Rotational grazing supported by additional water points [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
Чаронидани даврави бо нуктахои обнуши ва чойхои дамгири
technologies_1519 - Tayikistán
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 21 de agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 2 de noviembre de 2021 (public)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 8 de agosto de 2017 (inactive)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 19 de julio de 2017 (inactive)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 14 de marzo de 2017 (inactive)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Knowledge Management for Integrated Watershed Management and Disaster Risk Reduction (SDC / IWSM)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Livestock Committee at Village Level [Tayikistán]
Livestock committees were established with the goal to improve livestock health as well as natural resource management in the watersheds where the village pastures were situated. Livestock committees in the Muminabad district are organised at village level and coordinate their activities through the registered livestock association at district level.
- Compilador: Sa'dy Odinashoev
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
After the end of the Soviet era, an increased number of livestock with less grazing land available, has led to the deterioration of the pastures, including overgrazing, reduction of plant diversity, poor livestock health and soil erosion. To tackle the problem, Caritas Switzerland together with livestock committees at village level introduced rotational grazing supported by extra water points and rest places.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
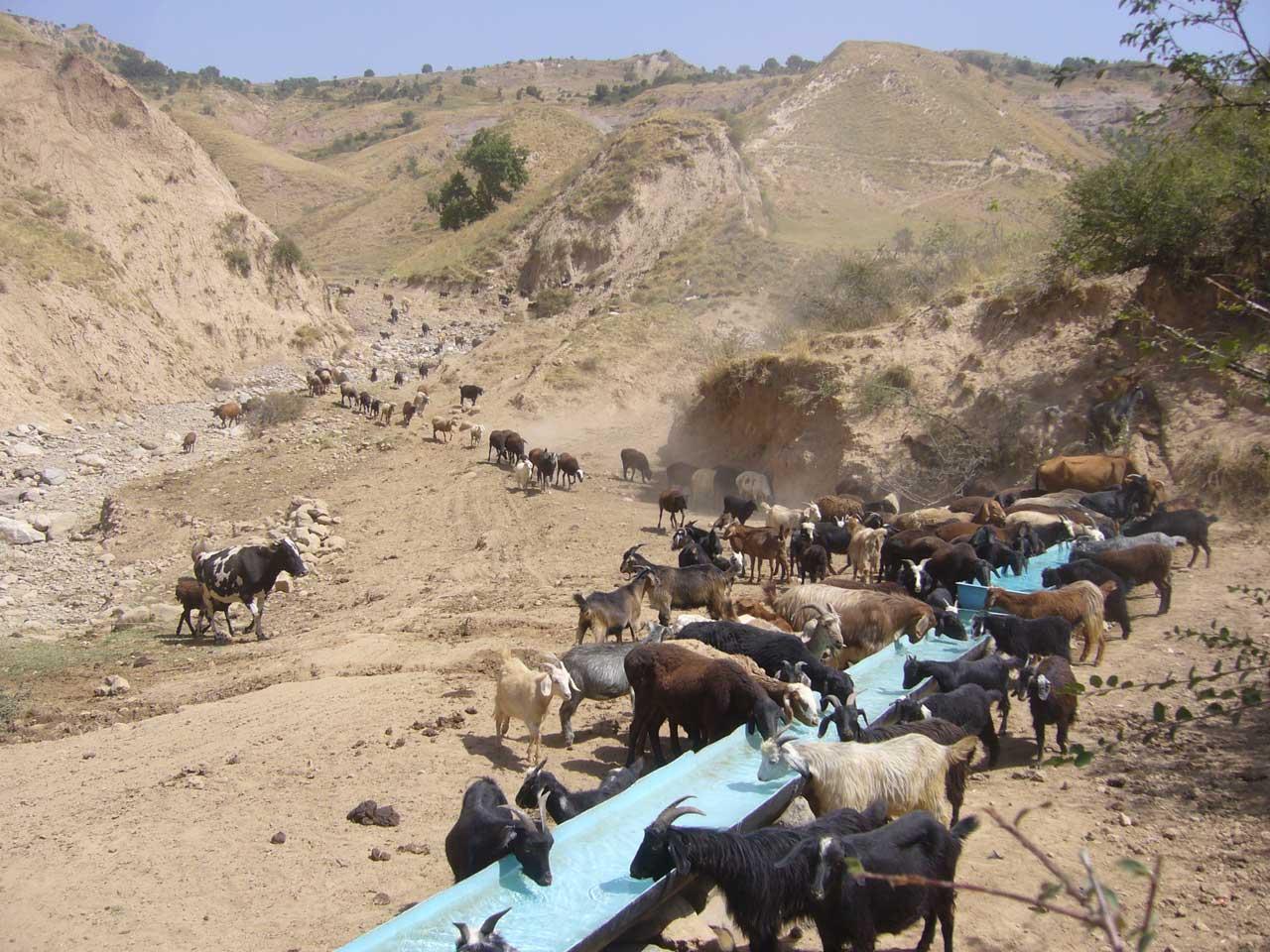
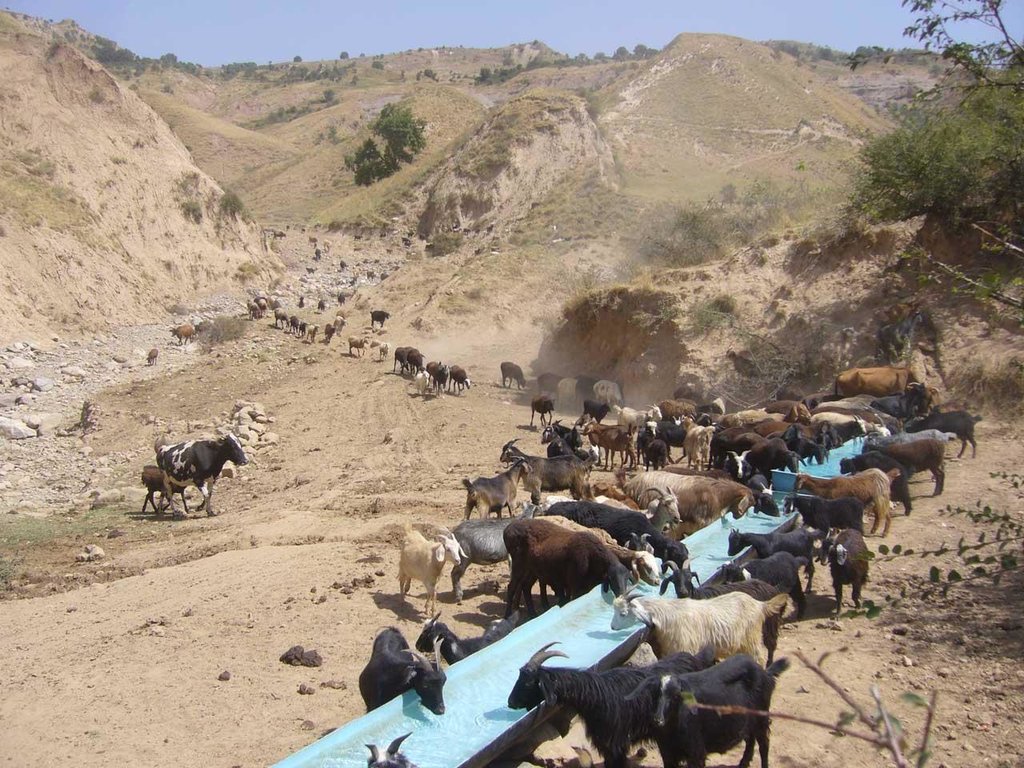
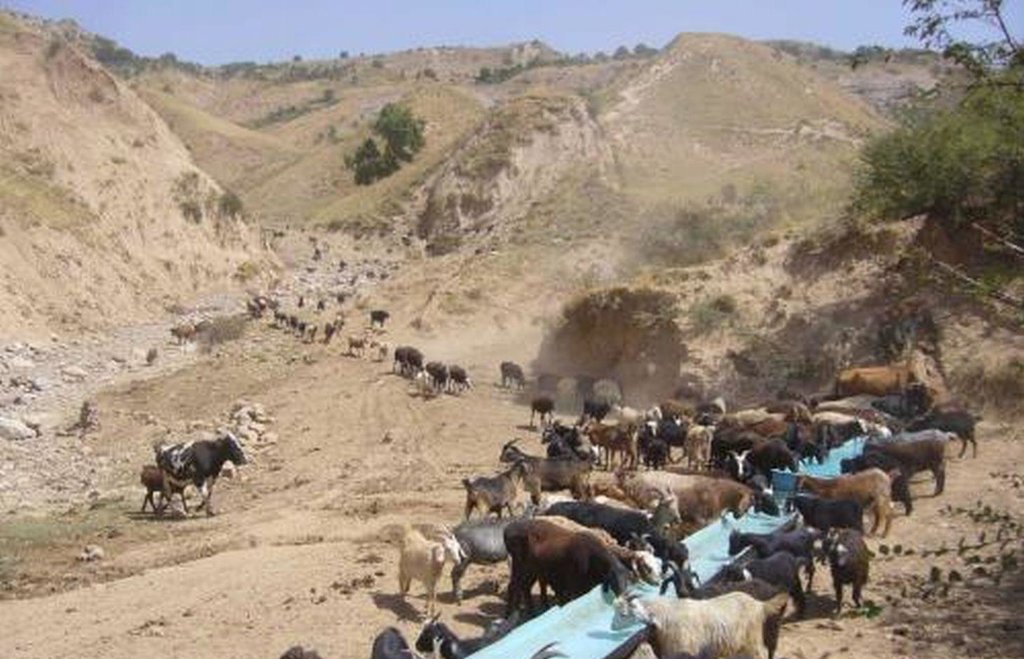
When in 2009 the project started in the two watersheds of Fayzabad and Gesh in Muminabad district, the communities had identified insufficient livestock water points in the pastures, and poor pasture management as top priorities concerning natural resource management in the watersheds. At that time, one of the biggest problems for livestock and herders was the difficult access to water when grazing the daily pastures above the villages. At lunch time, herds had to walk long distances (4-5 kilometers) and actually had to come back to the villages for drinking water. Climbing twice a day to the pasture costs the cattle a lot of energy leading to a yearly loss of up to 40-50 kg, according to a Caritas Switzerland study. One initial measure to improve the condition of the livestock was therefore to establish water points in the pastures. At first, water sources that supply water throughout the year were identified.
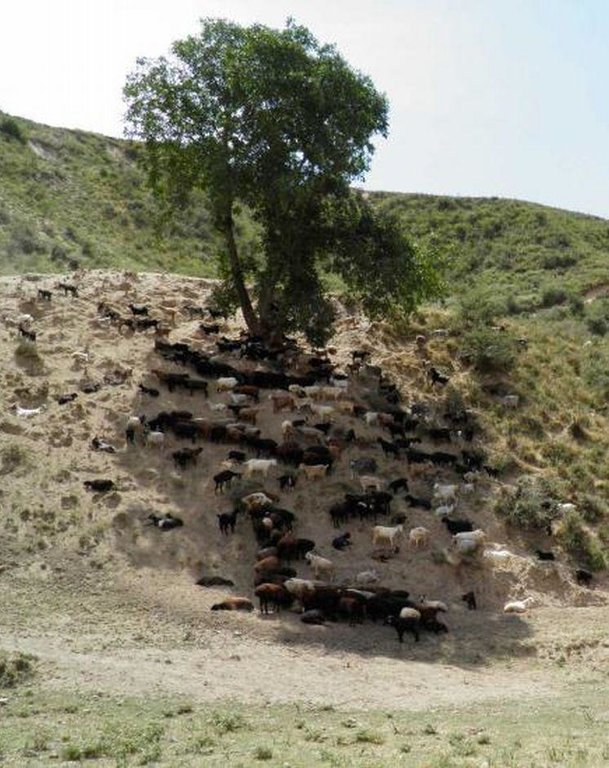
Purpose of the Technology: The water is now collected in a cement catchment, from where it is channelled through pipes to the drinking water points for animals. In some cases water tanks are placed above water points, to collect water and to distribute it to the water points. Additionally, rest places were found for the livestock, where they can have a rest in the shade after drinking water on hot summer days.
In conjunction to the establishment of water points, a rotational grazing scheme was introduced. The pasture land in the watershed was divided into ten parts and in each plot the animals were allowed to graze for five to eight days, assuring longer growing times for grass on specific pastures and thus increasing the quantity of grass and the quality of the pastures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Livestock committees, consisting of five people, were organised. They took the lead in developing appropriate grazing schemes and discussing the location of the water points with the villagers. They are in charge of further maintenance of the water points, and the daily organisation of the rotational grazing. One of the five committee members is the shepherd. Every morning he accompanies the herd and checks the water points and the rest places. Once a month he collects one Somoni from each family to cover costs arising from this method of pasture management in the watershed.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented on pasture land where animal drinking water is readily available only in spring, and during the rest of the year the distances to water sources are long. Daily pastures in stony terrain with steep slopes and pastures situated higher up are difficult to reach. The livestock grazing on common grazing land are controlled by the head shepherd with the task of coordinating the different helpers and having overall responsibility for herding the livestock.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tajikistan, Khatlon
Especifique más el lugar :
Muminabad
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 100-1,000 km2
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 93.74 km2.
11 projects applied this technology, however, in the cost section of this case study costs are calculated for only one of these 11 projects (Faizabad watersheds)
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- bayas
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- frutos secos (castañas, pistachos, nuez, almendras, etc.)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 145Longest growing period from month to month: March-September

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
- rotational grazing
Tipo de animal:
- cabras
- Livestock density (if relevant): > 100 LU /km2

Bosques
Productos y servicios:
- Otros productos forestales
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Animal trampling and little vegetation cover, wind erosion, water erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Bad pastures, bad access to water points.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: rotational grazing
Grazingland comments: Healthy livestock go out to the summer pastures and cows that are used for milk stay in the village along with the sick animals.
Type of grazing system comments: Healthy livestock go out to the summer pastures and cows that are used for milk stay in the village along with the sick animals.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (bad management of pastures), population pressure (many animals in the pastures)
Secondary causes of degradation: inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
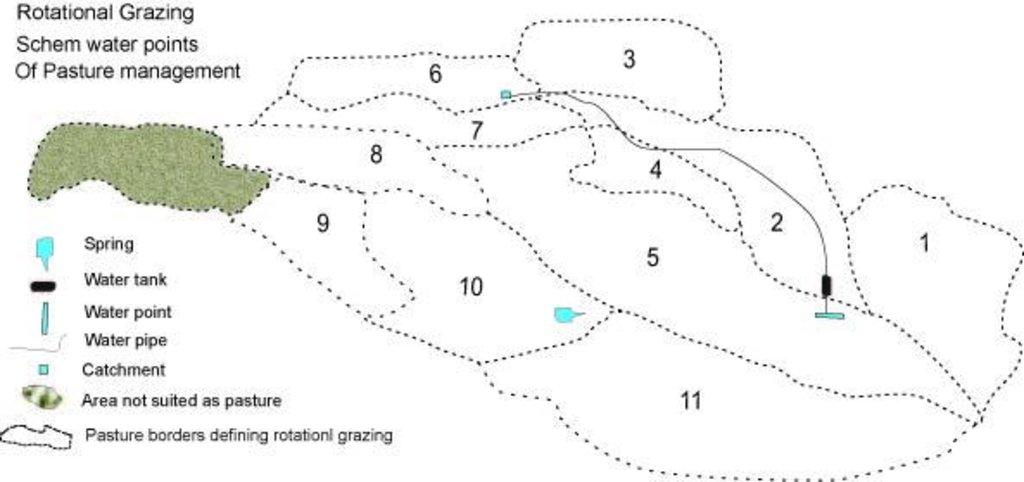
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Rotational grazing map for pasture management.
Location: Muminabad district. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Date: 2010-12-27
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5.00
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6.00
Trees/ shrubs species: maple
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, wallnut
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 80.00%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from grazing land to rotational grazing land
Layout change according to natural and human environment: water points
Autor:
Sa'dy Odinashoev, Muminabad
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
6.00
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting trees to create rest places for livestock | spring |
| 2. | Planting trees to create rest places for livestock | |
| 3. | water points | 2 months |
| 4. | construction of the pipeline from the spring to the water points | 1 month |
| 5. | catchment device on the spring | |
| 6. | catchment device on the spring | |
| 7. | calculating carring capacity and number of days of grazing period on each plot | |
| 8. | calculating carring capacity and number of days of grazing period on each plot |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Planting trees incl. seeds | Persons/day | 20,0 | 5,5 | 110,0 | 20,0 |
| Mano de obra | Waterpoints construction labour | Persons/day | 160,0 | 5,5 | 880,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Pipeline Construction incl. Watertanks etc | pipeline | 1,0 | 6648,0 | 6648,0 | 30,0 |
| Equipo | Catchement device | device | 1,0 | 353,0 | 353,0 | 20,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 7991,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 7991,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Caritas
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protecting young trees with dead branches from thorny bushes | 2-3 years |
| 2. | Protecting young trees with dead branches from thorny bushes | |
| 3. | Watering of trees (done by sheperd) | 1-2 years |
| 4. | Watering of trees (done by sheperd) | |
| 5. | rotational grazing and checking the water catchment and distribution system (salary for shepherd) | 8 months |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | rotational grazing and checking the water catchment and distribution system | ha | 800,0 | 0,7975 | 638,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Protecting young trees with dead branches from thorny bushes | Persons/day | 20,0 | 5,5 | 110,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 748,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 748,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: spade, possible water tap, shovels, spades
The costs were calculated for infrastructure establishment, labour etc. applying to the whole area of 800 ha.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Distance to the water source, and the availability of high resolution satellite maps (the technology is cheaper if maps are available because the planning process gets facilitated).
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landforms occure also in ridges.
Slopes on average are also moderate sometimes.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average can somtimes be deep.
Soil fertility is low on spring pastures, medium where the animals are grazing and high on the top of the watershed.
Topsoil organic matter is on the top high and medium in the middle.
Soil drainage / infiltration is good on the top of the watershed and medium in the middle of the watershed.
Soil water storage capacity is high on the top, medium in the middle and very low on the bottom.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table is everywhere 5-50 m
Water quality (untreated) is als sometime poor.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The men do most of the work out in the fields, such as carrying water and walking to the fields.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
2% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: most families have remittances from Russia
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
Comentarios:
Common grazing land (500ha / 400 households)
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
in the upper area more grass
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
perenial plants
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
milk, meat
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
No water available previously
calidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
No water available previously
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
less money spent on vets
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
more milk prduced
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
less walking for herders
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
pasture area
Comentarios/ especifique:
road to the new pastures
Water payments
Comentarios/ especifique:
No payment previously
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades culturales
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
livestock commitee have respect in the village
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
villagers
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Previously a lot of conflict in this area, regular meeting have helped reduce these.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
Empowerment of women and marginalised groups. Women are involved in the workshops
collaboration between different stakeholders
Comentarios/ especifique:
watershed group in livestock committee in the village
Livelihood and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
water points
calidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
filtering in the spring
escurrimiento superficial
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
more grass
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cattle do not need to walk over soem areas
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to better management
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
more plants
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
grass
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
Increase in temperature --> install more water points
Increase or decrease in rainfall --> adapt the rotational grazing system
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
500 households in an area of 93.7 km^2 (10 persons/km^2)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
Comentarios:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
480 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: nine other villages would like to adopt this technology
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
More water points How can they be sustained / enhanced? Less risks for their animals |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Rotational grazing to improve grass cover |
|
Better incomes for the farmer and at the same time pasture ressources are better managed How can they be sustained / enhanced? more meetings and workshops |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| difficult to work with maps | one day workshop |
| one person had to share their water with the rest of the village | organise meetings --> good communication, show the advantages to everybody |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| One year for such a project is too short | project should be extended to 2-3 years as within three years the trees in the rest places will be well established |
| only one water point it is not enough to improve soil and water conservation | rotational grazing and rest places have to be implemented together with water points |
| young trees have to be protected | Using PET bottles or thorny bushes |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
16/07/2010
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Livestock Committee at Village Level [Tayikistán]
Livestock committees were established with the goal to improve livestock health as well as natural resource management in the watersheds where the village pastures were situated. Livestock committees in the Muminabad district are organised at village level and coordinate their activities through the registered livestock association at district level.
- Compilador: Sa'dy Odinashoev
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos