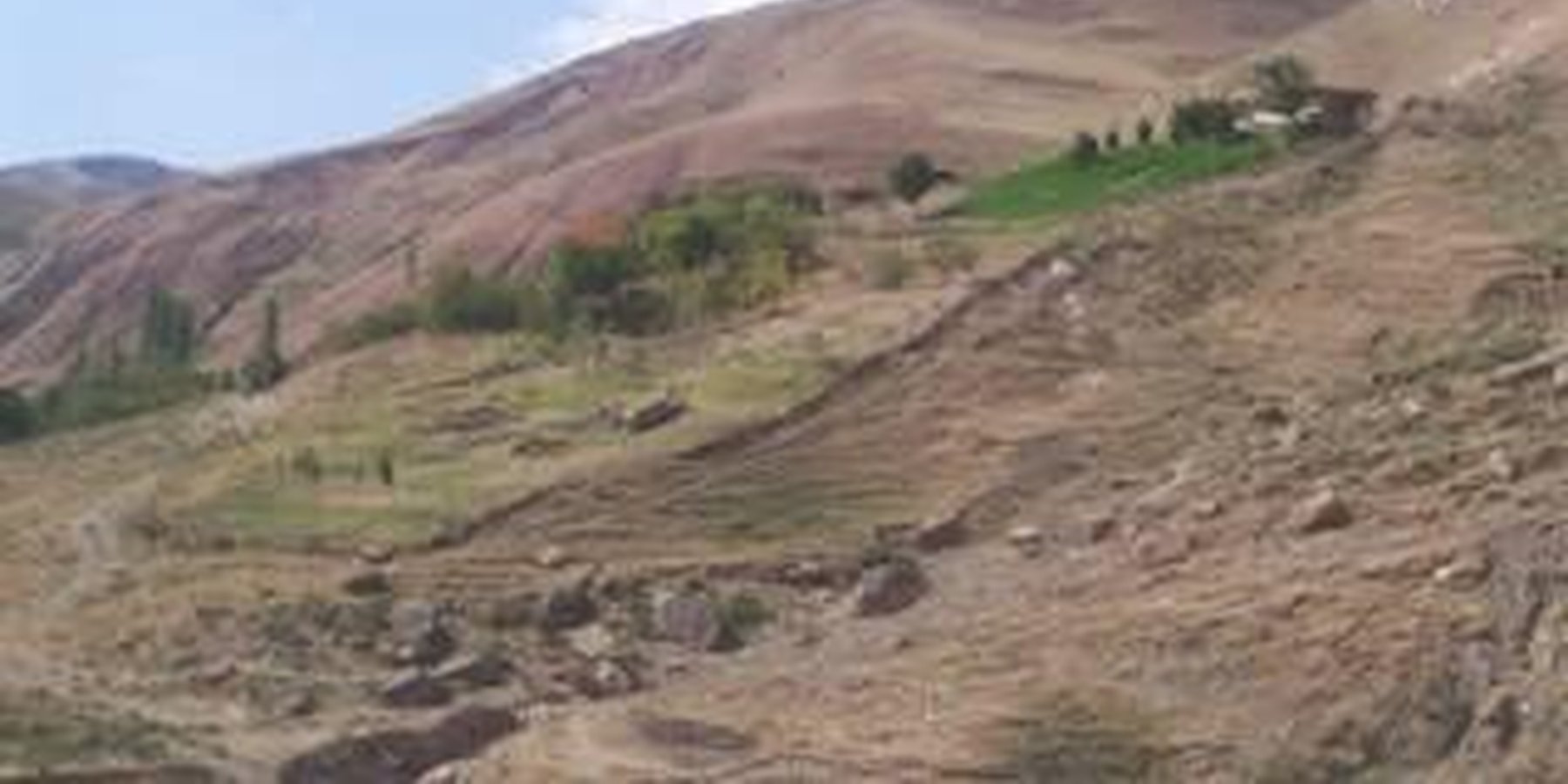
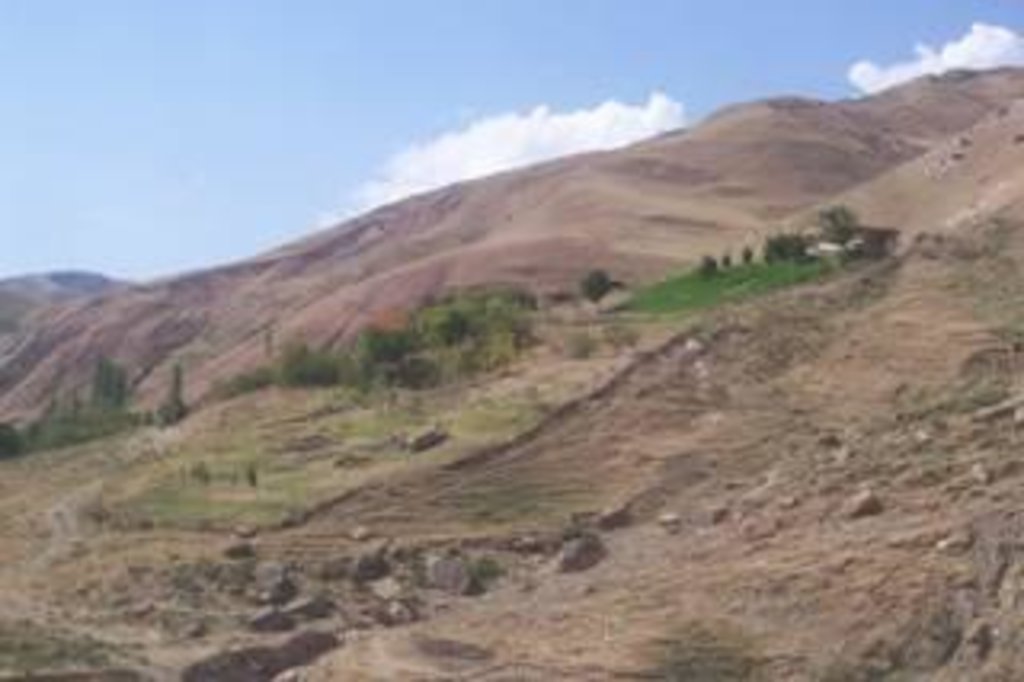
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
RRP
Especifique más el lugar :
Varzob, Luchob
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
1984
Año de conclusión (si el Enfoque ya no se aplica):
2014
Comentarios:
The small area was all that the family could manage, as there was an initial large workload, clearing stones and fence building, etc
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- Local initiative enhanced by programme activity
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused on SLM only
The prime, initial aim in taking over this “ruined and abandoned land” was to improve and better assure the quality of his family’s lifestyle through enhanced and assured food and fodder production. He also recognised the potential for future profit, through sale of his excess produce to market. Now, he wants to expand the area within the enclosure to 1 ha with extra fencing and supplementary irrigation supply from another spring.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main problem to be addressed was reducing poverty, to help achieve a better and more sustainable lifestyle by producing better quality food and fodder.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
normas y valores sociales/ culturales/ religiosos
- impiden
This family were one of the first in this region to take over this area of “ruined” land and begin improvements. However, the farmer did not see this as arduous, rather he welcomed the chance to work hard and provide for his family
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Family working together to improve land
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
The farmer could improve his SLM but would need financial assistance
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
entorno institucional
- impiden
He has now gained a certificate of ownership that ensures ownership until his death. The government still owns the land and he pays $5 US a year in tax (total).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Application for land entitlement certificate
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: There was no compelling need for the farmer to get a “entitlement certificate” but he did so anyway.
- impiden
Not applicable. The water (irrigation) is “free” and there are no current disputes over his use of the spring water
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
The family provided their own solutions to any problems since the project began in 1984
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
carga de trabajo, disponibilidad de mano de obra
- impiden
The family have worked consistently for 26 years, slowly but have created better land and vegetation conditions
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Only the land users (family)
The men focused on the heavier labour tasks of fence building and stone removal. The women focus on the garden, and fruit production and bee keeping.
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | auto-movilización | The extended family, when available |
| planificación | auto-movilización | Principally the husband and wife – Mr Enomali and wife |
| implementación | auto-movilización | The family |
| monitoreo y evaluación | auto-movilización | Mr Enomali and his wife are continuously evaluating the production quantities and quality from their labours |
| Research | ninguno | Not applicable |
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- solamente usuarios de tierras (autoiniciativa)
Explique:
The family has chosen and implemented all methods within the enclosure with no external assistance of any type.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). The family has chosen and implemented all methods within the enclosure with no external assistance of any type.
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
No
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
No
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- no
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: The family, generally, take note of the effect of their practices in terms of production
economic / production aspects were None monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
No
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- < 2,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (The Emomali family): 100.0%
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
No
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
all labour was family-provided
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
There is a dramatic visible difference in both the degree of erosion and vegetative land cover between the enclosure and the surrounding land (see picture in 1.3.3). Also, the production quantity and quality of food and fodder from this enclosure has continued to increase.
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
After the fall of the Soviet Union, many in Tajikistan experienced poverty, particularly food shortages. This farmer foresaw this and commenced his enclosure enrichment work. In this way he ensured
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The farmer says that several of his neighbours have been doing similar interventions to his – fencing, stone removal, planting orchards etc. What he has done is very visible from the main road through the valley, and many people have observed the results of his efforts over the years
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
His family eat well, plentiful and very fresh/organic produce from their own household plot
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
- conciencia medioambiental
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- sí
Si respondió que sí, describa cómo:
The farmer never had external “support” in the first place, so his approach continues to improve, with no support.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| As above, as these words were transcribed during the farmer interview, on site |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Though not an initial objective, the farmer now recognises that he has dramatically improved land quality and vegetation cover within the enclosure, further assuring continued increased production through improved soil conditions (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By continuing to do what he has been doing for 20+ years already. ) |
| The farmer has achieved what he wanted; assured quantity and quality of food/fodder production to assure his family’s livelihood. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: He wants to increase his enclosure area by 5 times. To do this he will require fencing and pipe for irrigation.) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| As above, as these were the sentiments of the farmer during on site interview |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The farmer does not have sufficient financial means to purchase the additional fencing and irrigation pipe he requires to extend the current enclosure area to 1 ha size | Involvement of local banks |
| The total lack of institutional support. This has not necessarily negatively impacted on the farmer – but rather has led to a reduced uptake of his (excellent) practices elsewhere, both locally and nationally. | Immediate visits of local agronomic staff (governmental) to record the modalities of what has been achieved at this site, to help ensure the wider implementation for improved land quality and vegetative cover, at a more national level. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
There is no relevant documentation
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Brush Layering [Lesoto]
The technology requires removal of invaders as resources for layering. The technology enhances accumulation of silt and moisture storage in dry-lands due to increased organic matter content in the soil from the brush.
- Compilador: Matoka Moshoeshoe
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos