Earth checks for Gully reclamation [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Daniel Danano
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1069 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Estifanos Zena
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development
Etiopía
Especialista MST:
Desta Hiwot
Boditi, Department of Agriculture and Rural Development
Etiopía
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItaliaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - Etiopía1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
30/05/2011
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
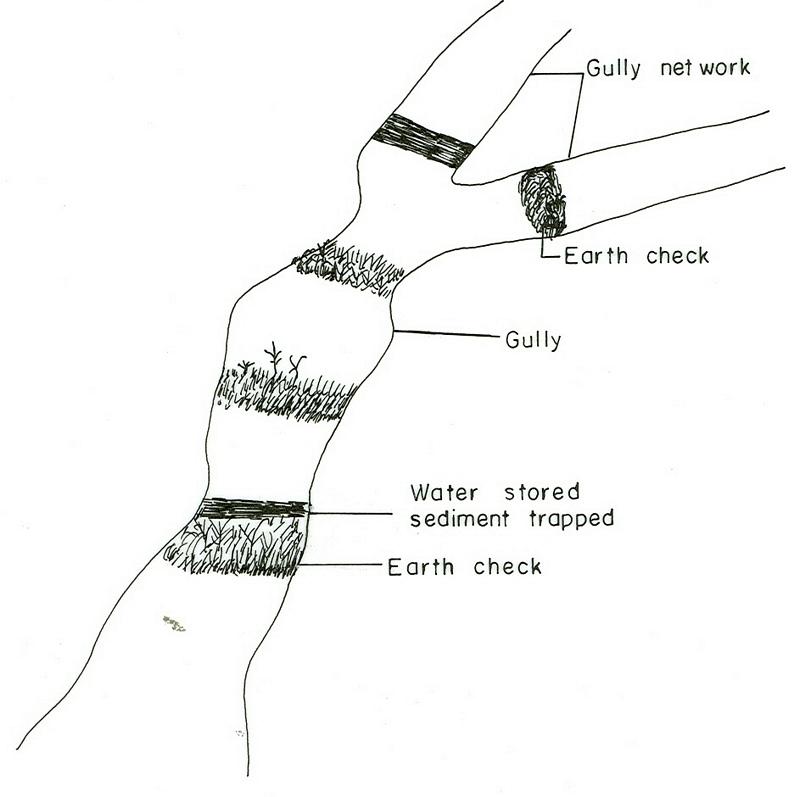
Earh-checks are constructed of earth embankment put across in a deep gully in such a way to trap sediment and store water passing by it.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Active deep gullies are plugged by digging earth from the bottom as well as gully sides and embanked forming a barrier to runoff passing through it. The embankment is reinforced by planting useful plants such as banana, sesbania, gravillea, gesho, etc., The purpose is to rehabilitate gullies having depth and expand along sides and towards the head. By constructing earth checks the water is stored in the checks. The water percolates down the ground enriching the ground water. The soil is trapped in the checks and later brings up the gully gradient higher. As a result, a cultivable/cropable strip is formed. Weeding and cultivation done to plants established.The gully fence and breaks are repaired. The technology is seen to be suitable to humid highlands where land loss by gully is a serious problem and land under cultivation and grazing is getting here and there. In brief it is suitable in areas where land degradation problem is increasing with currently cultivated and grazed lands are encroched by gully expansion.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
SNNPR
Especifique más el lugar :
SNNPR/Damot Galle/Bilate
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology is introduced but highly modified by adjesting design, layout and by increasing use of locally available materials for construction.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Teff
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize, sweet potato, enset
Major other crop annual cropping: Taro, potato
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Sugar cane
Major cash crop tree and shrub cropping: Sugar cane
Major other crop tree and shrub cropping: Fruit trees

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agro-silvopastoralismo
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Monocropping, soil erosion, fertility mining, overgrazing, improper runoff management.
Grazingland comments: Livestock such as cows, oxen, donkeys and horse are thethered at a very small piece of land left infront of houses usually meant for social purposes. Some farmers thether their animals in a piece of land left uncropped in the field. The most part of livestock feed comes from crop residue which is collected from crop fields. Maize stalk, teff straw and enset leaves are fed stall.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize-sweet potato-Teff-potato-sorghum
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 180 Second longest growing period from month to month: Aug - Jun
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
- cosecha de agua
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 51.2 m2.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: Also rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
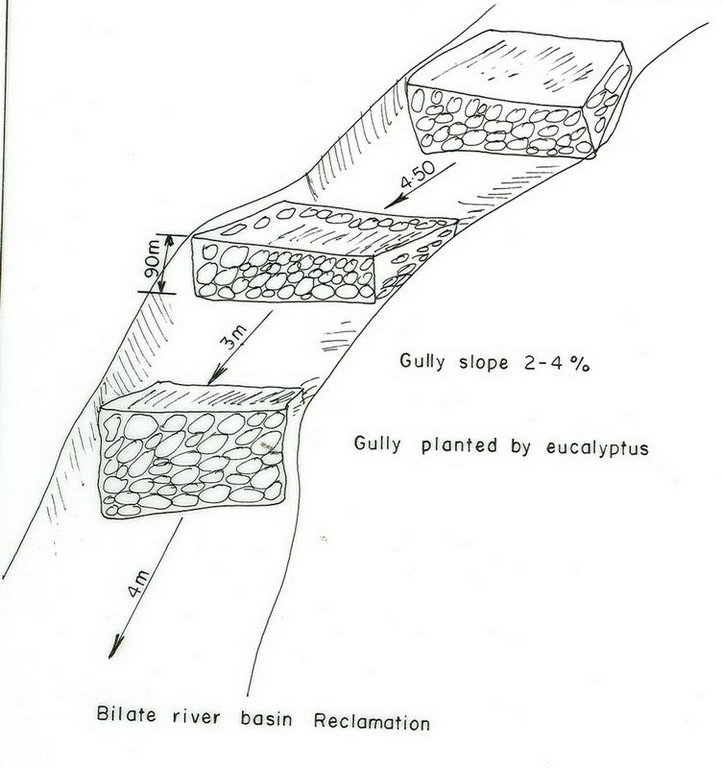
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Early planting
Material/ species: maize
Quantity/ density: 85000/ha
Remarks: sawn in lines
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize-sweet potato/haricot bean
Remarks: inter cropped & strip cropped
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: maize-taro-enset
Mulching
Material/ species: enset
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: maize, potato, sweet potato, traro
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Teff, maize, sorghum
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: maize-tarro-sorghum
Remarks: only rotations
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: primary and secondary oxen tillage
Contour tillage
Remarks: tillage done following contour
Agronomic measure: harrowing
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2-0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2-4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5x1.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2x2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena, Sesbania, Grevillea
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, papaya, Avocado
Perennial crops species: Casava
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 8.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-75
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Construction material (earth): Most of the structural measures are made by earth involving excavation and embankment.
Construction material (stone): Stone is mainly used for demonstration.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: The land after treatment is closed
Control / change of species composition: Grazing land changed to plantation and cropping
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level - Grazing land changed to plantation and cropping
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Birr
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
8,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
0.60
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | Vegetativas | September, october |
| 2. | Sugar cane planting | Vegetativas | November |
| 3. | Sugar cane cultivation | Vegetativas | January/August |
| 4. | Casava planting | Vegetativas | April |
| 5. | Casava cultivation | Vegetativas | June |
| 6. | Maize planting | Vegetativas | January-1st plough, April 2nd plough |
| 7. | Maize cultivation | Vegetativas | June |
| 8. | Sweet potato planting | Vegetativas | September |
| 9. | Sweet potato cultivation | Vegetativas | October |
| 10. | Fruite trees | Vegetativas | June |
| 11. | Digging foundation | Estructurales | November-February |
| 12. | Forming embankment | Estructurales | November-February |
| 13. | Side wall shaping | Estructurales | November-February |
| 14. | Planting trees and shrubs | Estructurales | March-1st planting & June 2nd planting |
| 15. | Excluding animals by fencing and guarding | Manejo | all year |
| 16. | Construct cutoff drain | Manejo | dry season |
| 17. | Establish buffer zone between Area enclosure and crop land by strip of plantation | Manejo | June/July |
| 18. | Construct earth checks and trenches in the gully | Manejo | dry season |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 282,3 | 282,3 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 270,6 | 270,6 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 117,6 | 117,6 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 670,5 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | Agronómicas | september, october / 2 times |
| 2. | Sweet potato planting | Agronómicas | September / each cropping season |
| 3. | Sweet potato cultivation | Agronómicas | October / each cropping season |
| 4. | Maize planting | Agronómicas | January/April / each cropping season |
| 5. | Maize cultivation | Agronómicas | June / each cropping season |
| 6. | Teff sawing | Agronómicas | |
| 7. | Teff weeding | Agronómicas | |
| 8. | Prunning | Vegetativas | october /once |
| 9. | Mulching | Vegetativas | october /once |
| 10. | Thining | Vegetativas | october /once |
| 11. | Fencing | Vegetativas | any time /once |
| 12. | Weeding | Estructurales | June/each cropping season |
| 13. | Cultivation | Estructurales | March/each cropping season |
| 14. | Replanting | Estructurales | June/each cropping season |
| 15. | Repair in breaks | Estructurales | November-February/each cropping season |
| 16. | Fence | Estructurales | each cropping season |
| 17. | Repair breaks on cutoff drain and earth checks | Manejo | dry season / 2 years |
| 18. | Prunning, weeding and cultivation | Manejo | end of rains / each cropping season |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: spade, hoe
Length and width of structure
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Factors affecting costs in this technology are the depth and width of gully, steepness of slope, planting and replanting of vegetative materials.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked 1, about 70%), gentle and rolling (both ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Deep (Soils are very deep (75%))
Soil texture: Medium (fertile loam soils)
Soil fertility is medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (ranked 1, in the crop lands), low (ranked 2, degraded areas) and high (ranked 3, around the homestead)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (ranked 1, on crop land) and high (ranked 2, on flat plateau land)
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich.
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
45% of the land users are poor.
40% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have SWC measures on their land produce more and hence have better financial income, which could allow them get involved in petty trade and other activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, crop lands) and manual work ( ranked 2, homstead and gully lands)
Market orientation of cropland production system: subsistence (self-supply, maize) and mixed (subsistence/ commercial, sweet potato, teff, coffee)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comentarios:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha (more than 80% of farmers) and 1-2 ha
grazing land: 0.5-1 ha (communal grazing lands are severly degraded)
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Shortage of grazing land: Animals are thethered in a small plots
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
teams are formed
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
many wants to be beneficiaries but only the poor given the opportunities
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Otros impactos ecológicos
Biodiversity enhancement
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
all runoff retained
colmatación río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
all soil trapped
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos