Natural forest conservation using apiaries [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Philip Ileta
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Utunzaji misitu kwa kufuga nyuki (swahili),
technologies_1152 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Government:
Waluce Michael
Ngara District Council
Tanzania, República Unida de
Government:
Mugishagwe Wilson
Ngara District Council
Tanzania, República Unida de
Government:
Sangatati Josephat
Ngara District Council
Tanzania, República Unida de
Especialista MST:
Kaihura Fidelis
+255 754273849
Fidelis.kaihura@fao.org
K-TAMP
P.O.Box 127 Bukoba
Tanzania, República Unida de
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItaliaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida de1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Community intergrated catchment ecosystem management [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Adaptive Agro-ecosystem Micro-catchment Approach.
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
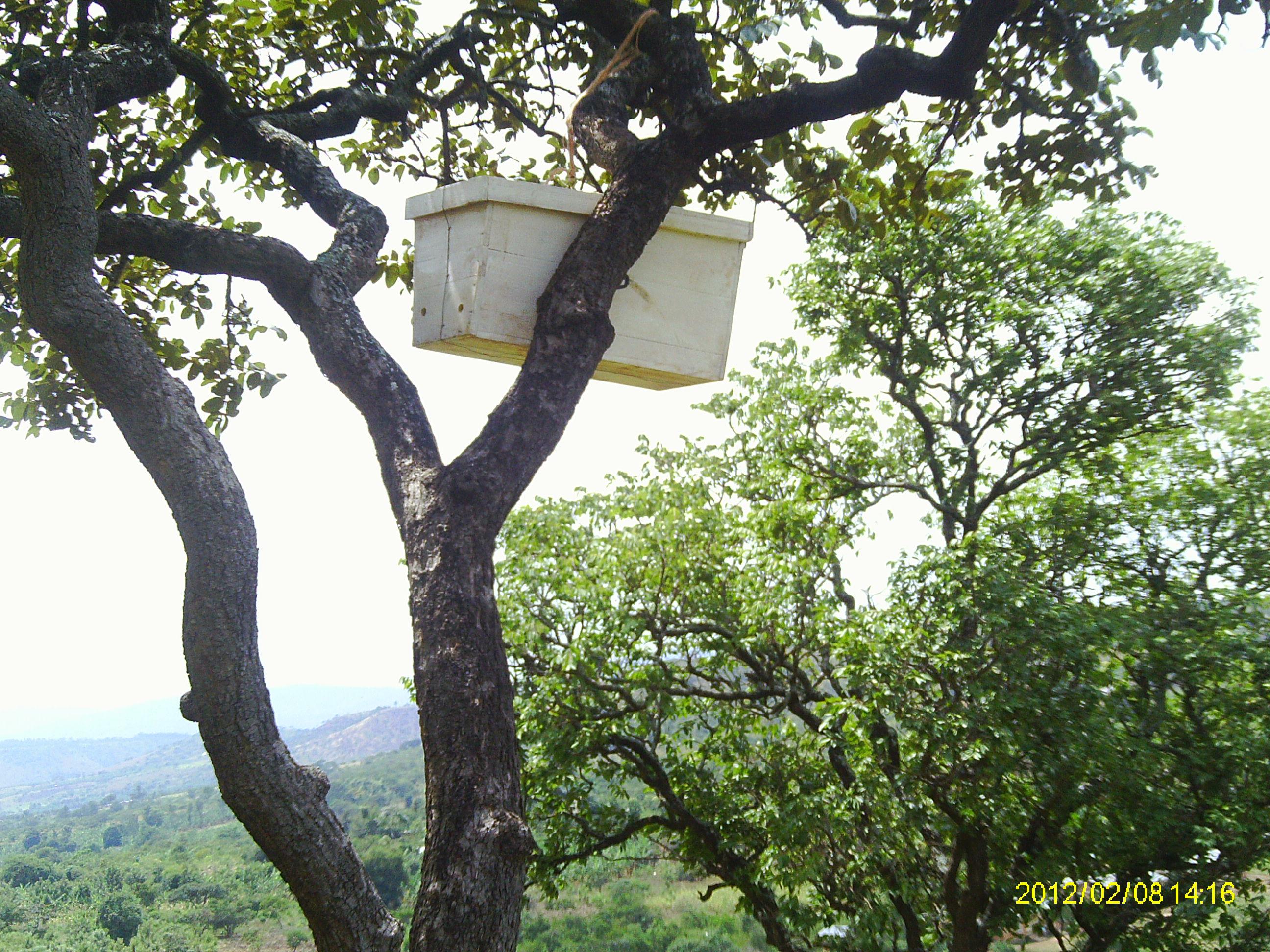
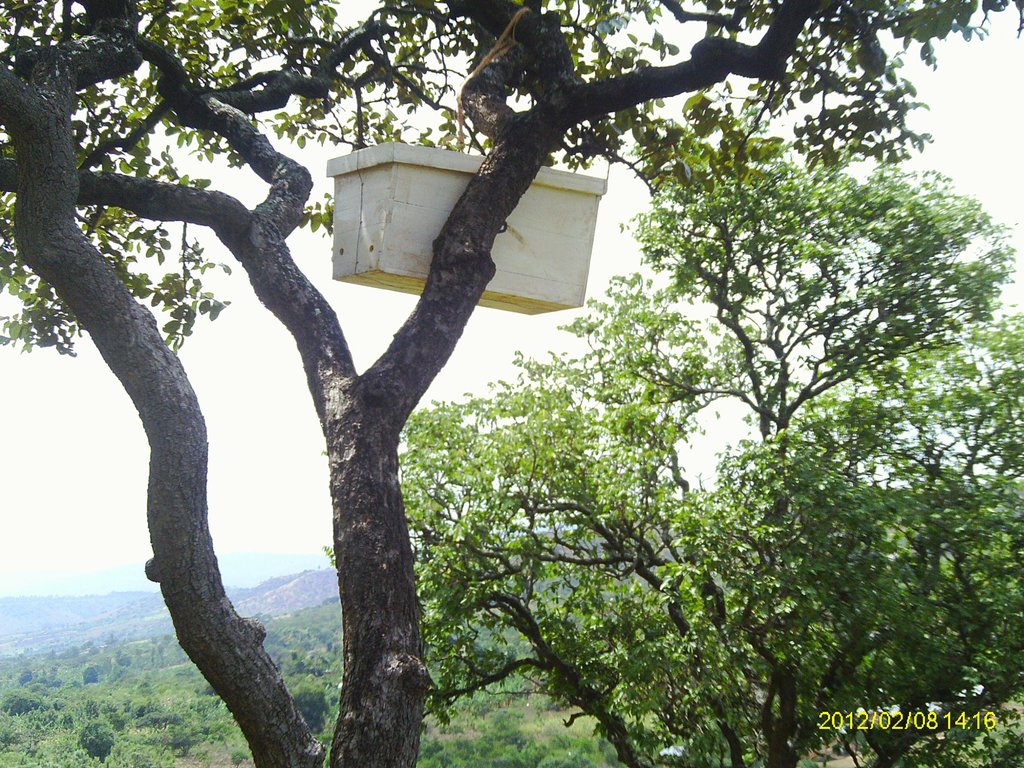
Establishment of apiaries in natural forests to retard forest mismanagement and improve honey production
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
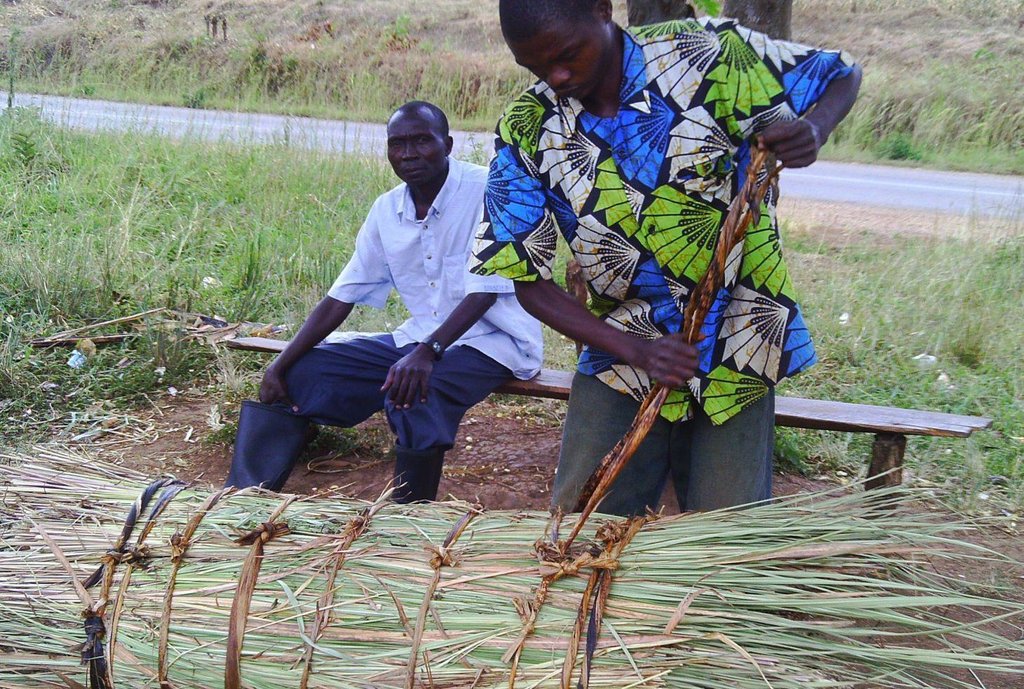
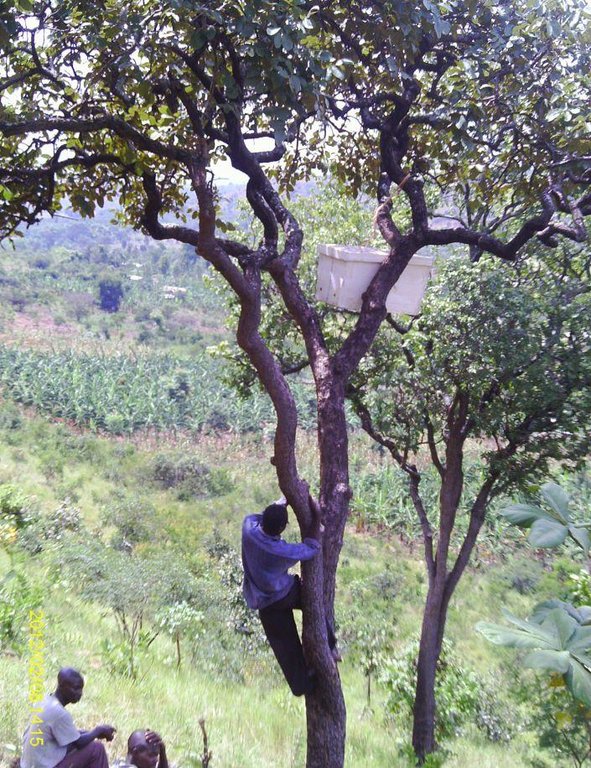
This technology has been practiced in Ngara region for the last 50 year and involves construction and upkeep of apiaries for honey and related goods production. The apiaries are constructed by farmers (traditional) or purchased (modern box hieves) and then positioned in a designated forest area that is away from settlements and public places. The apiaries should be hanged on a strong branches of trees with good shade and the honey production process takes from 9 to 12 months.
Purpose of the Technology: It is recommended to apply this technology in the forest that is exposed to deforestation as apiaries help to enhance forest protection. The establishment of apiaries help to improve management of the natural forest while increasing production of honey. This will contribute to the better livelihood of the community and environmental wellbeing.
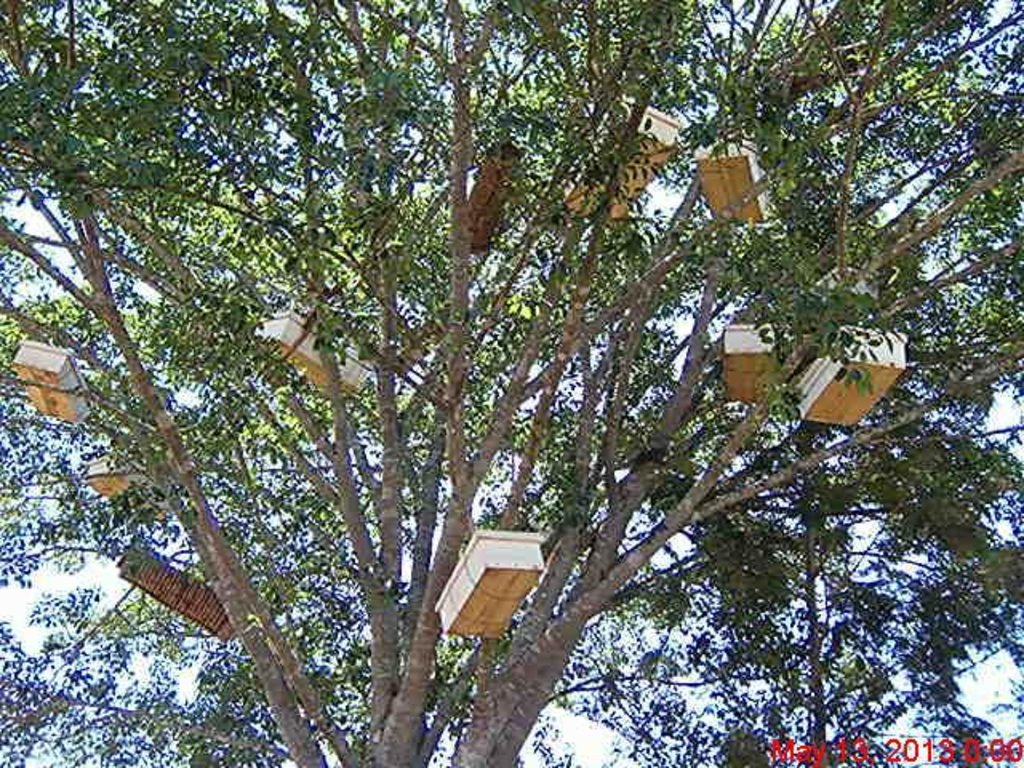
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The described technology covers area of enclosed 4 hectares of natural forest and establishment of 365 apiaries (338 traditional, 27 box hives); the group of practitioners consist of 10 members (7 male and 3 female). The establishment procedures require: a) identification of forest at risk of degradation, b) ermarcation of the apiary forest, c) creefing of fire breaks d) reparations for and hanging the beehives (traditional and box hives). Maintanance acivities include a) regular slashing of grasses and bushes around the trees with hives b)grading with hand hoes the fire breaks/ roads around the entire forest for fire protection before each dry season c) cleaning of hives,repairs and harvest honey with bee protectives (bee smoker,bee veils,gloves) to eliminate the risks of fire in the forest.Patrol and guard tresspassers d) monitoring pests and diseases
Natural / human environment: Natural occuring tree species include: Combretus spp., Albizia spp., Parinari spp., Pericopsis spp. and Eucalyptus woodlots. Grazing areas are nearby but restricted by village by laws to tress pass in the forest apiary
The aipiaries should be located near permanent water sources because bees use water for honey production and cooling in the hives. Farmers with bee hives become more committed to protect their forest when they hang beehives in the area. Honey is harvested for consumption, trade and medicinal mixtures
The land users are small scale subsistance farmers with poor to average income/wealth,organised as a group of 10 farmers. the population density is between 200-500 people per square km and anual population growth at 2-3% Land ownership is both individual and communal but there are natural forestl areas owned communally through village governments where groups may access temporarily by request to establish environmental friendly activities such as forest apiaries.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tanzania
Especifique más el lugar :
Ngara District
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Beekeeping using local hives is a tradtional practice among the the Hangaza and Shubi ethinic tribes of Ngara district
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Bosques
Productos y servicios:
- Leña
- Otros productos forestales
- Pastoreo/ ramoneo
- Conservación/ Protección de la naturaleza
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation and fire burning during dry season
Reduction of biodiversity
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Droughts and vegetation burning during dry seasons
Problems / comments regarding forest use: the natural forest has been set aside for establishing bee apiaries therefore only forest managenet operation are conducted(slashing of grass)
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Sept-December; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- veda de zona (detener uso, apoyar la restauración)
- apicultura, acuacultura, avicultura, cunicultura, sericicultura, etc.
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
The described technology covers area of enclosed 4 hectares of natural forest. Applied 365 bee hives (338 traditional, 27 box hives); the practitioners group has 10 members (7male and 3 female)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A6: Otros

medidas de manejo
- M3: disposición de acuerdo al entorno natural y humano
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bf: efectos nocivos de los fuegos
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bf: detrimental effects of fires, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation through cutting of trees), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Mainly for firewood), industrial activities and mining (Firewood for burning bricks made from clay), droughts, land tenure (Lack of village land use plans for the area), governance / institutional (Weak natural resources enforcent institution at village level)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
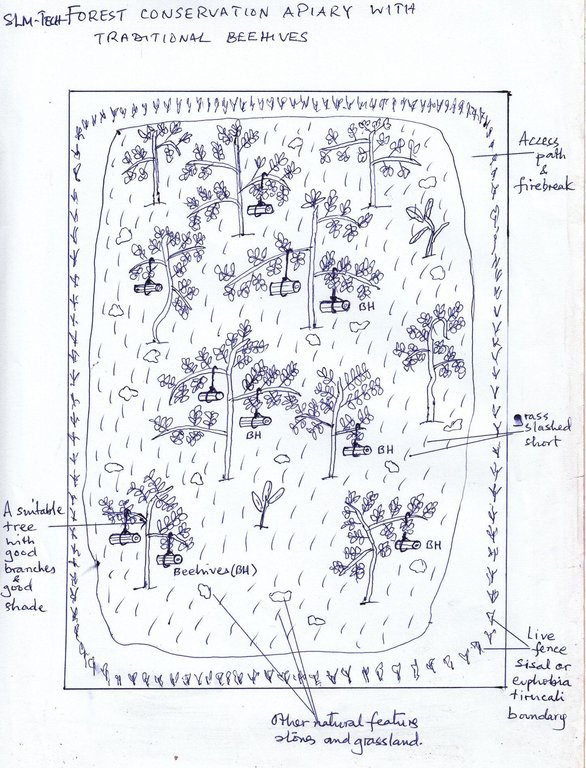
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Layout of natural apriaries (beehives BH) placed on the trees (good braches with shade), access path and firebreak and live fence.
Ngara district Council
Date: 15 May 2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (To extend knowledge/skills on modern/sustainable beekeeping)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (To add/improve skills on existing indigineous knowledge)
Main technical functions: indirectly minimize deforestation, indirectly increase of biomass
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: O : other
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Establishment of bee apiaries in forest to add on value/productivity and optimise diversification of land use
Layout change according to natural and human environment: The site should be away at least 400m from nearby settlements/public places
Major change in timing of activities: Twice per year Feb and Sept during honey harvesting season management activities are at their peak.
- Fire breaks established in June /July before dry season commence
Control / change of species composition: Various flora and fauna organisms get time to establish and grow well due to absence of burning
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.25
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of hives and binding wires | Manejo | Before dry season |
| 2. | Purchase of beekeeping protectives | Manejo | Routine |
| 3. | Slashing, screefing bushes and tall grasses; planting hedge around forest boundary | Manejo | Before dry season |
| 4. | Baiting and hanging apiaries | Manejo | Before dry season |
| 5. | Purhase of cuttings (euphobia spp) | Manejo | wet season |
Comentarios:
FOREST CONSERVATION APIARIES technology REVISED PART-November 2013 Description and purpose This is a practice where farmers hang bee hives on branches of trees in the forest and keep the honey bees between six to twelve months whereby honey is already mature for harvesting. Conventional beekeeping methods have introduced other practices such as placing beehives on stands/platforms and keeping many hives in the shelter bee houses whereby honey production can be increased. The trees and forest where bee hives are hanged are normally respected and not felled indiscriminately.
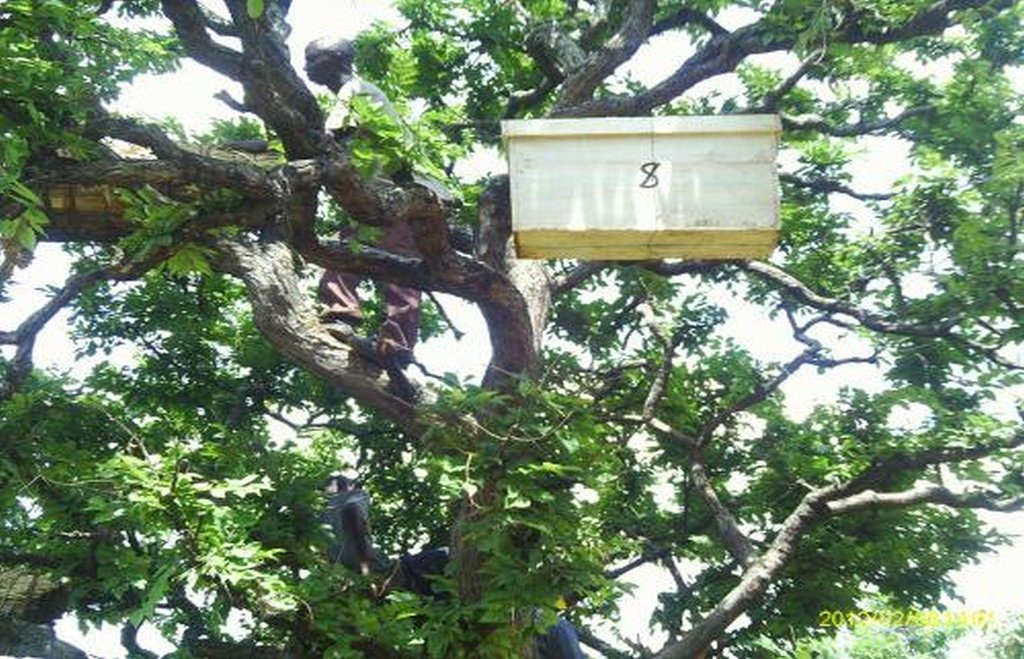
Identification of suitable trees/forest Bees forage on nectar and pollen from flowers of many trees, herbs, shrubs and field plants. However there are specific plant species which are more preferred were bees visit more frequently. The forest or locality with rich biodiversity of the suitable trees/plants is conducive for establishment of a bee apiary. Prominent tree species in this zone include Parinari curatelifolia, Combretum spp, Brachtegia spp, Albizia spp, Acacia spp and cultivated crops such as banana, coffee, and annual crops which include maize, bean and sorghum The source of permanent water should be nearby preferably not more than 3kms because bees use much water in feeding, making honey and to perform cooling in the hives. Demarcation of the apiary forest It is usual for the beekeepers to demarcate the areas so as to inform and alert the community members the existence of the beehives. The demarcation signs may involve partially debarking part of the stem bark of the border trees. The use of colour paints, planting of hedge rows and other boundary marker plants are increasingly becoming popular around many forest apiaries. The common plants for live fence include Euphorbia tirucali, Agaves sisalana and Dovyalis caffra. Types of bee hives Common traditional beehives involve log hives, small poles/withies hives, straw hives, calabashes and clay pots. The use of modern box hives has increased in recent years mainly due to development projects support in modern beekeeping methods. Local hives are cheap but not durable limited to one to three years lifespan and the production is low compared with box hives which may last for ten or more years under good care. Preparations for hanging the beehives i) Bait materials Farmers utilize some materials to attract bee colonies establish in the hives. These include smoking or burning of dry honey combs and rubbing of beeswax inside the hives. Other methods involve sprinkling of either maize flour, cassava flour, raw honey or sugar. The use of many types of herbs and other less known substances(less revealed) to rub and smoke in the beehives before hanging is observed to be more effective in some communities. Some traditional beekeepers have become popular and earn money and respect through providing such services .The swarming periods which normally happen in January/Feb and Mid August/ Sept are suitable for hanging the beehives because it may not take long time to pocess the bee colonies ii) Ropes and tree climbing devices The hives has to be carried to the apiary and be hanged up on a tree branch. This may involve transporting the beehives using any transport means and carry on head load for some distance depending on accessibility and the location of the forest apiary. One or two person has to climb the tree and others remain on the ground to lift the hive. The hive is round bound with strong tree bark ropes before hanging The use of sisal ropes and binding wires have replaced the traditional methods to tie and fix the hives in modern beekeeping apiaries. A tall ladder may be helpful to assist in climbing of tall trees in case of aged individuals. The bee shelter house/huts and hive stands These are normally located in the forest apiary and constructed with local materials especially tree poles, straws and thatched on top roof with dry grass or other leafy vegetation such as banana, coconut and many others plants depending on availability. The hut walls are left open without covering the round walls with earth to facilitate cooling with the fresh air movements. The bee hives are placed on top of each other on the 1.2 m high erected tree poles stands. This practice enables to have many bee hives in one house which are easy to manage and protect provided the surrounding flora has good potential of bee forage plants. Water and sugars may be provided in special containers as extra feeds during bad weather conditions
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Slashing, screefing bushes and tall grasses | persons/day | 100,0 | 0,63 | 63,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Baiting and hanging apiaries | persons/day | 100,0 | 0,63 | 63,0 | 100,0 |
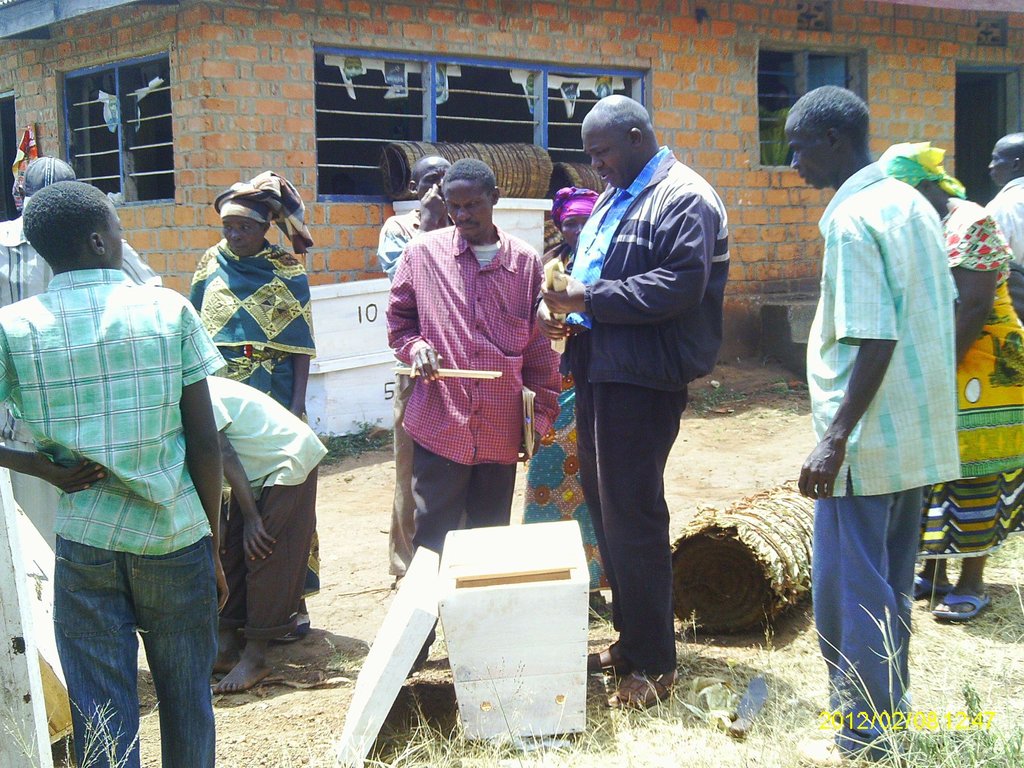
| Equipo | Hives and binding wires | pieces | 400,0 | 2,25 | 900,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipo | Beekeeping protectives | sets | 4,0 | 93,75 | 375,0 | 80,0 |
| Material para plantas | Cuttings | bundles | 200,0 | 0,3 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1461,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing grasss,bushes and firebreaks | Manejo | Before dry season |
| 2. | Apiaries repair | Manejo | Regular |
| 3. | Monitoring of bee pests and diseases | Manejo | Regular |
Comentarios:
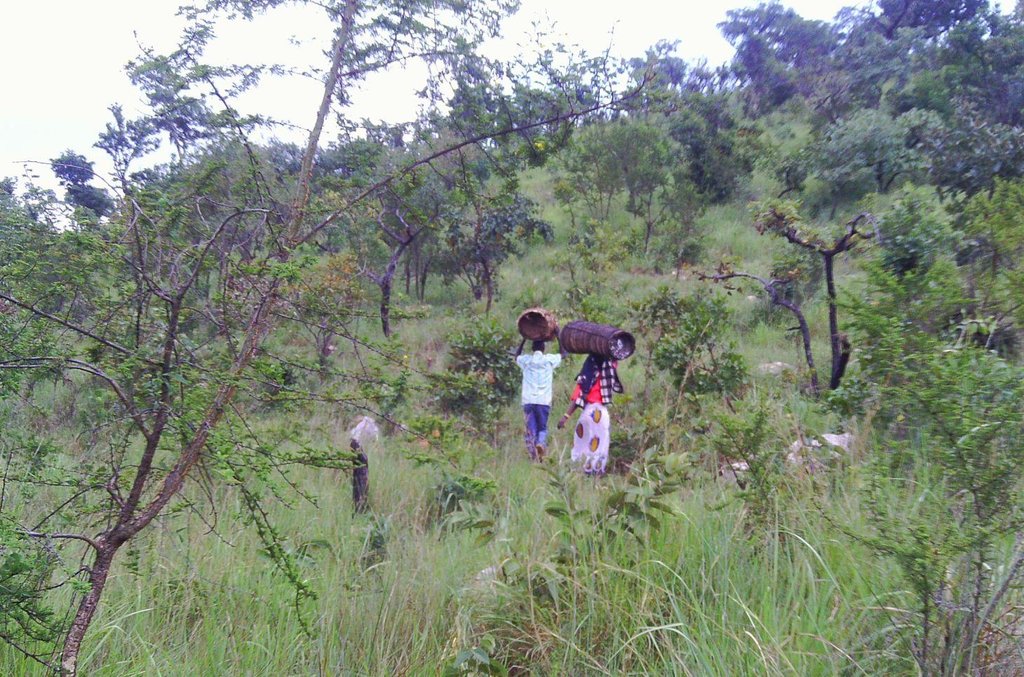
Bush fire control This is done before the onset of the dry season by establishment of firebreaks around the apiary and slashing short the tall grass and other unwanted vegetation in the apiary forest. Cleaning, repairng and fixing the beehives The beehives that have become loose ,damaged or fallen due to strong winds, rains and disturbance by intruders or animals and birds requires replacement or renovations. In many cases pests such as ants, termites and rodents attack bees and make them abandon the hive. Such hives require repairs and cleaning inside before another bee colony can establish Honey harvesting. There is usually one major honey flow season starting May/June to Sept/October in most places, but another minor season may occur in February depending on the abundance of flowering in the previous season. Traditional honey harvesting equipments and tools include clay pots and other local containers, a hive knife and a smoking/burning grass appliance like torch to kill or scare away the bees. Modern beekeeping make use of special set of equipments and protective clothes that include an overall, a veil, a hat, a bee smoker, gloves, boots and hive tool. During harvesting the last two to three combs of honey are left in the hive to enable the colony continue to feed and resume manufacture honey for the following season Honey processing, packaging and marketing Raw honey is strained and filtered from the chopped honey combs through a clean linen or cotton cloth. The honey storage devices include plastic buckets, jerry cans and small (0.5 to 1 litre) plastic or glass bottles which sales between 2 to 4 US dollars at roadsides in the local market. Uses of honey The sweet and delicious fluid becomes ready for consumption or sale. There are many other uses which include brewing, medicine, in cosmetics, making candles and shoe shine pastes. Bees wax is obtained after boiling and cooling the filtered honey combs juice. Good quality raw honey should be light brown in colour, free from impurities such as any dirty, bee legs, wings and less pollen. Honey can be stored for many years due to its bactericidal and bacterial static properties. Boiled honey is of less quality, light in density, colour and loses most of its chemical and medicinal properties Philip Ngara Tanzania
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Slashing grasss, bushes and firebreaks | persons/day | 60,0 | 1,25 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Apiaries repair | persons/day | 20,0 | 0,8 | 16,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Monitoring of bee pests and diseases | persons/day | 20,0 | 0,8 | 16,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 107,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Matchets,Slashers,Hoes,,Ropes,ladder for climbing trees.Binding wires
labour per hectare year 2011
tools per piece/each year 2011
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
High prices of equpipment an (especially box hives) and labour
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Bimodal-(sept to december)and Feb to May/June
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. Hot months(June,July,August,September),cold months(March,April),cool months(May,October)
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average: The technology is not affected with slope variations
Landforms: The site of the forest apiary is located on hill slopes
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: The depth of soil affects the vigour of grass,trees and other vegetation thus amount of biomass available for fire threat during fire season,the labour required for maintanance etc
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: On hill slopes
Water quality (untreated): The site for good drinking water is located some 400m proximal to the natural spring water source used for domestic supply and the Ruvuvu river is not far approximatle 2.kms. Poor drinking water at valley bottoms and wetlands nearby (4kms) and water for agricultural use only in wetlands, is used seasonally for dry season agriculture
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Degraded mostly by fire,overcutting of trees for firewood
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: -Very few women were invoved trditionally-due to climbing of trees to hang bee hives and honey harvesting.These are activities usually performed by men
-Women perform slashing of grass, processing of honey and marketing of products
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
80% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: A small number of people practice off farm activities in burnt bricks making and petty trade
Market orientation of production system: Honey for market, very little for consumption
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
The population density is low with a large ares of forests(55% of total area) still marginally disturbed
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- grupal
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
The group was allocated the forest area of approximately 4 ha by village govt to establish the forest apiary.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de madera
Comentarios/ especifique:
Trees not scotched by fire,trees growing smoothly
riesgo de fracaso de producción
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased productivity per area of forest
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased opportunities for crop pollination in nearby fields
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Honey and beeswax primary products for sale from apiary
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Sale of bee products during good harvest to contribute to household income
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Honey demand in herbal mixtures for diseases cure
oportunidades culturales
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduce fire incidences
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
The forest is beautiful to visit
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
Group cohesion due to common interests/income opportunities
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased income for the group members through sale of bee products honey as food and for diseases treatments members have attended various training for forest management and modern beekeeping members have incresed access to loans and credit organisations
dangers of bee attack
Comentarios/ especifique:
When tresspassing people and animals or during swarming and harvesting honey
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
compactación de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
diversidad vegetal
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
velocidad de viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
Retention of permanent vegetation cover
Otros impactos ecológicos
pollination of forest and crops
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
By planting fire tolerant plant species around boundaries of the forest, beehives will be more secure from fire damage and the forest apiary remain with vegetative soil cover -such species includes agaves sisalana,euphobia tirucali etc
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
After initial high establishment costs,maintanance costs are minimal and the box hives are durable for at least 10 years when made from durable well seasoned timber
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
32 households in an area of 10 ha
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 10-50%
Comentarios:
17 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The box hives and beekeeping protectives were subsidies from projects/programmes under NGOs and governemnt support
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
15 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Traditional beekeepeing with indigineous knowledge used traditional hives only.Government and some NGO s support improved by availing box hives and modern beekeeping knowledge
Comments on adoption trend: more 4 groups emerging who request for support n the area
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Increased income and income sources for farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Intergrate modern box hives, processing gears and improve markets for bee products. |
|
Decreased bushfire incidences How can they be sustained / enhanced? Strengthern bylaws administration procedures to punish persons causing bushfires, harvest honey in late evening and during the nights.Use beesmokers during harvesting |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Enhanced forest conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve management/tending activities in the forest and administation of bylaws |
|
Improved vegetation cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enrichment planting with suitable bee forage plant species |
|
Incresed income and divesification of income sources How can they be sustained / enhanced? Intergrate modern beekeeping and improved processing of bee products.Construct beehives shelter house in the forest to accomodate more hives |
|
Decrease bush/grassfire incidences How can they be sustained / enhanced? Screefing firebreaks using hand hoes, conduct regular firepatrols during dry season,use proper honey harvesting equipments especially beesmokers. Environmental education and campaigns |
|
Continuous production of honey for consumption,sale and medicine How can they be sustained / enhanced? Reservation of more forests for practicing cormecial beekeeping |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Bee stings for people and livestock | Use of bee protective gears during honey harvesting |
| Regular conflicts with grazing of livestock in the forest during dry season when grass in other areas are already burned-Damaging of beehives by pastoralists | By laws administration and operational |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High costs for box hives and bee protective gears | Intergrate modern box hives with durable traditional hives |
| Require large/extensive aeas/Competing demands especially firewood for energy domestic use/trade and grazing land areas |
By laws administration,Planting trees/woodlots have participatory and operational village land use plans |
| Bee stings for people and livestock | establish forest apiaries away(>400m) from human settlements and public places |
| Danger of falling from trees during hanging of hives and harvesting | Use ropes,ladder and tree climbing devises, |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Kagera TAMP Project website
URL:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Community intergrated catchment ecosystem management [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Adaptive Agro-ecosystem Micro-catchment Approach.
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos