Roof rainwater harvesting system [Botswana]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Julius Atlhopheng
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Lekidi
technologies_1417 - Botswana
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
University of Botswana (University of Botswana) - Botswana1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
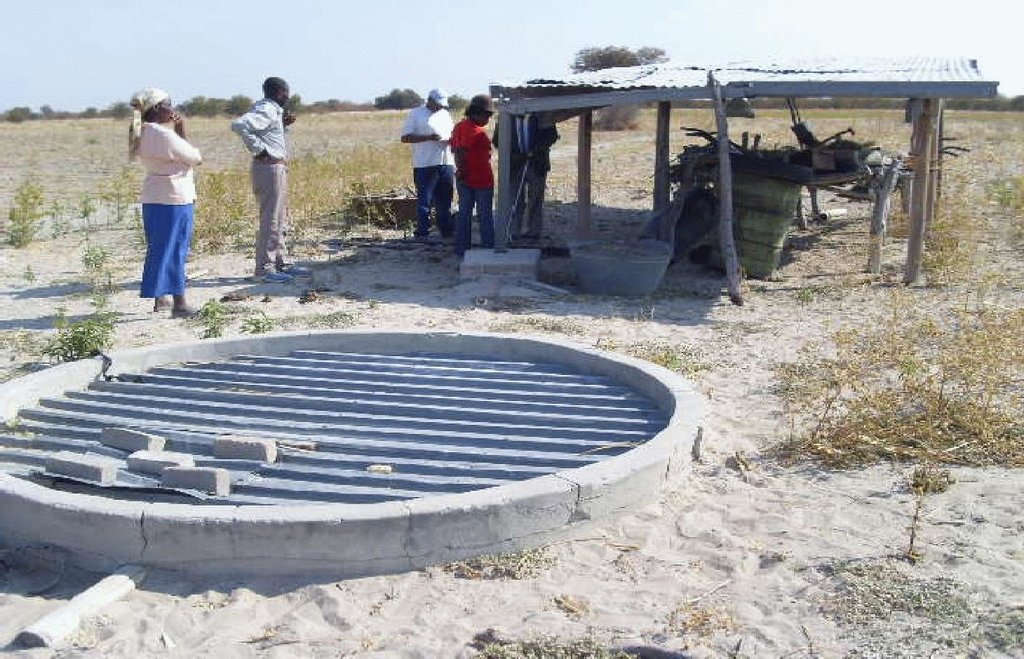
Roof rainwater catchment system using galvanised iron roof material, feeding underground water tank.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
A roof of galvanised iron (corrugated iron) with the dimensions 7 x 6m is constructed on a support of gum poles (see photos). The roof catches the rain. The rain water flows over the roof into pipes at the rear end of the roof (sloping side) into an underground conical water tank. The tank is made of bricks and mortar. The underground tank serves two key roles: i) it stores water for use during the dry spells or times of no rain; and ii) the tank keeps the water cool in this hot environment. The technology is most preferred for so-called ‘lands’ areas, to provide household drinking water. On average, these lands are distant from water sources (e.g. 2-15 km). Other benefits of storing rainwater include less pressure on natural water ponds, but this would be a secondary concern
Water is critical for human consumption and needed around the home. The cool water is effective in quenching the thirst; it reduces labour time to collect water thus freeing time to concentrate on other farm activities. The water is mainly for household drinking and household chores like washing. Some is used as drinking water for chickens and for the animals used for draught power (e.g. donkeys during ploughing). The units are for use by individual farmers and thus restricted to individual households. The owner or the farmer has exclusive rights to the use of the water. Some farmers indicated that, in times of no rain, or before the first rains, they collect water from the village in drums, and pour it into this underground water tank, thus using it as a reservoir. They especially like the persistent coolness of water stored in the underground tank.
The technology is for rainwater collection in four villages. Rainwater that flows over the roof is collected, for example, on galvanised iron roofs. The water then runs through gutters and a pipe to the underground water tank. To build the underground tank, the ground is excavated, to about 2m deep and about 3m wide. Within this hole, a drum-like feature is built with concrete bricks and mortar. After the wall of the tank is complete, it is then lined with mortar from the inside, and the base is also lined to form the completed tank. It is then sealed at over most of the surface leaving an opening with a lid. This opening is large enough for a man to enter for occasional cleaning of the groundwater tank. Thus the system comprises a roof, for collecting rainwater, and an underground tank for storing it.
The environment is semi-arid and seasonal rainfall dominates during the summer months of October to April. People depend on nearby boreholes for water in the lands areas or have to travel to the village (about 2-5km away on average, but can be up to 15km) to fetch water. Most boreholes are either privately owned or communal and water is rationed to about two drums per week or even fortnightly. Most of the borehole water in the area is brackish. Thus roof rainwater (which is fresh) acts as the preferred alternative source of water. The underground tank, once full, is equivalent to 110 drums. Most normal rain events fill the tank, and the water remains in use till the next rainy season, which was found to be the case at all four pilot sites visited. Thus the rainwater catchments systems offer water security in the lands areas; water of very good drinking quality (sweet taste, cooler).
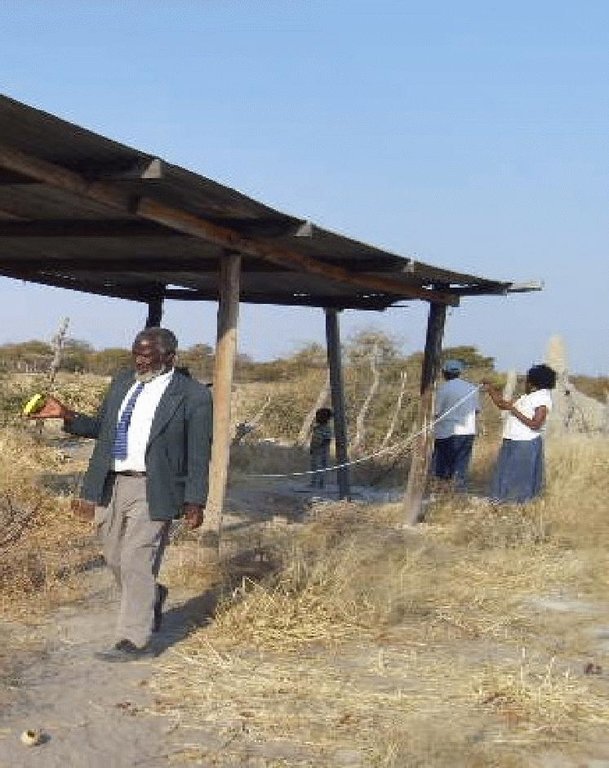
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
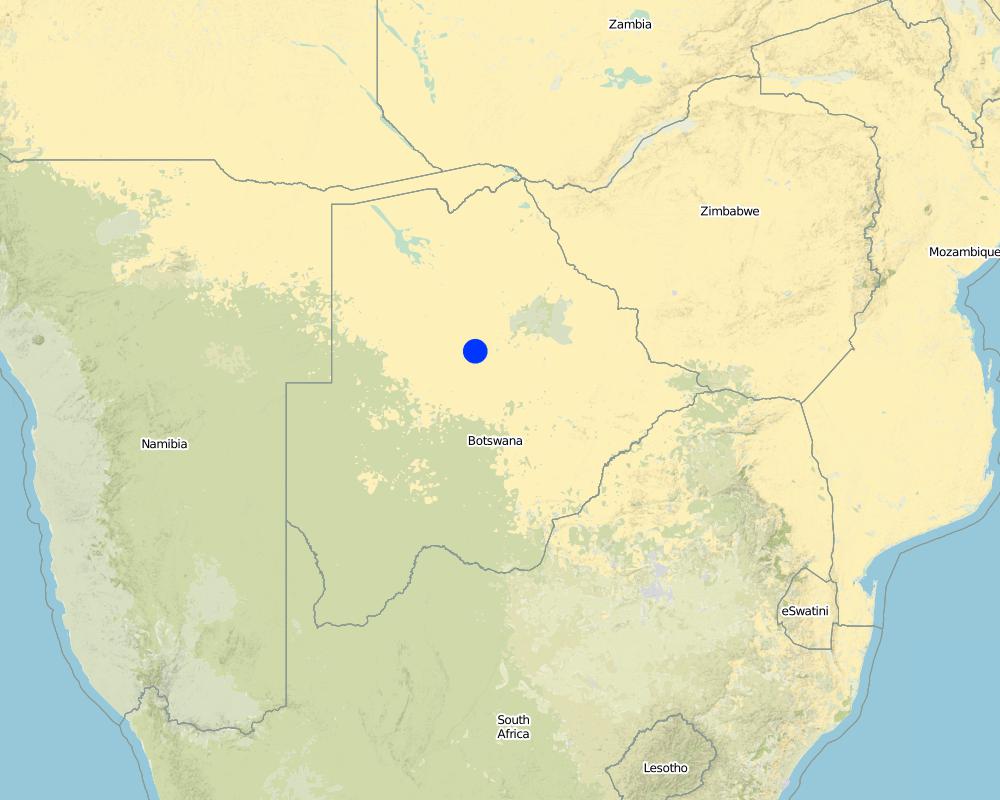
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Botswana
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Boteti area, in Central District of Botswana
Especifique más el lugar :
Central District
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
This is a roof rainwater catchment system which is about 7m by 6m = 42 m2. The collection tank has a capacity of 10 000 litres.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
This is an ALDEP (arable lands development project) which is specifically for arable lands areas, to ascertain water provision and it started in the 1980-1990s, then up to mid 2008.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 197, Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
- Ganadería de hacienda
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The water harvesting system is critical in a semi-arid environment, where water shortages are common. To augment water supplies, storage is needed especially in arable land areas where there are no coordinated water distributions like standpipes, as is the case in villages. People at the lands eke a living out of the arable fields, and assured water availability enables families to remain longer close to the fields for essential crop management, hence increased yields.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water shortage and poor water quality.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Very little in a way of cash crops as the production system is subsistence based.
Type of grazing system comments: Free range grazing
Constraints of settlement / urban: piped water is cheap
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cosecha de agua
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: droughts (Reduced water/moisture due to droughts), land tenure (livelihoods depending on fragile ecosystem)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (high stocking rates in dry areas), population pressure, poverty / wealth (limited access to water and saline water)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
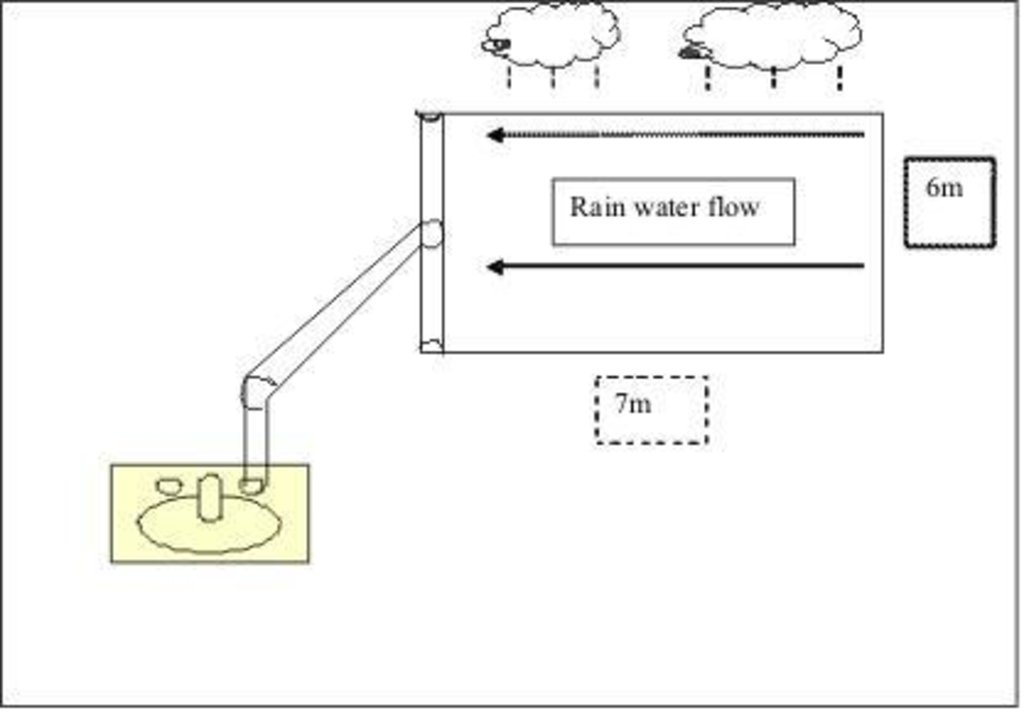
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The top lid of the underground tank:
Rain water falls onto the corrugated roof surface, which usually measures 7 x 6m. This water flows down into the gutters, then down through the pipe into an underground water storage tank (built from concrete blocks which are lined with a coating of mortar, or mortar is applied to wire mesh. Most storage tanks, when full, have a capacity of about 110 drums (a drum holds 200 litres). Without this system, a farmer usually only has about 2 drums per week.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Easy strycture or system to explain)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Needs professional builder to construct, but easy to run)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: is used as open storage for farm equipment, offers shade against the heat, as well as temporary shelter
Structural measure: Roof rainwater system (roof)
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 7
Structural measure: Tank specifications (conical)
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.75
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.5
Construction material (earth): To mix with cement
Construction material (wood): gum poles, rafters for supporting iron roof
Construction material (concrete): To build tank foundation
Construction material (other): iron
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10m3
Catchment area: 42m2
Beneficial area: 5m2
Autor:
Atlhopheng Julius, Botswana
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Pula
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
8,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5.00
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging pit | |
| 2. | Transporting sand, cement and concrete blocks | |
| 3. | Construction |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | labour by gov (8 person days) | ha | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | |
| Material de construcción | sand, cement, concrete block | ha | 1,0 | 1500,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 2012,5 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 251,56 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning roof | once a year, before onset of rains |
| 2. | Cleaning storage tank | once a year, before onset of rains |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 12,5 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 1,56 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Stock bricks, corrugated iron sheets, meshwire, gutters, wire nails. No machinery, just broom and bucket to collect sediment and dispose of it.
Prices of construction material for the roof rainwater system, fitted with the underground water storage system. All prices and exchange rates were calculated for 29 September 2008. The government subsidy was such that, men pay 30% of all costs, while women pay 20%. The 20-30% could be paid through labour (i.e. digging the pit, transporting sand and cement and serving as a labour hand during construction. Thus if the farmer offers labour, then he does not pay anything. The costs are calculated with labour input and its price or the local wage.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Cost of building materials, specifically iron sheets, timber, bricks, concrete and the professional builder from the government.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: subtropics. sub-tropical thermal climate (hot summers, cool winters)
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
- muy rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 50% of the land (rich cattle barons).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (most inhabitants).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (subsistence farmers).
Off-farm income specification: Saves labour time to fetch water. Very limited off-farm income opportunities for everyone, including non-adopters of the technology
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Comentarios:
Communal grazing and individual land ownership for ploughing. Water availed through communal boreholes in lands and cattle posts, but with individual standpipes in villages. Open access to surface water resources for livestock e.g. pans after rains. Dual grazing rights problem, whereby private ranchers graze in the commons, but the opposite not possible.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0.15 t/ha/y
Cantidad luego de MST:
0.195 t/ha/y
Comentarios/ especifique:
30% increase due to more time to manage crops better e.g. weeding
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
mainly chickens and small stock
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
40%
Cantidad luego de MST:
10%
Comentarios/ especifique:
more time on farm
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
water year round
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Cantidad antes de MST:
5%
Cantidad luego de MST:
90%
Comentarios/ especifique:
at construction phase only
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Cantidad antes de MST:
3%
Cantidad luego de MST:
25%
Comentarios/ especifique:
from horticulture, chickens etc
disparidades económicas
Cantidad antes de MST:
5%
Cantidad luego de MST:
90%
Comentarios/ especifique:
poor cannot afford it
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
no time lost in collecting water afar
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Cantidad antes de MST:
5%
Cantidad luego de MST:
35%
Comentarios/ especifique:
better yields with more on-farm time
situación de salud
Cantidad antes de MST:
5%
Cantidad luego de MST:
40%
Comentarios/ especifique:
the water is better than in region
instituciones comunitarias
Cantidad antes de MST:
6%
Cantidad luego de MST:
50%
Comentarios/ especifique:
uplifting of the disadvantaged
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Cantidad antes de MST:
4%
Cantidad luego de MST:
50%
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
conflicts exist over boreholes
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
improved water provision, not affordable for the poor (unless subsidized)
contribution to human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Many educational tours made on these demonstration sites. Fresh rainwater is good for health compared to borehole (salty) water.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
5%
Cantidad luego de MST:
80%
Comentarios/ especifique:
water year round
calidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
not salty/saline, to clean roof and tank annually (temporarily)
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
1%
Cantidad luego de MST:
90%
Comentarios/ especifique:
resource from previous year used
evaporación
Cantidad antes de MST:
1%
Cantidad luego de MST:
90%
Comentarios/ especifique:
underground water tank, sealed
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Cantidad antes de MST:
1%
Cantidad luego de MST:
90%
Comentarios/ especifique:
clean technology
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
2 drums/we
Cantidad luego de MST:
42drums/we
Comentarios/ especifique:
all this water saved due to technology
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
The roof area is such that, some limited amounts of rain do fill or add some water into the storage tank
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Very costly to set up, if no government aid. It is however, very good for long term water provision.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is one such structure per village in Boteti sub-district - and they are all demonstration schemes. There was no public uptake following demonstration, as government subsidy changed and was later stopped.
It is too costly e.g. building materials, hiring of professional builder and cement to set up in lands areas.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
High capital or start-up costs. The area has low income groups who get water from communal boreholes, while rich cattle owners obtain water from their private boreholes, and hence desalination is favoured rather than rainwater systems.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Useful as shelter or storage |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Provides cool water in hot summers |
| Provides water in lands areas, where it is most needed |
| Farmers appreciate the good water quality and clean system annually |
| It has low maintenance costs, it is easy to use |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Costly to set up, due to price of building materials | Government subsidies, priviate sector, NGOs |
| Fear that their land would be taken away by the government after financial assistance | Education about subsidies to allay fears |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Costly to set up | subsidies by government, NGOs, private sector |
| Seen as dependent on rains, thus fails during droughts | research, information dissemination to stakeholders |
| Water quality issues (concerns) | education on keeping storage clean and boiling water for human consumption |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
03/06/2011
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Ministry of Agriculture Headquarters, Department of Crop Production, Engineering Division, Water Development Section,
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
P/Bag 003, Gaborone,
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
en.wikepedia.org/wiki/rainwater-harvesting
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
website
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
www.harvesth2O.com
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
website
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
www.rainwaterharvesting.org/index.htm
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
website
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
www.rainwaterharvesting.co.uk
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
website
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
cgwb.gov.in/Ground Water/roof-top.htm
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
website
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos