Compost application on rice fields [Cambodia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Christoph Kaufmann
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, Nina Lauterburg
ការប្រើប្រាស់ជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៏នៅក្នុងស្រែ (Khmer)
technologies_1218 - Cambodia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Khonhel Pith
Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC
Cambodia
Especialista MST:
Mesa Say
Society for Community Development in Cambodia SOFDEC
Cambodia
Especialista MST:
Sreytouch Bin
Society for Community Development in Cambodia SOFDEC
Cambodia
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
23/06/2014
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Model farmer [Cambodia]
Model farms were introduced by a NGO in order to spread knowledge about SLM (compost, System of Rice Intensification SRI, and other technologies) in the project area.
- Compilador: Christoph Kaufmann
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
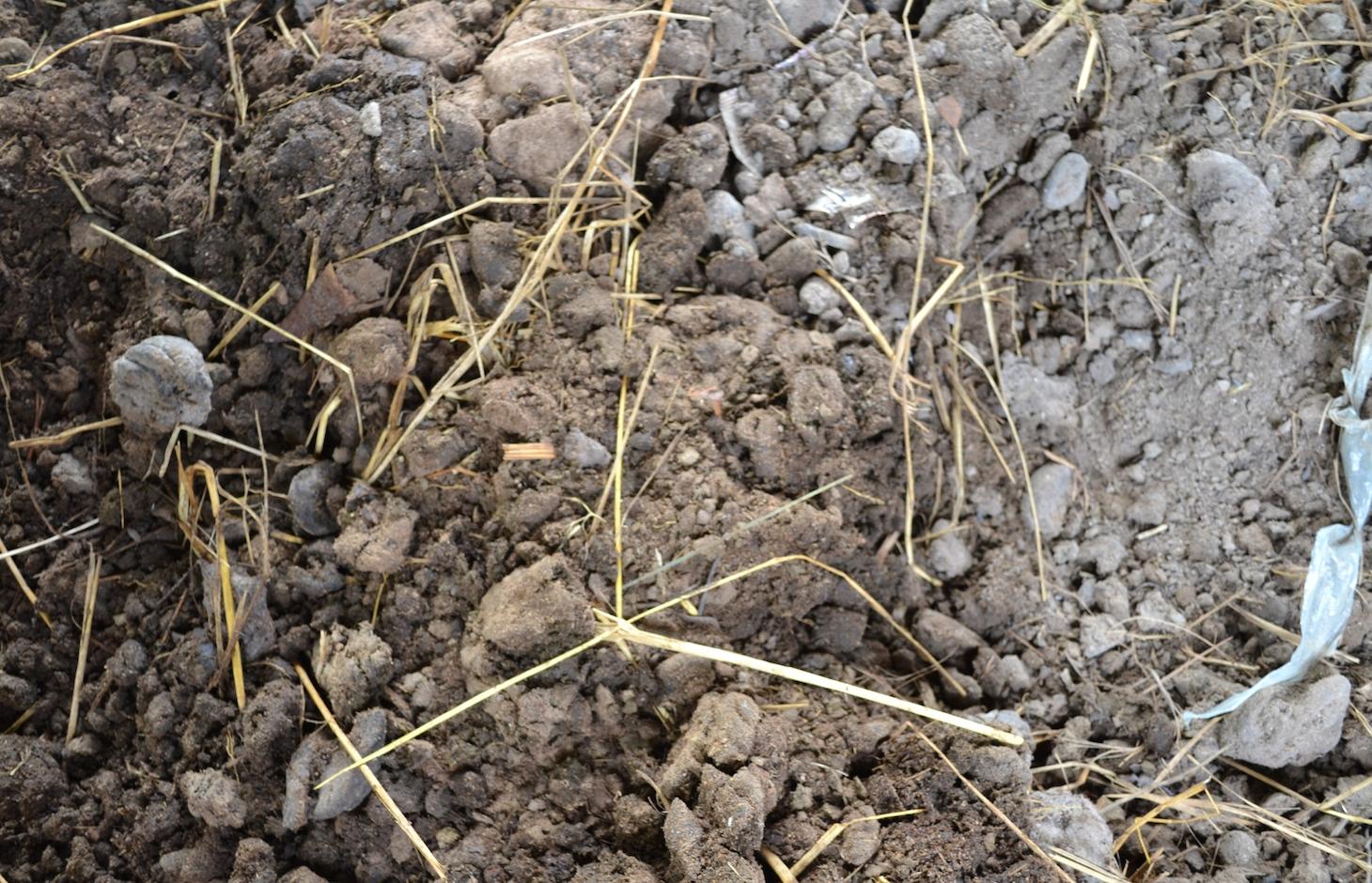
Manure, leaves and rice straw are gathered in a compost house and the produced compost is applied twice a year to the rice field.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Compost is produced in compost houses and is seen as a good and easy soil amendment. It is produced by mixing organic components (in this case study cow manure, rice straw, different leaves and ash) which are locally available. The ideal mix of ingredients shows an N-to-C ratio of approximately 1 to 25. By adding compost to the topsoil, its humus content is increased, and therefore the soil fertility and water holding capacity are enhanced. Although the technology can be applied with little technological knowledge, the land user’s workload is augmented. This can be detrimental in a human environment with constantly decreasing available labour force.
The purposes of compost production are multifaceted. From the land user’s point of view, the increased yields are certainly one of the most determining factors. This is due to the augmentation of organic matter and nutrients in the topsoil which results in a higher soil fertility. Therefore, the use of chemical fertilizer can be diminished while the yields stay the same. This results in the amelioration of the land user’s livelihood, since he needs to buy less fertilizer. Also, the improved soil structure (according to the land user, the soil is softer and easier to cultivate) and water retention capacity are of importance in this area, since the soils are sandy/loamy, and due to climate change the rainfall is more erratic and droughts more recurrent. Compost also buffers the soil’s pH and prevents acidification. As a consequence, the nutrient availability is increased. Finally, compost adds more biota to the soil.
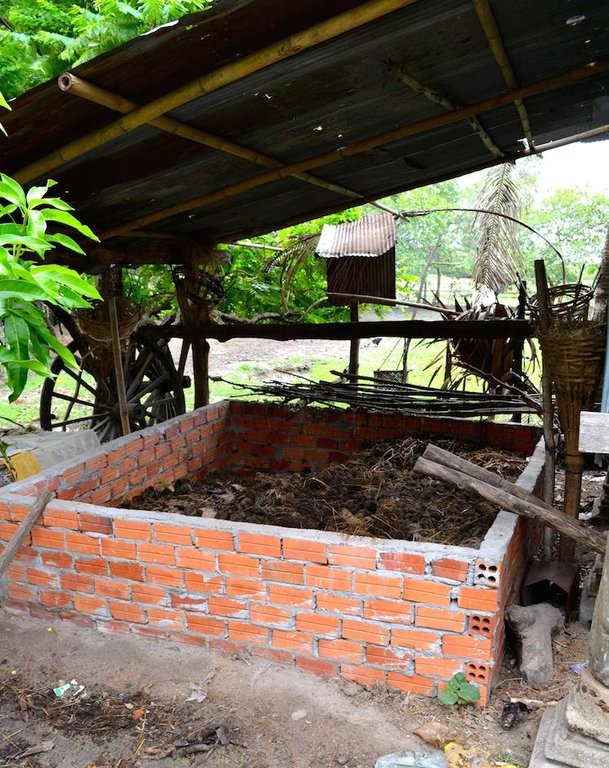
First, the compost house is built. This can be done either with external inputs such as bricks, cement, and a tin roof (the initial investment is higher, but the recurrent maintenance activities lower), or with locally available, natural inputs such as rice straw and clay for the walls and dried sugar palm leaves for the roof (the initial investment is lower, however there are more recurrent maintenance activities which can be detrimental for the continuation of compost production).
Once the compost house is built, the organic matter (approximately 70 % cow manure, and 30 % rice straw and different leaves, with a small amount of ash) is collected in the surroundings and carried to the compost house. In this case study, compost is produced once during the dry season and once during the wet season. During the dry season, water is added to the organic matter in order to facilitate the composting process. Ideally, the organic matter should be turned in order to guarantee a complete composting process. However, this includes a rather big workload. As a result, turning is not always practiced in the area (high migration rates result in a decrease of available labour force).
When the composting process is completed, the compost is carried to the fields with the use of animal traction. This is done several times: once when the fields are plowed, once when the rice seedlings are transplanted and once while the rice is growing (“top dressing”).
The analyzed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate with a (dry and a wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils have a low fertility, contain little organic matter, the pH is sinking, the area has been deforested a long time ago and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, land users notice more erratic rainfalls, temperatures rise and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), the cattle are released to the paddy fields.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area. This has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Cambodia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Kampong Chhnang
Especifique más el lugar :
Rolear Pha-er
2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
A local NGO provided a training on compost making, about 5 years ago.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación del suelo
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agropastoreo
Principales productos/ servicios:
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of organic matter, lack of water retention in soil, irregularity of rainfall, low soil fertility (sandy soil), monocultures, bare soil during dry season, ploughing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Rice field: lack of nutrients, need fertilizer and compost otherwise no good yield. Not enough compost available, need to use also small amount of chemical fertilizer even though compost is applied. Lack of water. Soil erosion.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June - December
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
- Ca: acidificación

degradación biológica
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing, soil is left bare for several weeks), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Rice monoculture (rice serves as staple food)), change of seasonal rainfall (More erratic beginning of wet season), droughts (On dry soil, rice cannot be planted and if already planted, rice cannot grow), labour availability (High migration rates from the villages to garment industry, cities or abroad, influences agricultural activities (e.g. broadcasting instead of transplanting of rice seedlings)), education, access to knowledge and support services (Khmer Rouge regime in the 1970s, a lot of knowledge got lost.)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Rice straw is removed for different domestic uses (cattle, mushroom cultivation, etc.)), overgrazing (Cattle eats rice straw left after harvest, less organic matter on the field, grazing is not managed.), change in temperature, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure (Some incidents of land grabbing, land use rights not clear), poverty / wealth
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación del suelo
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
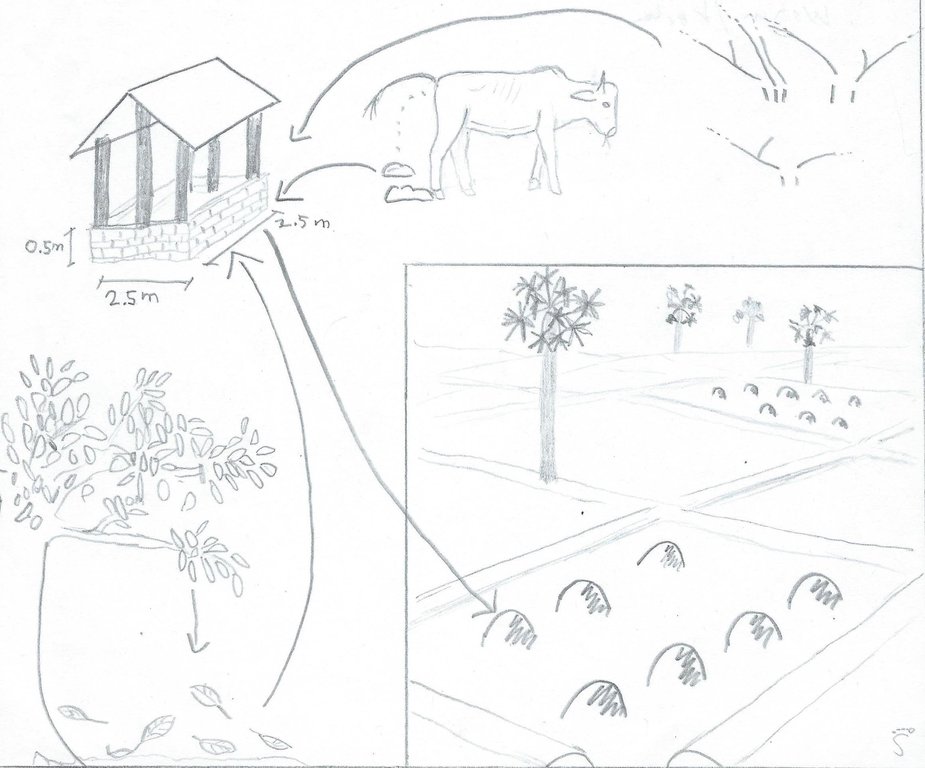
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Manure, straw, ash and leaves are gathered in a compost hut, and later on dispersed on the paddy fields.
Kampong Chhnang
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (It is not difficult to make compost, however it increases the workload of the land user. This might lead to the adaptation of the Technologies in order to decrease the additional workload.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Cow manure, mango leaves, rice straw, wood ash, green plants.
Quantity/ density: 3.7 t/ha
Remarks: 1 part at the beginning of the rainy season (rice transplantation), 1 part during the growing period
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of compost house | ||
| 2. | Clay: Dig pit (10 cm) and add clay from the rice field | ||
| 3. | Bricks and cement: make brick walls | ||
| 4. | iron roof | ||
| 5. | poles | ||
| 6. | nails | ||
| 7. | labour |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 | |
| Material de construcción | iron roof | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 | |
| Material de construcción | bricks and cement | 1,0 | 31,0 | 31,0 | 100,0 | |
| Material de construcción | poles and nails | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 71,0 | |||||
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Gather material for compost, prepares compost and adds water in dry season | Agronómicas | all year round |
| 2. | Bring compost to fields | Agronómicas | June - September |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 140,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Please note that the interviewed land user owns cows that are used for bringing the compost to the field. Hence, the costs for animal traction in this case study are zero.
1 compost house, around 4m^3.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Cost are affected by the availability of material to build the compost house (bricks, roof, etc.), which can be used long term.
Locally available, free material (sugar palm leaves for the roof, straw and clay for the walls) can be used as well, but it decays more quickly than the material used in this case-study (more recurrent maintenance activities).
The transport of manure to the fields is also an important expense. It is often done with the ox carts. As nearly all families owning oxen have a cart for different uses (firewood and product transportation), it is difficult to calculate this cost
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. 27°C to 35°C
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The application of compost depends mainly on the commitment of the land users – gender and level of wealth are not determinative. However, the work is divided between men and women (physical strength).
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: The land user manufactures handicrafts that she sells. Also, one of her daughters works in the garment industry. In addition, she owns pigs and chicken she sells.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The farmer uses less chemical fertilizer. The yields remain the same on the short term.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less chemical fertilizer used
mitigación de conflicto
contribution to human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the use of compost, land users are less dependent on chemical fertilizers. Therefore, the cost of production decreases while the income remains the same.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 10-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support 20 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 50-90%
Comentarios:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology was first introduced by a training (20 people attended), and then the neighbors of these farmers copied it. For each farmer trained, approximately 5 neighbors copied the technology.
85% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
130 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Compost making increases the workload of the land users an that impedes the spontaneous adoption of the Technology.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Less chemical fertilizer is used for the same yield, so the farmer can save money since she buys less chemical fertilizer. |
| Soil fertility is better. She sees more earthworms in the fields. |
| Ploughing became easier, because the soil is less hard after compost application. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Low cost, locally available and effective fertilizer/soil improving material. |
| Soil quality (organic matter, nutrient content, water retention, soil biota) is improved |
| The resilience is increased; farmers are less dependent on external inputs (fertilizer…) |
| Long term increased yields. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The collection of the material and the preparation of the compost (turning) is time consuming. | Monitoring the cost/benefit ratio to show the benefit to the farmer |
| It is difficult to transport the compost to the field. | Collaboration between neighbors to lower costs of hiring someone or lending machines. |
| She cannot make enough compost for all the fields | Work toward an integrated production. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Not enough organic matter to make enough compost (number of cattle is low, rice monoculture). | Work toward an integrated production. |
| Increased workload while labour availability is decreasing due to migration. | Increase the handicraft work on the farms. Diversification of the production with less labour intensive species. |
| Low motivation of the land user because the composting work has to be done each year again. | Monitoring to show the long-term cost/benefit ratio. |
| The composting process is not completely understood; weed and rice seeds survive and are growing on the fields. | Explanations about seed survival and dormancy to explain the purpose of composting. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Society for Community Development in Cambodia SOFDEC
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
www.sofdec.org
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Model farmer [Cambodia]
Model farms were introduced by a NGO in order to spread knowledge about SLM (compost, System of Rice Intensification SRI, and other technologies) in the project area.
- Compilador: Christoph Kaufmann
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos