Crop diversification with the application of rotation techniques [Cambodia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Navin Chea
- Editores: Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Revisores: Nimul CHUN, Ursula Gaemperli
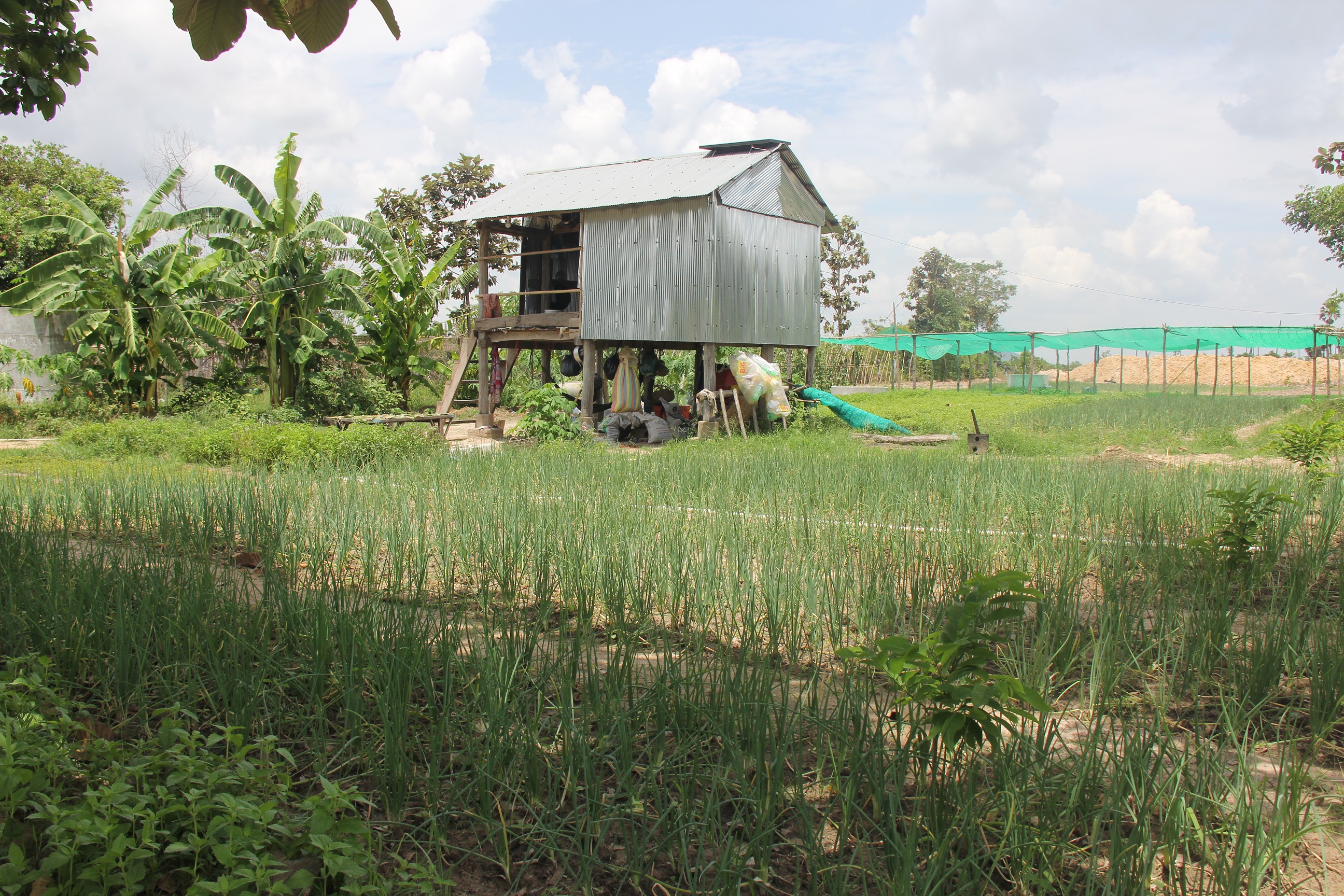
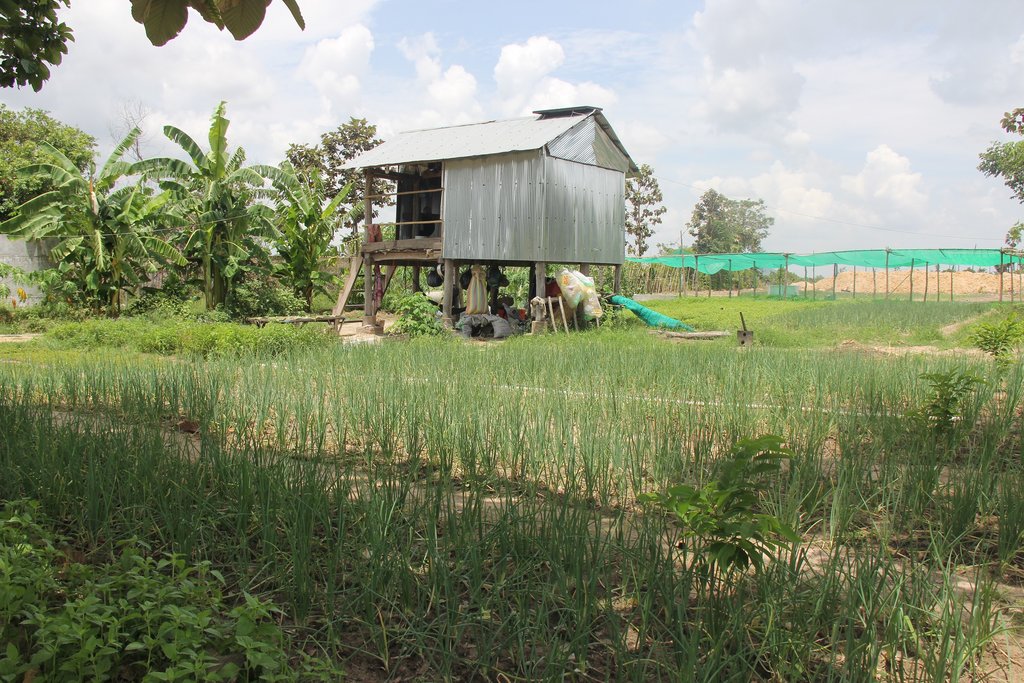
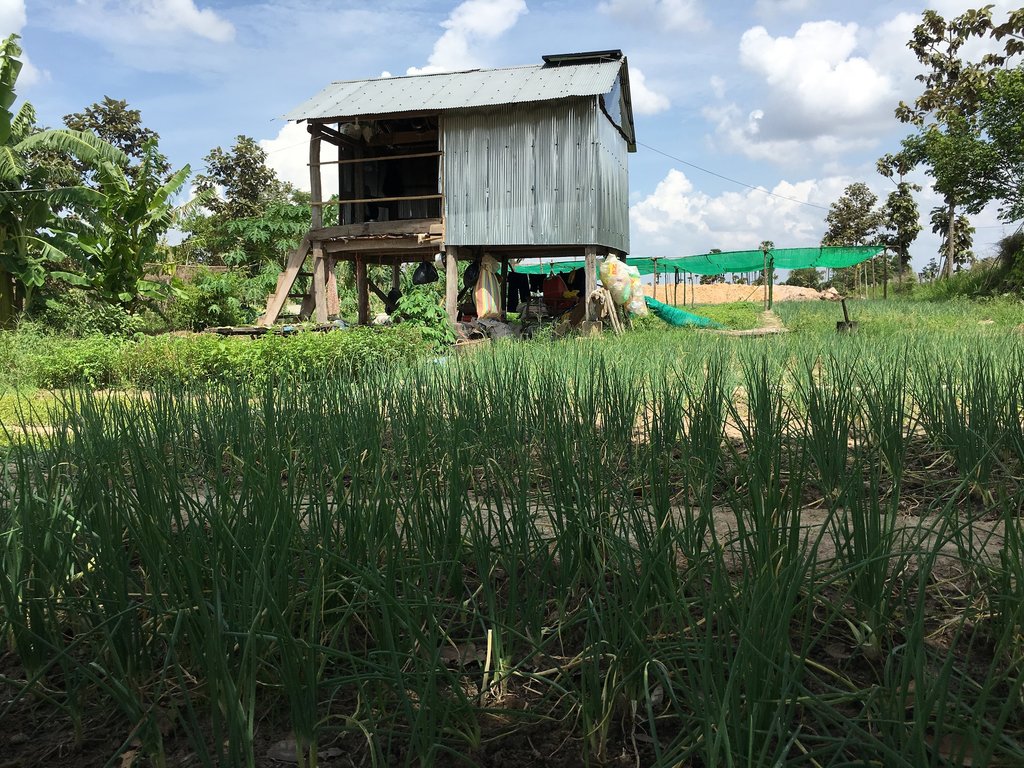
Crop diversification farm
technologies_3145 - Cambodia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Phrum Thon
(+855) 95 211 223 / (+855) 69 40 6550
N/A
Land User
Ruessei Duoch village, Banteay Peal Commune, Rolea B'ier District, Kampong Chhnang Province.
Cambodia
Vice Chief of Agronomy Office at Agricultural Office of Rolea B'ier :
Chhim Bunleang
(+855) 77 797324
chhimbunleang@gmail.com
Agricultural Office of Rolea B'ier.
Prey Puoch village, Chrey Bak commune, Rolea B'ier district, Kampong Chhnange province.
Cambodia
Vice Chief of Agricultural Extension Office at Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Kampong Chhnang province:
Chief of Agricultural Office of Tuek Phos:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
22/05/2017
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
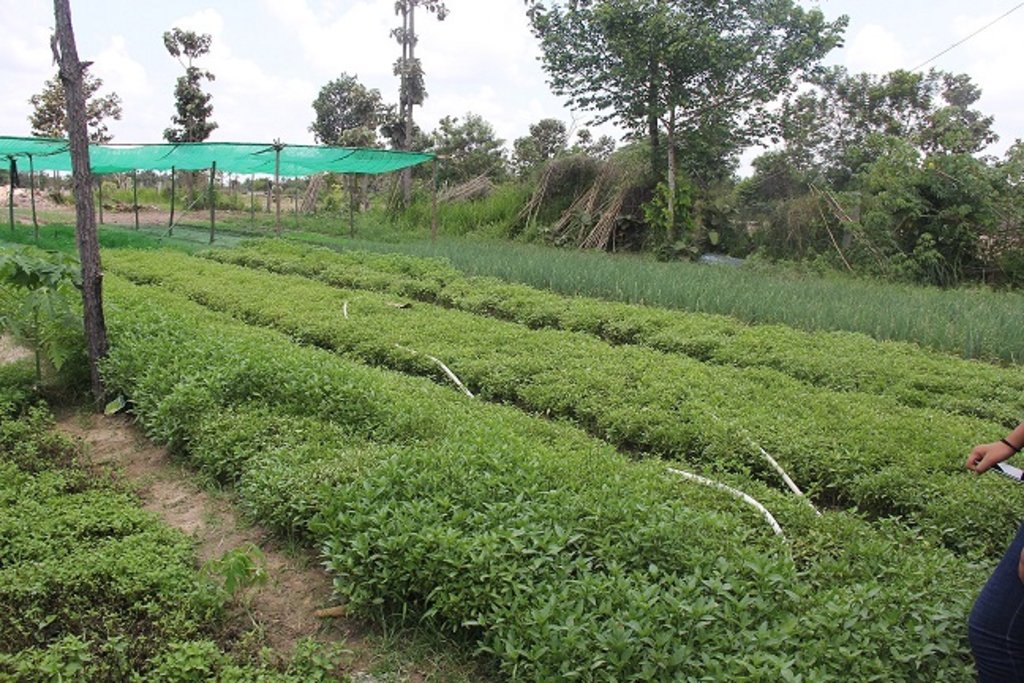
Crop diversification is the practice of simultaneously cultivating two or multiple varieties of crops in a given area whilst at the same time applying crop rotation and/or intercropping. In this case study the land user has been practicing crop diversification with eleven different crop varieties.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Crop diversification entails simultaneously growing two or multiple varieties of crops in a particular place with the application of crop rotation techniques and/or intercropping. The selection of the crop varieties will depend on the purpose of the land user. In general, a diversity of crops will provide a range of benefits such as food security, nutritional diversity, income generation, soil conservation, pest and disease control as well as adaptation to climate change (CGIAR, 2017, Makate et al, 2016, MoEYS& VVOB Cambodia, 2013).
Mrs. Prum Thon has been cultivating a diversity of crops with the application of rotation techniquesfor about 10 years, which involves exchanging an entire crop in a particular row. This means that cultivation can take place throughout the year without having to leave the land fallow. At the time of the interview eleven different crops had been cultivated including spring onions, anise basil, Cambodian mint, bok choy, choy sum, escarole, mint, long beans, cucumbers, bitter melons and lettuce. Almost all of these crops have an average lifespan of three months, except for the anise basil which can grow for one or two years depending on the way it is cultivated. After she has harvested a particular crop, she will then rotate this crop row with a new distinctive crop species. For instance after having harvested spring onions she will then plant mint in that row, and in the row where she was previously growing mint, she will rotate that with either spring onions or cucumbers.
The practice of crop diversification whilst at the same time rotating the crop in each of the rows aims to achieve the following main objectives:
Crop diversification enables the farmer to generate a daily income to offset her daily expenses which thereby becomes a means of improving her livelihood. Growing a diversity of crops can also enable her to meet a variety of market demands and generate a high daily income. If a farmer grows only one crop specie she can usually earn about 15,000 Riel per day, but if she plants four crop species such as anise basil, bok choy, long beans and cucumbers she can increase her income to about 20,000 Riel per day, However if she grows one more specie such as lettuce or grows eleven different crops, she would be able to increase her income up to 40,000 or 80,000 Riel per day. The practice of crop diversification enables her to generate an income on a daily basis.
Crop diversification with the rotation of the crop in each row after the harvest could assist in reducing soil degradation. According to her experience and observations each crop absorbs different nutrients from the soil. If one row is repeatedly used to cultivate spring onions, they tend not to flourish so well and the roots have a tendency to decay. However if they are rotated with another crop and the spring onions are then grown in another row, they are able to thrive and the roots and stems are less likely to spoil. Crop diversification also has other functions as the cover crops help to reduce soil degradation through expose to sunlight, maintain soil moisture, make the soil less compact and add beneficial micro-organisms to the soil. In addition crop diversification can control pests especially the practice of growing companion plants such as herbs or spring onions as this can prevent crops from being damaged by pests.
The use of this technology assists in improving livelihoods, reduces migration because she does not need to move in order to find a job in another location, and enables her to generate a daily income. In addition this technology is able to reduce the risk of crop failure resulting from damage by pests and insects.Furthermore it reduces the risks associated with changes in market demand as the farmer produces a diversity of crops and also it prevents and reduces soil degradation. In order to effectively use this technology there needs to be sufficient water supply such as a river, stream, well or pond.This enables the land user to grow crops throughout the year round and reduces damage of crops as the result of unpredictable adverse climate conditions such as changes in rainfall, or the occurrence of drought.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Cambodia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Ruessei Duoch village, Banteay Peal Commune, Rolea B'ier District, Kampong Chhnang Province.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- durante experimentos/ investigación
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Through her experience and training from Cambodian Center for Study and Development in Agriculture (CEDAC).
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Spring onion, anise basil, Cambodian mint, bok choy, escarole, choy sum, mint, long bean, cucumber, bitter melon, lettuce.
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Degraded forest land.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
There is one open well and a pond for crop irrigation during drought.
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 3
Especifique:
Crop rotation throughout the whole year. The land is alway coverd by corps (no fallow period).
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- sistemas de rotación (rotación de cosecha, cosecha rotatoria con descanso, agricultura migratoria)
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
- manejo integrado de pestes y enfermedades (incl. agricultura orgánica)
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
It is spread over an area of 2700 square meters.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques

otras medidas
Comentarios:
The farmer grows specific companion plants on the same plot with the aim of improving the plant growth and the pest control.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
At the first time when she cultivated the land the soil was fertile. At that time she grew only cassava but she realized soon that if she grows always the same crop, the soil will be less fertile from year to year.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
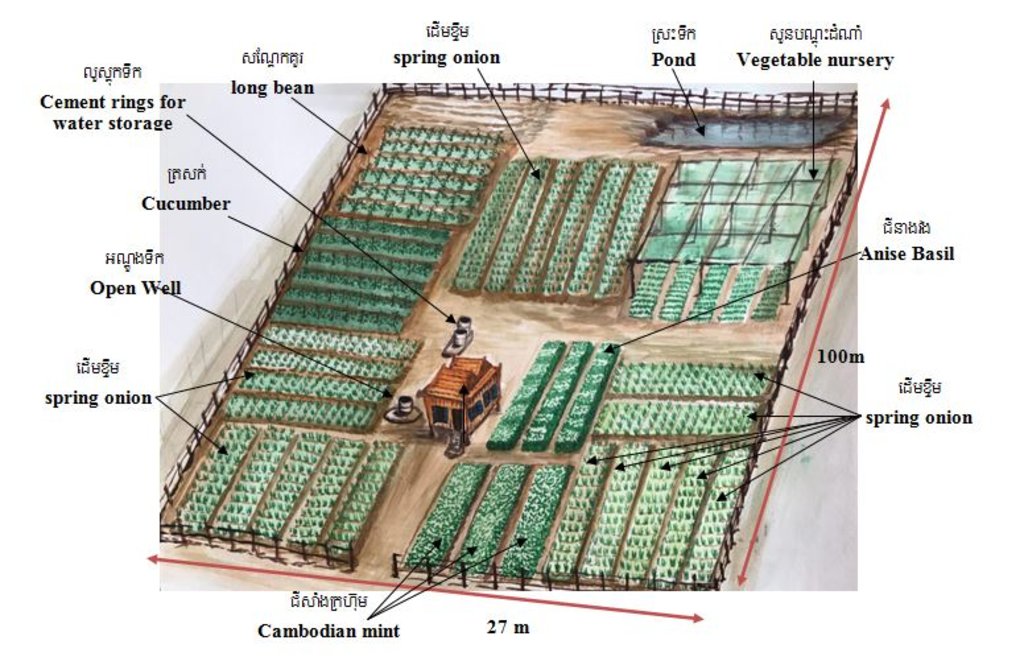
The total area on which the technology has been applied amounts to 2700 square meters (27 meters x 100 meters). Each of the diverse crop species such as spring onions, anise basil, bok choy, choy sum, escarole, Cambodian mint, long beans, bitter melons and lettuce have been divided into separate blocks.
The spring onion crop has been divided into 5 blocks out of which the first block measures 8.50 m x 8.50 m = 72.25 square meters and it contains a total of five rows. The length of each row is 8.50 m and width is 1.4 m and space between each row is 4 centimeters. The second block measures 14.60 m x 13 m= 189.3 square meters and it has been divided into two rows. Each row is 14.60 m in length and has a width of 1.4 m with a space of 4cm between the two rows. The third block measures 9.60 m x 3.90 m= 37.44 square meters and it contains 6 rows. Each of the rows is 9.60 m x 1.4 m and the space between each of the rows is 4 cm. The fourth block measures 6.35 m x 4.55 m= 28.89 square meters and it is divided into 4 rows. Each of the rows is 6.35 m in length and 1.4 m in width, and the space between each of the rows is 4 cm. The fifth block measures 11.60 m x 14.70 m = 170.52 square meters and it contains 6 rows. Each of the rows is 11.60 m in length, and 1.5 m in width and the space between each of the rows is 4 cm.
The block in which the anise basil is grown is 14.60 meters in length and 1.4 meters in width with a 4 cm space between the 3 rows. The block of cucumbers is divided into 6 rows with the length of each row being 10 meters and the width being0.5 meters. Each row rises to a height of about 1.5 cm and within the row the space between each cucumber clump is 0.5 cm. In the block of the long beans there are 6 rows with each row being 10 meters in length and 0.5 meters in width. Additionally the height of each row is 1.5 cm and space between each clump of long beans is 2 cm.
The nursery containing escarole, choy sum and lettuce is 14.60 meters x 13.50 meters and its roof has a height of 2 meters. There are two cement rings which also have a cement base that have been constructed for water storage. Each cement ring is 1 meter in height and 1 meter in diameter. Furthermore there is also one open well and a pond which provide water for domestic supply and the irrigation of crops.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
2700 square meters
Si utiliza una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea :
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
KHR
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
4000,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
15000
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig open well | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 2. | Dig pond | Estructurales | During dry season |
| 3. | Plough the soil two times and dry the soil by sunlight | Agronómicas | After harvest |
| 4. | Buy crop seeds | Agronómicas | At the beginning of soil preparation |
| 5. | Prepare pipe lines into cement rings | Estructurales | At the beginning of soil preparation |
| 6. | Buy net to cover the roof of the nursery house | Otras medidas | At the beginning of soil preparation |
| 7. | Buy materials such as spit, handled basket, hoe ect | Otras medidas | At the beginning of soil preparation |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Plough the soil for the first and second time | person-day | 11,0 | 15000,0 | 165000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Clear land for growing 11 different crops | person-day | 15,0 | 15000,0 | 225000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Dig the open well and put the cement ring | person-day | 84,0 | 15000,0 | 1260000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Dig pond | person-day | 133,0 | 15000,0 | 1995000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Bamboo sticks | Piece | 50,0 | 1500,0 | 75000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Hoe | Piece | 2,0 | 17000,0 | 34000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Spit | Piece | 2,0 | 1300,0 | 2600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Handle basket to carry soil | Pair | 1,0 | 6000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Spring onion | Kilogram | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Bok choy | Can | 12,0 | 1500,0 | 18000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Escarole | Package | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Choy Sum | Can | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Anise basile | Package | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Mint | Kilogram | 3,0 | 4000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Cambodian mint | Kilogram | 2,0 | 2500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Long bean | Kilogram | 1,0 | 60000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Buy cow manure for the use of one year | Two wheel handle tractor | 10,0 | 70000,0 | 700000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Buy chicken manure for the use of one year | Bag | 20,0 | 4000,0 | 80000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Buy soil of termite mounds | Two wheel handle tractor | 10,0 | 40000,0 | 400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Buy botanical pesticides | Liter | 6,0 | 4000,0 | 24000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Rice husk | Bag | 30,0 | 1500,0 | 45000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Buy Bat manure for soil preparation | Bag | 5,0 | 70000,0 | 350000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Water Pumping Machine | Piece | 2,0 | 880000,0 | 1760000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Cement rings which also have a cement base that have been constructed for water storage to irrigate crops. | Piece | 2,0 | 70000,0 | 140000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Net for making the roof to prevent sunlight and water. | Set | 2,0 | 220000,0 | 440000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Cucumber | Can | 1,0 | 40000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Lettuce | Package | 5,0 | 15000,0 | 75000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Bitter melon | Package | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 7974100,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Generally, the rate for digging a pond in Cambodia is USD 50 per hour if the contractor does not obtain the soil, but if he does the cost of digging the pond will be less. Cost calculations of this technology are based on crop cycles (the average lifespan of crop being three months with a diversity of eleven crops). The farmer uses her own labor force to implement this technology without hiring any external labor. In reference to the costs indicated in the table above, there may be minor errors compared to the actual costs because the land user did not make exact records, and the costs that were provided are only estimates.
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering | Agronómicas | Two times per day or three times per day depend on the weather. |
| 2. | Apply cow manure | Agronómicas | When dig the soil near the crop root. |
| 3. | Apply bat manure | Agronómicas | When dig the soil near the crop root. |
| 4. | Weeding | Agronómicas | Once a week |
| 5. | Spraying pesticides | Agronómicas | When there is insects. |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | When weeding, dig the soil near the crop root and apply fertilizer for elevent diversify of crops. | Person-day | 12,0 | 15000,0 | 180000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Spray pesticides | Person-day | 3,0 | 15000,0 | 45000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Diesel | liter | 10,0 | 3000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Liquid fertilizer made of bat manure buying from fertilizer company. | liter | 1,0 | 70000,0 | 70000,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 325000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The estimated maintenance costs base on one crop cycle of 3 months. It is not calculatee for the whole year. The land user does not hire wageworker as she is doing the work by herself and by the support of her husband.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Cow manure, chicken manure, rice husk, botanical pesticides has to be bought. Digging the pond and buying the water pumping machine are the most important factors affecting the costs. However these equipments are longlasting.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1209,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The annual rainfall in 2015 is 1209 mm. In 2014 is 1420.74 mm and in 2013 is 1367.5 mm
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Ministry of water resources and meteorology, 2015
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
There are two seasons: Rainy season and dry season.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
PH=6
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
In this technology only two persons are involved in the technology (husband and wife). The interviewee is the wife is 50 years old. She finished grade 8.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
The technology is applied on 2,700 square meters. The homeland is 3,900 square meters. Degraded forest land is 8,250 square meters and rice paddy field is 0.50 hectare.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The crop diversification and the subsequent cultivation of vegetables and herbs during the whole year, as well as the distinct crop rotational plan increased considerably her crop production.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The application of natural fertilizers and botanical pesticides, as well as the method of crop rotation and selection of companion plants led to better crop quality.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the permanent soil cover, the high crop diversification and the sophisticated pest control the risk of production failure decreased.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
There are diversify of crops and grow all year round.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
demanda de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
The plantation of a large variety of vegetables and herbs all year round let to higher irrigation water demand especially during the dry season or at drought events.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
The crop diversification requires a lot of monetary inputs mainly for the establishment and also for the maintenance (labor for digging the pond, water pumping machine, natural fertilizers has to be bought - she does not raise animals).
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Although the land user had to invest a lot of money for this technology, she got and get still better and regular daily income from the sale of the wide range of different crops at the market compared to what she earned before. All in all she was able to improve the household's livelihood.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
This technology is sophisticated and rather time consuming compared to conventional growing methods (mono-cropping of cassava for example). In this case study the land user invests only her own and her husband's labor force.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
The self sufficiency increased as she gets every day her own vegetables from the vegetable plot. And at a daily base she gets money from the sale of her vegetables to meet all needs of the household. Further, she was able to reduce the risk of crop failure which increased the food security.
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
The health situation of the farmer and her husband were improved as the production is near to be fully organic very low use of chemical pesticides/biocides. And by the health production she supports also the health of the other consumers.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
The land user got a broad knowledge about the crop diversification and crop rotation technology. Mainly regarding the reduction of chemical soil degradation and regarding how to support better plant growth.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
calidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to very low application of chemical pesticides.
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the improved soil cover by the different vegetables and herbs all year long the evaporation deceased.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil moisture increased due to the improved soil cover that could reduce evaporation into environment.
compactación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The soil compaction is less due to better soil moisture, crop rotation and using natural fertilizers.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
The soil organic matter increased due to the application of natural fertilizers.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
All year long the soil is covered by different vegetables and herbs.
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Before she has cultivated only one crop on the area but she grows now eleven different vegetables and herbs.
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
The soil life increased regarding bacteria and fungi, earthworm, ant, and centipede due to the crop rotation system and the use of natural fertilizers and botanical pesticides.
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
The nearly organic cultivation provides a habitat for a large variety of soil organisms such as earthworm, termites or ants.
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
The pest and disease control is improved due to the rotational system, the use of botanical pesticides, and the cultivation of companion plants such as anise basil, Cambodian mint and spring onions.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | disminuyó | bien | |
| temperatura estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | disminuyó | bien |
| temperatura estacional | estación seca | incrementó | bien |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien | |
| lluvia estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres biológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| enfermedades epidémicas | moderadamente |
| insectos/ infestación de gusanos | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 10-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
7 families
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Provides a daily income. |
| The quality of the soil is better through crop rotation and the exchange of crops in the rows. Additionally cow manure and soil from the termite mound can be used as fertilizer. |
| The actual work can be done by oneself which involves physical exercise and is good for one’s health. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Grow a diversity of crops which reduces the risk of production failure from damaging from insects, disease and market. |
| The farmer is able to generate a daily income, thereby improving her livelihood and it gives her the means to cope with her daily expenses. |
| Crop rotation could reduce soil degradation. |
| Reduces migration as now she has her own job and as this technology improves her livelihood. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| During some months it is not possible to grow herbage vegetables. | Can grow other crops such as anise basil. |
| She has to water the crops only by herself which is very exhausting | Must try harder. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Farmer spends a lot of time for watering the crops. | Could change and start using a sprinkler or drip irrigation system in order to reduce labor. |
| Must properly record expenses and income so as to verify the net income. | Provide training in recording income and expenses. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
One specific location where the technology applied.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
one person
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
3 persons
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
CGIAR. (2017). Crop diversification strategies for Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. Retrieved December 11, 2017, from
URL:
https://ccafs.cgiar.org/blog/crop-diversification-strategies-cambodia-laos-and-vietnam#.Wi4Hu1WWbIU
Título/ descripción:
Makate, C., Wang, R., Makate, M., & Mango, N. (2016). Crop diversification and livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Zimbabwe: adaptive management for environmental change. SpringerPlus, 5(1), 1135.Retrieved December 11, 2017, from
URL:
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2802-4
Título/ descripción:
MAFF. (2006). Technology stardardize: Home gardening. In Khmer. (Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries). Phnom Penh. Retrieved December 11, 2017, from
URL:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B3kkBprEzhDoMWtPeXZUNE4teTQ/preview
Título/ descripción:
MoEYS & VVOB Cambodia. (2013). Teaching Methodology for Agricultural Life Skills Education for Teacher Training Centers:Part 3 Organic gardening (1st editio). Phnom Penh: Ministry of Education, Youth and Sport. Retrieved December 11, 2017, from
URL:
http://www.vvob.be/cambodia/sites/default/files/content_manual_part_3_organic_gardening.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos