Holistic demonstration [India]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Samagra Jalanayan Abhivrudhi Pratyakshike (Kannada)
technologies_1084 - India
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
12/03/2004
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Holistic demonstration includes integrated cultivation of Agri-Horti-Silvi technologies. Along with the Soil & water Conservation structures suitable to the site.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Holistic demonstration was taken in the upper reach, middle reach and lower reach (2 hectares each) in a village in the watershed. The demonstration units includes soil & water consercvation structures also. Crop demonstration with integrated pest management, seed treatment, pitcher irrigation practices, varietal trails were implemented to increase the overall per capita income of the farmer. However, the suitable SWC was according to the site of lower reach/ upper reach or middle reach. The plot was accommodated with suitable field crops, horticultural species either on the bunds or in the fiels itself and some fodder crops, some forestry species etc.
Purpose of the Technology: The demonstration units now serve as the units of awareness brining in understanding the holistic approach and also to encourage the other farmers to replicate the same in their fields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: (1) site selection with concerned farmer, (2) design and preparation of estimates by the project staff, (3) discussion with the VWDC and community, (4) discussion regarding contribution with the farmer (5) layout and construction by the project staff with the contribution from the concerned farmers.
Natural / human environment: This technology was taken up in the semi arid condition and in the erratic rainfall conditin.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
India
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Karnataka
Especifique más el lugar :
Chitapur taluk of Gulbarga district
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Mainly from the SWC specialist
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agro-silvopastoralismo
Principales productos/ servicios:
Major cash crop annual cropping: Redgram
Major food crop annual cropping: Jowar
Major other crop annual cropping: Sesamum
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody cropping): Mango
Major food crop perennial (non-woody cropping): Drumstick, curryleaf
Major cash crop agroforestry: Bengalgram
Major food crop agroforestry: Mango, sapota
Major other crop agroforestry: Neem, teak
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop land : Low yields due to erosion, less soil moisture, shallow to medium soils. Poor and erratic rainfall, water holding capacity is less.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop land - Uncertain rainfall, more soil loss and poor yields.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: the village cattle are let free for grazing on the common land for some time in the day and they go back and then I is again stall feeding.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: others (scattered)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: During kharif (monsoon) season the main crop is redgram (Tur), in addition few cereals were taken, followed by jowar in the major rabi (post-monsoon) crop. No cultivation was o\bserved in summer, farmer are now cultivating vegetable and fruit crop,
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding (both ranked 2)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- perturbación mínima del suelo
- manejo integrado de pestes y enfermedades (incl. agricultura orgánica)
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.12 km2.
The technology area comprises of 2 ha area each in upper reach, middle reach and lower reach in a village of the watershed. In this area cultivation of agri-horti-silvi practices, agronomic trials, in-situ conservation etc were taken with active involvement of the the farmers.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
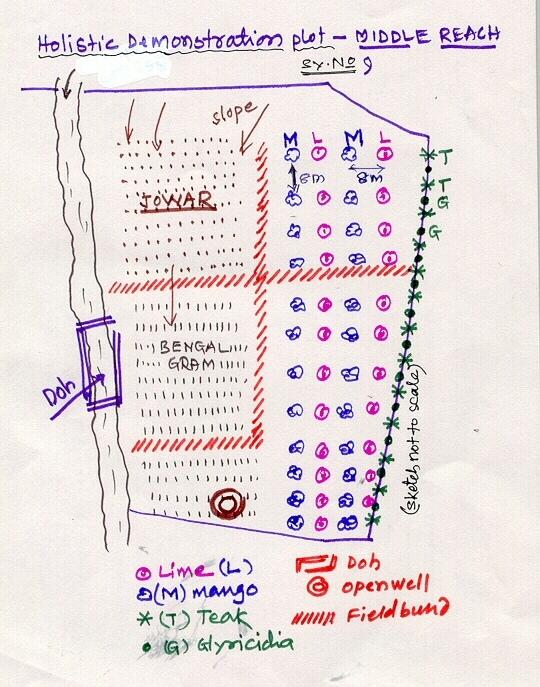
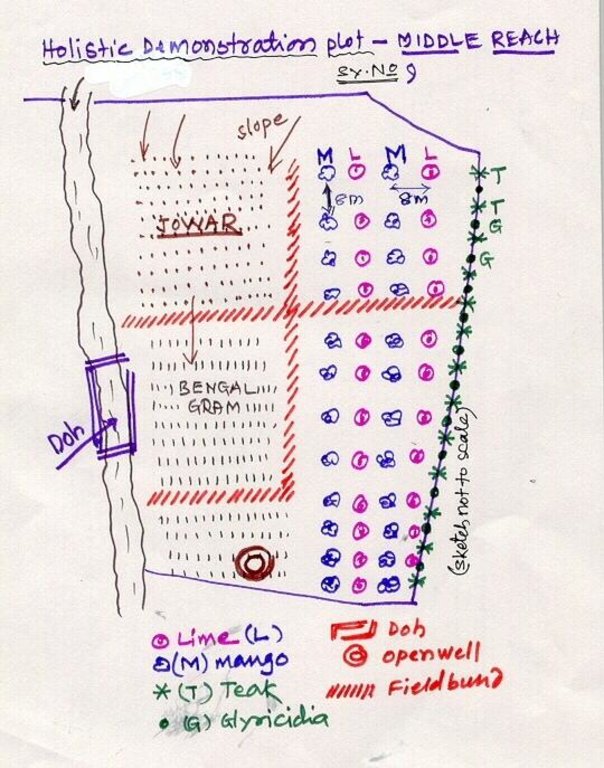
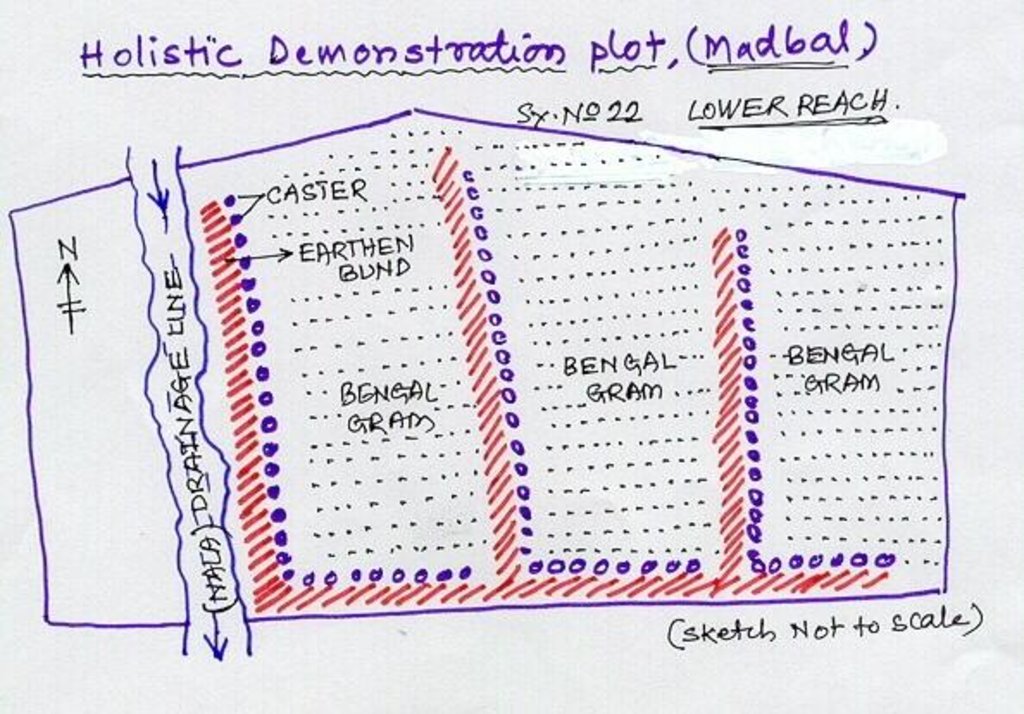
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Lower Reach holistic demonstration plot showing various soil & moisture conservation structures, field crops and bund stabilization by vegetation.
Location: Bennur-B nala watershed Chitapur taluk. Chitapur taluk, Gulbarga District (Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: saplings
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: layout
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: sapplings
Quantity/ density: 360
Remarks: layout
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200
Remarks: layout
Agronomic measure: others (vermicompost)
Material/ species: material
Minimum tillage
Remarks: material
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: pit, sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: other (brushwood dam)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Multidimensional participatory holistic farming system, fallow to cultivable land
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Rupees
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
46,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
0.73
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of pits | Vegetativas | Sumer |
| 2. | Procurement of seed/ seedlings | Vegetativas | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Sowing of grass, shrub seeds | Vegetativas | After first shower |
| 4. | Planting of sappling | Vegetativas | After first shower |
| 5. | Survey/ layout | Estructurales | April |
| 6. | Excavation of ditches | Estructurales | may |
| 7. | Transportation of stones to the site | Estructurales | May |
| 8. | Construction of bunds, farm pond | Estructurales | may |
| 9. | Construction of brushwood dam, doh | Estructurales | June |
| 10. | Training, capacity building of the farmer | Manejo | february - March |
| 11. | Establishment of sructural measures | Manejo | April-June |
| 12. | establishment of vegetative measures | Manejo | July-September |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 510,0 | 510,0 | 10,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 114,0 | 114,0 | 3,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 169,0 | 169,0 | 74,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 157,0 | 157,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 76,0 | 76,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construcción | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 110,0 | 110,0 | 3,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 3,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 26,0 | 26,0 | 2,0 |
| Otros | Pitcher pots | ha | 1,0 | 72,0 | 72,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1259,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching | Agronómicas | Summer / each cropping season |
| 2. | Across slope ploughing | Agronómicas | Summer / each cropping season |
| 3. | In-situ maisture conservation | Agronómicas | before sowing / |
| 4. | Watering | Vegetativas | summer /once in 10 days |
| 5. | Weeding, mulching | Vegetativas | 2-3 months after planting /twice in a year |
| 6. | Re-seeding of grass/ shrub | Vegetativas | before first shower /up to 2 years |
| 7. | casualty replacement | Vegetativas | before first shower /1, 2, and 3rd years |
| 8. | fencing | Vegetativas | during sumer period /every summer season of 2nd, 3rd and 4th year |
| 9. | Repair of breaches in bund | Estructurales | July to september/as required |
| 10. | Desilting of traps | Estructurales | October-November/annual |
| 11. | Refresher interaction with farmer | Manejo | / seasonally |
| 12. | Rgular meetings | Manejo | / as and when required |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 51,0 | 51,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 11,1 | 11,1 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 16,9 | 16,9 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 15,7 | 15,7 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 7,6 | 7,6 | |
| Material de construcción | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Pitcher pots | ha | 1,0 | 7,2 | 7,2 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 124,1 | |||||
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Non availability of stones, boulders
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
750-800 mm
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (422.8 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateu/plains (3-4% slope, ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (3-4%)
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (60 cm, ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (eroded soils)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (absence of vegetation)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (high run-off from stony surface)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
- pobre
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
7% of the land users are average wealthy and own 26% of the land.
65% of the land users are poor and own 58% of the land.
28% of the land users are poor and own 16% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off season employment
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha: Joint farmers, land shared by brothers (ranked 1), 1-2 ha (ranked 2), 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha: Not much grazing land is available in the village.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Drought from last 3 years
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
producción de madera
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
SWC takes small piece of cultivable land
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
Village watershed development committee, users groups etc.
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Project support is expected by most of the farmers at a time.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Area was previously barren
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Good vegetative cover
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Ground cover established with vegetative hedges.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
velocidad de viento
Otros impactos ecológicos
Soil fertility
Comentarios/ especifique:
Introduction of legume species (glyricidia)
Biodiversity
Waterlogging
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not a genereal problem. But only on this plot.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
In-situ conservation
sedimentos transportados por el viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
Establishment of ground covers
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
452
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
417 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Overall returns fro\m the piece of land is increased owing to horticulture and agriculture crops. Biomass increases. This is seen by other farmers and they are motivated to go for its adaption.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Economic sustainability How can they be sustained / enhanced? vegetative and green manure vermicompost etc. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Effective SWC How can they be sustained / enhanced? maibntenance by the individual farmers |
|
water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting structure |
|
Integrated approach How can they be sustained / enhanced? regular contact |
|
increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated cultivation |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Production (benefits) adversly affected due to drought. | Due to longer dry spel in the area (last three years) |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Non-availability of agricultural improved seed material at local level | by linkage of VWDCs with the Agricultural Research Station and Krishi Vignyan Kendra. |
| conflicts | demands by more number of farmers could not be met by the project at a time. |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos