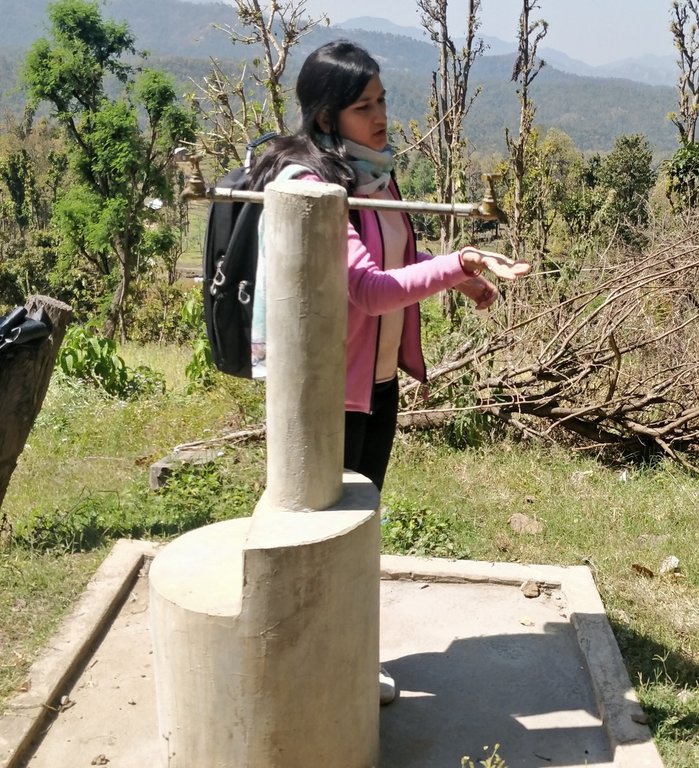
Gravity-Fed Multiple Use Water System (MUWS) : Odaltaal [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Jhuna Kattel
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Renate Fleiner
Odaltaal Ghaito
technologies_5182 - Nepal
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Water User:
Sunar Kopila
Nepal
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Prospects and challenges of water use systems as climate adaptive option for sustainable water management in Himalayan RegionNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Kathmandu University (KU) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology used serves as a source of providing water for drinking and other multiple uses; such that it acts as a means to conserve and manage water resources rather than degrade them.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
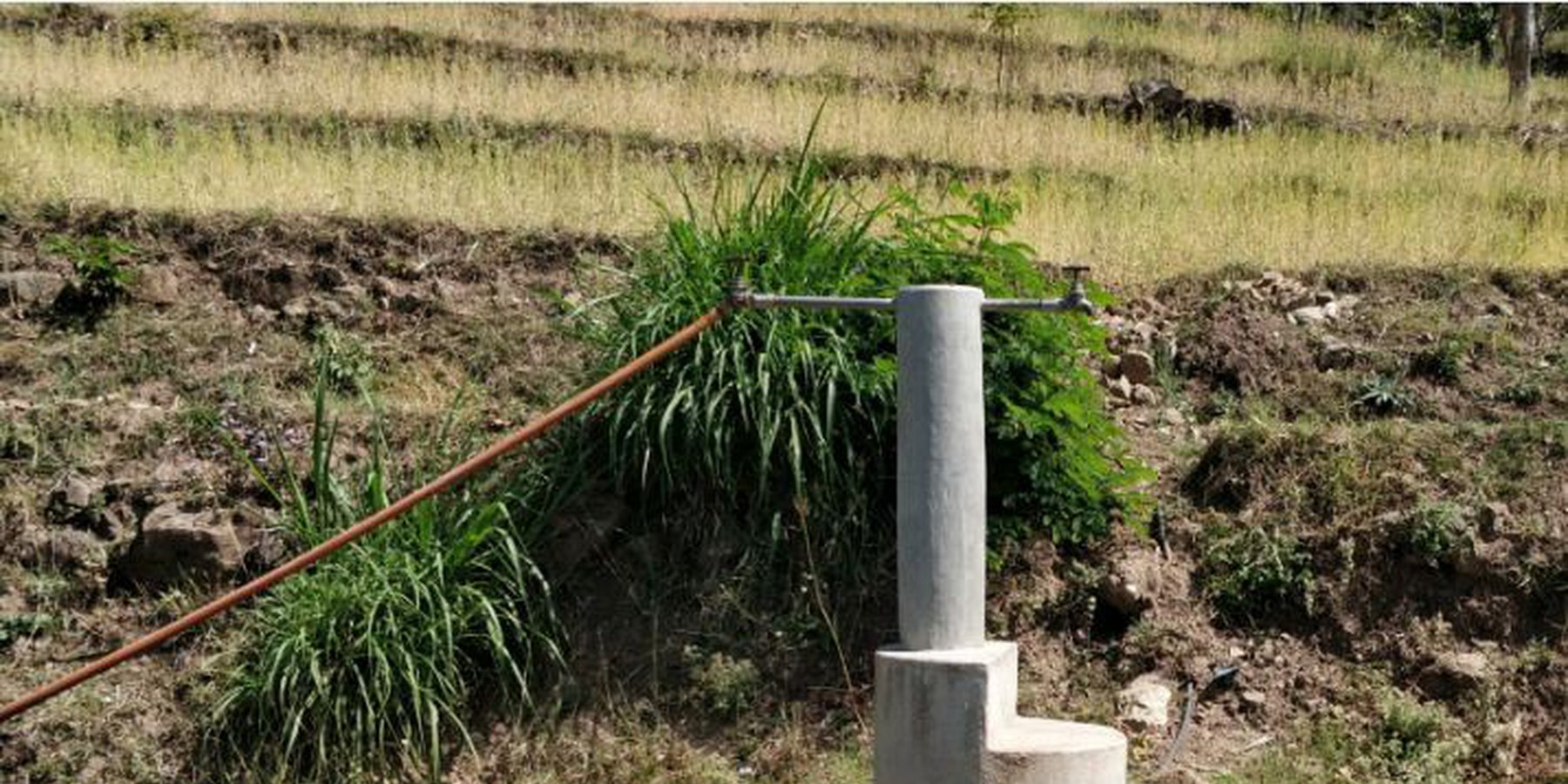
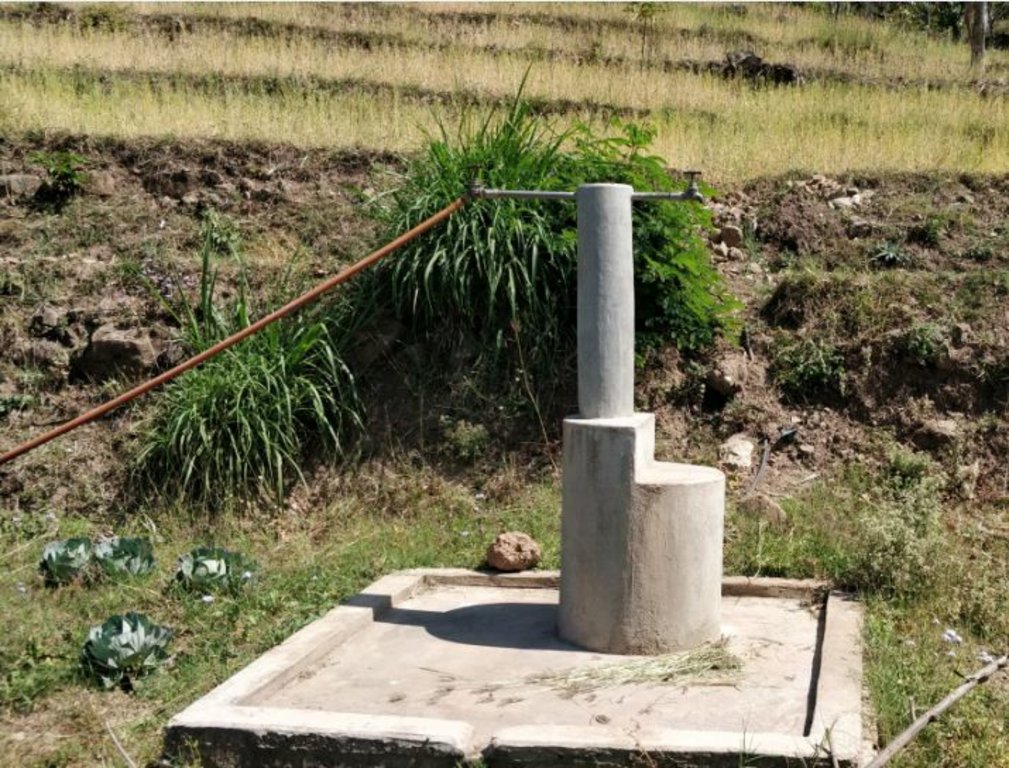
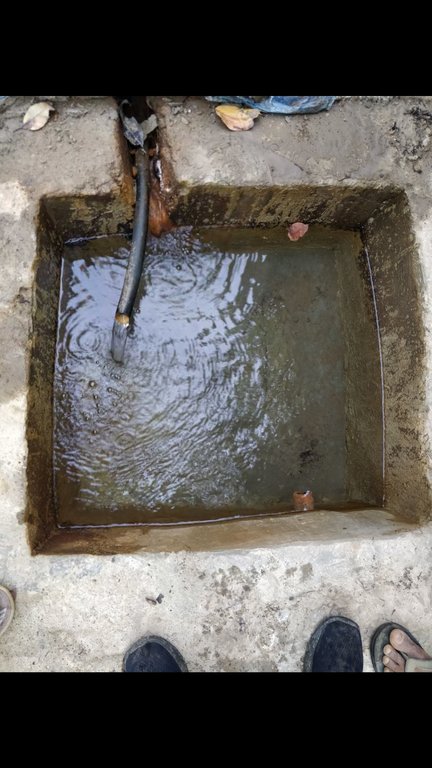
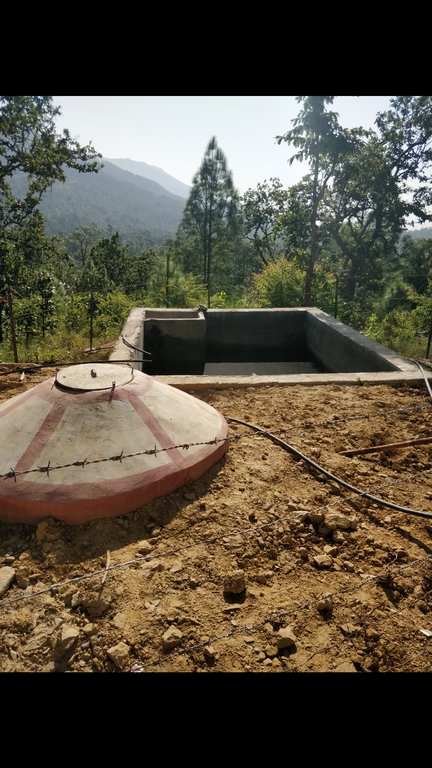
Water from source in hill top is collected in a small reservoir (to preserve natural source), then passes onto a Reservoir Tank (RVT) / Ferro-Cement Tank / "Ghaito" for drinking water with a capacity of 4000L. When the RVT gets filled, water overflows, is collected in another concrete irrigation pond (10,000L) for irrigation. From the ferro-cement tank (Ghaito) and concrete irrigation pond, two pipelines are fed and water supplied into individual tap-system or MUWS tap towers for multiple purposes.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The technology is applied in a natural environment, i.e. natural water source. The source of water is a natural source of water that sits atop a small hill which is owned by the government. From the source, water is collected in RVT ( for drinking water) and concrete irrigation pond ( for irrigation). PVC pipes are fed onto the tanks to distribute the water for multiple purposes to 4 MUWS tap towers or tap systems or "Thaado". These MUWS tap towers consist of two faucets each- one for drinking and the other for irrigation and other purposes.The major purposes of this technology are to supply clean water for drinking and other multiple purposes through a cheap, effective and simple system. The natural source of water is locally maintained. Operation and maintenance works are not mandatory, however the locals are responsible for maintaining it should the need arise. The system was financed through a public-private-partnership (PPP) program; out of which some amount was funded by a Non-Governmental Organization (NGO)- Sundar Nepal ( NPR. 2,77,000 ), some amount by the Village Development Committee (VDC)- (NPR. 2,63,000), and the remaining amount was collected by a locals’ group (NPR. 60,000). For establishing the system, labor and construction materials were needed for building the tanks and pipeline systems. For the maintenance, manual labor is necessary. The quality of the water that is supplied to the households is good and the quantity seems sufficient for the 19 households. Sustainable use of water resources through a MUWS system, cheap and effective way to conserve water resources, ensuring availability of clean water even through dry seasons are some of the technology's advantages. Similarly, clean water, more water for irrigation for vegetable farming, simplifying day-to-day life are some of the strengths of the technology. Dislikes could be the limited availability of water during the dry season and that out of 4 systems only 2 are in operation and the other ones are in a non-working condition.
Management system in place for MUWS:
A separate committee is set up for the smooth operation of the system, which consists of 20 members- 10 males and 10 females. The head of the committee is Mrs. Kopila Sunar. The committee conducts a monthly meeting to discuss the problems and need of maintenance. During the initial setup, the connection of pipelines from the tap systems to the reservoir tanks was, however, done with the contribution of the locals. Every month, each family from the 19 households contributes NPR. 100 ( One Hundred Rupees) , which goes to a fund that is set up for the times of need. The labor contribution by the people of the VDC was dependent upon the number and availability of family members in the household. Similarly, the use of the MUWS system and water from it is also dependent upon the availability of family members. Little to no maintenance was done to the system till now from 2075 B.S. ( 1 years) . Equal number of male and female members are in the committee dedicated to the MUWS system.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Nepal
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Province-6, Mid-Western Development Region
Especifique más el lugar :
Kunathari VDC-10, Odaltaal
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2018
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Sundar Nepal- a non-governmental organization (NGO) helped with Odaltaal Multiple Use Water Systems
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- improve water security and increase efficient use at a household level
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - cebada
- cereales - maíz
- cereales - arroz (tierras altas)
- cereales - trigo (verano)
- cereales - trigo (invierno)
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- areca
- banana/plátano/abacá
- caña de azúcar
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 3
Especifique:
The water used for irrigation is used in fields for 2-3 cycles of crop growing (annual) like rice, maize and barley and into kitchen-farming/tunnel farming (perennial) where vegetables grown are cucumber, tomatoes, chilli, bitterguard, peas, etc.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Rice, Maize and Wheat are cycled according to the seasons.

Otros
Especifique:
Drinking Water
Comentarios:
Drinking water used directly from the tap systems. Some boil it but most of them use it straight from the tap systems and consume without filtration.
Comentarios:
Irrigation and Multiple Uses: The locals use the technology in order to irrigate their cropland so that the plant productivity is increased. As well, the introduction of this technology has opened up doors to new possibilities like construction of tunnels ( green houses) so that the locals can grow seasonal and off-seasonal vegetables in their backyards. Animal husbandry has also been an increasing practice. Human uses like washing, cooking, cleaning, bathing, etc are amply sufficient due to adequacy of water from this technology.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - cebada
- cereales - maíz
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
Comentarios:
Before the introduction of the technology, the land productivity was minimal. Water for human uses like bathing, cleaning, washing, cooking, etc. were scarce; especially during the dry seasons. No green houses were constructed. They used to rear very few cattle.
3.4 Provisión de agua
otra (ej. post-inundación):
- Natural source (Mool) of water in foliage atop a hill
Comentarios:
The supply of water comes from a natural source ( 'mool' in local language) , where a small enclosure is constructed so that the source is preserved and water is amply supplied to the ferrocement RVT for drinking purposes ( 'Ghaito' in local language) and concrete irrigation pond for irrigation purposes.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cosecha de agua
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
- manejo de agua subterránea
- Gravity Fed Multiple Use Water System (MUWS) , New Scheme
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas
- S7: Equipo para cosechar agua / provisión de agua/ irrigación
- S11: Otros
Comentarios:
The technology is comprised of structural measures, barbed wire fences to surround natural water source, iron lid top, cement enclosure for water source, pipes feeding onto the source, ferro-cement RVT, tap towers, faucets, concrete irrigation pond, etc.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
Comentarios:
Before setting up the technology, much of the water during dry seasons would evaporate from the natural source ( mool) and there would be scarcity of water during dry seasons. This has been addressed by the technology, where securing the natural source of water prevented evaporation and storing water in enclosed tanks helped supply water during dry seasons.
Similarly, due to no preservation of the source and no storage tanks, the water would be soiled by sediments, wastes and insects' larvae. After setting technology up, the quality of water has vastly improved as well.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
The technology prevents water source degradation, improves perennial water availability, helps tackle with the effects of natural calamities like drought, etc.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Source: Natural (mool) atop a small hill, secured by wire fences and preserved with concrete and metal lid ( to prevent evaporation).
Water from source collected in Ferro-Cement Tank (RVT) / "Ghaito" in local language, with capacity 4000Ltrs.
Water overflows from RVT into an Irrigation Pond (Open Top, Concrete) with capacity 10,000Ltrs.
PVC Pipes leave the RVT and Pond into 4 MUWS Towers ("Thaado" in local language) to serve 19 households.
One faucet supplies drinking water from RVT and next faucet supplies water for irrigation and other multiple purposes (drip irrigation, tunnel farming, etc.).
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
5-6 dhurs
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha = 590 dhurs
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
NPR
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
110,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
N/A ( voluntary labour from each household)
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Enclosement for the groundwater source | Before rainy season |
| 2. | Construction of Ferro-cement tank for Drinking Water | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Construction of Concrete pond for Irrigation | Before rainy season |
| 4. | Securing the perimeter for the tanks | Before rainy season |
| 5. | Laying down the PVC pipework | Before rainy season |
| 6. | Construction of 4 individual MUWS tap towers ( Thaado in Nepalese language) | During rainy season |
| 7. | Final touch-ups, Setting up faucets, Preliminary checking | During rainy season |
Comentarios:
A total of 3 months ( roughly 90 days ) was required for the construction of the technology to be complete.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Voluntary by locals | 100,0 | ||||
| Equipo | Irrigation Pond | 1,0 | 275000,0 | 275000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipo | Ferrocement Tank ( Ghaito) | 1,0 | 225000,0 | 225000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipo | Securing fences, Perimeter securing for tanks and water source | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipo | Setting up MUWS tap towers ( Thaado in local tongue) | 4,0 | 12500,0 | 50000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipo | PVC Pipes | 100,0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 600000,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 5454,55 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
1.Village Developmment Committee:NPR. 2,63,000 2.Sundar Nepal NGO: ~ NPR. 2,77,000 3.Water – Users : NPR. 60,000
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plan on Changing PVC pipework for a Galvanized-Iron (GI) pipe | 1 time after PVC pipes damaged by wear and tear, lime, etc |
| 2. | Plan on Construction of another Drinking Water Tank | When the one tank is not sufficient for providing enough water |
Comentarios:
Construction has been completed and technology is in use since a year only, so no maintenance works till now. However, construction of another drinking water tank and changing the PVC pipes for GI pipes is imminent in near future.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Voluntary | 100,0 | ||||
| Equipo | Drinking water tank construction | 1 | 1,0 | 75000,0 | 75000,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipo | Laying down GI pipesinstead of PVC Pipes | 1 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 25,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 125000,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 1136,36 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The non-governmental organizations and government offices (Village Development Committee) have expressed an interest to help financially in the construction of another drinking water tank and GI pipes laying should the need arise.
Comentarios:
These are the expected costs should the need of such arise.
The water users' committee, along with NGO's and governmental bodies shall bear the costs in the said maintenance works.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The construction materials- rods, concrete, cement, bricks and Galvanized Iron (GI) pipes would cost the most
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Monsoon/ Rainy Season 2-3 months ( June-August)
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Meteorological Forecasting Division, Nepal ( www.mfd.gov.np)
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
en superficie
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Before the introduction of MUWS technology, the water used to be a problem during the dry seasons. However, after the technology was applied, the natural ground water source is conserved, people have been monitoring the water levels cautiously and nowadays, the water sustains the locals during the dry seasons as well.
Salinity is not a problem, but the presence of lime in the water is a problem.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Birds are abundant, new fowls are sighted regularly.Lampuchhre ( Long-tailed widowbird),Ravens,Hawks,Peacocks and peafowls,Peasants,Guinea fowls and other fowls; rarely seen before are common after setting up the technology.
Animal sighting is rare. Forests, although consisting of a few varieties of trees, like Saal ( shorea robusta), Sadhana ( Moringa) , Belauti ( Guava), Sallo ( pine tree), Aap ( Mango). very few species are abundant in a given stretch of land.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- niños
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Members of the community: 1:1 ratio of males to females
Age : mostly middle-aged, a few children and few elderly
Caste/ Ethnicity: Thakuri, Dalit and Janajati
Literacy: 1 person completed High – School level (+2), rest are literate ( Class 5)
Total Land Holding: < 10 ropanis of land, Human Settlement since 2040 B.S. ( since last 36+ years) in search of better opportunities and access to better services of water, roads, etc.
Total households: 19
Jobs: Males : bread- earners, construction workers, labour, farming
Females: Housewives, Farming. Most of the males in the village have been to foreign country ( India specially) for manual labour and mostly females are present in the village.
Ethnicity: Few families are of Upper- Caste: Thakuris ( as per Nepalese traditions) and most are Dalits and Janajatis, who were considered low-caste previously. The term "lower-caste" has been abolished now.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
19 households occupying less than 10 ropanis of land.
(1 Hectare = 19.66 ropanis)
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- The source, tanks fall under community forest area- owned by the Government
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
Especifique:
Previously, the society had a caste system in which the higher and lower caste discrimination was done and the water tainted by the lower caste ( Dalits, Janajatis) were deemed “unfit” by the upper caste ( Thakuris, Brahmins, Chhetris). However, after the abolishment of the caste system, everyone enjoys equal rights to the access to water.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
The access to health, education and markets along with other facilities is only accessible after a 15 minute journey to the ‘bazaar’ or market area from the village.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
calidad de cultivo
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
producción animal
producción de madera
calidad de bosques
producción de productos forestales no madereros
riesgo de fracaso de producción
diversidad de producto
área de producción
manejo de tierras
generación de energía
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
calidad de agua potable
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
calidad de agua para ganado
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
demanda de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
disparidades económicas
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Knowledge about the technology (MUWS) improved
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
evaporation of water decreased after the construction of enclosures / tanks.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
acumulación de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
salinidad
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
acidez
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
especies invasoras extrañas
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
impactos de sequías
Comentarios/ especifique:
As per water users, effects of drought were imminent in the dry seasons, leading to less water available for drinking and irrigation. However, after the MUWS was installed, the effects of drought could be tackled; mainly due to the availability of water for drinking and drip irrigation, even during the dry and arid winter seasons.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
MUWS focuses mainly on the preservation of water resources through its sustainable use.
Similarly, this technology also addresses the water shortage issues (especially in dry seasons), tackles effects of climate change, ensures water availability in geographically challenged areas, uses minimal modern technologies (relies on gravity for water supply) , is cost-effective ( little to no maintenance costs) and also ensures the social and economic well-being of water users through off-farm and farm incomes ( with the help of drip irrigation).
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
Since this technology is adapted in a small area, without any significant construction, there is virtually no off-site impact at the moment.
However, beneficial off-site impacts can be expected in the long run.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| temperatura estacional | verano | incrementó | moderadamente |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | disminuyó | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | moderadamente |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The system has been in operation since a year only. Thus, long term effects are yet to be visible. Evident from the cost of operation and maintenance with the benefits of the technology, there is a positive impact evident.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Substantially less amount of lime present in water than what was previously found. |
| Availability of water even during the dry seasons. |
| Increase in the productivity of perennial vegetables in kitchen garden, construction of tunnels for farming vegetables possible |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Water quality vastly improved, no lime and/or saltiness present in water |
| Need of alternative sources of water during dry seasons not present after construction of MUWS system |
| Overall productivity of land improved through effective irrigation of water |
| Self-sufficiency in the aspect of water and crops, as well as alternative sources of income increased leading to improved quality of the lives of the water users. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Water levels not rising in two tap systems of the four | Technician could oversee the problem of elevation and give a viable solution so that 4 out of 4 tap systems could be functional again |
| Pipes’ diameter and quality could be improved | If the government and/or NGO could add to the savings of the group, good quality of GI pipes could be installed instead of the PVC pipes used |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The tank for irrigation is left open at the top | Closing the top of the tank |
| The pipes used are not sustainable | The use of heavier PVC pipes and/or hybrid GI pipes could result in less chances of system failure due to lime in the water |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
> 10
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
> 1
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
26/05/2019
Comentarios:
Data collection, compilation done through field visits ( 3 times).
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos