Disability inclusive, flood resilient cluster village [Bangladesh]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Subir Saha
- Editores: Subir Saha, Manuel Rothe
- Revisor: Alexandra Gavilano
"Protibandhita Bandhob Bonna Sohisnu Gucca Gram"
technologies_2005 - Bangladesh
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Christoffel Blindenmission (CBM) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
09/11/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Not problematic with regard land degradation. It provides efficient and sustainable use of available land resources.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [Bangladesh]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- Compilador: Subir Saha
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
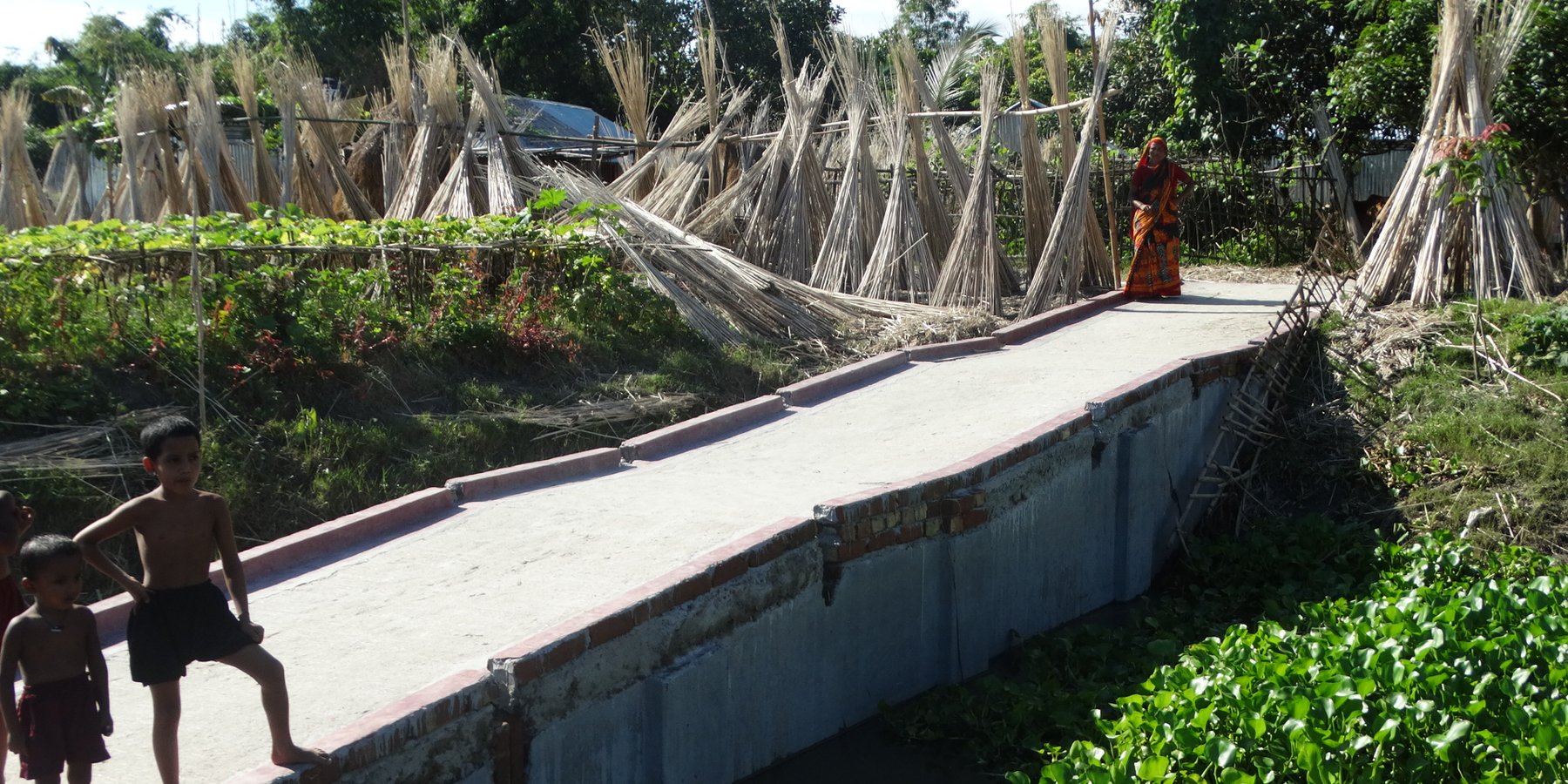
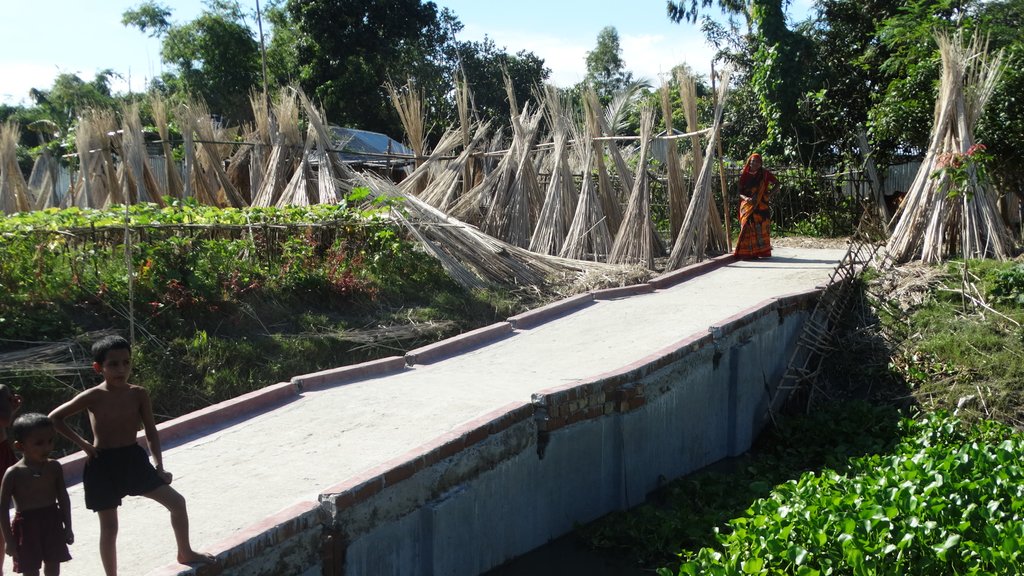
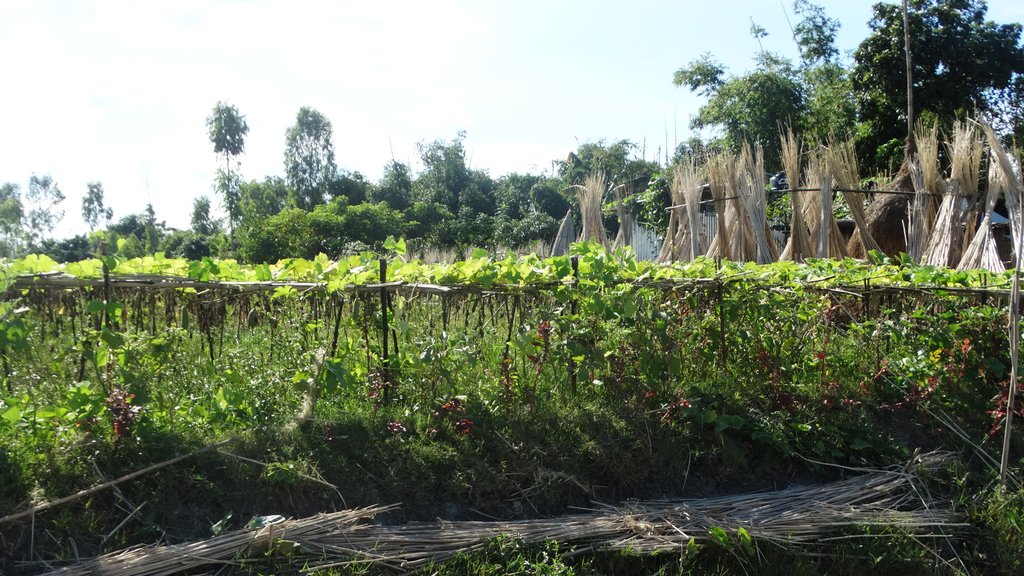
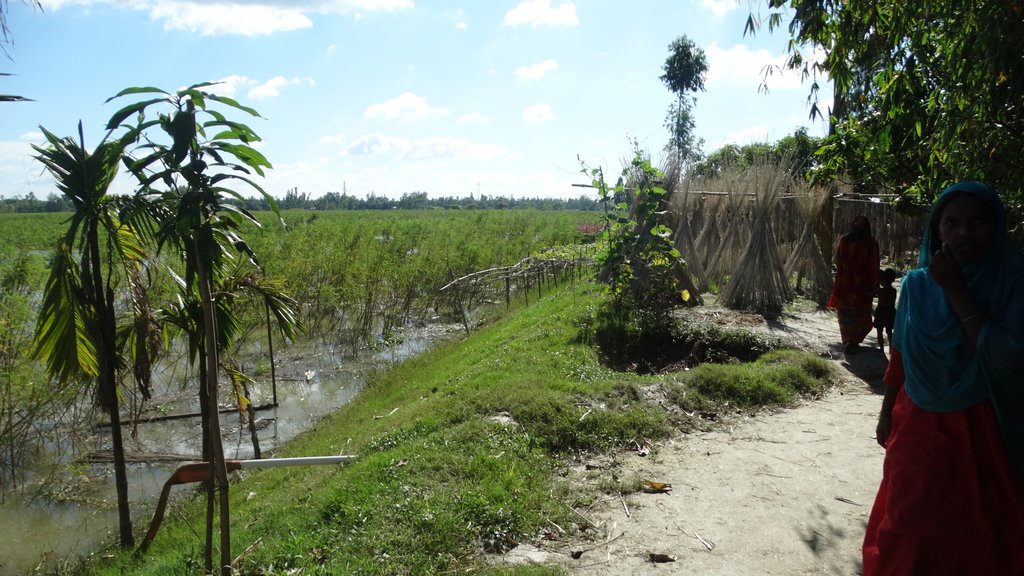
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village provides safe housing, food security and income generation for multiple families, including persons with disabilities, in a highly flood prone area of Gaibandha District in northern Bangladesh. The land was raised above flood level and is protected by deep rooted fruit trees to prevent soil erosion and provide income for the land users.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
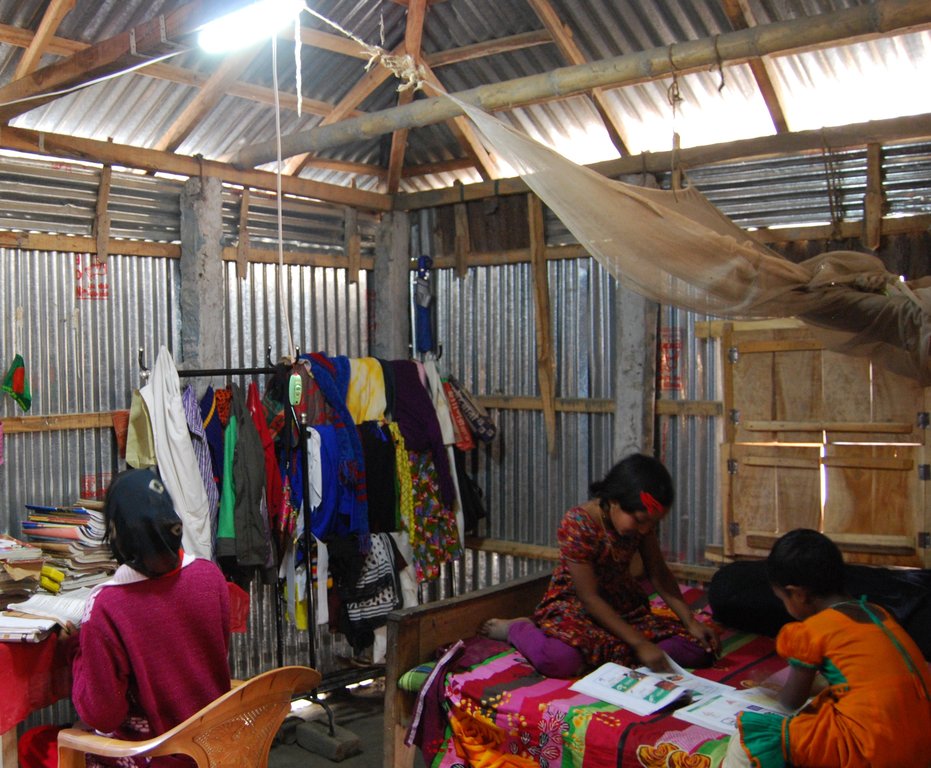
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village was introduced in a rural area with a high risk of recurring monsoon floods. The purpose of the technology is to provide safe housing, safe shelter for livestock, food security and income generation for ten families, including persons with disabilities.
The main components of the technology are:
1) The raising of a piece of land by seven feet (213cm), to three feet (91cm) above expected highest flood levels. Solid soil was banked up to encircle a 30'000 square feet (roughly 50x57m) piece of land and then the space within was filled up with sand collected from a nearby river bank. A one-foot layer of solid soil was added to cover the entire area.
2) The protection of the raised land from soil erosion during floods by planting a combination of deep-rooted fruit- and medicine trees around the border of the raised land. The trees include a number of different types of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees and one type of medicine tree, Azadirachta Indica, locally known as "Neem". In addition, the slope of the border area was covered by grass turf to protect the soil from being washed out by rain. Two types of deep-rooted and flood resistant grasses were used. A drainage system was installed to facilitate water runoff.
3) The planting of a 150 square feet (14m2) commonly used homestead vegetable garden at the center of the cluster village. The cultivated vegetables include red spinach, jute leaf, basella leaf, spinach, radish, cabbage, okra, bottle-guts, cucumber and beans, allowing for a summer and a winter harvest. Together with the fruit trees, the vegetable garden provides food security during prolonged flooding. They also provide improved nutrition and income generating opportunities through selling of a part of the harvest in the market.
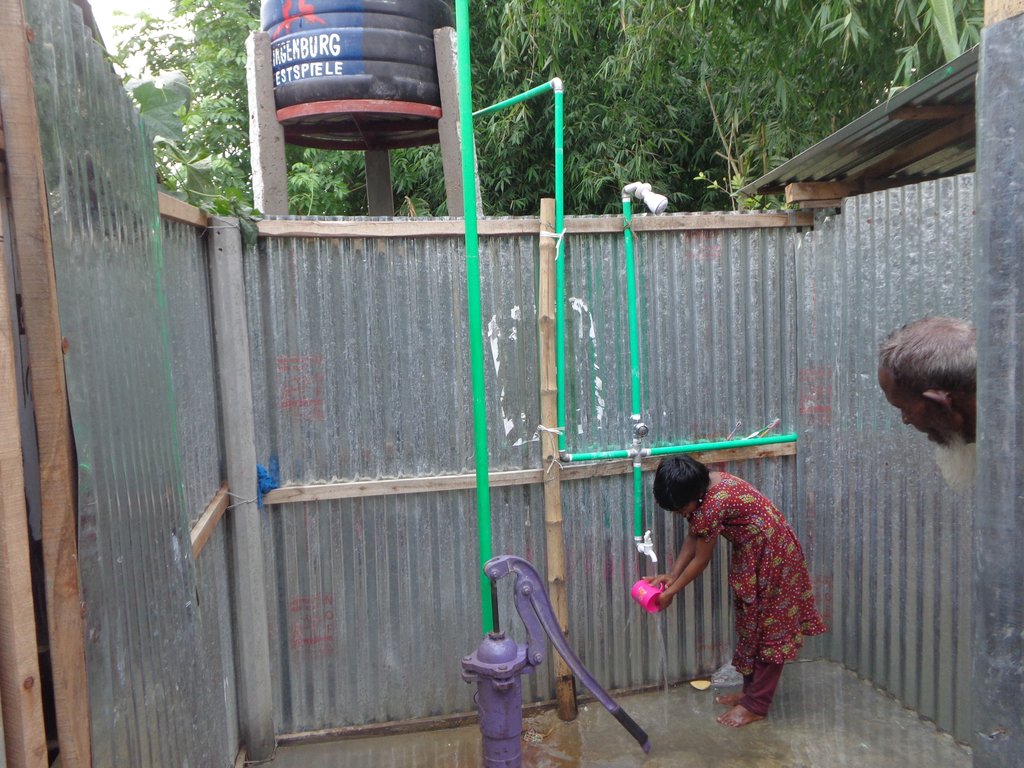
4) Making the village accessible for persons with disabilities through different accessibility measures, including the construction of a ramp, connecting the cluster village entrance with the road, and of accessible common Water-, Sanitation- and Hygiene (WASH) facilities, including a latrine, deep bore hole water source and water storage tank.
5) Installation of a solar panel to ensure uninterrupted, flood-resilient power supply. The level of power supply is sufficient to ensure coverage of electricity needs during flood season, when regular supply is around 15% below annual average.
The Cluster village was constructed as part of a disaster risk reduction project by CDD (Center for Disability in Development) from Bangladesh, with the support of CBM (Christoffel Blindenmission), an international development organization and funded by a donor from Germany. The main cost for inputs were provided to the land users by the project, including rent of construction machinery, paid labor, soil and construction material for the ramp and WASH facilities. The land users contributed labor and seedlings for the planning of the border trees and the homestead vegetable garden.
The main benefits of the technology from the perspective of land users are the protection it provides for houses and livestock, which would otherwise be in danger of loss during floods. The availability of food, water and electricity allows land users to remain in their homes during floods and avoid evacuation and the risk associated with it, including for example protection risks or the risk of theft. The flood protected vegetable gardens and fruit trees provide a year-round, sustainable source of food and income, providing food security and improved nutrition. The Neem tree provides medical and hygiene uses of the branches and leaves.
The cluster village is used as a safe space for the land users and other members of the community and their livestock during floods. Land users who are persons with disabilities or elderly benefit from the accessible infrastructure. With multiple families sharing land, the cluster villages provides optimal utilization of land resources. An additional benefit mentioned by land users is that the joint use by multiple families led to a more progressive social culture.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Bangladesh
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Gaibandha District
Especifique más el lugar :
Horipur Union, Sundargonj Sub district,
Comentarios:
Kani Charitabari, Horipur Union, Sundargonj sub district, Gaibandha District.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2016
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was introduced as part of a disaster risk reduction project, implemented the Center for Disability in Development (CDD) with the support of Christoffel Blindemission (CBM) and with participation and leadership of the local community. The project was financially supported a group of donors from Germany.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Asentamientos, edificios
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Summer and winter
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
Livestock are available in every household.
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- medida de pendiente transversal
- jardines domésticos
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S7: Equipo para cosechar agua / provisión de agua/ irrigación
- S8: Saneamiento/ estructuras para aguas residuales
- S9: Refugios para plantas y animales
- S10: Medidas de ahorro de energía

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
- M6: Manejo de desperdicios (reciclado, reutilización o reducción)
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wr: erosión de riberas
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
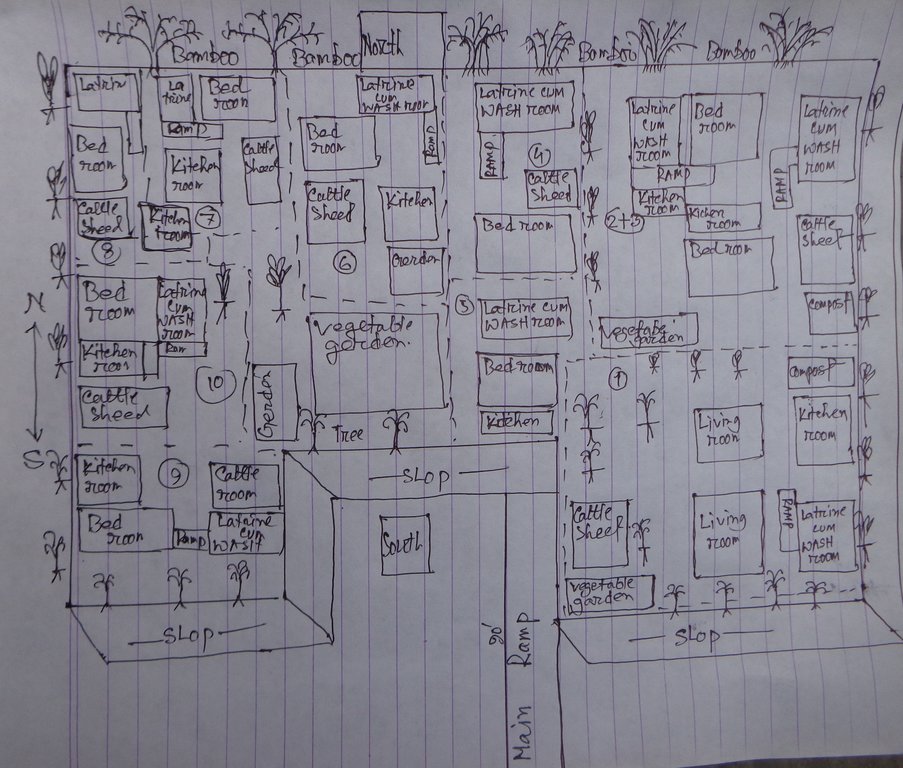
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The drawing shows the layout of the disability inclusive, flood resilient Cluster village. The components of the technology are:
Raised land/plinth: 1) Purchase of land of a total area of 18'000 square feet (ca. 40x40m). Land ownership transferred to joint ownership of 10 families. 2) Collect 15'000 cubic feet (425m3) of solid soil from different pieces of land in the community. The soil was donated by members of the community, who were either related to the land users of the cluster village or donated in support of the construction of a safe space which can be used by the community during floods. 3) Banking up of 3 feet (91cm) of solid soil along the borders of the land. 4) Filling of area with 140'000 cubic feet (3965m3) of sand, extracted from a nearby riverbank with a rented sand extraction machine, raising the land to 6 feet (183cm). 5) Covering the entire area with one additional foot of solid soil, rasing the land to 7 feet (213cm), which means 3 feet (91cm) above the maximum expected flood levels.
Soil protected through deep-rooted trees: 1) Planting of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees, surrounding the entire border of the raised land. The trees include deep rooted fruit trees like mango, black berry, jack-fruit, guava, coconut and areca nut, light-rooted fruit trees like banana and Papaya, a deep-rooted medicine tree, locally called "Neem" and the light-rooted Dhol Kalmi tree (pink morning glory). The number of deep-rooted threes was 100, with a spacing of around 5 feet in between each. They were planted to cover the entire perimeter of the raised land. In between the deep-rooted trees, 60 light-rooted trees were planted. In front of the deep-rooted trees, 60 bamboo bushes were planted to provide additional protection from wind and rain. 2) Turfing of the entire slope surrounding the cluster village with two flood resistant grasses: Durva (Cynodon dactylon) and Catkin grass. 3) Installation of a central drainage system with 15 plastic pipes ensuring water runoff from the wastewater pond.
Road access through ramp: The connecting ramp of the cluster village is 90 feet length, 6 feet width. There are five landing point of this ramp with smooth slopping. The construction material includes class one brick, brick stone, cement, sand, polythene and red oxide color for color contrast, which is appropriate for low vision and visually impaired persons. There is a 5 inch border on both sides of the ramp for safe movement of a wheel chair user.
Accessible household water and sanitation facilities: Latrine and wash-room are constructed for every house in the cluster village, following universal design standards. Latrines are connected to the wash room and the main house through ramps. There is a railing on both sides of the latrine and the entrance is wider for access of a wheel chair users. Water system for the latrine and wash room is provided from a water tank on three pillars behind the latrine, which is also connected to the main house for provision of drinking water. The tank is filled by hand pump ('magic pump') which functions with minimal hand pressure. The WASH facilities are accessible and usable by everyone including persons with disabilities, pregnant women or aged persons.
Home vegetable gardens: Every household has an individual homestead vegetable gardens where land users cultivate seasonal vegetables year-round. Gardens vary in size between averaging about 1.5 decimal (60m2) in size and are surrounded by bamboo fencing. The land owners are using organic fertilizer/compost for the vegetable production of their choice. By using cow's manure and wastage they are producing the compost in the behind of their houses in a ditch.
Solar system: A mini solar system is installed on the roof for each house by using a small panel with a 12-volt battery . Each system has the capacity of providing power for light for 8 hours. An introduction to system maintenance was given to the land users by the provider of the solar system.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Cluster village
Especifique volumen, largo, etc. (si fuera relevante):
18'000 square feet piece of land
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Bangladeshi Taka
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
80,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
300
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selecting the place for cluster village construction | Manejo | During rainy season in 2015 |
| 2. | Establish collaboration with 10 families who will become land users | Manejo | December 2015 |
| 3. | Land Raising & Ramp construction | Estructurales | December 2015 to March 2016 |
| 4. | Reconstruction the existing houses of the land users on the raised land | Estructurales | April 2016, before onset of rainy season 2016 |
| 5. | Planting of deep- and light-rooted fruits trees, bamboo bushes and grass turfing along the boundery | Agronómicas | February 2016 to March 2016 |
| 6. | Install accessible water & sanitation system | Estructurales | April-June 2016 |
| 7. | Establish home garden in front of each house | Vegetativas | June-July 2016 |
| 8. | Install mini solar system for each house | Otras medidas | Aug-sep 2016 |
| 9. | Prepare livestock shed for each house | Estructurales | October 2016 |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si fuera posible, desglose los costos de establecimiento de acuerdo a la siguiente tabla, especificando insumos y costos por insumo. Si usted no pudiese desglosar los costos, proporcione un estimado de los costos totales para establecer la Tecnología:
1777380,0
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Land raising, tree planting and turfing on slope | person days | 290,0 | 300,0 | 87000,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Ramp construction | person days | 115,0 | 350,0 | 40250,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | House reconstruction and WASH facilities | person days | 200,0 | 400,0 | 80000,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Solar system installation | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | WASH equipment (latrine, magic pump, water tank, pipes, switch, pillars and other) | pieces | 10,0 | 46658,0 | 466580,0 | |
| Equipo | Solar system | pieces | 10,0 | 6300,0 | 63000,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Deep rooted trees | pieces | 100,0 | 40,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seed for vegetable | KG | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Sapling purchase | pieces | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Light rooted tree | pieces | 60,0 | 30,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Organic fertilizer (compost) | KG | 600,0 | 10,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Rent for shallow machine for sand extraction | Daily rent | 10,0 | 28800,0 | 288000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Grass turfing | square feet | 15000,0 | 10,0 | 150000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Allowance for house reconstruction material | House | 10,0 | 2000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Ramp construction | Piece | 1,0 | 125750,0 | 125750,0 | |
| Otros | Project management (monitoring and support) | persons-days | 180,0 | 2400,0 | 432000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1777380,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The project, human resource supported by CBM, CDD and a funded by private donor.
Comentarios:
Labor for tree plantation, home stead gardening & house reconstruction was contributed by the land users.
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turfing: Repair leakages, replace grass etc. | Estructurales | before onset of rains |
| 2. | Tree maintenance: Cutting branches, manure of roots etc. | Agronómicas | Rainy season |
| 3. | Vegetable gardening | Vegetativas | Summer & Winter season |
| 4. | Housing repairs | Estructurales | After harvesting season/ once in a year |
| 5. | Water and Sanitation system servicing and repairs | Manejo | After harvesting season/once in a year |
| 6. | Solar system maintenance | Manejo | Winter season/once in ayear |
| 7. | Village group meeting for decision making and conflict resolution | Manejo | Once in a month |
| 8. | Organic composting/fertilizer production | Otras medidas | Continuous |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si fuera posible, desglose los costos de mantenimiento de acuerdo a la siguiente tabla, especificando insumos y costos por insumo. Si usted no pudiese desglosar los costos, proporcione un estimado de los costos totales que se necesitan para el mantenimiento de la Tecnología:
85000,0
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | House repairs | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Ramp repairs | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Plingth raising and plantation | person days | 30,0 | 300,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Solar system servicing by technical experts | piece | 10,0 | 500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seed for vegetable gardening | KG | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Soil for slope maintenance | square feet | 5000,0 | 10,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Sand for slope maintenance | KG | 5000,0 | 2,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 85000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Land users are agreed to contribute 100% maintenance cost
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Market fluctuation and scarcity of goods in the flood season.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Heavy rainfalls are one of the causes for flooding
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Age of land users includes children, youth, middle-aged as well as elderly.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Land users jointly own the land of the cluster village. They do not own any additional agricultural land and work as daily laborers and sharecropers.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- grupal
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
Comentarios:
Land users own the land of the cluster village jointly, including a proportional share of land- and water use rights.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Fruit and vegetable production increased after introduction of the cluster village. Because of decreased loss of home and property during floods, labor is freed for crop production which increased overall crop production in the wider area.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Fruit and vegetable quality is improved because of availability of Irrigation.
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Livestock mortality rate is reduced because of safe space in Cluster village.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Homestead vegetable garden and fruit tree plantation above flood level has a significantly reduced risk of production failure.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
The flood-protected homestead vegetable garden allows for higher product diversity.
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased availabilty of flood protected land for vegetable gardening.
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Energy supply was not available before installation of solar panel.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
calidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
calidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Irrigation available to land users after installation of deep tube well.
demanda de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Demand for irrigation water increased because of vegetable garden.
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase of farm income through selling of fruit and vegetables.
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Additional income source through selling of fruit and vegetables.
disparidades económicas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Decreased income disparities between the land users of the cluster village due to fruit and vegetable production available to all land users, Decrease income disparities between land users of the cluster village and other members of the communty because of the reduction of loss from flood damage.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Somewhat increased workload for maintenance of technology but decreased because of avoidance of damaged from floods.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased food security through flood prodected homestead garden and tree plantation.
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Higher attendance of health workers because the cluster village offer suitable group meeting rooms and accomodation. Cluster village was constructed in vicinity of community clinic. Better hygiene through WASH facilities.
oportunidades culturales
Comentarios/ especifique:
The cluster village is a suitable meeting point for the entire community, for social gatherings or festivals.
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cluster village offers common space for children and other land users for Joint recreational activities.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
Much improved situation for persons with disabiltiies who are part of the land users. All persons with disabiltiies in the wider community use the cluster village as a safe space during floods. Improved situation for all land users who are from marginalized parts of society (daily laborers and share croppers).
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil erosion during floods decreased because of deep- and light-rooted border tree plantation.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Comentarios/ especifique:
Raised land as safe space above flood level.
impactos de sequías
Comentarios/ especifique:
Drought impact in summer season decreased because of Irrigation.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
available shelter and safe space
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cluster village provides additional safe space/shelter for the wider community.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 10-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Around 10-15% of households which equals roughly 70 households.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
The technology is replicated by households who receive assistance from local government for families at risk of flood damage.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Si fuera así, indique a qué condiciones cambiantes se adaptó:
- mercados cambiantes
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Peoples of cluster villages are selling vegetables and fruits in the local market and some of them are carrying the fruits in the distance market. They are becoming more interested to plant more fruit trees in the cluster village. If it is continue in future it would be a fruits and vegetable market in the cluster village. At the same time they started selling cows milk in the local market and its demand is increasing day to day.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Ownership of the land user's are there. Its a community driven initiative & disability inclusive in all respect. They are happy to give shelter to the other villagers during flood season. There is an opportunity to create an example of a model village in this area. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Its an innovative program. Peoples participation and their contribution is the main asset. Universal accessibility of the cluster village communicating benefit to other villagers during rainy as well as flood season. This pilot program can be replicated to other riverine areas in Bangladesh. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The intensity of floods is difficult to predict. With average flood levels rising, land users still have to live with the risk of flood levels going beyond the level of their rised land. | More research on changing weather/climatic patterns and scientific measurement of expected flood levels. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Government and Non government organizations extension services are not available in this area. Livelihood of the cluster village peoples depending on seasonal agriculture. | Income raising multiple activity need to be introduces. A small scale disability inclusive comprehensive project could be implemented here. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
7
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
10
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
1
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
4
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [Bangladesh]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- Compilador: Subir Saha
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos