Holistic demonstration [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Samagra Jalanayan Abhivrudhi Pratyakshike (Kannada)
technologies_1084 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
12/03/2004
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Holistic demonstration includes integrated cultivation of Agri-Horti-Silvi technologies. Along with the Soil & water Conservation structures suitable to the site.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Holistic demonstration was taken in the upper reach, middle reach and lower reach (2 hectares each) in a village in the watershed. The demonstration units includes soil & water consercvation structures also. Crop demonstration with integrated pest management, seed treatment, pitcher irrigation practices, varietal trails were implemented to increase the overall per capita income of the farmer. However, the suitable SWC was according to the site of lower reach/ upper reach or middle reach. The plot was accommodated with suitable field crops, horticultural species either on the bunds or in the fiels itself and some fodder crops, some forestry species etc.
Purpose of the Technology: The demonstration units now serve as the units of awareness brining in understanding the holistic approach and also to encourage the other farmers to replicate the same in their fields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: (1) site selection with concerned farmer, (2) design and preparation of estimates by the project staff, (3) discussion with the VWDC and community, (4) discussion regarding contribution with the farmer (5) layout and construction by the project staff with the contribution from the concerned farmers.
Natural / human environment: This technology was taken up in the semi arid condition and in the erratic rainfall conditin.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Karnataka
有关地点的进一步说明:
Chitapur taluk of Gulbarga district
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Mainly from the SWC specialist
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林牧业
主要产品/服务:
Major cash crop annual cropping: Redgram
Major food crop annual cropping: Jowar
Major other crop annual cropping: Sesamum
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody cropping): Mango
Major food crop perennial (non-woody cropping): Drumstick, curryleaf
Major cash crop agroforestry: Bengalgram
Major food crop agroforestry: Mango, sapota
Major other crop agroforestry: Neem, teak
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop land : Low yields due to erosion, less soil moisture, shallow to medium soils. Poor and erratic rainfall, water holding capacity is less.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop land - Uncertain rainfall, more soil loss and poor yields.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: the village cattle are let free for grazing on the common land for some time in the day and they go back and then I is again stall feeding.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: others (scattered)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: During kharif (monsoon) season the main crop is redgram (Tur), in addition few cereals were taken, followed by jowar in the major rabi (post-monsoon) crop. No cultivation was o\bserved in summer, farmer are now cultivating vegetable and fruit crop,
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding (both ranked 2)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.12 km2.
The technology area comprises of 2 ha area each in upper reach, middle reach and lower reach in a village of the watershed. In this area cultivation of agri-horti-silvi practices, agronomic trials, in-situ conservation etc were taken with active involvement of the the farmers.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
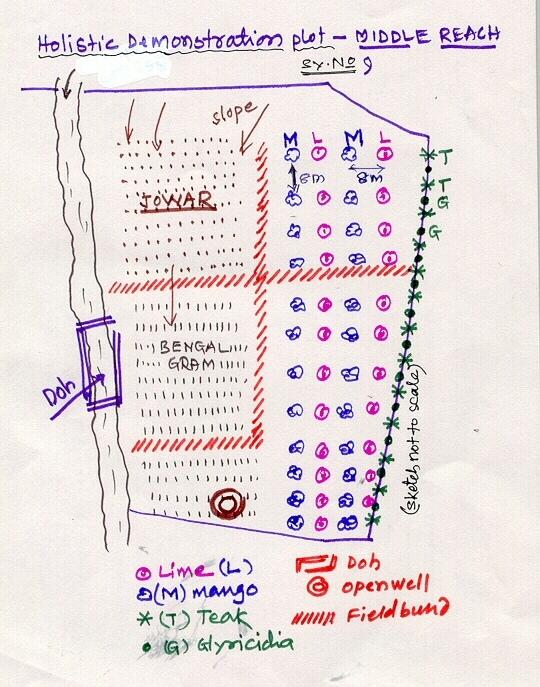
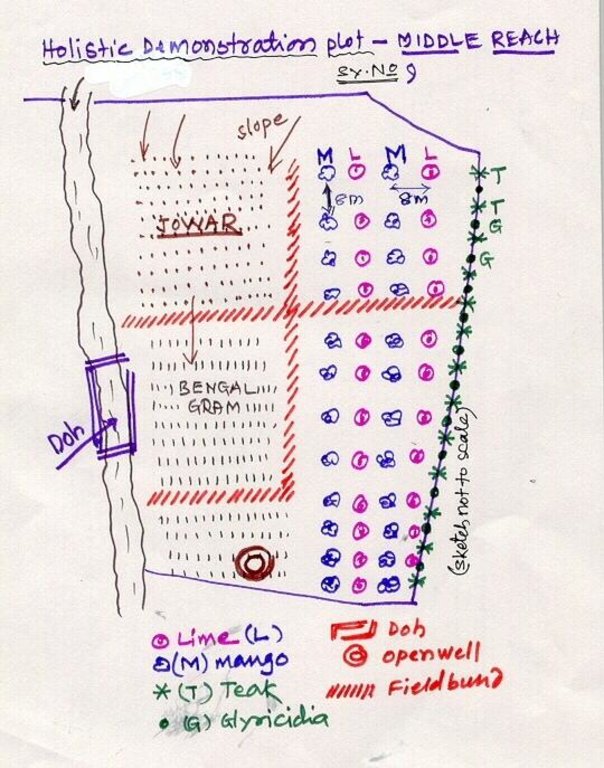
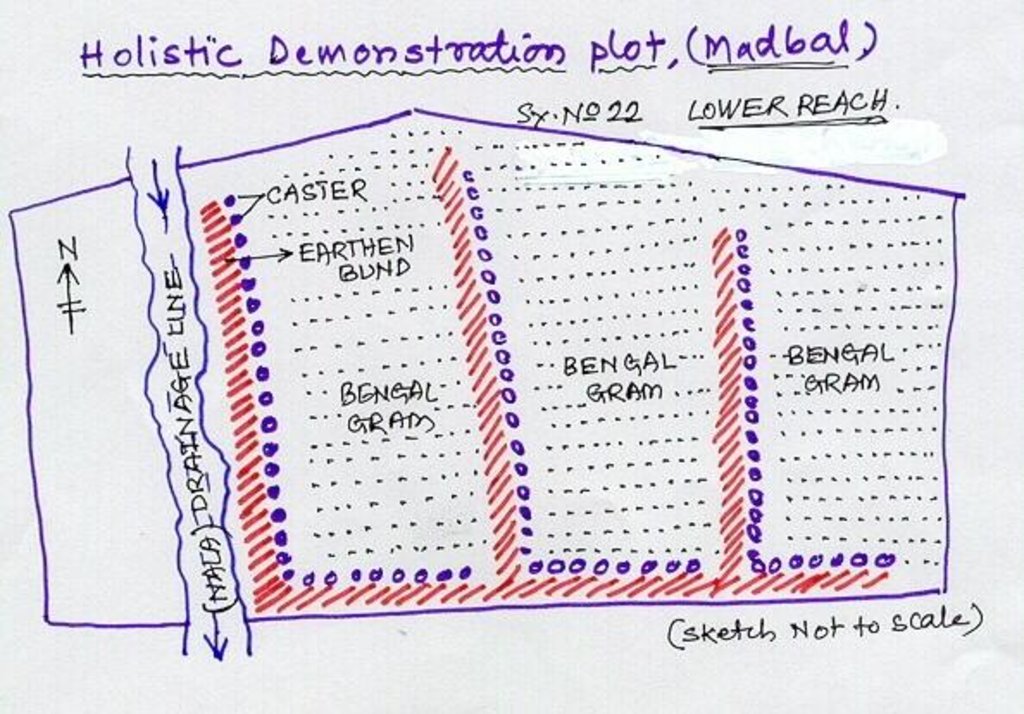
Lower Reach holistic demonstration plot showing various soil & moisture conservation structures, field crops and bund stabilization by vegetation.
Location: Bennur-B nala watershed Chitapur taluk. Chitapur taluk, Gulbarga District (Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: saplings
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: layout
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: sapplings
Quantity/ density: 360
Remarks: layout
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200
Remarks: layout
Agronomic measure: others (vermicompost)
Material/ species: material
Minimum tillage
Remarks: material
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: pit, sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: other (brushwood dam)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Multidimensional participatory holistic farming system, fallow to cultivable land
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupees
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
46.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.73
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of pits | 植物性的 | Sumer |
| 2. | Procurement of seed/ seedlings | 植物性的 | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Sowing of grass, shrub seeds | 植物性的 | After first shower |
| 4. | Planting of sappling | 植物性的 | After first shower |
| 5. | Survey/ layout | 结构性的 | April |
| 6. | Excavation of ditches | 结构性的 | may |
| 7. | Transportation of stones to the site | 结构性的 | May |
| 8. | Construction of bunds, farm pond | 结构性的 | may |
| 9. | Construction of brushwood dam, doh | 结构性的 | June |
| 10. | Training, capacity building of the farmer | 管理 | february - March |
| 11. | Establishment of sructural measures | 管理 | April-June |
| 12. | establishment of vegetative measures | 管理 | July-September |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 510.0 | 510.0 | 10.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 114.0 | 114.0 | 3.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 169.0 | 169.0 | 74.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 157.0 | 157.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 76.0 | 76.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 3.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 |
| 施工材料 | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 2.0 |
| 其它 | Pitcher pots | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1259.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching | 农业学的 | Summer / each cropping season |
| 2. | Across slope ploughing | 农业学的 | Summer / each cropping season |
| 3. | In-situ maisture conservation | 农业学的 | before sowing / |
| 4. | Watering | 植物性的 | summer /once in 10 days |
| 5. | Weeding, mulching | 植物性的 | 2-3 months after planting /twice in a year |
| 6. | Re-seeding of grass/ shrub | 植物性的 | before first shower /up to 2 years |
| 7. | casualty replacement | 植物性的 | before first shower /1, 2, and 3rd years |
| 8. | fencing | 植物性的 | during sumer period /every summer season of 2nd, 3rd and 4th year |
| 9. | Repair of breaches in bund | 结构性的 | July to september/as required |
| 10. | Desilting of traps | 结构性的 | October-November/annual |
| 11. | Refresher interaction with farmer | 管理 | / seasonally |
| 12. | Rgular meetings | 管理 | / as and when required |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 51.0 | 51.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 15.7 | 15.7 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 7.6 | 7.6 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Pitcher pots | ha | 1.0 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 124.1 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Non availability of stones, boulders
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
750-800 mm
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (422.8 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateu/plains (3-4% slope, ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (3-4%)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (60 cm, ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (eroded soils)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (absence of vegetation)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (high run-off from stony surface)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
7% of the land users are average wealthy and own 26% of the land.
65% of the land users are poor and own 58% of the land.
28% of the land users are poor and own 16% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off season employment
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha: Joint farmers, land shared by brothers (ranked 1), 1-2 ha (ranked 2), 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha: Not much grazing land is available in the village.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Drought from last 3 years
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
SWC takes small piece of cultivable land
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Village watershed development committee, users groups etc.
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Project support is expected by most of the farmers at a time.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Area was previously barren
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Good vegetative cover
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Ground cover established with vegetative hedges.
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
Introduction of legume species (glyricidia)
Biodiversity
Waterlogging
注释/具体说明:
Not a genereal problem. But only on this plot.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
In-situ conservation
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Establishment of ground covers
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
452
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
417 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Overall returns fro\m the piece of land is increased owing to horticulture and agriculture crops. Biomass increases. This is seen by other farmers and they are motivated to go for its adaption.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Economic sustainability How can they be sustained / enhanced? vegetative and green manure vermicompost etc. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Effective SWC How can they be sustained / enhanced? maibntenance by the individual farmers |
|
water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting structure |
|
Integrated approach How can they be sustained / enhanced? regular contact |
|
increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated cultivation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Production (benefits) adversly affected due to drought. | Due to longer dry spel in the area (last three years) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Non-availability of agricultural improved seed material at local level | by linkage of VWDCs with the Agricultural Research Station and Krishi Vignyan Kendra. |
| conflicts | demands by more number of farmers could not be met by the project at a time. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块