Irrigated agro-biodiversity system in arid high mountain area [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Gulniso Nekushoeva
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1034 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TayikistánNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - Tayikistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
21/06/2010
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
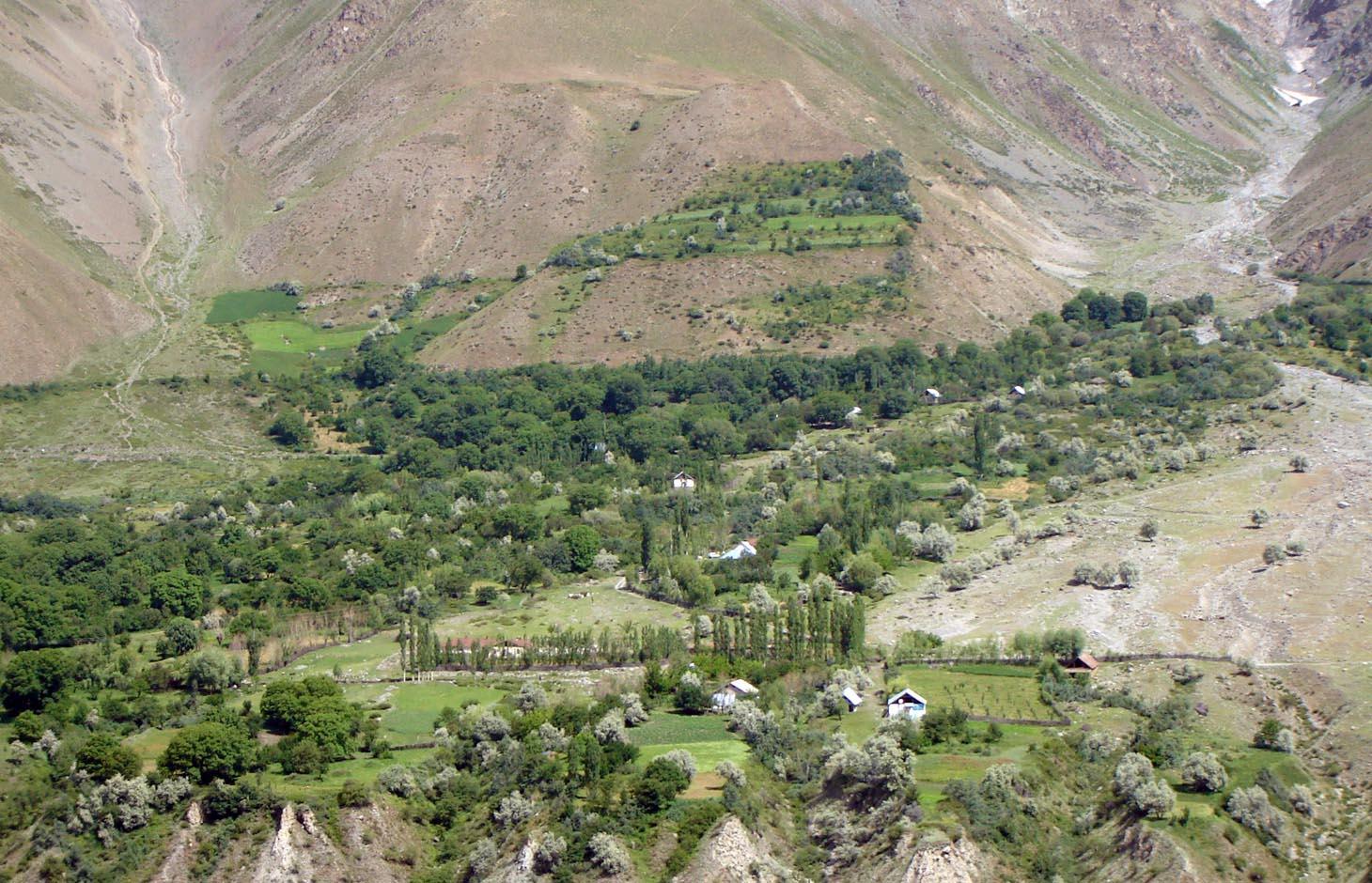
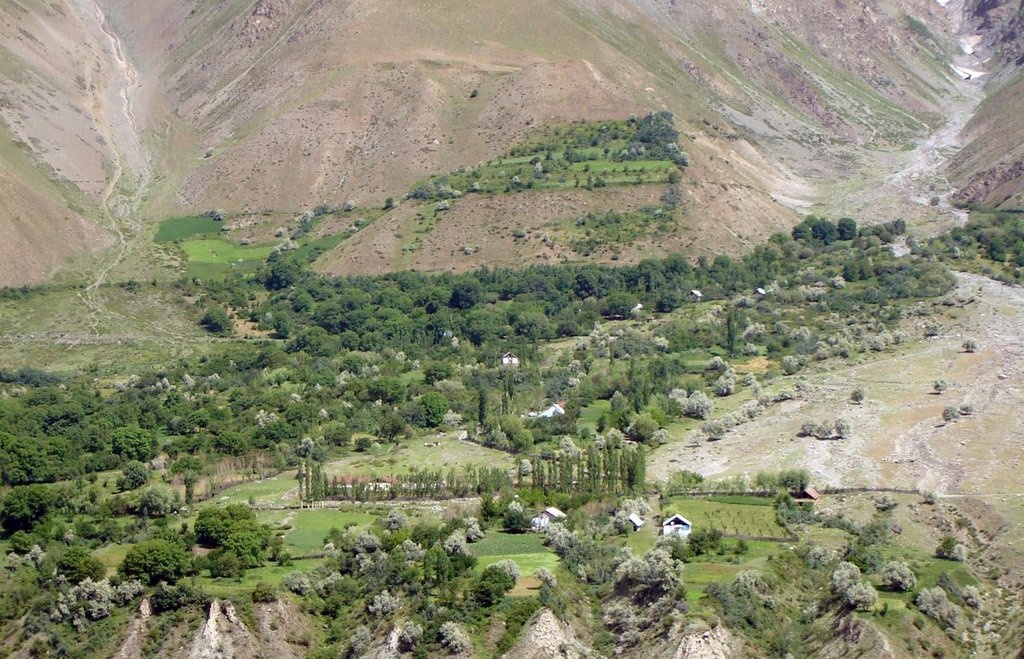
An individual farmer family, has changed an overgrazed pasture area on a steep slope in the upper part of the village into an irrigated agro-biodiversity system, by constructing an irrigation canal, by tilling and removing stones from the terraces for crop production and afforesting the surrounding area with fruit trees and bushes.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The site was established in 1989, with the construction of an irrigation canal. The canal brings water from a small watershed and the slowly melting snow fields within. In years with limited snowfall, the water is insufficient for irrigation throughout the summer months.It is a open, mud canal, 730 m long. When establishing new cropland, removal of stones from the plots is the most laborious part of the work. After an initial removal of stones, the land is tilled and appearing stones are again removed. This process is repeated several times.
Year round maintenance work is required to keep the canal functioning. Maintenance work on the cropland includes stone removal, manuring of potatoes fields, weeding and tilling.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
GBAO
Especifique más el lugar :
Vanj / Udob / Trit
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
A traditional agroforestry system is implemented on a steep slope above the village, as there is a lack of flatter cropland. This requires improved and carefully adapted land practices.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- conservar el ecosistema
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
major food crop: potato, wheat, barley, alfa-alfa

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agroforestería
Principales productos/ servicios:
Old wallnut forests are used for agroforestry: there are potato, wheat, alfa-alfa and vegetable gardens below the nut trees.
Newly irrigated areas, are without wallnut trees and used for annual cropping and for perennial cropping.
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water scarcity is the major factor limiting vegetation growth and agricultural production in this arid areas. The soils are stony and slopes are steep (20-30 degrees).
The area is irrigated from streams fed by snow and glacier melting, and therefore water availability is strongly depending on yearly snow precipitation. If due to climate change snowfalls are decreasing in the future, this is a threat for agriculture in the region.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As the area is on steep slopes there is a high risk of small land slides triggered by irrigation. Fast snow melting in spring time may also cause land slides.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Old wallnut forests are used for agroforestry: there are potato, wheat, alfa-alfa and vegetable gardens below the nut trees.
Newly irrigated areas, are without wallnut trees and used for annual cropping and for perennial cropping.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- totalmente irrigada
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: May - September
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- agroforestería
- medida de pendiente transversal
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
This technology can be found all along Vanj valley.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
- M3: disposición de acuerdo al entorno natural y humano
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking crust / sealed surface, breaking compacted topsoil, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bh: loss of habitats, Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts (in years with droughts part of the perennial vegetation may dry up), land tenure (common grazing land), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (access to irrigation water, access to markets)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (early grazing, overgrazing), labour availability (mostly manual work and thus labour intensiv), governance / institutional (limited access to market, no water association)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Vast practical knowledge is required, through practical experiments, the practices were improved over time.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Agronomic measure: crop rotation on wheat fields
Material/ species: perennial fodder plants (alfa-alfa)
Remarks: high density of alfa-alfa plants
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cow manure
Quantity/ density: 15
Remarks: for patatoe fields
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: "super phosphat" or "silitra"
Quantity/ density: 0.025
Remarks: for wheat fields
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Contour tillage
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: willow, "sangid", "Jachman bushes", "Kort (big bush)";
Fruit trees / shrubs species: sea-buckthorn, walnut, plum, appel, pear, apricot, mirabelle, whitethorn, cherry, dog rose
Grass species: graminoids and legumes
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2500
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 750
Construction material (earth): The waterways are all dug into the ground, and are mostly fortified with bushes and trees.
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: extensive grazing to agroforestry
Layout change according to natural and human environment: carefully designed layout taking advantage of flatter areas for cultivation of annual crops, and protecting steep slopes with perennial tree and bush cover
Control / change of species composition: mix of cultivated and wild plants (trees, bushes and grasses)
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Tajik Somoni
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
4,4
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
30.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | Vegetativas | spring |
| 2. | Construction of irrigation canal | Estructurales | autumn |
| 3. | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | Estructurales | spring |
| 4. | Alfa-alfa seeds (12kg/ha) | Agronómicas | for 4 years, then can produce own seeds |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | Persons/day | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Mano de obra | Construction irrigation canal | Persons/day | 100,0 | 30,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | Persons/day | 30,0 | 30,0 | 900,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Alfa-alfa seeds | kg/ha | 6,0 | 20,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 4020,0 | |||||
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wheat (barley) sowing | Agronómicas | anually |
| 2. | Wheat (barley) sowing | Agronómicas | |
| 3. | Tilling potato fields | Agronómicas | 3 times per growing season |
| 4. | Irrigating wheat (barley, alfa-alfa) | Agronómicas | times per growing season |
| 5. | Planting potato | Agronómicas | during planting |
| 6. | Planting potato | Agronómicas | |
| 7. | Applying fertilizer to wheat fields | Agronómicas | 3 times per growing period |
| 8. | Maintenance of canal and on-farm water distribution network | Estructurales | spring and after rains |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Sowing wheat with ochses | Persons/day | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Tilling with ochses | Persons/day | 6,0 | 40,0 | 240,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Irrigating wheat, barley alfalfa | Persons/day | 6,0 | 30,0 | 180,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Planting potatoe | Persons/day | 8,0 | 30,0 | 240,0 | |
| Equipo | Ochses for wheat sowing | Ochses/ha | 2,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Ochses for potatoe tilling | Ochses/ha | 6,0 | 30,0 | 180,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Donkey for carrying dung to the fields | loads | 120,0 | 0,66666 | 80,0 | |
| Equipo | Labour: Going with donkeys | Persons/day | 8,0 | 40,0 | 320,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Wheat seeds | kg | 200,0 | 1,2 | 240,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost/manure | tons | 12,0 | 50,0 | 600,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Poatoe seedling | kg | 800,0 | 1,0 | 800,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fertilizer for wheats | kg | 140,0 | 0,58571 | 82,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 3102,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Costs were calculated fro an area of 5 ha. The length of the irrigation channel from the creek to the plot is 730 m.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
With regard to the establishment costs, the most determining factors are: the distance to the creek from where water is channeled away and the steepness of the slope and amount of stones when preparing the land for annual cropping. With regard to the maintenance costs it is the exposure of the water channel to rock fall and small land slides.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Most of the precipitation consits of snow, the main rainfall period is March / April
Zona agroclimática
- árida
Thermal climate class: temperate. high mountain area
A2240 m asl
gricultural areas need irrigation, which is supplied by snow and glacier melt
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: 2240 m a.s.l.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich.
10% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The here described farmers family has very limited off-farm income. The farm provides sufficient fuel, fodder, fruits and potatoes for subsistence farming.
In general, seasonal migration to Russia is widespread in the area, which provides additional income in form of remittances. Only households with only young children, elderly and sick persons have no family member working in Russian.
Level of mechanization: One uses ochses for plowing, motorized is really rare.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
Comentarios:
The land use right for the individual farmer is documented with an official land user certificate.
Water use right has been agreed on with the village council.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no muy bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
1 Household
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos