No Till [Federación Rusa]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Peter Liebelt
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, David Streiff
Нулевая обработка
technologies_1319 - Federación Rusa
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Sustainable land management in the Russian steppes (KULUNDA / GLUES)1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
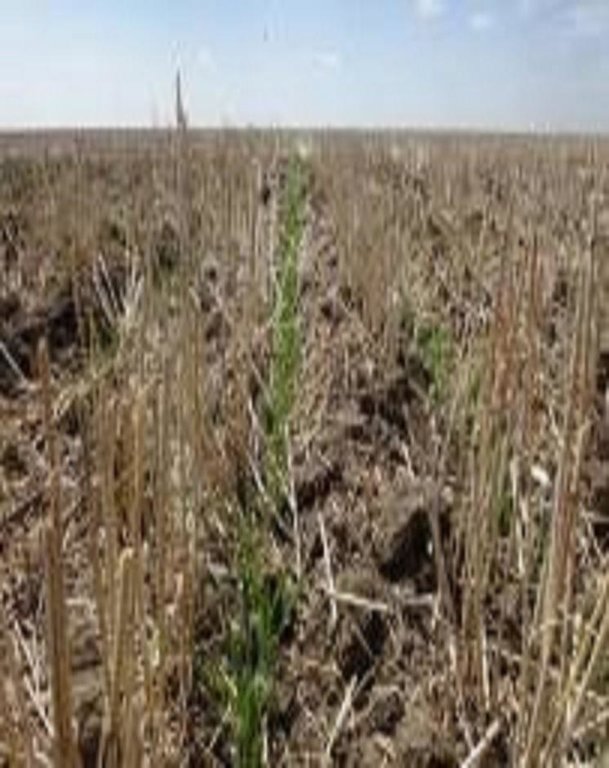
No tillage is based on direct seeding with the innovative/ modern direct seeder Condor and works without any kind of soil disturbance.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
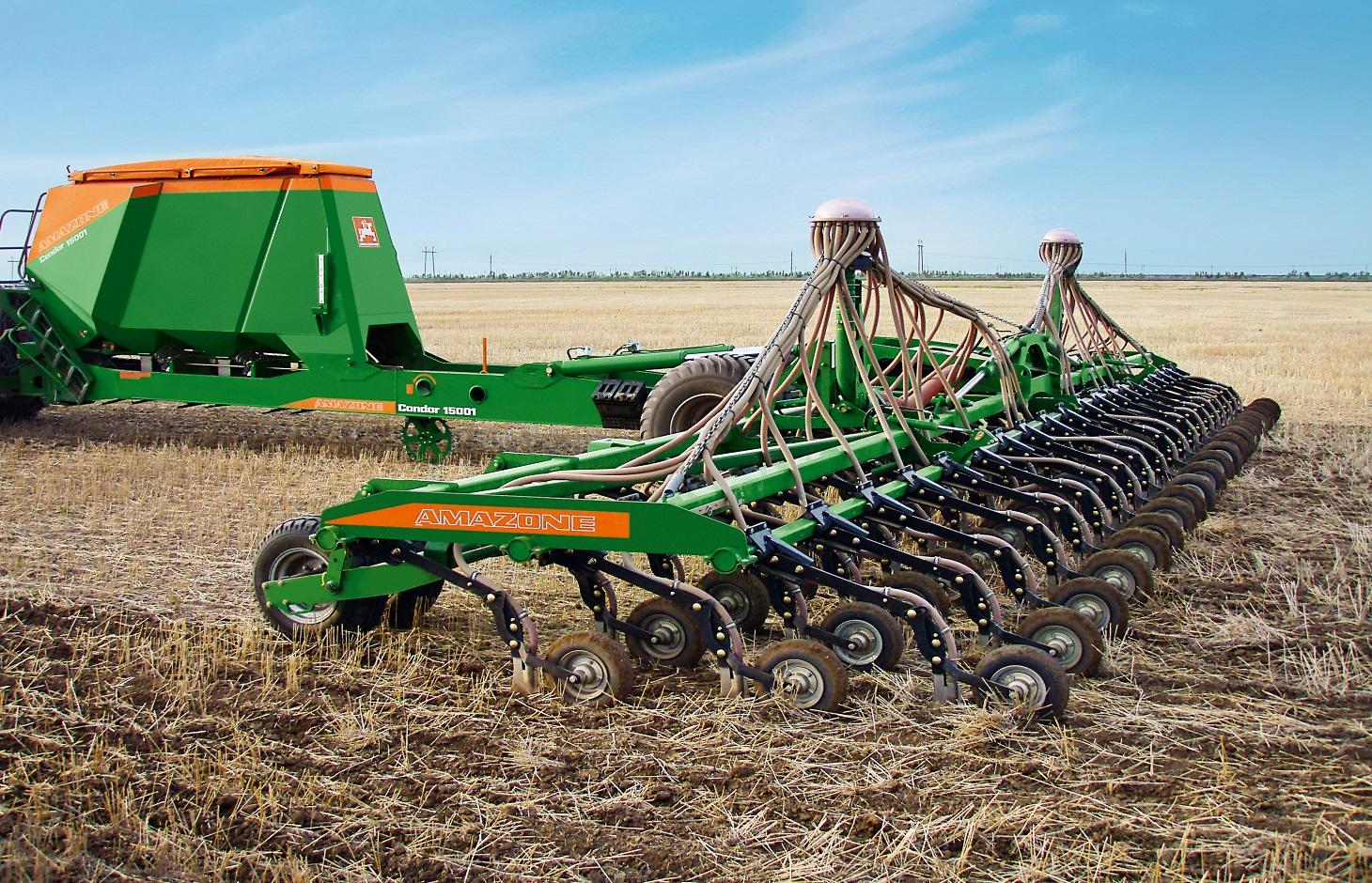
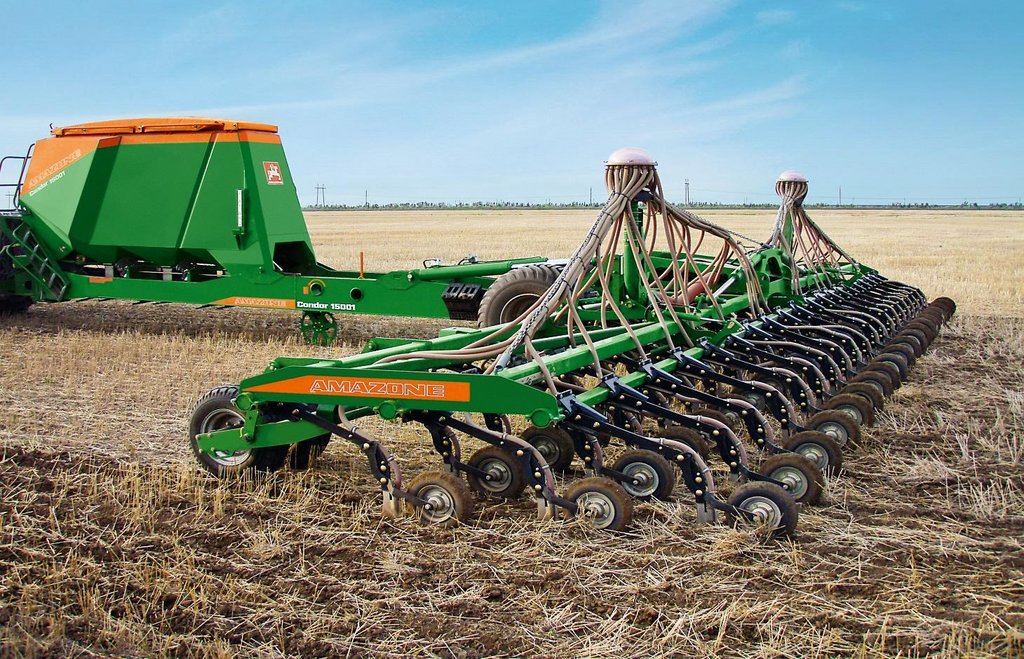
"No-Till" is a key element of the ‘modern cropping system/ Canadian System’ in the Kulunda steppe. In contrast to minimum tillage an innovative modern direct seeding machine is used. The successful implementation of “No-Till” requires an adaptation of the whole cropping system including crop rotation. Rotation includes a succession of cereal crops (e.g. spring wheat), legumes (peas), and oil seed crops. In the study area predominantly spring cereals are grown. The direct seeder ‘Condor tine seeder’ (Amazone) was used for direct seeding. In contrast to the SZS 2.1 seeder used for minimum tillage it has flexible, individually depth-guided tine coulters, which ensure a high precision of seed placement. When opening the seed furrow, the narrow coulter moves little soil, so that the valuable soil moisture remains in the soil, and there is sufficient fine soil to ensure the optimum seed/ soil contact. Straw is safely cleared from the seed furrow, preventing the "hairpinning-effect" which is the pressing of straw by the coulter into the sowing slit. During the sowing period fertilizers are applied and broad spectrum herbicide in autumn and selective pesticides in the growing season are sprayed which help to increase yield.
No-till works without intensive primary tillage and stubble cultivation that saves time, fuel and reduces soil water evaporation. No-till increases soil aggregate stability, helps to reduce the risk of soil erosion, leads to a higher soil fertility and reduces soil water losses. Weed control through crop rotation and herbicide application allows to omit mechanical weeding and thus to protect the soil against fertility decline and soil water loss. Fertilization becomes more important, because of the decreased mineralization rate under no soil tillage, especially at the beginning of the conversion of the cropping system and until soil organic matter could build up in the soil.
The Technology including crop rotation was tested in the field in 4 test plots with 4 repetitions at the test site in Poluyamki. Results showed that the intensity of soil tillage and seeding methods used had a great influence on crop establishment and expected yields. It was demonstrated that no tillage leads to higher water use efficiency and highest yields. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Minimized soil disturbance led to higher aggregate stability, which leads to a lower risk of wind erosion, increased soil organic carbon storage and soil fertility as well as available soil water content. The Modern Canadian system caused fixed production costs in form of annual depreciation and also additional costs due to the application of fertilizers and pesticides, the prices of which increased in the last four years. Due to not finalised land rights reforms, uncertain credits and harvest insurance farmers are reluctant to invest in new machines.
The test site in Poluyamki is located in the dry steppe of the border region next to Kazakhstan, where, due to the climatic conditions, no natural afforestation occurs, and the planted windbreaks don’t grow vigorously due to the prevailing aridity. The annual precipitation is under 300 mm a year. Probably the greatest climatic influence factor is the precipitation - in terms of quantity and space/ time distribution and, due to high summer temperatures, the high rates of evapotranspiration. The total yearly precipitation rate is the primary yield-limiting factor in all steppe regions. The ratio between precipitation and evaporation is negative. In the late weeks of spring, prolonged droughts must be expected in 5-year cycles, limiting germination and crop establishment. The soils are classed among those of cool-tempered grasslands. Due to their physical and chemical characteristics, these soils (Chernozems and Kastanozems) have high agronomic potential.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Federación Rusa
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Russian Federation/Altai Krai
Especifique más el lugar :
Mikhaylovski district (Pavlovski district, Mamontovski district)
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la Tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente a lo largo de un área, especifique el área que cubre (en km2):
0,13
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comentarios:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Centre latitude: _52° 4'3.00"N Centre longitude: 79°54'26.16"E Test site Poluyamki
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.13 km2.
The total investigation area of the SLM Technology “Minimum Tillage” refers to our test site areas: 1. Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon: 13ha managed by Minimum Tillage; 2. Pervomayskiy, Mamontovskiy Rayon: 10ha managed by Minimum Tillage; 3. Komsomolskiy, Pavlovskiy Rayon: 3ha.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union increasingly innovative conservation technologies that are being developed in research experiments are implemented in practice. But the no technology of "No-till" as the most extreme form of conservation tillage is rarely applied in the study area. Thus the tested no-system is highly innovative for the Kulunda steppe.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación del suelo
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 110, Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): It's the decrease of soil organic carbon content in the soils, topsoil thickness through deflation and soil compaction, which lead to a decrease of soil fertility. Additionally, the negative soil water balance due to the high summer temperatures and evaporation and in addition the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation as a serious problem relating to the lack of soil water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land user that we work with and that implement the our new farming practices have a similar opinion relating the land use problems like the research staff of the project. But there are still a lot of farmer, that underestimate the ecological risks of soil degradation resulting from traditional soil management.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- perturbación mínima del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo
A3: Diferencie sistemas de labranza:
A 3.1: Sin labranza
Comentarios:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, green manure, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable
- Ed; deflación y deposición
- Eo; efectos de degradación fuera del sitio:

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Conventional soil tillage by ploughing), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Bare fallow without vegetation cover), Capital for investments (Lack of capital for investment in modern adapted agricultural technologies)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms (Strong winds and storms - Sukhoveijs - from the southwestern central-Asiatic semi-desert regions cause a higher risk of wind erosion especially on traditional cultivated cropland without plant cover), droughts (The frequently occurring early-summer drought periods are particularly problematic for agricultural production), education, access to knowledge and support services (Need for better know how how to manage no-till systems. Need for more effective measures for knowledge transfer and capacity building.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación del suelo
- reducir la degradación del suelo
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
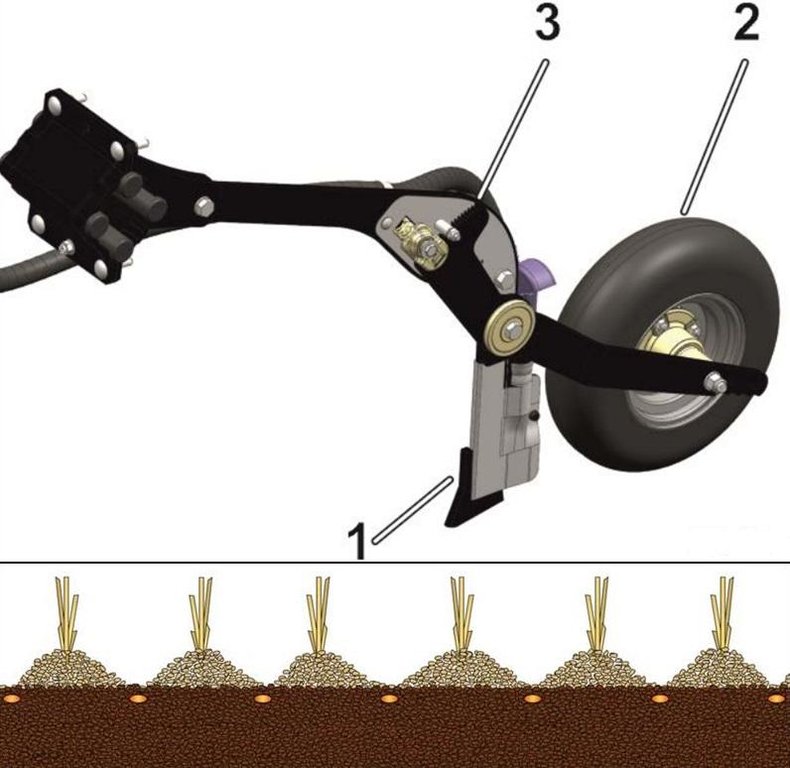
The coulter system of the direct seeder Condor based on an individually depth guided tine coulter. When opening the seed furrow, the narrow coulter moves little soil, so that the soil moisture remains in the soil. The accurate depth control and the packer wheel lead to an optimum contact between seed an soil, which is very important especially in dry regions like the Kulunda dry steppe in Poluyamki. 1-Chisel coulter 2- Packer wheel 3-Air diffuser. Illustration: seed grains placed between the former sowing rows
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Crop rotation without bare fallow
Green manure
Material/ species: Pea (once in a rotation)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: with calcium ammonium nitrate
Quantity/ density: yearly
Remarks: 100kg/ha (spring wheat and rape), 50kg/ha (pea)
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat-pea-wheat-rape
Quantity/ density: 4 years
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Direct seeder Condor (Amazone company)
Autor:
AMAZONE Werke GmbH & Co KG
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Direct seeding | Late april/ early may |
| 2. | Fertilizer application | |
| 3. | Pest management | period of vegetation |
| 4. | Harvest | september |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,12 | 4,12 | |
| Equipo | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 15,96 | 15,96 | |
| Equipo | fuel | ha | 1,0 | 25,49 | 25,49 | |
| Material para plantas | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 19,37 | 19,37 | |
| Material para plantas | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 30,83 | 30,83 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 9,42 | 9,42 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 105,19 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 105,19 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor MTS 1221, Tractor Kirovets K 701, Harvester Don 1500, Direct seeder Condor 15001, Sprayer UX 5200
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
High initial investment in new machines. Compared to the Traditional Soviet System with conventional deep ploughing without fertilizer application fertilizer and pesticides are the main additional cost factors.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
- muy rico
Individuos o grupos:
- empleado (compañía, gobierno)
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There are generally less woman than men in rural regions caused by rural-urban migration. Furthermore, jobs in the in the field of crop production are not so attractive for woman. Traditionally, much more women work in the field of livestock farming.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
state: 45%, the data refer to the Altai Krai
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
In the first years after the change of the cropping system, there is an increased risk of crop losses due not correct/suitable management of the new cropping system
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Initial costs, first years for herbicides
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
but increase of costs for pesticides and fertilizer, decrease for fuel and labor
Impactos socioculturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
in general yes, but food security is not a problem in this region
mitigación de conflicto
contribution to human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors, like precipitation or the economic situation and financial power of the farmers
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
compactación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is a lower risk for compaction damage than under under traditional ploughing
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
especies benéficas
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
velocidad de viento
Otros impactos ecológicos
use of herbicide application
Comentarios/ especifique:
The no-till system works without mechanical weed control, therefore it must be a chemical weed control especially in the first years of no-till system.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
higher content of soil moisture
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The 3 farms where we have tested the technology of minimum tillage will partly apply this technology on their farming land. But it must be considered that the test farms of the KULUNDA project were interested in conservation technologies already at the beginning at the project and they are able to invest in new machinery to implement the tested SLM technology, that is not representative for the whole Kulunda-region.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
There is a trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors like the precipitation or conditions an economic situation of the financial power of the farms. For example the drier the conditions, the more sense is to minimize the tillage. But there is a need to invest in new machinery. In contrast to the Adapted cropping system (with minimum tillage) the modern Canadian system require new seeding machinery that that means high establishment cost. Therefore the implementation growth is not so significant compared to the adapted system that use already existing Soviet seeding machinery.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Increase of soil aggregate stability and improved soil structure thus better erosion control and protection of soil organic matter will improve soil fertility and water holding capacity |
| Minimization of evaporation losses through better soil cover |
| Lower input costs (materials, fuel, labour, time) and quicker field operations |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Application of chemical herbicides leads to higher costs and possible ecological risks. | Selective spraying using the “Amaspot” system that is based on infrared detection of weeds. |
| Higher requirements for fertilizers, especially at the beginning, due to lower mineralization rates and less nutrient availability compared to conventional cultivation. | Higher fertilizer application in the first years after conversion. |
| High initial investment costs for buying direct seeders | share machine and costs with other land users. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos