FISH POND MANURING USING CRIB METHOD [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Philip Ileta
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
UFUGAJI WA SAMAKI KWENYE BWAWA
technologies_1154 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Zawadi Waziri
Enviroment Ngara
Tanzania, República Unida de
Especialista MST:
Mugishagwe Wilson
Forestry Ngara
Tanzania, República Unida de
Especialista MST:
Josephat Sangatati
Livestock Ngara
Tanzania, República Unida de
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida de1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
This is a practice of fish farming whereby farmers excavate ponds ,fill in fresh water,stock-in fish fingerings and manage them to mature or marketable size
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
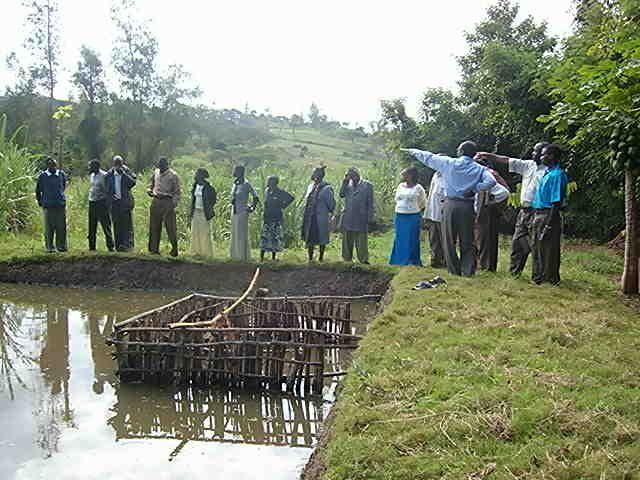
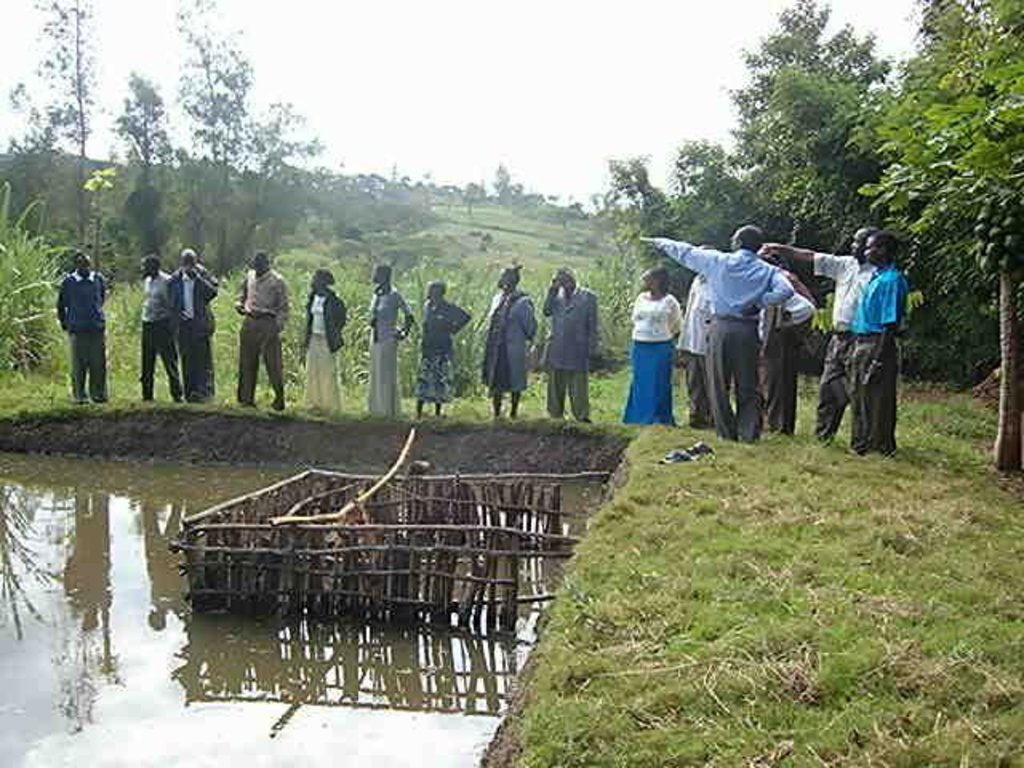
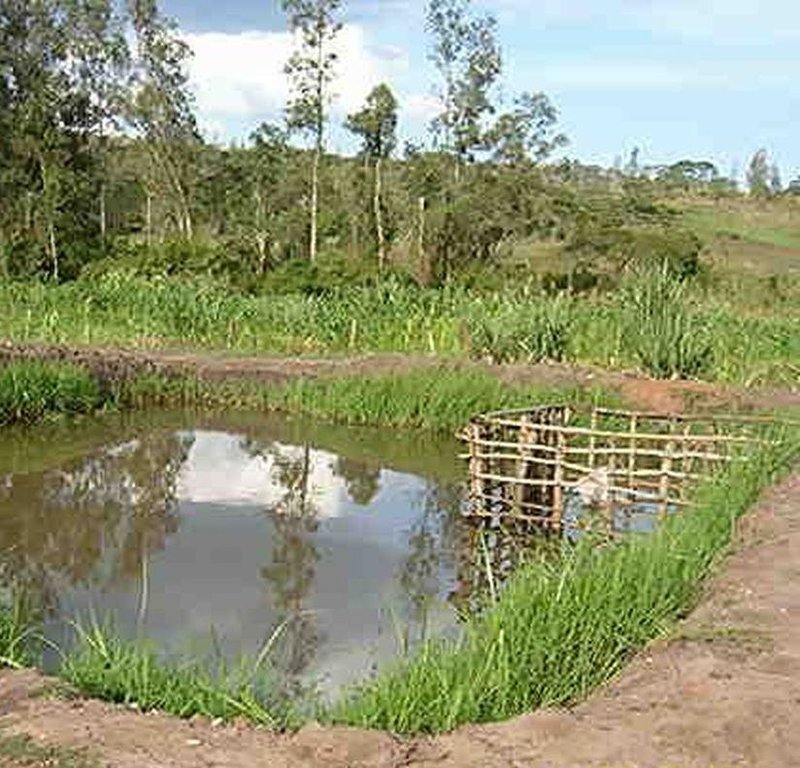
Select a suitable area/site with permanent water source or alongside the flowing river/stream preferably with a clay soil and excavate a suitable sized pond(30mx20m)and a depth of 1,5-2m at the upper and lower side respectively. A crib of 4 m2 for application of manure is constructed using short tree poles at the shallow portion of the pond before filling in water and introducing fish fingerings
Purpose of the Technology: The crib provides an area where Farm yard manure or compost is put to decompose and thereby stimulate the growth of fish foods (phytoplanktons).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT
-Selection of suitable area and pegging to required size/area
-Excavations to suitable depth
-Dig inlet canal from the water source through the shallow side and outlet canal from the deeper portion of the pond back to the main stream (Alternatively use small metal pipes,bamboo or plastic pipes for inlets and outlets)
-Compact the embankment and stabilize soil by planting suitable grass species such as vetiva spp etc
-Cut 2.5m long strong poles and construct a crib for manure application
-Spread manure at the bottom of the pond and wait for weeds growth (normally 2 weeks)
-Fill in water and stock in fingerings( 1 fingering per sq meter)
-Protect the pond by fencing preferably planting around live fence trees such as Dovyalis caffra,Pthecelobium dulce etc
MAINTANANCE
-Regular cleaning of the pond,and weeding the sorounding environment
-Feeeding with extra foods such as rice/maize brun,rice husks,chopped vegetables,pumpkins and potatoes etc
-Weekly application of farm yard manure or compost(1 tin 15-20 kg) by putting and tying by hanging a sac full in a crib.
-Shaking once daily the hanging sac while in water to release nutrients
Natural / human environment: The pond site should be easily accesible and where possible near homesteads for security purpose
-Harvesting may done by draining the water from the pond, using a seine net,and catch the desired size of fish while returning the young fish to continue growing
In good pond management/feeding farmers are able to harvest every after six months
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tanzania
Especifique más el lugar :
Ngara District Council
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
fish farming in Ngara has been supported since the 1980s by UNICEF,DRDPS and recently by DANIDA through NGOs(REDESO and TCRS)
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Estanques, diques
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): -less utilisation of wetlands resources to contribute in improving (livelihood) nutrition and groups/huosehold income
-some fish species (larvifish)may be stocked in ponds to feed on diseases vectors such as mosquitoe larva and reduce malaria incidences
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): To obtain fish for food and surplus harvest for income
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers cultivate small plots of vegetables,sweet potatoes in valleys near fish ponds and chop them to supplement fish meals
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: October to January; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- apicultura, acuacultura, avicultura, cunicultura, sericicultura, etc.
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 ha.
The group owns a fish pond of size 30mx20m in a wetland located in Kasulo village and is stocked with Tilapia spp fingerings
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A6: Otros

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques

medidas de manejo
- M5: Control/ cambio de composición de las especies
Comentarios:
Secondary measures: management measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: water storage for fish culture
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
Comentarios:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (over exploitation of fish in natural water bodies)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Causing siltation,flooding of already constructed fish ponds), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (blocking of water channels, ponds due to mud)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
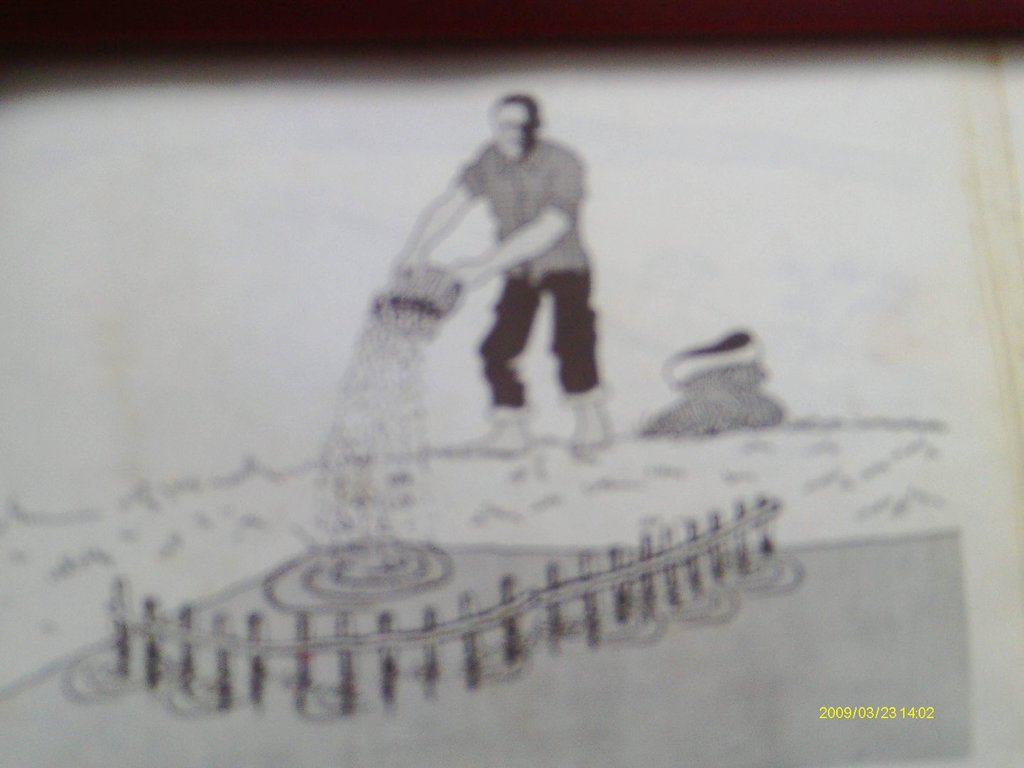
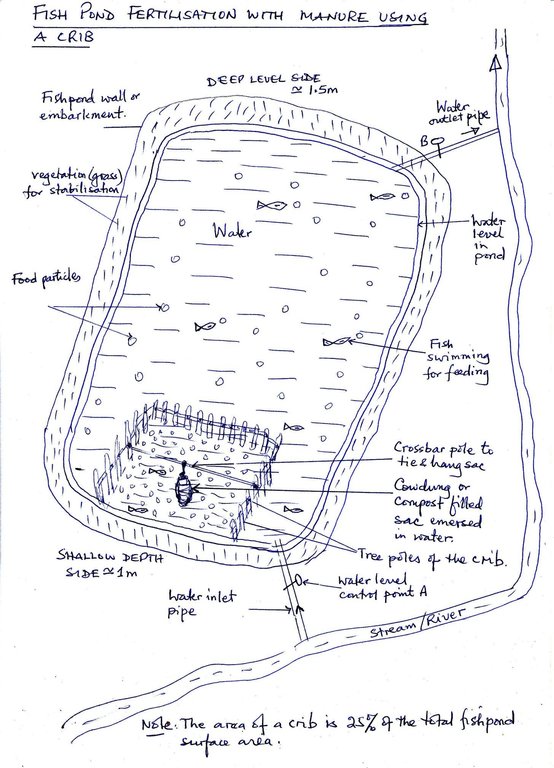
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Fish pond fertilization with manure using a crib
Location: yyy village. Ngara District Council/Tanzania
Date: 15 May 2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Once the fishpond is established,the extension kit requires regular monitoring for improvement of fish feeds and outbreak of diseases which are relatively few compared to other livestocks such as pok)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Following the fish pond manual developed by the district is simple with regard to pond management and feeding regimes)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cowdung
Quantity/ density: 50 kgs
Remarks: applied in crib once weekly per pond
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 300
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): seedlings
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Grass species: vetiva planted to stablise pond embarkments
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 30
Reshaping surface
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Construction material (earth): The pond has the deeper side 1.5m and shallower side 1.0m,with the top earth compacted 2m wide
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Wetlands were marginally used only for dry season agriculture and some vegatable growing-now aquaculture intergration adding productive value to it
Control / change of species composition: Most farmers preferered Tilapia nilotica for stocking in fishponds,phytoplanktons growth promoted
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Fishpond
Especifique volumen, largo, etc. (si fuera relevante):
30m x 20m
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Tanzania shilling
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
1600,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.25
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying of vetiva | Vegetativas | during the rains |
| 2. | Planting of vetiva on embarkments | Vegetativas | during rains |
| 3. | Allignment and layout of pond | Estructurales | before rains |
| 4. | Excavation of the pond | Estructurales | before rains |
| 5. | Raising embarkments,compaction construction inlets and outlets | Estructurales | before rains |
| 6. | Collect cow dung | Agronómicas | |
| 7. | Purchase fish fingerings | Agronómicas | |
| 8. | Purchase tools | Agronómicas |
Comentarios:
Lifespan of dung, fish fingerings and tools: 3 years
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Planting of vetiva on embarkments | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Allignment and layout of pond | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 50,0 |
| Mano de obra | Excavation of the pond | persons/day | 120,0 | 1,88 | 225,6 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Raising embarkments,compaction construction inlets and outlets | persons/day | 3,0 | 1,25 | 3,75 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Fish fingerings | pieces | 1000,0 | 0,06 | 60,0 | 20,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | pieces | 4,0 | 12,5 | 50,0 | 20,0 |
| Equipo | Vetiva | pieces | 300,0 | 0,16666 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Cowdung | kg | 50,0 | 1,25 | 62,5 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 456,85 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Application of cowdung | Agronómicas | weekly |
| 2. | Application of extra feeds | Agronómicas | fortnight |
| 3. | Clean weeding | Agronómicas | monthly |
| 4. | Trimming the live fence,weeding and monitoring | Vegetativas | dry seson |
| 5. | Repairing of walls | Estructurales | after heavy storms |
| 6. | Management of fingerings -monitoring of growth,control of overpopulation | Manejo | monthly |
| 7. | Cowdung application and manipulation for nutrients release | Manejo | weekly |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Clean weeding | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Trimming the live fence,weeding and monitoring | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Repairing of walls | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Management of fingerings | persons/day | 4,0 | 1,6 | 6,4 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Extra feeds (maize and ricebran) | kg | 10,0 | 1,88 | 18,8 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Cowdung | kg | 50,0 | 1,25 | 62,5 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Cowdung application and manipulation for nutrients release | persons/day | 1,0 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 96,45 | |||||
Comentarios:
the costs are calculated per fish pond of size 20m width,30m length and depth 1.5m
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
labour especially during excavations(establishment phase)
cowdung when the land user buys instead of obtaining from the homestead/kraal
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
950,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Length of dry periods 4 months
Main rain season Oct to Dec/January, Second season March to Mid May
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. Hot during the days slighly cold nights,avarage temp range18-30C
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, loamy to heavy clayey basement) and moderately deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter is medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor and retains water in pond permanently, but medium in severe dry spell and water level decrease to half pond depth.
Soil water storage capacity is high near wetlands and permanent streams. Sometimes also very high
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
en superficie
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water: Good (ranked 1) and excess (ranked 2, the site of the pond is located such that at maximum flooding it shoul d not be reached by flood water to prevent fish escape/overflow)
Water quality (untreated): For agricultural use only: Wetlands used for dry season farming and small horticultural gardens. Farmers fetch water in the streams due to unavailability of safe water points
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Decreasing rapidly due to pollution of water sources, deforeatstion and overexploiation of natural fish stocks
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Excavations usually by men labour but for maintanance activitiies women play increasing roles
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
60% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Most of the farmers with ponds have livestock and apply cow dung instaed of compost
Market orientation of production system: Mixed (farmers sell some surplus fish although productivity still below avarage)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- grupal
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
water use is free for use by all community members especially for agricultural activities
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Phytoplanktons feeds
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0.06
Comentarios/ especifique:
This is the surface area of the pond
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
100
Cantidad luego de MST:
375
Comentarios/ especifique:
Market for fish is available when good size
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
From increased income
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Animal protein source menu, but malaria and bilhazia vectors when ponds are not well kept/managed
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
When the suitable species of fish is stocked and proper fish pond management procedures adhered to -the harvest are high-at least once to twice per year-but this requires high initial and maintanance capital -routine extension from aquaculture experts is highly needed to enable farmers realise profits
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
From decomposition of cow dung
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Phytoplanktons and water weeds
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
Other water fauna and flora which are not predators may be allowed to flourish
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water retained in ponds when adopted farmers increase
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
The productivity of the fish pond is determined by many factors including the selected species of fish,the feeding levels and the temperature of water. Most tropical fish species grows well when the temperature of the pond water remains warm
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
Initial establishment capital high
Cow dung may be obtained free from kraal or altenative use compost
manure
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
3 households
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
3 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The fish ponds project attracted many families to engage in the activities,the constraints were high capital investments and poor pond managent
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: especially for well off farmers with land holdings near wetlands and streams
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Availability of permanent water sources especially streams How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation bylaws enforced on bufferzones |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Availability of permanent water sources especially streams How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation bylaws enforced on bufferzones |
|
Farmers owns cattle/shorts How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enhance crop and livestock intergration |
|
Wetlands are owned comunally and by village governments How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws enforcement to prevent encroachment and pollution |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High capital investments | Family oriented groups have some success ,to think of some subsidies throgh government or simple credit schemes |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High capital investments | Group approach used -although many groups fail to sustain the ponds |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos