Partnership with beneficiary communities in project implementation [Kenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Fredrick Ochieng
- Editores: Boris Orlowsky, Nicole Stolz
- Revisores: Renate Fleiner, Boris Orlowsky, Alexandra Gavilano
N/A
approaches_597 - Kenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Persona(s) de referencia clave/s
Fredrick Ochieng:
Kenia
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
14/10/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
The approach focuses on community engagement on a partnership basis. The model is a departure from the traditional approaches where the community mostly is reduced to being a beneficiary of project services without substantive responsibility.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
The Approach is hinged on community empowerment and partnership. The model is a departure from the traditional approaches where the community is reduced to a mere beneficiary of project services without substantive responsibility.
The main purpose of the approach is to enhance ownership, while fostering needed capacity for management of project outcomes. Ultimately, it is estimated that sustainability of project results is achievable with good community empowerment and meaningful participation. The approach also aims at cost effectiveness as the community is required to substantially contribute locally available materials, labour and sometimes cash.
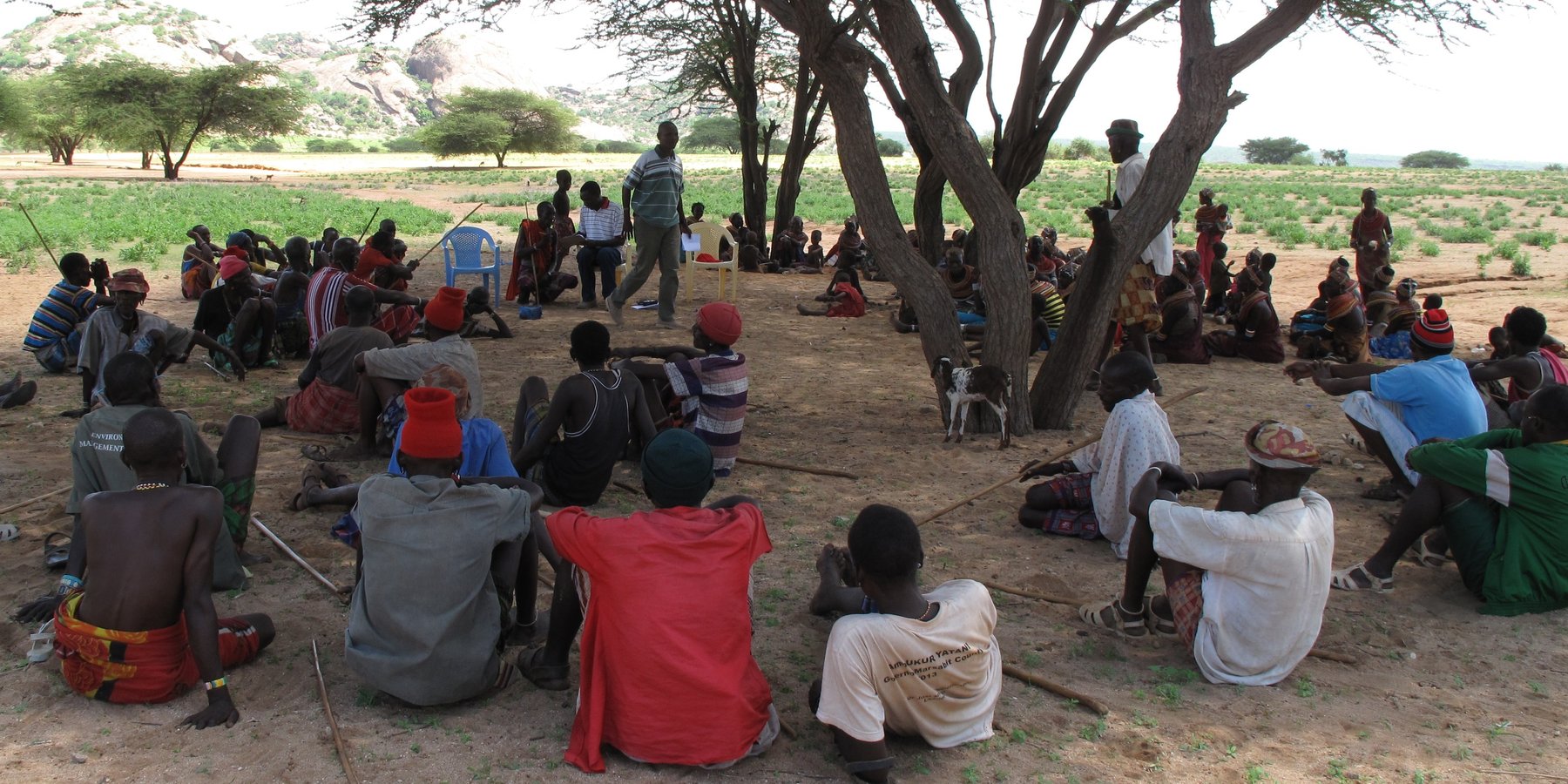
Community mobilisation and capacity building is central to ensure that the community is prepared to undertake their roles and responsibilities. Mobilisation happens through discussions, sometimes aided by applying participatory tools and methods. Capacity building is done through workshop-type and/or on-the-job training. It is noteworthy that the communities do have indigenous knowledge and skills which are useful in processes of development at the community level. These skills and knowledge inform the project design, planning and implementation of activities. To enhance local skills, selected community members are trained as they work alongside the hired skilled artisans during the construction of the rock catchment system. The aim is to prepare and equip the locals with basic skills for operations and maintenance of the rock catchment system. Others are trained to get equipped with skills on hygiene and sanitation promotion.
The project was designed based on pre-project assessment. The assessment, besides identifying water and hygiene needs, also identified three areas/communities which had rock catchment potential - Ndikir, Manyatta Lengima and Mpagas. Initial meetings were done with support from community leaders and the local government administrators (chiefs). During the meetings the project was explained and discussed in view of the community needs and the roles for all stakeholders - Caritas Switzerland (CACH), the community, government and leaders. Agreed roles and responsibilities were drafted and formed the main part of the memorandum of understanding (MOU) between CACH and the community. The MOU was signed before the entire community for collective ownership and formalise the relationship between CACH and the project.
At the county and sub-county level, the stakeholders are provided with progress updates, engaging with government and other leaders. The local leaders were useful in helping in community mobilisation and addressing areas of concern wherever issues arose.
The approach left the community more motivated with a desire to manage the project benefits for posterity. The community has appreciated that the project ended with a number of community members having acquired basic skills for operations and maintenance. Above all, they were proud that they significantly contributed to the successful implementation of the project. Initially the community were opposed to the idea that they had to contribute so much, since before they had mostly received assistance without any requirement on their side to contribute.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.4 Videos del Enfoque
Comentarios, descripción breve:
The video is taken on an early morning shower and shows how water is collected, dammed and channelled downstream to the masonry tanks.
Fecha:
08/12/2014
Lugar:
Ndikir village, Marsabit County, Kenya
Nombre del videógrafo:
Fredrick Ochieng
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Kenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Laisamis sub county, Marsabit County, Kenya
Especifique más el lugar :
Implemented with three different communities in three locations, Ndikir, Manyatta Lengima and Mpagas
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
2013
Año de conclusión (si el Enfoque ya no se aplica):
2015
Comentarios:
The Rock catchment project was implemented from 2013 to 2015
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
1. Community mobilisation
2. Active community participation and ownership of the project and outcomes
3. Sustainability of the project outcomes
4. Enhanced skills and capacity to manage the Technology
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
normas y valores sociales/ culturales/ religiosos
- impiden
The community was accustomed to receiving food and non-food handouts. This culture was a major huddle in working with community where they were expected to make substantial contribution towards the project activities.
entorno institucional
- facilitan
The institutional setting, especially the traditional authority of elders, was supportive during implementation. Once the elders were convinced and persuaded to make certain decisions beneficial to the project, it was always easier for the rest of the community members to rally behind.
colaboración/ coordinación de actores
- facilitan
The Approach requires that stakeholders (other non-state actors and government) coordinate well so that approaches employed by all are complementary and all build into sustainable results. It is common however that there have been approaches that dis-empower communities. Good coordination and collaboration would enhance sharing and learning across the actors and minimise such programming pitfalls.
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
Land tenure in the northern Kenya is mostly communal. This was an enabling factor so that there were no complex and usual elaborate and expensive legal requirements to construct a rock catchment water system. Had land been adjudicated and subdivided for individual ownership, there would have been a need for negotiations and legal procedures to be done with those who own the land where the public asset is to be located.
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
The project was implemented with participation of the communities who are the local land users
Community's role was to ensure that locally available materials were delivered on the site of construction, hygiene and sanitation promotion, unskilled labour, record keeping of all construction materials, security of workers and construction materials on site
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
Caritas had a technical team of three staff who were based within the project location in the field. This team was supported through experts in the office in the capital city Nairobi.
The technical team implemented all project activities such as community organisation/mobilisation, construction of infrastructure as well as hygiene and sanitation promotion.
- gobierno local
Chiefs, Members of County Assembly, Ward administrators
Opinion leaders were critical in the process of community mobilisation and following-up the commitments made by the community under the signed MoU.
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
County Steering Group (CSG), sub-County Steering Group (SCSG)
Coordination with other development agencies and government departments at the County level
- organización internacional
Caritas Switzerland
Overall leadership in project planning, implementation and supervision
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | interactivo | Planning for project activities was jointly planned between the community and the project staff specialists |
| planificación | interactivo | More technical planning was done as advised by the technical project team. Planning for day to day field activities during implementation was jointly done with the community |
| implementación | interactivo | Community participation was more interactive in planning for specific project activities. However, there were specific tasks which required hired labour and by common agreement the community provided such labour for payment. |
| monitoreo y evaluación | interactivo | Monitoring with community was mainly done during project reflection/review meetings. Monitoring in this respect was more limited to evaluation of project activities progress and timeliness with which the activities were being achieved. |
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
Descripción:
The flow chart summarises the Approach's key components, activities and steps for community mobilisation, capacity building and stakeholders engagement. The stakeholders include the relevant government departments - Water, Health, Environment, Drought Management - and non-state actors in the County. There is a monthly forum known as the County Steering Group (CSG) which brings together all the heads of government departments and NGO representatives at the county level. Similar forums also take place at the sub-county level.
Autor:
Fredrick Ochieng
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- todos los actores relevantes, como parte de un enfoque participativo
Explique:
The project was designed initially without direct community involvement other than the pre-project information collected.
Especifique las bases que sustentaron la toma de decisiones:
- la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
- hallazgos de investigaciones
- la experiencia personal y opiniones (no documentadas)
- Government policies
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
Forma de capacitación:
- en el contexto de trabajo
- áreas de demostración
Temas avanzados:
Basic construction skills, management of water system (rock catchment), hygiene and sanitation promotion
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
Describa/ comentarios:
The community has (in theory) access to government advisory services. However, the nearest government offices are about 20-50 kilometres away without reliable means of transport. The technical staff of the county government is often unable to offer quality and effective extension work, mostly due to transport limitations but also due to low motivation. However, this gap is being bridged through the work of various NGOs operating in the region who provide advisory services in addition to other interventions such as in water, health, livelihoods, and education.
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, moderadamente
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
Describa la institución, roles y responsabilidades, miembros, etc.
The Approach led to establishment of Water Management Committees. The committees have been trained and equipped to manage the systems.
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- financiero
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
- equipo
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
One key lesson from this and other projects is that one-off trainings are rarely effective even if properly done. A continuous support/follow-up is necessary to maintain the skills and knowledge acquired.
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
No
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
No
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 2,000-10,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Internal organisational funding and external donors
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
Sí
Si respondió sí, especifique el tipo o los tipos de apoyo, condiciones y proveedor(es) :
Caritas procured the bulk of construction materials whereas the community contributed locally available materials - sand and hardcore stones
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
The labour contribution was split between the organisation and the community. Caritas paid 3 USD per day whereas the standard amount per day is 5 USD. This was discussed and agreed at the inception of the project. The consideration was that those who work on site will not have any other time for other work for their household daily needs.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
5.5 Otros incentivos o instrumentos
¿Se usaron otros incentivos o instrumentos para promover la implementación de Tecnologías MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque empoderó a los usuarios locales de tierras, mejoró el involucramiento de las partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Community's participation was initially a new concept for the communities in this region. Through various meetings, persistency and flexibility the community participation improved and was achieved during the project period.
¿El Enfoque facilitó la toma de decisiones basada en evidencia?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Due to the nature of working with the community, it was always possible to review certain elements of project activities based on learning
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The Approach's aim was to build the required capacity of the community members to better manage the Technology well after the project ends.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la coordinación e implementación efectiva en costos de MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Community's contribution in labour and locally available materials (hardcore stones and sand) significantly reduced the cost of construction. These are materials that otherwise would have been procured from far off sources at a much higher cost.
¿El Enfoque movilizó/mejoró el acceso a recursos financieros para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The SLM was implemented with funding support aimed for drought recovery. The country had just gone through a major drought. The Approach, however, focused more on mobilising communities towards meaningful participation by providing local available resources such as hardcore, sand, and unskilled labour.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de los usuarios para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
A significant element of the Approach was capacity building which was achieved through on-the-job and workshop training for the selected community members
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de otras partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The project was implemented with close involvement of county government officials and other development organisations. There have been requests by other development actors in the region wanting to know more about how Caritas Switzerland succeeded in working with the communities and achieving these impressive results.
¿El Enfoque construyó/ fortaleció instituciones, colaboración entre partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The project's mandate was limited to community institutions capacity building. Beyond community empowerment the Approach did not target to raise capacity of other stakeholders.
¿El Enfoque mitigó conflictos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The region within which the project was implemented in has resource based conflicts, mostly conflicts over water and pasture land. The Approach led to successful implementation of the Technology which reduces pressure on water resources. In addition, the management of the newly constructed water points ensures that community members benefits equally
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
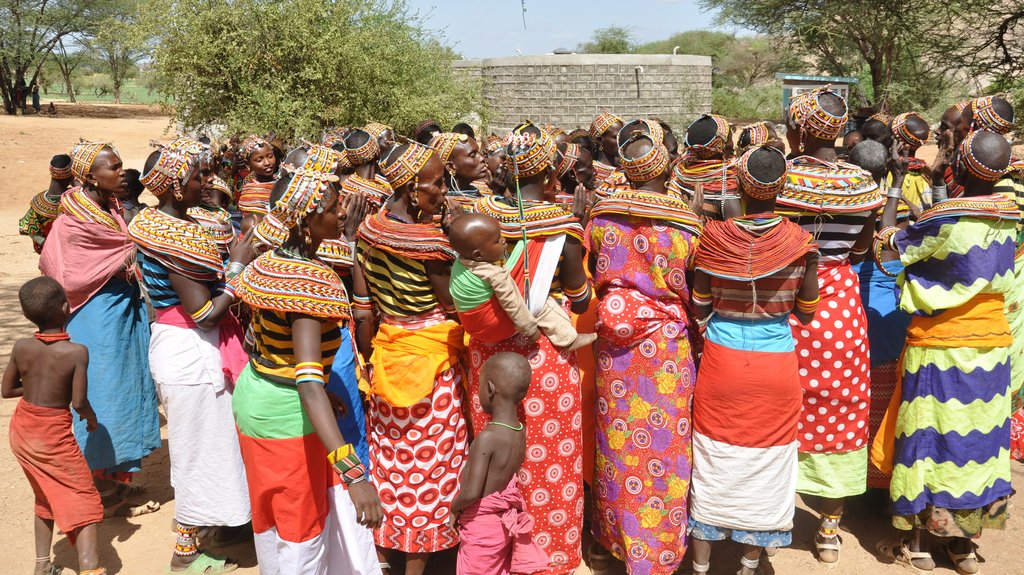
Women are the main beneficiaries of the Approach. They were more active than men in offering semi-voluntary labour. Their motivation was that they bear the greater burden than men as it is their responsibility to provide household water .
¿El Enfoque alentó a jóvenes/ la siguiente generación de usuarios de tierras a involucrarse con MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Youth participation was minimal due cultural barriers. Young men do not participate in most of community activities. They are expected to have minimal contact with the rest, and especially women hence most of their time they are in the bush
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Land tenure system in the area where the Approach was implemented is communal.
¿El Enfoque resultó en mejor seguridad alimentaria/ mejoró la nutrición?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
It is expected that nutritional status will improve with increased access to better quality water. However, no survey was carried out to confirm this assumption.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el acceso a los mercados?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Community members who initially would spend substantial amount of time to search for water now have more time freed to engage in trade and other diversified sources of income
¿El Enfoque llevó a un acceso mejorado a tierra y saneamiento?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
There is improved access to water. The three benefiting communities no longer need water supply emergency. However, impact on sanitation was less than satisfactory.
¿El Enfoque llevó a un uso más sostenible/ fuentes de energía?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The project's mandate under which the Approach was implemented was limited to water and sanitation
¿El Enfoque mejoró la capacidad de los usuarios de tierras a adaptarse a los cambios climáticos/ extemos y mitigar desastres relacionados al clima?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Increased water supply has greatly increased community's resilience to droughts. With a prudent management of water harvested, they have successfully avoided negative drought impacts.
¿El Enfoque llevó a oportunidades de empleo, ingresos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
There is no direct employment except that the community members can now engage more in other rewarding businesses
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- reducción del riesgo de desastres naturales
Increased water supply has greatly decreased community's vulnerability to droughts.
- carga de trabajo reducida
The community was highly motivated by the challenges of acute and perennial water shortages they have experienced for many years. They had a great desire to change and overcome this challenge.
- mitigación de conflicto
Reducing water scarcity likely leads to less conflict on water. However, no survey data is available to validate this assumption.
- improved water acess
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- sí
Si respondió que sí, describa cómo:
The Approach greatly focused on capacity building, community empowerment and strengthened institutions. It is expected therefore that they will sustainably manage the Technologies that have been constructed.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The Approach leads to greater ownership of the technology thus leading to better equipped community groups with skills for operations and maintenance. The Approach galvanises a community towards a common goal hence promotes cohesion and better organisation. |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| It takes time to achieve the community´s buy-in so that they can adequately fulfil their obligations. This is particularly the case in a region where varied development approaches have been implemented, most of which create dependency and discouraged self-initiative. | This can be changed through long terms engagement processes with all stakeholders such as county government and NGOs to advocate for approaches that foster community empowerment. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Community elders, chiefs, water management committee members, and users
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
The water management committee
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
James Ndenga, staff of Caritas Switzerland
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
End of project report
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
A Handbook of gravity-flow water systems for small communities; Thomas D. Jordan Junior; 1980; 978 0 94668 850 0
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Caritas Switzerland office, Nairobi
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos