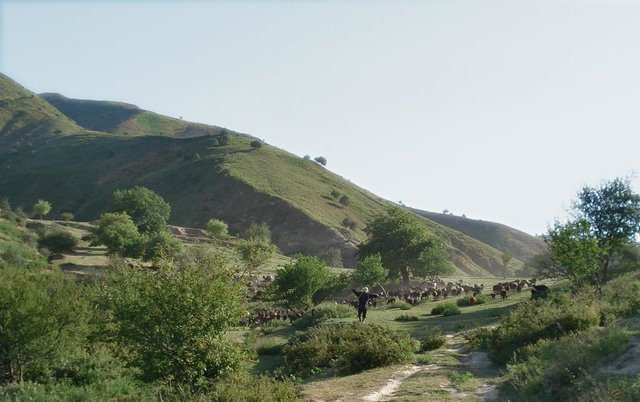
Daily and seasonal rotation on grassland [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Dajmardei Kaspi (professional herder)
technologies_1407 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirguistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Seminomadic individual herding [Tayikistán]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Extensive grazing of sheep and goats by the means of a precise rotational scheme
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
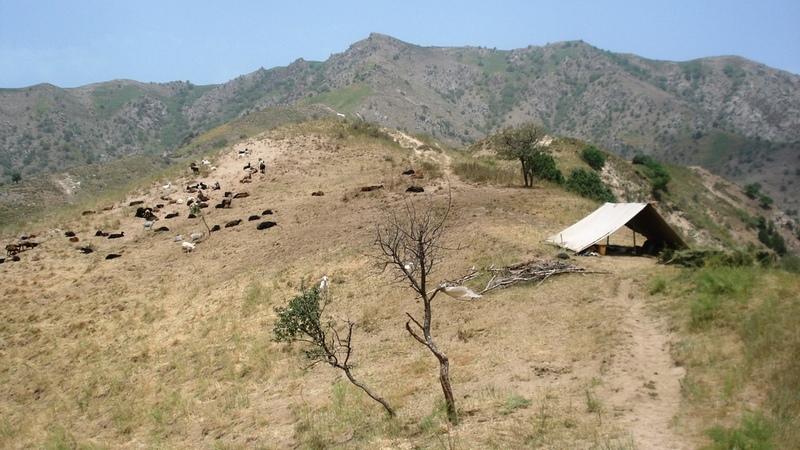
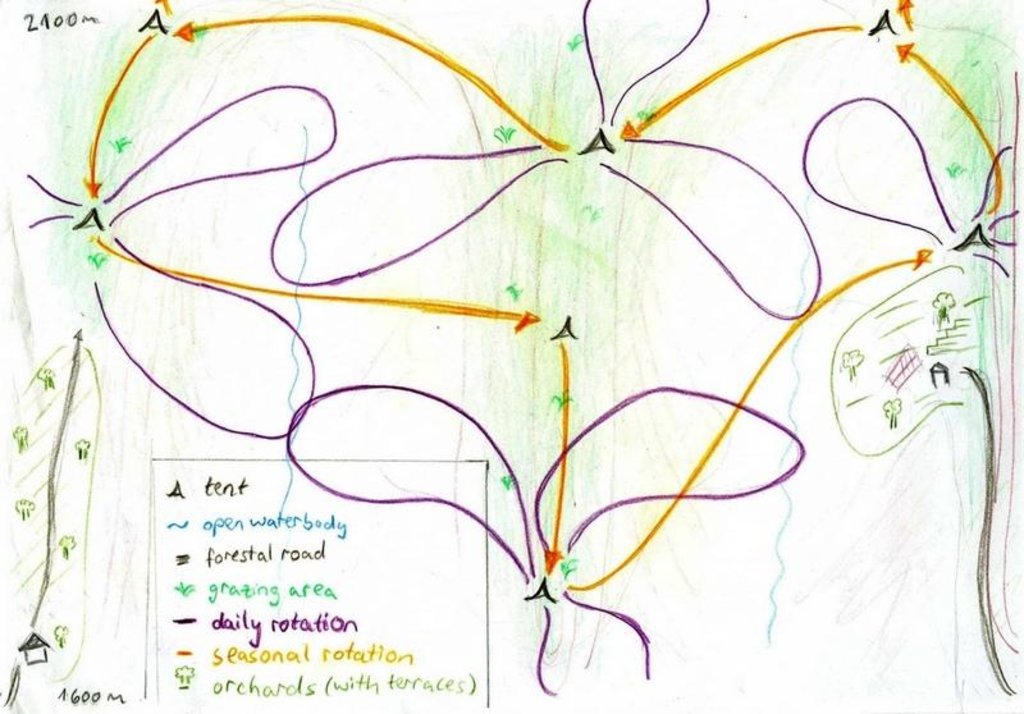
Half-year herding with 500 sheep, goats and cows (very few), with 7-8 different locations of the herder's tent. The herder visits each place twice to thrice per grazing season and stays in one place for one week to maximally one month (during the Ramadan period, due to limited forces). The area is grazed from the higher zone (around 2000m) to the lower zone (around 1600m) twice per season, in a sort of circle. Every day the herder starts in another direction from his tent and leads the animals to the pastures, once in the morning and once in the evening. He passes a stream once (autumn) to twice (summer) a day.
Purpose of the Technology: The grass should not get dusty and dirty, explaining why the herder daily changes the pastures, only revisiting the same places every two to three days.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After accompanying his father as a child and a kind of an apprenticeship (of one year) later on, M. is considered by the villagers as a good herder and they give him their animals for herding. But M. applies for land on the forest department only after working as a guardian and as a tractor driver for 20 years. For the herding profession observing the animals precisely is necessary, in order not to lose any of them. And the maintenance of the pastures is guaranteed by the strict rotational scheme.
Natural / human environment: The pasture-area is in a generally well-conserved state. Moderate to high values of fractional vegetation cover can be observed and only few signs of recent erosion processes (through water) are visible. The area is characterised by steep slopes where still signs of past tree-planting during the USSR period are visible by some trees, many little platforms made for tree-planting and a few terraced areas. Eventhough, many trees have been grazed and do not stand anymore. Besides steep areas there are small, quite flat areas (where the herder installs his tents), that used to be cultivated (wheat) till 1966. These areas generally have low cover-values and signs of rill-erosion, which the herder attributes to the past tilling activity. However, it might also be the trampling and sitting of the animals (staying near the herder's tent at noon-time and during the night) causing this erosion. Nutrient management is provided for by the dung of the animals which is not collected, contrarily to the pastures near the villages.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Region of Republican Subordination
Especifique más el lugar :
Faizabad
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 km2.
The half of the herded area is rented by another person from the village, who gives his animals to the herder. Apart from the interviewed herder there are varying numbers of other semi-nomadic herders with similar management practices, some of them from other regions.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
There are traditional herding peoples like Kuagwates, Kaleks, Lakais, Duramanes, Kurtshaliks), not Tajiks. These often move around with their whole families.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

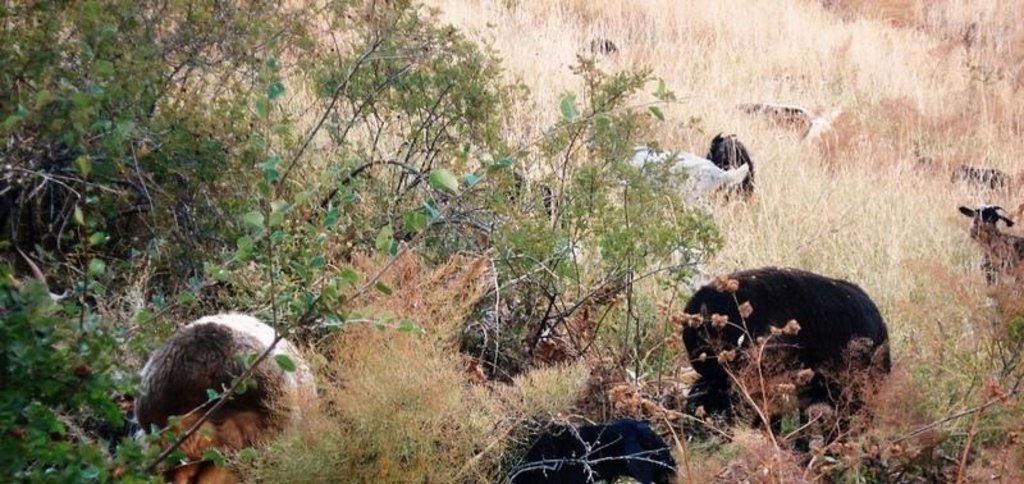
Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
Tipo de animal:
- cabras
- ovejas
- cows
Especies:
cabras
Conteo:
500
Especies:
ovejas
Conteo:
500
Comentarios:
Livestock density (if relevant):
< 1 LU/km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The trampling of the animals near the tent, the feeding on young trees and the daily passage of the herd of a limited number of streams (eutrophication).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): No major land use problems due to good management. Only the first rain that cannot be absorbed by the dry soils is a problem.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: sheep* / goats* / cows
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jun
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M4: Cambios significativos en la programación de las actividades
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

degradación biológica
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
Comentarios:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Causing Pc, Bc, Wt), droughts (Causing Pk, Pc, Ha), degradation of near-village pastures (The pressure on more distant areas increases)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (passed tilling with impact on Wt), floods (Intensive rains causing Wt), land tenure (Little interest in tree-planting if land can only be rented annually)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Daily and seasonal rotation.
Location: Above Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 05.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Obeying to what the herder says)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is necessary to know how to lead animals, more than in the case of the common pasture-area)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of fires, palatable fodder
Change of land use type: From afforestation and limited use as cropland to extensive grazing
Major change in timing of activities: Introduction of a strict rotational grazing scheme
Autor:
Christian Wirz, Switzerland
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
6.10
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying a herd | constantly investing |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otros | Buying a herd | animals | 50,0 | 87,7 | 4385,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 4385,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 4385,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rent fee for land of forest department | once per year |
| 2. | Salary of an assistant herder (normally, but not in 2008) | at the end of the season |
| 3. | compensation for dead animals | at the end of the season |
| 4. | Animal medecine | if necessary |
| 5. | Salt | daily |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Salary of an assistant herder | Days | 120,0 | 6,1 | 732,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Rent fee for land of forest department | 300ha/d | 180,0 | 0,4888888 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Compensation for dead animals | animals | 2,0 | 44,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Animal medecine | per year | 1,0 | 88,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Salt | kg | 1000,0 | 0,08 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 1076,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 1076,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The costs are valid for a herd of 250 animals kept by the herder alone for six months and additional 250 animals kept during summer holidays with the help of additional workforce. The salary indicated was not valid for 2008 (the grandsons helped the herder), but for years when M. hires external workforce. For all costs, including 50 own animal, prices in 2008 are taken.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Buying an own herd and looking for the animals are the most expensive factors, expecially if there are sick or dead animals.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Mainly in spring and also in autumn, with a trend to decrease
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: Pasture area around 1600 to 2000 m
Landforms ridges: Small, not so steep areas where the tent of the herder is installed
Landforms mountain slopes: The pasture area is generally very steep
Slopes on average steep (31-60%): The areas mostly frequented are steep
Slopes on average very steep (>60%): The areas dominating spatially are very steep
Slopes on average hilly (16-30%): Ridge areas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average shallow: Most grassy areas
Soil fertility is low: on the surface of 300 ha the summed up dung of 500 sheep and goats cannot compensate for the loss of topsoil by wind and water
Soil drainage / infiltration is good: Generally high infiltration capacity enhanced by high vegetation cover values
Soil water storage capacity medium (dominatig the area): Loamy soils and high cover values, but generally little trees and dried vegetation in August
Soil water storage capacity can also be good: Near the streams higher water retention, according to herder
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water quality (untreated): Locals drink the water, but are affected by diarrhoea
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Diversity higher than near the villages, but not comparable with biodiversity hot-spots
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Herding is considered as a male profession, inherited from father to son. In nomadic peoples the whole families are mobile and women are responsible for domestic work.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are rich (100).
Off-farm income specification: The herder claims to nourish himself and his wife with the income from herding. But, once he willl not be able to work as a herder anymore, he might depend on off-farm income from his children (remittances)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
3 households can afford to pay the services of the professional herder (clearly a minority of village population)
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Higher vegetation cover and biomass values than for village-pastures
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Much less impalatable species' frequency
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The animals get much fatter and are sold for around 50% higher price than animals from common pastures
producción de madera
Comentarios/ especifique:
The herder says that tree density has decreased, due to livestock but also to chopping. Additionally chopping of living trees is generally forbidden (since the 1960s, when the forest department was created as a new land use type), not making possible the
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The use of the land for fruit production is not possible with animals grazing, but this was also the case before, as to the herder's opinion
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
calidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to reduced stocking rates in comparison with village-pastures (and the soviet times), better water quality
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
oportunidades recreativas
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Better control of runoff, but steeper land
drenaje de agua en exceso
Suelo
cubierta del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
40%
Cantidad luego de MST:
80%
Comentarios/ especifique:
Higher cover than on village-pastures
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Cantidad antes de MST:
36 species
Cantidad luego de MST:
47 species
Comentarios/ especifique:
More plant systematical diversity
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
According to forest department the area above Karsang, due to ist trees, is more prone to fires than other areas
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
A possible adaption to dryer conditions would be smaller herds.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
4 Years ago a herd of 400 animals had to be sold due to disease. Since then M was able to rebuild a herd of 500 animals. On a short term investing into animals is expensive but pays quickly. The maintenance costs are finally decisive, but quite constant.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
1 Household
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The herder gets paid by the villagers for taking care of their animals
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: According to the herder, young people do not (want to) bear the very physical work.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Grazing stabilises the soils and is thus a prevention against gully erosion in areas with low cover (former cropland). Animals have the same effect as the terraces built years ago. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing activity should continue, once M. is too old for working. |
| The animals provide for soil fertility by their dung, instead of the fertilisers used in Soviet times. This positively influences the share of palatable plants and cover in general and, by this, soil moisture. |
| The area on the forest department is a good alternative to the much too small pasture-area near the village |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Form of land use making it possible to take some pressure from the common pastures without great damages. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It needs to be assured that also poorer families, who depend even more on livestock breeding than richer ones, can give their animals to M. or other professional herders. This could be realised by engaging herder assistants from poor families |
|
The rotational scheme is much more elaborated than in the case of the villages' pastures, which can be explained by more land available How can they be sustained / enhanced? Land users like M. should be addressed by forest administration to elaborate legal forms of herding with little damages on natural resources on this land. This will probably require land reforms. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Tree planting is not possible as long as the area is used for grazing. | By giving people land for longer periods (than one year) and with more freedoms in its use, people would gain interest in diversifying use: They would split up "their" land into haymaking, orchard and pasture areas. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The main problem of this form of grazing is that it doesn't allow the regrowth of trees. | Changing the areas use for grazing, respectively haymaking, every few years. |
| Cover is markedly reduced around the places where tents are installed. | By changing the camping place (but: limited flat areas!) or not keeping the animals in the same place at noon time and during night time, these areas might recover. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Seminomadic individual herding [Tayikistán]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos