Joint village land use planning [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Fiona Flintan
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Simone Verzandvoort, Donia Mühlematter
approaches_3336 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
Sustainable Rangeland Management Project (ILC / ILRI)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
ILRI International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
30/11/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Joint village land use planning is a process facilitated by Tanzania's land policy and legislation. It supports the planning, protection and management of shared resources across village boundaries. It is an important tool towards land use planning and better rangeland management. This case study provides an example from a cluster of villages in Kiteto District, Tanzania.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
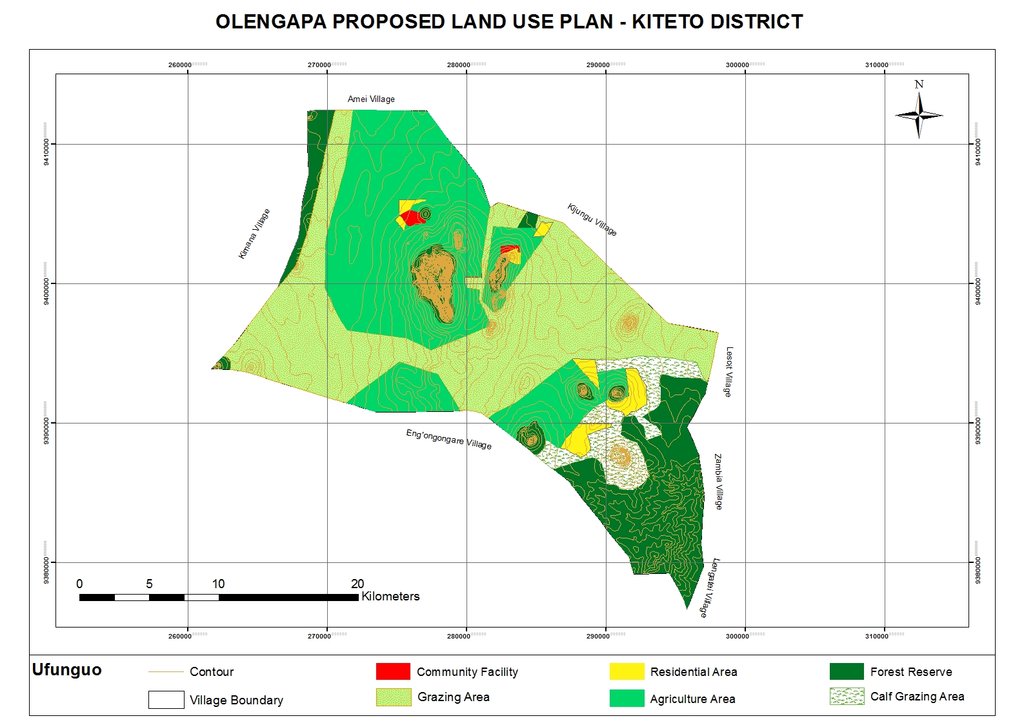
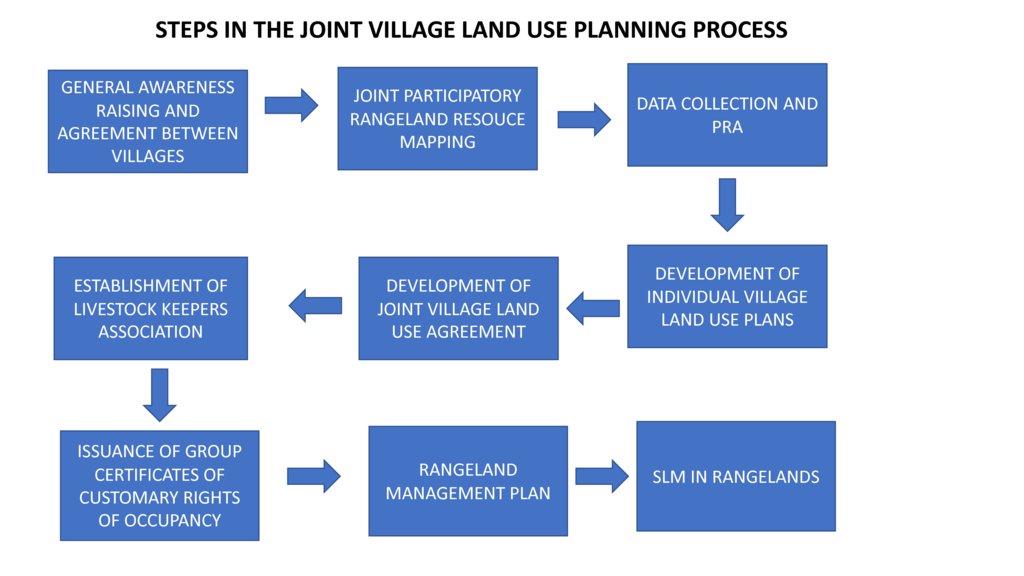
The Sustainable Rangeland Management Project (SRMP) is an initiative led by Tanzania’s Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries (MoLF), the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) and the National Land Use Planning Commission (NLUPC), with support from International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), Irish Aid and the International Land Coalition (ILC). A key innovation of the project has been the development of joint village land use planning (JVLUP). The JVLUP process in Kiteto District, Manyara Region began in November 2013, and included the villages of Lerug, Ngapapa, and Orkitikiti. The three villages share boundaries and grazing resources, and in order to illustrate a single shared identity across the boundaries, the name OLENGAPA was chosen - incorporating part of each village’s name.
The total area of the three villages is (approx.) 59,000 hectares. The majority of inhabitants are Maasai pastoralists with some Ndorobo hunter-gatherers, and some farmers - most of whom are seasonal migrants. Mobility is central to the survival of the pastoralists and takes place across the three villages, as well as to locations in Kilindi, Gairo, and Bagamoyo Districts.
Average annual rainfall is between 800-1,000 mm per annum. There are no perennial rivers flowing through the OLENGAPA villages. The only permanent surface water source is Orkitikiti Dam, constructed in 1954.
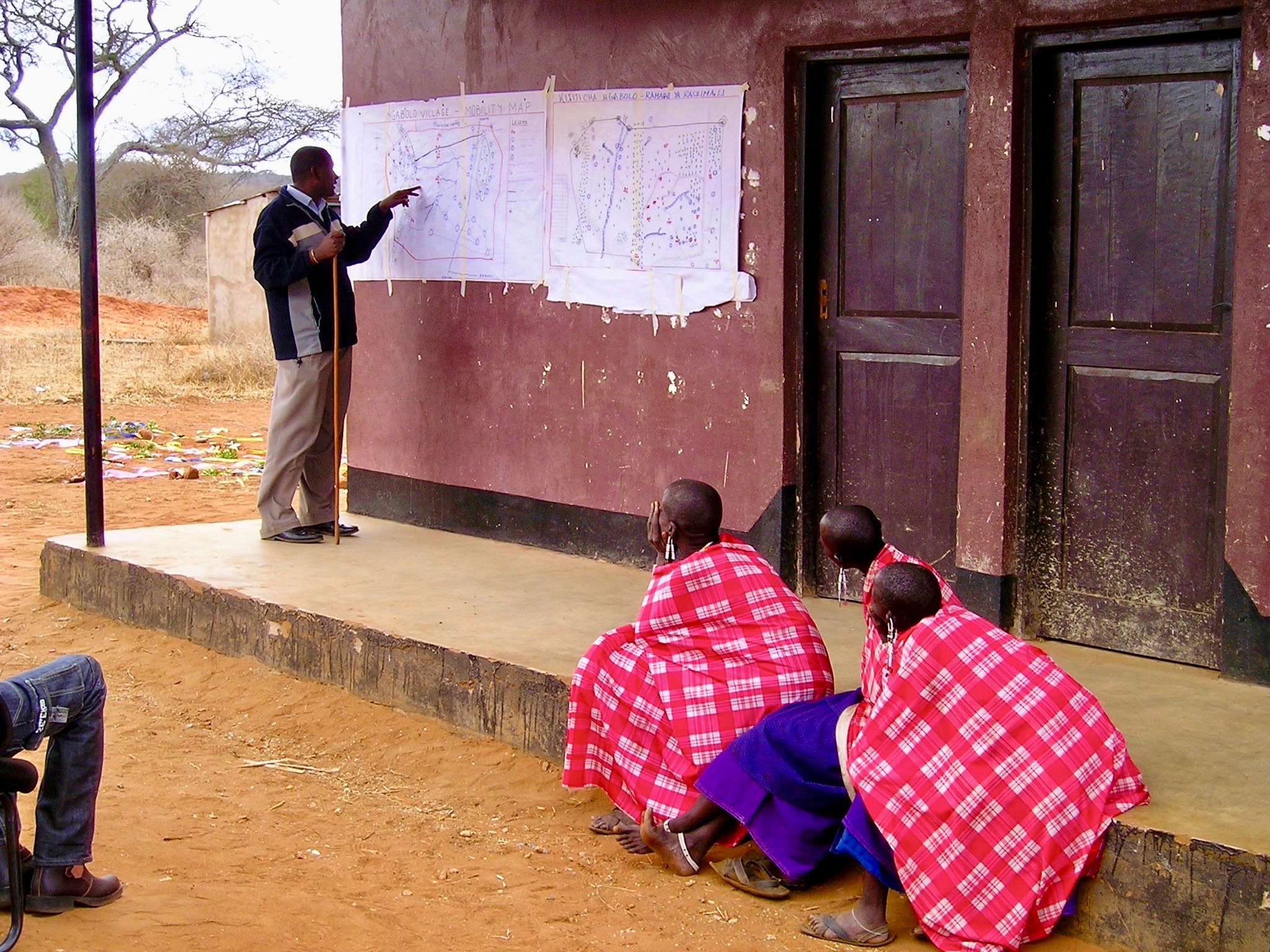
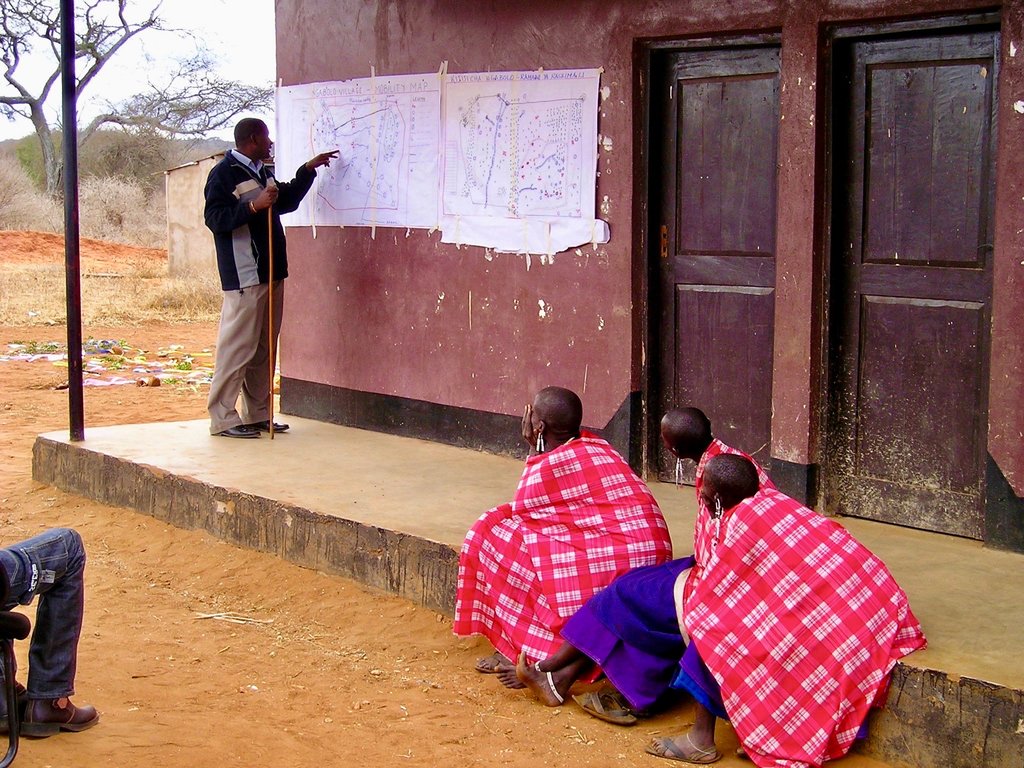
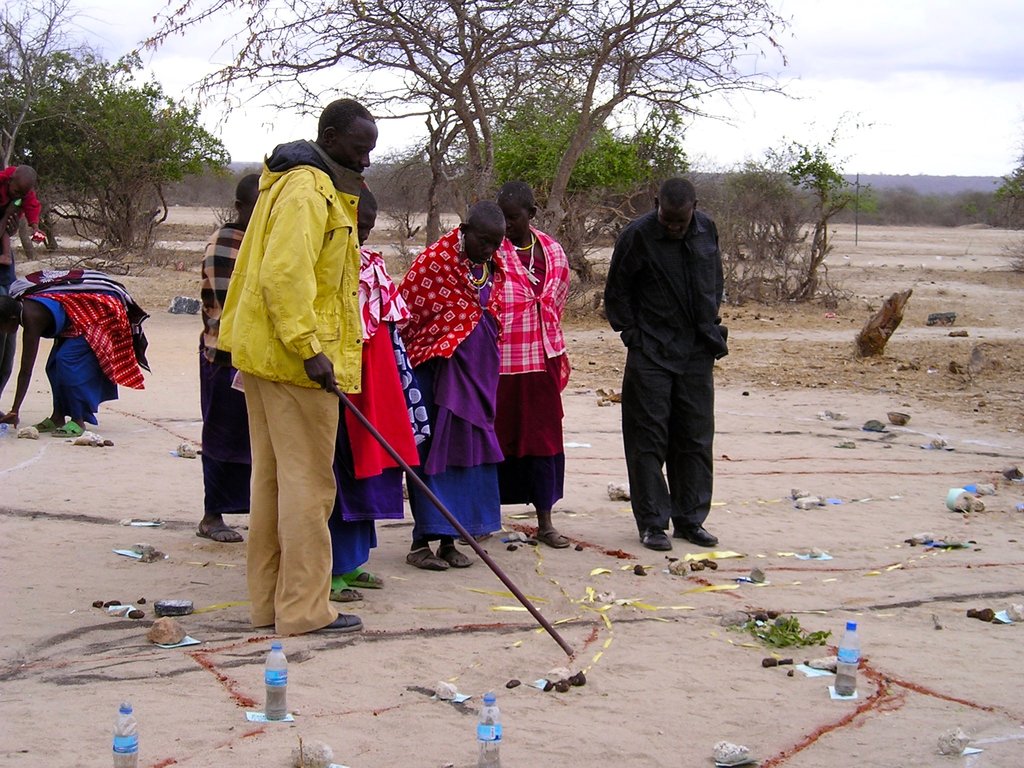
In order to understand the different resources such as grazing areas, water points, cropping areas, livestock routes, and cultural places, SRMP supported participatory mapping. This assisted in developing a base map for the village land use planning process: it showed which resources were shared by the villages and where they were situated.
SRMP then helped village members to agree the individual village land use maps and plans - which zoned the village land into priority land uses - as well as the joint village land use map and plan, and the joint village land use agreement (JVLUA). These specified the grazing areas, water points, livestock routes and other shared resources. Reaching agreement was a protracted negotiation process between the villages, and within villages also - between different interest groups. It involved numerous community meetings and considerable investment of resources. Finally, each Village Assembly approved the JVLUA, which allocated approx. 20,700 ha of land for shared grazing –around 40% of the total village area. By-laws for management of the resources were developed and adopted.
Following approval of the JVLUA, the three OLENGAPA Village Councils established a Joint Grazing Land Committee made up of members from all three villages. This Committee is responsible for planning, management, enforcement of by-laws applicable to the OLENGAPA, and coordination of the implementation of both the OLENGAPA land use agreements and joint land use plan. In addition, a Livestock Keepers Association was established, including 53 founding members – but with most households from the three villages being associate members. A constitution was developed for the Association, which was officially registered on 11 September 2015.
In January 2016 the Ministry of Lands approved and registered the village land boundary maps and deed plans for the three villages. The District Council has issued the village land certificates, and the next step is for Village Councils to begin issuing Certificates of Customary Rights of Occupancy (CCROs). The shared grazing area will require three group CCROs to be issued to the Livestock Keepers Association – one from each village - for the part of the grazing area that falls under its jurisdiction. Signboards and beacons marking the shared grazing area are being put in place.
In November 2017 a fourth village joined OLENGAPA, expanding the shared grazing area to 30,000 ha. The villages are now working to develop a management plan to improve rangeland productivity.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Manyara Region
Especifique más el lugar :
Kiteto District
Comentarios:
Kiteto District, Manyara Region, Tanzania
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
2010
Año de conclusión (si el Enfoque ya no se aplica):
2017
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
To secure shared grazing areas and other rangeland resources for livestock keepers, and to improve their management.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
normas y valores sociales/ culturales/ religiosos
- facilitan
History of collective tenure, management and sharing of rangeland resources as part of sustainable rangeland management practices.
- impiden
Marginalisation of pastoralists from decision-making processes at local and higher levels.
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
Village land use planning process is costly due to the requirement to include government experts in the process in order to gather required data and to authorise plans. Lack of government priority to village land use planning, so poor allocation of government funds to the process.
entorno institucional
- facilitan
Strong local government/community institutions for leading process at local albeit their capacity may require building.
colaboración/ coordinación de actores
- impiden
Poor coordination of different actors supporting VLUP in the past due to previous weakness of National Land Use Planning Commission (NLUPC). However, this is now changing as NLUPC becomes stronger and takes up coordination role.
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
Tanzania's legislation, if implemented well, provides an enabling environment for securing of community/village rights for both individuals and groups.
- impiden
Legislation allows village land to be transferred into public land if in the "public" or "national" interest - this facility confers insecurity on village land.
políticas
- facilitan
Tanzania possesses facilitating national land use policy for the joint village land use planning approach, together with guidelines.
- impiden
There are conflicting policies over land coming from different sectors including land generally, together with forests, wildlife and livestock. These cause confusion at the local level. Depending on power of actors one set of policies may be stronger than another - wildlife-related policy for example can have a lot of power because there are many strong and influential tourism and conservation bodies lobbying for stronger protection of land, with potentially negative impacts for communities who want to use that land for other purposes.
gobernanza de tierras (toma de decisiones, implementación y aplicación)
- facilitan
Decision-making has been decentralised to the lowest levels, giving local communities considerable power to decide on the uses of their village land.
- impiden
The process of village land use planning is costly due to the requirement for having local government experts involved, and the need to follow often complex procedures and steps. Many communities and even local government do not have adequate technical skills and knowledge to complete the long process, as well as not having adequate funds. This has held up the VLUP applications. Further few VLUPs move from their production stage to implementation stage including enforcement of bylaws and, for example, land management.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- facilitan
Good local knowledge of rangeland management based on historical practice. Communities understand need for better rangeland management.
- impiden
Lack of investment in rangeland management and the provision of technical support e.g. through government extension services. Lack of technical knowledge in rangeland rehabilitation and improving rangeland productivity at scale.
mercados (para comprar insumos, vender productos) y precios
- impiden
Lack of local markets and coordinated operations for livestock production.
carga de trabajo, disponibilidad de mano de obra
- facilitan
Well-structured local community bodies ready to provide manpower. Local government experts in place to support VLUP process.
- impiden
Lack of knowledge, skills and capacity amongst local communities and government experts to complete JVLUP adequately, including such as resolving conflicts between different land users.
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Village members (Assembly) of three villages - Orikitiki, Lerug and Ngapapa.
All village members as the Village Assembly have an opportunity to contribute to the land use planning process and to approve it.
- organizaciones comunitarias
Village Council, Village Land Use Management Committee (VLUMC), Rangeland Management Committee, Livestock Keepers Association.
Village government coordinated the planning process at local level. VLUMC develops plan. Village Council approves plans and issues CCROs. Rangeland Management Committee oversees development in rangelands. Livestock Keepers Association established made-up of all members of the villages that have livestock (nearly all village members) - they will be issued with CCROs as "owners" of the grazing land.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
Land use planning consultants
Provision of advice to the project team, local government and villagers on the JVLUP approach.
- investigadores
International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI)
Identification of good practice in village land use planning in Tanzania and ways to adapt and incorporate good practice into joint village land use planning to improve the approach. Research on role of and impact on pastoral women. Undertaking of baseline studies.
- ONG
KINNAPA Development Association (supported originally by CARE and Tanzania Natural Resource Forum).
KINNAPA is the local CSO partner working as part of the project to implement the JVLUP with local communities
- gobierno local
District Council including the PLUM (participatory land use management planning experts)
The District Council provides local government oversight of the planning process and approves the plan before submitting to national government body. The PLUM technically supports the development of the JVLUP working with the village government(s) and village committees.
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries, National Land Use Planning Commission (NLUPC), Ministry of Lands, Housing and Human Settlements Development,
Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries leading the planning process with a sectoral interest in protecting rangelands. NLUPC provides technical oversight and guidance. Ministry of Lands is the national body that approves the final plan.
- organización internacional
International Land Coalition (ILC)
ILC is the grant recipient for the funds from the donors. The project is implemented through ILC members such as ILRI. ILC coordinates its members work in Tanzania on land issues including the JVLUP through a national engagement strategy (NES). ILC also provides technical support to the process through its global/Africa programme - the ILC Rangelands Initiative. The ILC Rangelands Initiative is a platform for learning, sharing, influencing, and connecting on rangeland issues with the objective of making rangelands more secure.
- Donors
IFAD and Irish Aid
Provide funds for the project. IFAD also provides technical support on land tenure issues.
Si varias partes interesadas estuvieron involucradas, indique la agencia principal:
The lead agency is the International Land Coalition (ILC) working through its members including ILRI. In country, the main implementer is the Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | apoyo externo | The project supported communities to initiate the first steps taken to reach agreement on the need for planning and how this would be done. |
| planificación | interactivo | Communities were centrally involved in the planning of the VLUP process, with support from local NGO and government. |
| implementación | interactivo | Village government and community in general is responsible for the implementation of the planning process, with the support of local government. |
| monitoreo y evaluación | apoyo externo | The community is responsible for monitoring and evaluation, but lack skills and capacity in this regard requiring external support. |
| Research | apoyo externo | Research on information required for planning processes collected and generated by communities with the assistance of technical support from local NGO, local government and researchers. |
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- todos los actores relevantes, como parte de un enfoque participativo
Explique:
The policy and legislation lays down the steps to be followed for the VLUP/JVLUP process. However there is room to adapt these processes to local context - and here all stakeholders were involved to develop the process of JVLUP through its first piloting. This included communities, local and national government, local NGOs, researchers and development organisations.
Especifique las bases que sustentaron la toma de decisiones:
- la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
- government staff
Forma de capacitación:
- en el contexto de trabajo
- reuniones públicas
- cursos
Temas avanzados:
Land users were trained in land related and other relevant laws and the JVLUP process. Field staff/advisers were trained in land laws, the JVLUP process, gender, and conflict resolution. Local government were trained in the JVLUP process, gender and conflict resolution.
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
No
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, mucho
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
- nacional
Describa la institución, roles y responsabilidades, miembros, etc.
Local government bodies including Village Council, VLUMC (village land use management committee) and Livestock Keepers Association have all had capacity strengthened, but more is required (particularly for the latter). Capacity of the Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries and the National Land Use Planning Commission to implement JVLUP has been built.
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- financiero
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
- equipo
- data collected and database set up
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
M&E has not been strong in previous phases, but now is central with baselines being carried out in all new clusters of villages where the project will work so that impact can be fully assessed.
Si respondió que sí, ¿la documentación se utilizará para monitoreo y evaluación?
No
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Especifique los temas:
- sociología
- economía/ marketing
- ecología
Proporcione detalles adicionales e indique quién hizo la investigación:
Research was carried out to identify good practice (in terms of social, economic and environmental impacts) from which the JVLUP process was developed. In future phases the full impacts of this JVLUP in terms of social, economic and ecological impact are being researched.
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 10,000-100,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
IFAD, Irish Aid,
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
No
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- ninguno
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
Labour was voluntary with meal provided and/or travel costs covered.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
5.5 Otros incentivos o instrumentos
¿Se usaron otros incentivos o instrumentos para promover la implementación de Tecnologías MST?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Tanzanian policy and legislation states that all village should have a VLUP, therefore this was an incentive for stakeholders to invest in the process. In addition conflicts over land use are increasingly a problem in Tanzania - so the resolution of these was also an important incentive.
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque empoderó a los usuarios locales de tierras, mejoró el involucramiento de las partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Local village communities now feel strongly empowered in protecting and managing their land. The process has brought different stakeholders together and strengthened commitment to make the process work.
¿El Enfoque facilitó la toma de decisiones basada en evidencia?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The piloting of the JVLUP showed what is possible and the positive impacts realised (albeit they could have been better documented). On these results the process is being scaled-up.
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The planning process has laid the foundations for improved rangeland management - what is now required is investment in that management.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la coordinación e implementación efectiva en costos de MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque movilizó/mejoró el acceso a recursos financieros para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de los usuarios para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Land users have greater knowledge of the potential and need for rangeland management based on a better understanding of their land and resources gained through the JVLUP process, but they still need skills and resources to put this knowledge into action.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de otras partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
National and local government have seen the potential of the JVLUP to resolve conflicts over land use, and their capacities to implement the JVLUP in this regard has been improved.
¿El Enfoque construyó/ fortaleció instituciones, colaboración entre partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The approach is helping build relations between the Ministry Livestock and Fisheries and the NLUPC together with NGO(s) at national level, as well as between different stakeholders involved in JVLUP at local levels.
¿El Enfoque mitigó conflictos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Through the process of JVLUP the roots of land use conflicts come to the surface and must be resolved before agreement is reached. This may cause tensions and even conflict along the way - but the outcome should be positive.
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Pastoralists are often left out of village land use planning processes. This approach when implemented well gives greater opportunity for them to be involved. However this is still a challenge.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la equidad de género y empoderó a las mujeres y niñas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Women can be left out of village land use planning processes. This approach when implemented well gives greater opportunity for them to be involved. However this is still a challenge.
¿El Enfoque alentó a jóvenes/ la siguiente generación de usuarios de tierras a involucrarse con MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Youth can be left out of village land use planning processes. This approach when implemented well gives greater opportunity for them to be involved. However this is still a challenge.
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
By following the JVLUP process village land has been certified and secured, as well as the rights of access and use of livestock keepers to the grazing land.
¿El Enfoque resultó en mejor seguridad alimentaria/ mejoró la nutrición?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
This has not been specifically monitored but it assumed by having stronger security to land and resources, food security and nutrition will be improved.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el acceso a los mercados?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
This has not been specifically monitored but it assumed by having stronger security to land and resources, access to markets will be improved.
¿El Enfoque llevó a un acceso mejorado a tierra y saneamiento?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
In terms of water for livestock the JVLUP process has secured rights for the three villages to shared water resources.
¿El Enfoque llevó a un uso más sostenible/ fuentes de energía?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque mejoró la capacidad de los usuarios de tierras a adaptarse a los cambios climáticos/ extemos y mitigar desastres relacionados al clima?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
By having stronger security to land and resources local land users are better placed to adapt to climate change etc.
¿El Enfoque llevó a oportunidades de empleo, ingresos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
This has not been specifically monitored but it assumed by having stronger security to land and resources, income opportunities will be improved.
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
By protecting grazing areas, there will be more secure access to resources required for livestock production.
- reducción de la degradación de la tierra
By protecting grazing areas and improvement of rangeland management practices land degradation will be reduced.
- reducción del riesgo de desastres naturales
With more secure access to land and resources, local land users are better placed to manage their resources in order to reduce risks to disasters.
- reglas y reglamentos (multas)/ aplicación
By gaining protection from village certification, village land use planning and local bylaws developed as part of this, local land users are better placed to enforce rules and regulations relating to land use and to prevent encroachment/trespassing by outsiders.
- prestigio, presión social/ cohesión social
The JVLUP process improved the social cohesion and group identify of the three villages - expressed in the name OLENGAPA (made up of the three village names). There is a strong livestock keepers association now made up of livestock keepers from all three villages who are working more closely together.
- mitigación de conflicto
The JVLUP helped to resolve land use conflicts by opening up space to discuss root causes, find solutions and come to agreement between land users.
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- incierto
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
The community requires support from local government to protect their village lands including grazing lands from outsiders wanting to settle on the land - this is a constant problem to be addressed (despite the securing of village boundaries etc.). The community also needs capacity building and resources to improve the productivity of the land including the grazing areas. If they get these supports then they can sustain what has been implemented.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Improved the security of access and use to village land including grazing. |
| Brought attention to the challenges faced by land users in the area in protecting and using their village land, and the need for more investment and support for this. |
| Pastoralists are now more central to decision-making processes than they were before. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Collaboration of different stakeholders in implementing the approach has supported a new way of working. |
| Capacity of different stakeholders has been built along the way through joint problem-solving and learning-by-doing. |
| The approach - with adaptation - has application in other contexts/countries and shows that even if a rangeland is split by administrative boundaries there is opportunity to work across those village boundaries in order to maintain the functionality of the rangeland and land use systems such as pastoralism that depend upon this. |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Despite village land being theoretically protected, in practice it can still be encroached upon. | Greater support provided from government to enforce protection of land. |
| Time-consuming process which became more expensive than anticipated resulting in some gaps in funding. | Process needs to be refined through practice, and adequate funds allocated from beginning. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The selection of villages for JVLUP needs more care to ensure that enabling conditions for JVLUP exist. | In future selection of villages for JVLUP a set of criteria should be used that enable more enabling conditions to exist. |
| Information has not been methodologically collected on social, environmental and economic impacts of the approach. | In future the impacts of the approach need to be fully monitored and evaluated. |
| The VLUP is an expensive process to follow. | National government needs to identify ways to reduce the cost of the VLUP so that more villages can undertake it. Government needs to allocate more funds to VLUP. The VLUP is an expensive process to follow. |
| Need for an enabling environment. | The policy and legislation in Tanzania enables this process - it is not the case in the majority of other African countries. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
The compiler has been involved in the project/process since its inception and had access to all reports and existing documentation.
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Kalenzi, D. 2016. Improving the implementation of land policy and legislation in pastoral areas of Tanzania: Experiences of joint village land use agreements and planning. Rangelands 7. Rome, Italy: International Land Coalition.
URL:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/79796
Título/ descripción:
Daley, E., Kisambu, N. and Flintan, F. 2017. Rangelands: Securing pastoral women’s land rights in Tanzania. Rangelands Research Report 1. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI.
URL:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/89483
Título/ descripción:
International Livestock Research Institute. 2017. Sustainable Rangeland Management Project, Tanzania. ILRI Project Brochure. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI.
URL:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/80673
Título/ descripción:
International Land Coalition. 2014. Participatory rangeland resource mapping in Tanzania: A field manual to support planning and management in rangelands including in village land use planning. Rome: International Land Coalition
URL:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/51348
Título/ descripción:
Flintan, F., Mashingo, M., Said, M. and Kifugo, S.C. 2014. Developing a national map of livestock routes in Tanzania in order to value service and protect them. Poster prepared for the ILRI@40 Workshop, Addis Ababa, 7 November 2014. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI.
URL:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/64964
Título/ descripción:
Village land use planning in rangelands in Tanzania, F. Flintan 2012
URL:
http://www.landcoalition.org/en/regions/africa/resources/no-3-village-land-use-planning-rangelands-tanzania
Título/ descripción:
Protecting shared grazing through joint village land use planning
URL:
http://www.landcoalition.org/en/regions/africa/resources/protecting-shared-grazing-through-joint-village-land-use-planning
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos