Orchard establishment on a former wheat plot, by planting fruit tree seedlings in combination with sowing Alfalfa [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Malgorzata Conder
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1138 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - KirguistánNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Conversion of wheat monocropping into an Alfalfa plot with the aim to establish an orchard
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
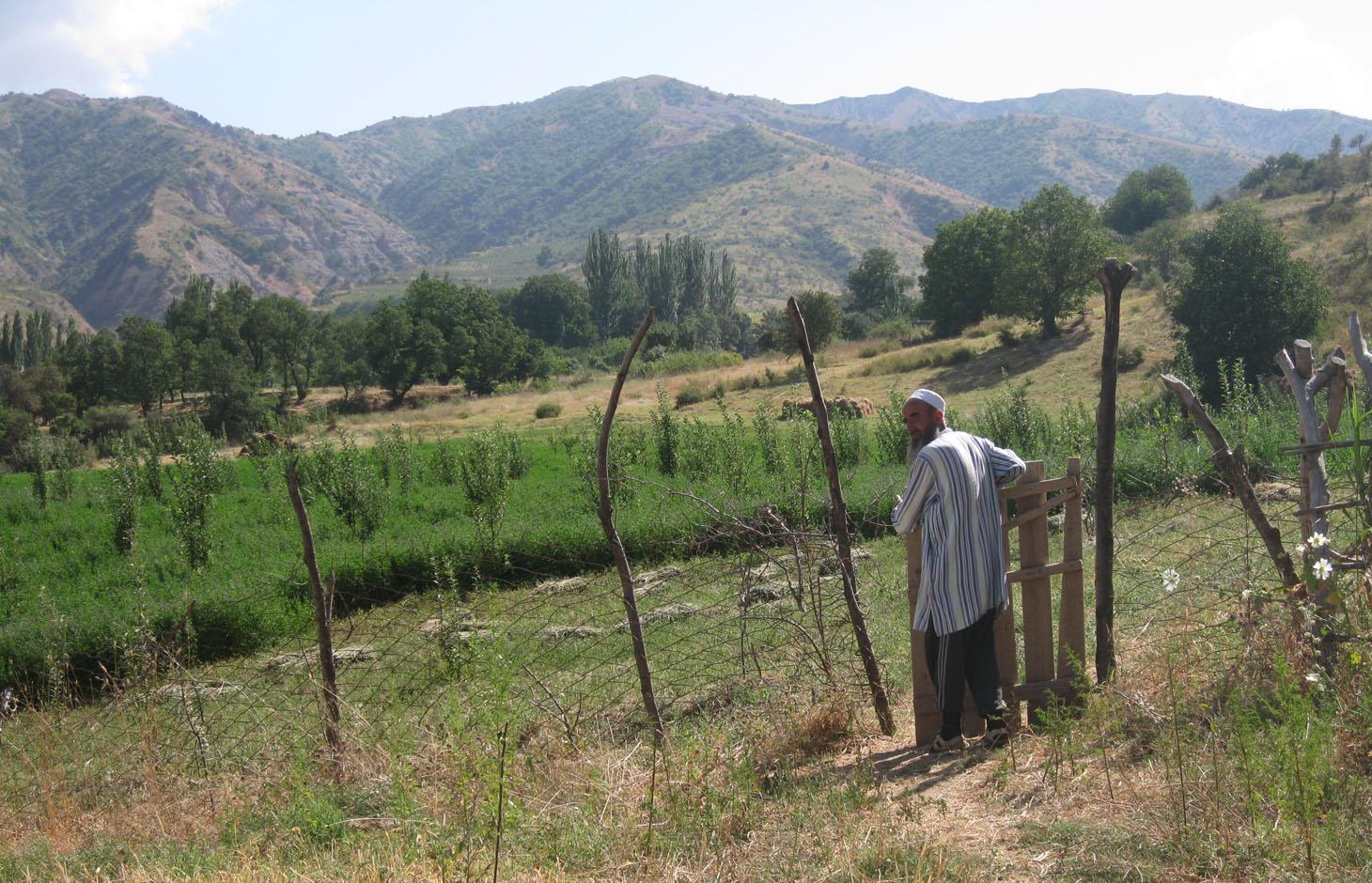
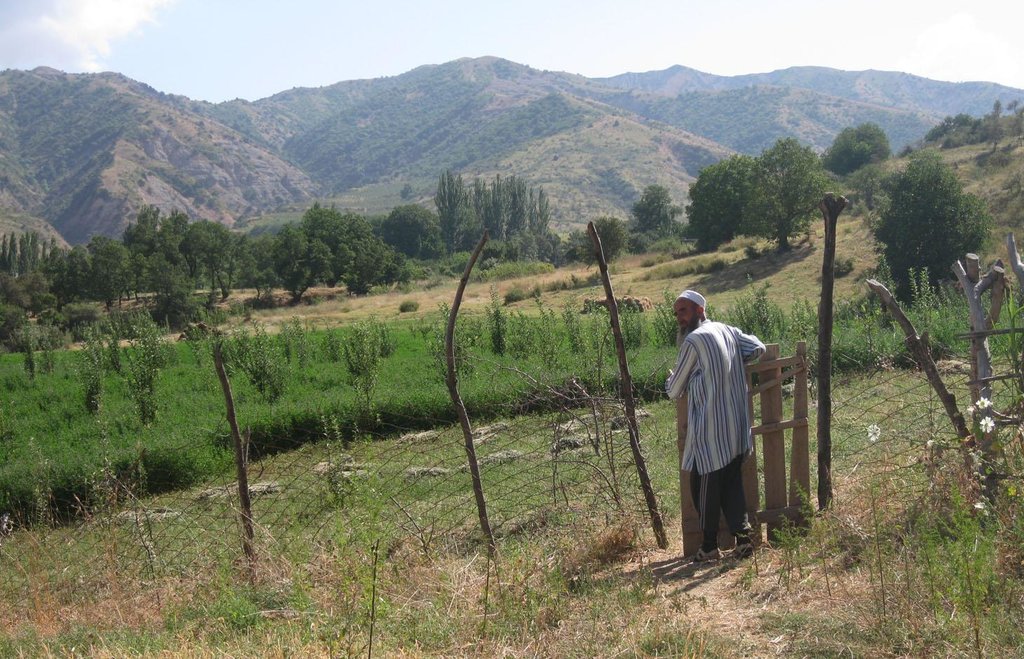
In 2009 the farmer changed his wheat plot into an Alfalfa plot where he also planted fruit tree seedlings in between to establish an orchard. One hectare is used for the perennial cropping of Alfalfa. Alfalfa cropping supplements beneficial soil functions which are crucial for the establishment of an orchard. The plot lies on a narrow plateau next to other wheat crops. The plot is mainly bordered by fruit and nut orchards on a gentle slope, and by a steep slope of the riverbed. A solid fence prevents boars from entering the area through the nut orchard. The plot is not accessible by the steep slope. Two fences are built from the side of the neighboring wheat plots. One fence works like an entrance gate to all the plots on that plateau. A second fence indicates the boundaries between the farmers' Alfalfa crop and the wheat plots belonging to other farmers. The whole family is working on the farm land, consisting of several plots which are distributed over the valley. The children are mainly guarding the cropland.
Purpose of the Technology: In order to establish an orchard, first the farmer planted Alfalfa, which maintains more moisture in the soil and hence creates favorable conditions for tree growth. The wheat cropping was drying out the soil. Therefore during heavy rainfall events water infiltration was limited, and the strong runoff washed away the wheat crop. It was the farmer’s initiative to change the crop management, but Caritas Switzerland supported him with a financial grant. Alfalfa can be harvested several times a year, which he can use as fodder for the livestock or as cash crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The first year after the crop rotation there was no benefit, as the Alfalfa did not give any harvest yet. According to the farmer, Alfalfa seeds were relatively cheap (15 TJS per kg) and result in a good harvest. Currently he is harvesting Alfalfa three times a year, wheat could only be harvested once a year. The whole family was involved in the establishment of the alfalfa crop and tree planting, by ploughing, sawing Alfalfa, planting the seedlings and constructing the fence. Despite the fence, the crop is often guarded by the farmer or his children because boars enter his property. After the first year some seedlings dried out which he had to replace. Presently, little maintenance is required, only guarding and cutting Alfalfa.
Natural / human environment: The farmer’s plot is situated on a plateau on the other side of the riverbed, from where the village of Momandion is located. It takes some 15 minutes to get from their house to the plot. One of his neighbors adopted the technology of sowing Alfalfa and planting fruit tree seedlings.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Especifique más el lugar :
Muminabad
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
Total crop size is around 1.5 ha, lucerne crop is around 1 ha. The remaining area is a small wheat plot and meadow with some sparse walnut trees. A fruit and nut tree orchard is above the fenced crop.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Farmers idea, one third was payed by himself, the rest was supported by Caritas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cultivos para forraje - alfalfa
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- frutas, otros
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, poor nutrient and moisture availability in the soil, high runoff
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, poor soil moisture availability, high runoff, declining yields
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Fruits of growing orchard will be food and probably cash crop in future
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
Comentarios:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- variedades vegetales/ razas animales mejoradas
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pk: desmoronamiento y encostramiento
- Pi: sellado de suelo

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), poverty / wealth (Fear of food insecurity pushed farmer to plant wheat, year by year)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (No knowledge about alternative and beneficial land management)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
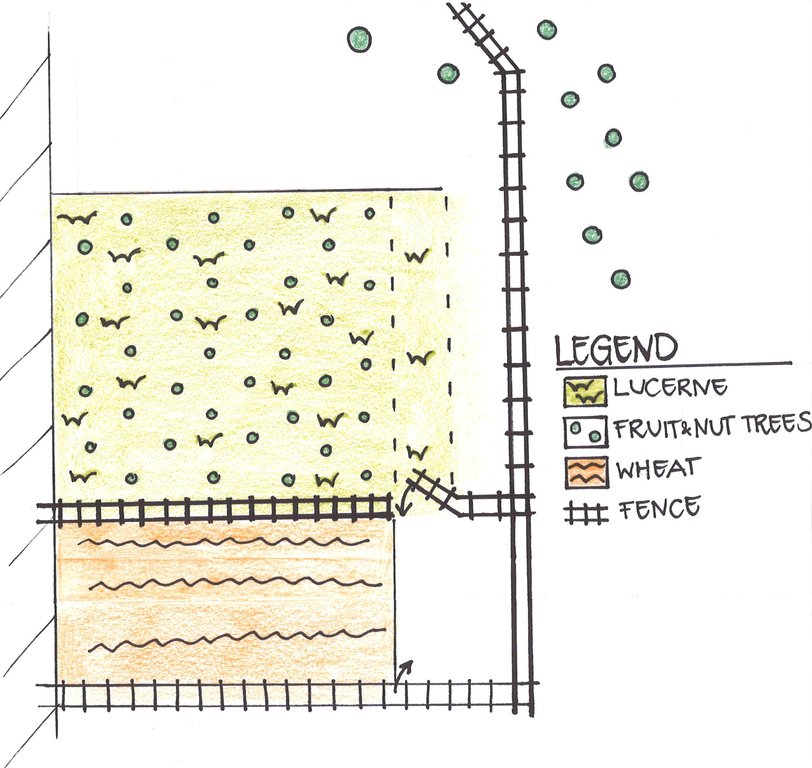
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The farmer’s property is located on a plateau, surrounded by an upper orchard on a slope (in the top right corner on the figure) and delimited by a steep embankment (on the left on the figure). The Lucerne plot is protected by a fence and the embankment to hinder intrusions of boars. There is a well locked entrance to get to the crop. A second fence protects the adjacent wheat crops and the Lucerne plot. Around 600 fruit trees are planted in the crop leaving a buffer strip of Lucerne.
Location: Momandion, Obishur watershed. Muminabad, Kathlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Alfalfa to recover soil for orchard
Aligned: -contour
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Change of land use type: Conversion from wheat to fenced Alfalfa crop and orchard
Alfalfa crop has a twofold function, as a crop which is harvested several times a year and as cover crop to reestablish soil properties
Autor:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
12.40
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying and planting 600 trees: 10 Min/ tree for digging | once |
| 2. | After first year: 100 trees dried out | once |
| 3. | Fencing 400 m, by 6-7 pers, 10-11 days (8 h a day) | once (spring) |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Planting trees | Persons/day | 12,5 | 12,4 | 155,0 | 37,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting trees for replacment | Persons/day | 2,1 | 12,4 | 26,04 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Plowing labour | Persons/day | 1,0 | 12,4 | 12,4 | |
| Mano de obra | Sowing | Persons/day | 0,27 | 12,4 | 3,35 | |
| Equipo | Plowing machine | days | 1,0 | 103,5 | 103,5 | 37,0 |
| Equipo | Petrol | litres | 120,0 | 1,1383333 | 136,6 | 37,0 |
| Material para plantas | Buying trees | trees | 600,0 | 0,62116666 | 372,7 | 37,0 |
| Material para plantas | Buying tree replacments | trees | 100,0 | 1,035 | 103,5 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | kg | 20,0 | 3,1 | 62,0 | 37,0 |
| Material de construcción | Fence | area | 1,0 | 1490,7 | 1490,7 | 37,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 2465,79 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 2465,79 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Caritas
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting/Cutting Alfalfa 3 times and seeds 1 time, 8 Pers one week (first cut) | 4 times a year |
| 2. | Soil loosening around 600 trees | spring/ once |
| 3. | Looking after the orchard, 2 or 5 hours per day | every day |
| 4. | Pruning after 5 years (in future), one month | spring/ once every five years |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Soil loosening | Persons/day | 9,375 | 12,4 | 116,25 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Looking after orchard | days | 365,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Mano de obra | Pruning after 5 years | Persons/day | 25,0 | 12,4 | 310,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Harvesting/Cutting Alfalfa | Persons/day | 192,0 | 12,4 | 2380,8 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 2807,05 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 2807,05 | |||||
Comentarios:
2.5.4.2 Harvesting and cutting labour input is estimated proportinally to the expected yield. The first cut has a max. yield, the second yield amounts up to 70%, the third some 50% of the initial yield. Labour input for harvest might be to high as it was not indicated by hours, but by days. The farmer paid only a part of the initial costs, which amount some 37% of the total costs.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Fencing is very expensive due to high material costs. It is a very laborious and time consuming work.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200mm asl, wheater station Muminabad)
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landforms hill slopes: Nut and fruit orchard right above the crop
Landforms foot slopes: Plateau
Slopes on average: 12-16%
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: High
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water medium: Winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm)
Availability of surface water poor/none: no rainfall from July to August
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Level of mechanization manual labour: Everything except plowing
Level of mechanization mechanised: Plowing
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
1.4 ha, if 7.7 pers per household
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
riesgo de fracaso de producción
diversidad de producto
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
demanda de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
No fertlizer, less controlling
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Livelihood and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no se sabe |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Alfalfa seeds are more expensive than other seeds (e.g. wheat) and in the first year just one cut can be done. In the second year already several cuts are possible and assure a high yield. It is expensive to establish an orchard and in the first 5 years there is no harvest.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Neighboring farmer adopted Technology on one of his plots (even though less technical), other is interested.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
After one time sowing, several cuts are possible from the second year on. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Spread the experience of the farmer. |
|
Perennial crops are beneficial to soil and increases the income of the farmer. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Spread technology through demonstrations, work shops etc. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Alfalfa gives good yield and is a good conservation measure for soil and water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Workshops or institutional incentives for farmers to promote perennial crops. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| First year might result in more input than output because just one cut is possible and an orchard must grow at least 5 years to give fruits. | Raise awareness about long-term benefits or give incentives in the establishment phase. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos