Hydraulic Ram Pump assisted river water lifting and application of stored water through drip irrigation for alley cropping [Pakistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Hydram Pump
technologies_5740 - Pakistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Maqsood Muhammad Mudassar
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Shrestha Arun Bhakta
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Nepal
Especialista MST:
Raza Haider
WWF-Pakistan
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Dhakal Madhav
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Nepal
Especialista MST:
Ali Ajaz
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Hassan Faizan-ul-
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Karim Fazal
WWF-Pakistan
Pakistán
Consultant:
Azeem-ullah
Azeemullah & Company Chartered Accountants
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Kundi Rehmat-ullah
GetGreen Tech
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Shah Ghulam Muhammad
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Pakistán
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Agricultural Water, Energy, and Hazard Management for Improved Livelihood in the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan (UIB, Pakistan)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
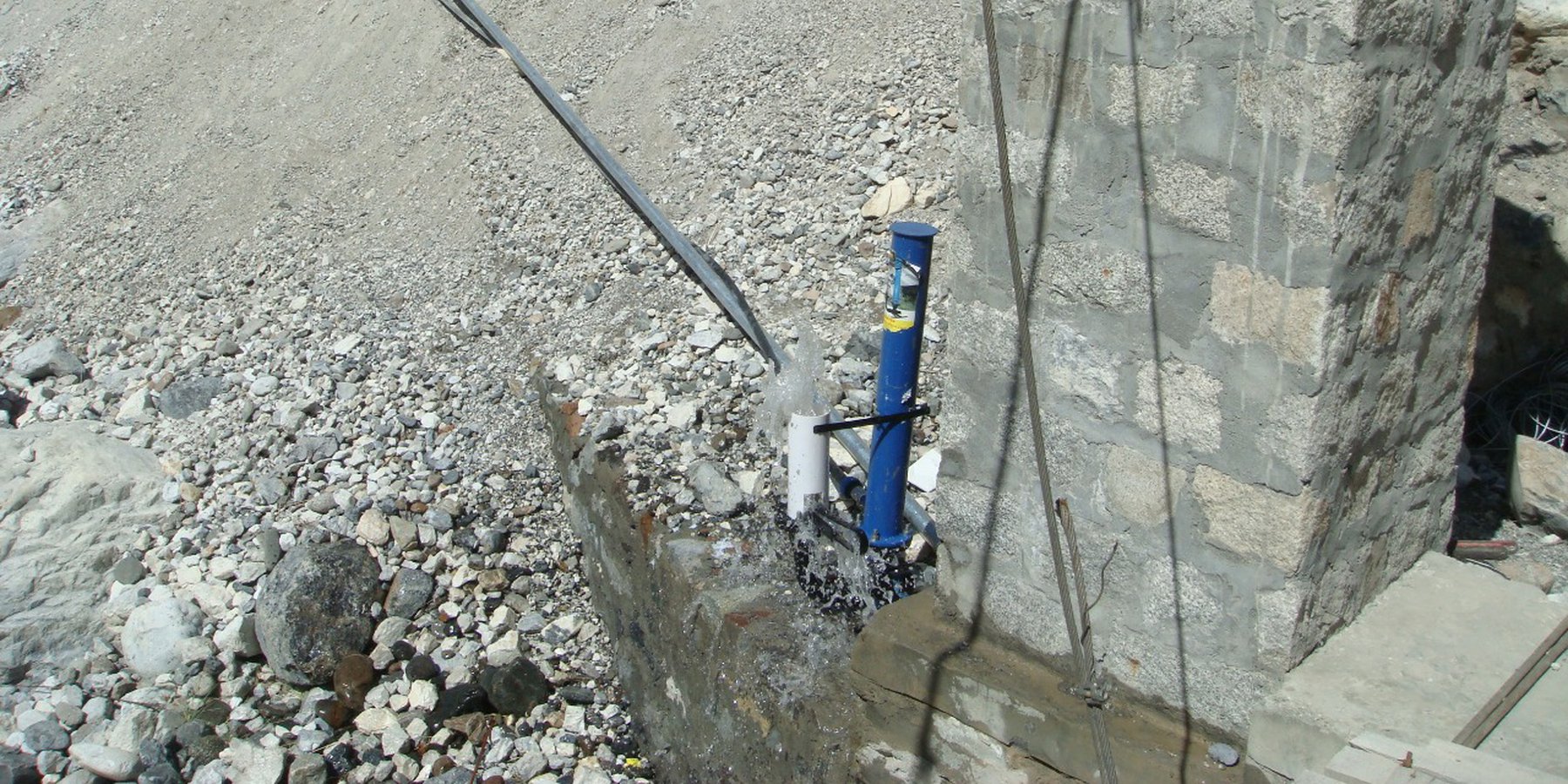
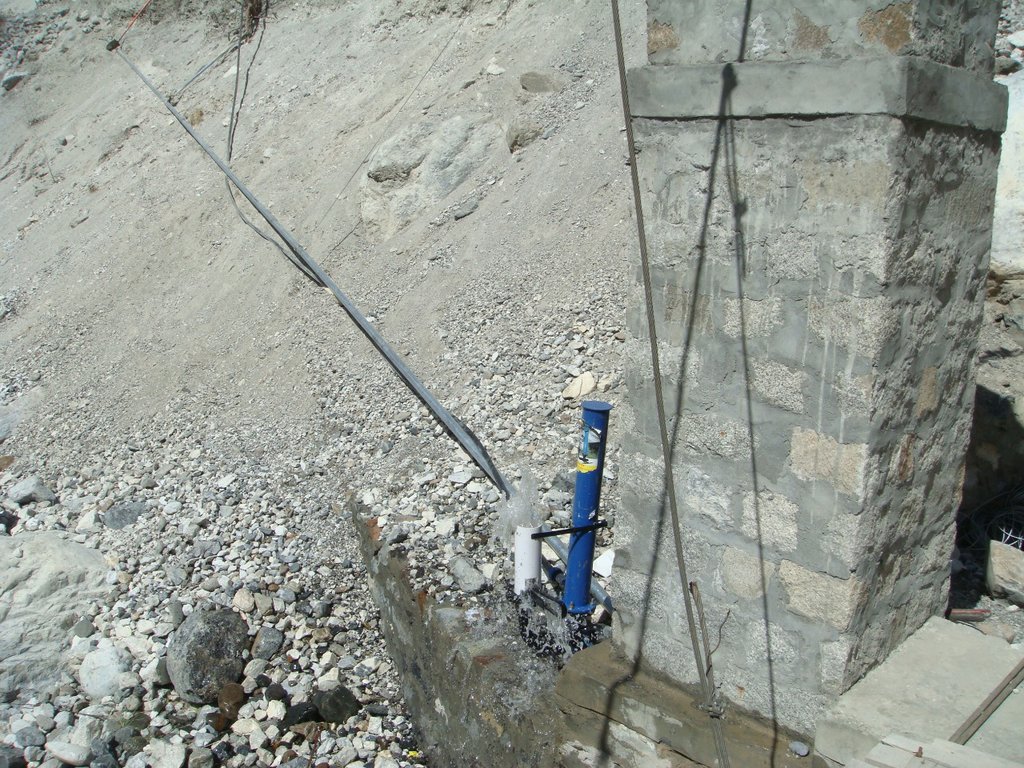
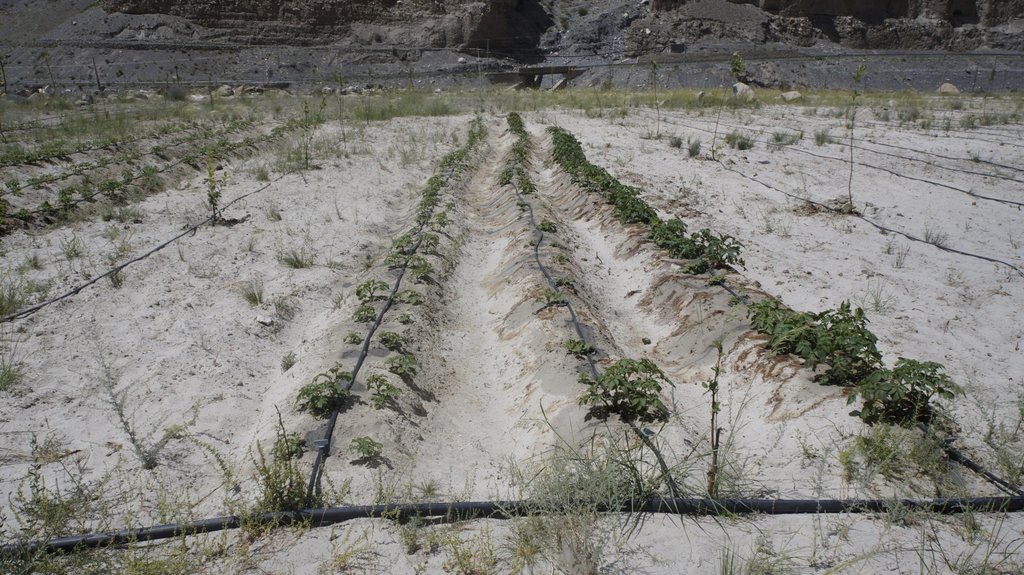
The water from a contour canal (off-taking from Khunjrab River) was lifted through hydro ram pump to uphill plastic storage and distributed to alley cropping (newly established orchard and vegetable rows) through drip irrigation.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Agriculture, livestock herding and tourism are the major contributors to Gilgit Baltistan economy. The arable land in this region is limited (only 2%) and more than half of which is still barren due to unavailability of irrigation water supplies. The reported dependency of irrigated areas on glacier fed irrigation is more than 90 percent, which now have been fluctuating due to changing climate. This region has been experiencing drastic changes in climate which resulting into lowering of glacier and water related disasters leading towards discontinuity of irrigation water supplies. The electrical power energy options are limited as well as unreliable and in situ replacements are very expensive.
The technological package was applied in arid climate at an elevation ranging from 2340m to 4877 m above sea level. Khyber is located at 36.56o N latitude and 74.79o E longitude. The area receives 150-200 mm annual rain-fall. The population of Khyber village is 1200 residing in 150 houses. Almost 46 percent of population is salaried, 20 percent own business and roughly 19 percent engaged with farming to earn bread and butter for families. The average landholding per household is 3.8 acres out of which 1.25 acre is cultivable waste due to insufficient water supplies and local labor.
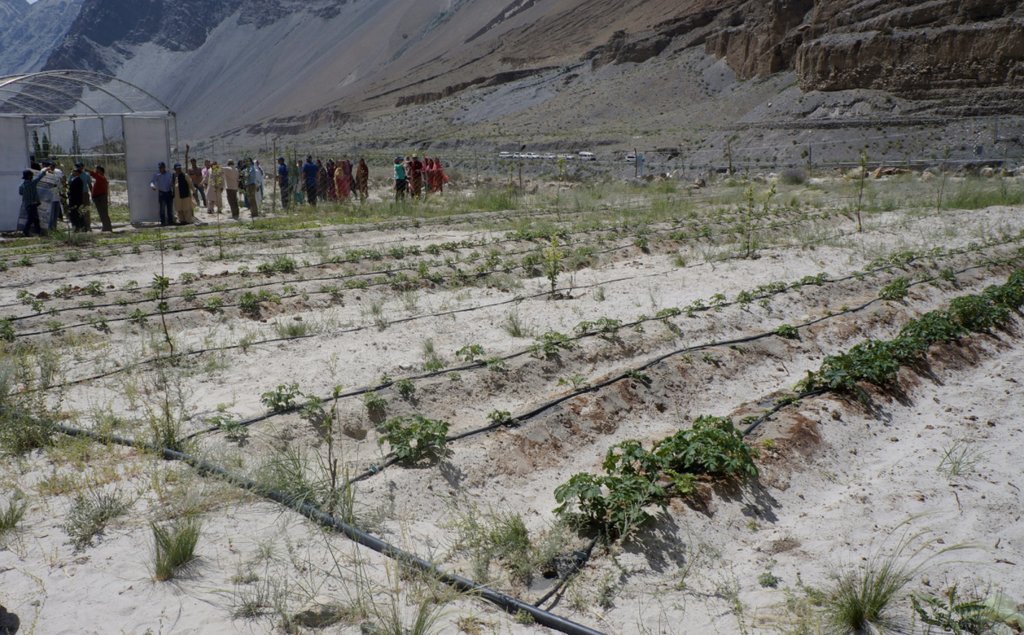
To address the above issues, the Indus Basin Initiative (IBI) of International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) through its a consortium of local partners including Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Mountain Agriculture Research Centre (MARC) and WWF-Pakistan has been demonstrating the alternative agricultural water management package of practices in lifting water for irrigation using Hydro ram pump. This study also presents the findings based on the experiment/demonstration and testing conducted in the pilot. The pilot site is located in Khyber village of Hunza, Gilgit Baltistan.
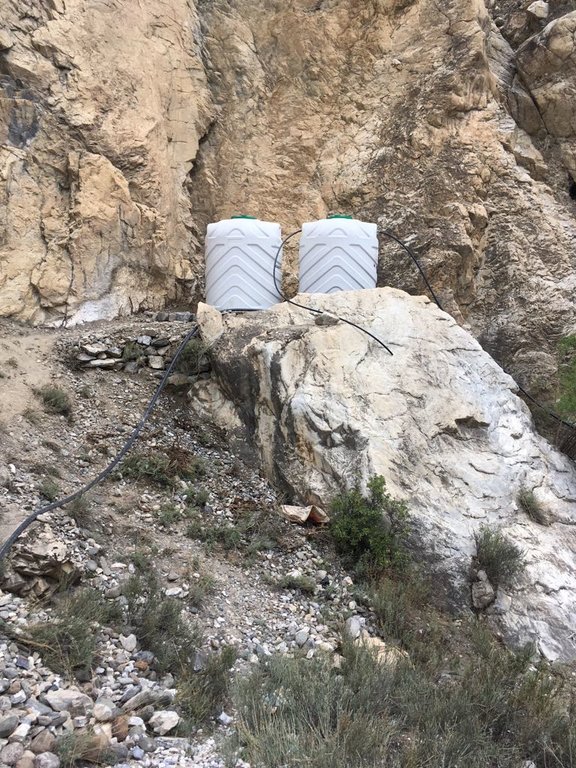
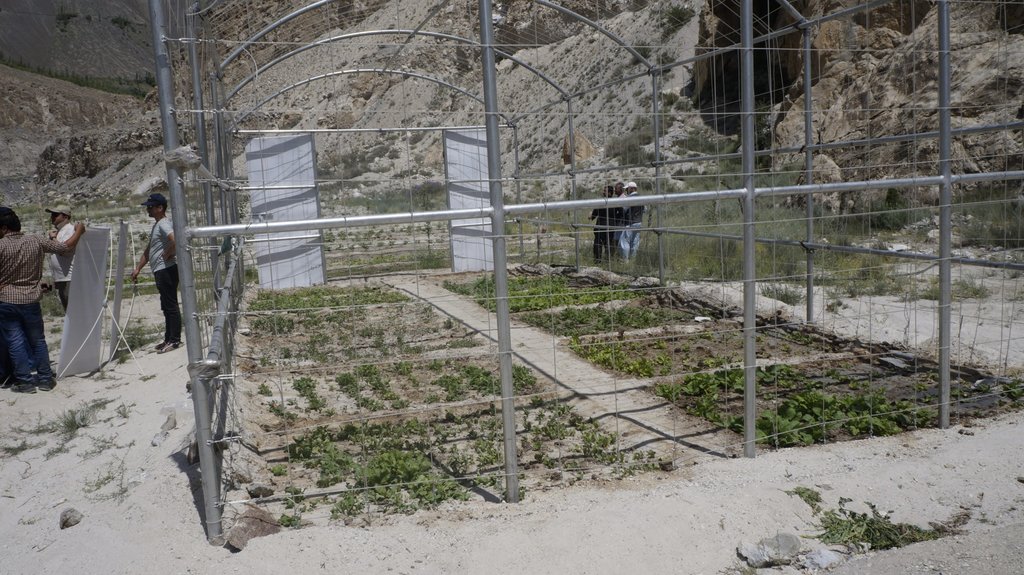
The pumping unit comprises a hydro ram pump (which is a zero carbon emission technology and needs no electricty to run, and it is locally customized having 1 inch/25mm out-take pipe) to lift water from a contour channel originating from the Khunjrab River and to carry the water to storage tanks (4000 liters) made up of plastic that has been placed upslope at 175 feet (53,3 m) vertical height from the river. The water from the storage tanks was supplied to alley cropping (apple sapling rows and vegetables rows) through pressure compensating drip irrigation system. The pumping capacity of the pump is 10.2 liters/minute, which is irrigating around 350 apple plants and vegetable rows at 2.5 acre (1ha). The storage tank was kept 45 feet (13,5 m) vertical height from the orchard field. Plan to plant distance and row to row distance of apple was maintained at 15 feet (4,6 m) and 20 (6 m) feet respectively. Drip irrigation system was established for each apple plant, as well as vegetables rows. Pits were constructed for planting apples and later they served also as water harvesting pits /check basins. Gilgit Baltistan chapter of WWF-Pakistan mobilized the local community, while PCRWR and MARC provided technical support to the Khyber Community in establishment of this pilot site. The community youth provided voluntary support during the land preparation, plantation and installation of hydro ram pump as well as drip irrigation system and the uphill storage tanks.
The cost of a complete package including hydro ram pump with accessories, storage tanks, intake and distribution systems, drip irrigation, apple plants and operational expenses for the site was US$ 25, 865 for 2.5 acre (1ha) of land. Women Organization of Khyber village takes care of the maintenance of technological package (fortnightly desilting of drip irrigation and storage tanks and annual repair of hydraulic ram pump). The fruit production has not yet started as it is a newly established farming site. However, seasonal vegetable farming has just started. The produce is small as soil fertility is still building up. Currently, the grown vegetables are being sold or used in the village at household level. However, with higher yield in future, the total income from the farm produce (currenty vegetables only) would be divided equally among the participating 150 households of Khyber Village. A comprehensive cost benefit analysis study has been conducted. It has been envisioned that apple orchard would mature in 4 to 5 years in cold climate of Gojal. By the 6th year, the farm would produce enough to the reach break-event point. The vegetable production has started now and the envisioned annual income is 15,000 PKR (almost 111 USD, if 1 USD=135 PKR).
The community welcomed the new technology and is now planning to outscale it in other areas to bring more land under cultivation. The women organization in the pilot site are positive about the less labourous agricultural activities and foresee to extend the alley cropping under drip irrigation to the rest of 7.5 acres, too. This technology is being dessiminated to different stakeholders including practitioners, policy and decision makers, academia, researchers and local farming communities. For this purpose, exposure field visits and farmers' field days have been arranged by the implementation partners.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Pakistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Gilgit Baltistan
Especifique más el lugar :
Khyber Village, Hunza District
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
The community has protected the site with barbed wire with wooden posts.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2018
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The Indus Basin Initiative of ICIMOD, with support of Government of Australia under Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio (SDIP), has been developing capacity (resilience to climate change) of vulnerable communities of Gilgit Baltistan through pioneer introduction of contextually new innovative technologies.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- vegetales - verdura de hojas verdes (ensaladas, repollo, espinaca, otros)
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- frutas, otros
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Only one crop is grown owing to the climate of this area
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
The seasonal vegetables are grown in between two successive apple orchard rows meaning Alley Cropping.
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierra no productiva
Especifique:
Barren land
Comentarios:
Due to unavailability of glacial-melt water, 50% of arable land in Gilgit Baltistan could never be cultivated. Before the interventions were implemented, this land was left barren.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- totalmente irrigada
Comentarios:
River water is being lifted throuh hydro ram pump, stored in elevated storage tanks and distributed through drip irrigation
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
- manejo de agua superficial (manantial, río, lagos, mar):
- tecnologías de eficiencia energética
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal, due to water related disasters.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Due to water access cultivation of before barren land was possible and vegetation cover improved.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
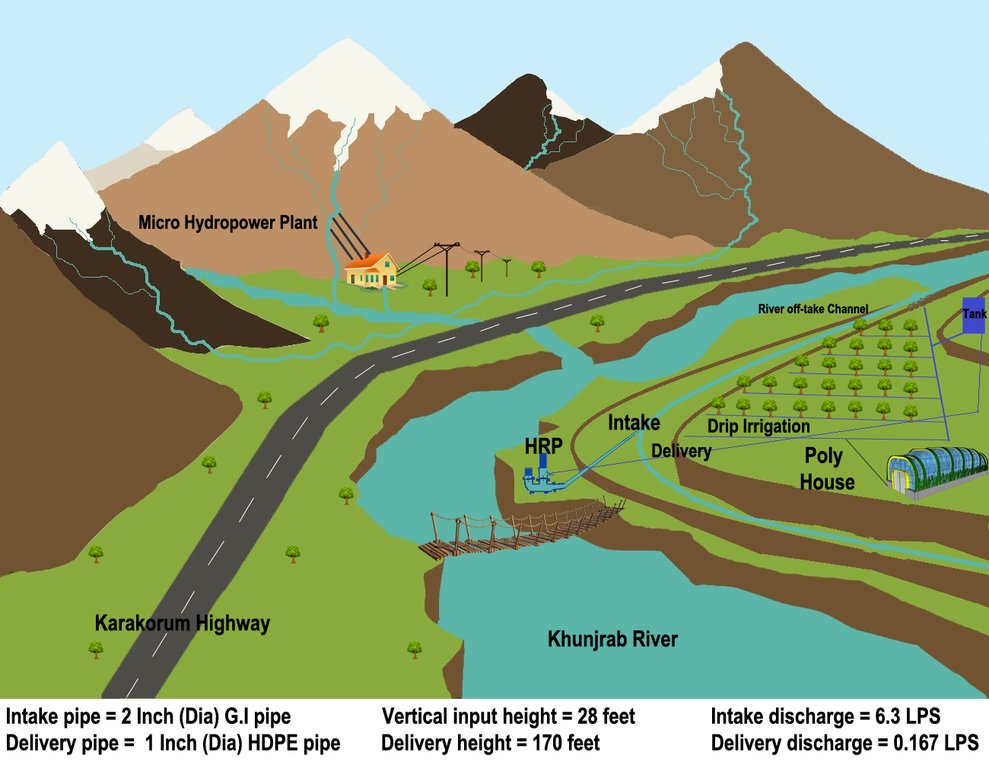
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Hydro Ram Pump: Locally manufactured with pumping capacity of the pump: 10.2 litres/minute. The intake G.I pipe (2 inch/50mm diameter) of 83 feet (25 m) long is connected to water channel. The vertical difference between hydro ram pump and water channel is 28 feet (25m). The out-take HDPE pipe of (1 inch/25mm diameter) of 200 feet (61m) carries water from hydro ram pump to plastic storages. The vertical distance between hydro ram pump and plastic storage tanks is 175 feet (53 m).
The capacity of storage tank: 4000 litres, location of storage tank: 175 feet height (53m, vertical) from the river and 45 feet height (14m, vertical) from the orchard field.
Drip Irrigation: Surface and pressure compensating. The spacing of dripping points: 15 feet (4.6m). Plant to plant and row to row distance of apple 15 feet (4.6m) and 20 feet (6m) respectively.
Autor:
Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood
Fecha:
25/03/2020
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Technological package at pilot site covering 2.5 acre (1 ha)
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
US$ 14.5 for skilled person and US$ 7.5 for unskilled person
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site identification in consultation with the communities | March 2017 |
| 2. | Detailed feasibility surveys of the site | May 2017 |
| 3. | Implementation agreement with the community | January 2018 |
| 4. | Installation of hydro ram pump | June 2018 |
| 5. | Installation of storage (plastic tank) with a line filter attached to it for the operation of the drip system and avoid sediment entry into the tank | June 2018 |
| 6. | Digging of pits for plantation of the apple orchard | June 2018 |
| 7. | Laying of drip irrigation systems | June 2018 |
| 8. | Plantation of tubed apple (Kala Kolu variety) it is bought from the local nursery | June 2018 |
| 9. | Training to selected farmers as caretakers of the technologies for its days to day repair and maintenance | August 2018 |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Plumbing and technical workers | 1 | 1,0 | 775,0 | 775,0 | 33,0 |
| Mano de obra | Installation charges | 1 | 1,0 | 968,0 | 968,0 | |
| Equipo | Ram Pump & Accessories | 1 | 1,0 | 8526,0 | 8526,0 | |
| Equipo | Drip Irrigation | 1 | 1,0 | 5813,0 | 5813,0 | |
| Equipo | Off-seasonal vegetable tunnel | 1 | 1,0 | 4715,0 | 4715,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Apple tree saplings (lumb sum) | 1 | 1,0 | 3165,0 | 3165,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost (250 kg) | 1 | 250,0 | 0,12 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Feasibility study | 1 | 1,0 | 1873,0 | 1873,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 25865,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 25865,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
ICIMOD through fundings from Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade under Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio
Comentarios:
The USD to PKR exchange rate while time of budget transfer was 1 USD=104.50 PKR
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of hydro ram pump | twice an year |
| 2. | Desiltation of plastic tanks | twice an year |
| 3. | Desiltation of drip irrigation system | once an year |
| 4. | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | once in 2 years |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Repair of hydro ram pump | 1 | 2,0 | 3,75 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Desiltation of plastic tanks | 1 | 2,0 | 7,5 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Desiltation of drip irrigation system | 1 | 1,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | 1 | 0,5 | 37,0 | 18,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Repair of hydro ram pump | 1 | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | 1 | 0,5 | 100,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Vegetable seeds | 1 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Diammonium phosphate (DAP) | 1 | 2,0 | 30,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost (250 kg) | 1 | 1,0 | 22,0 | 22,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 245,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 245,0 | |||||
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Since the most of the material (drip irrigation etc) is imported thus cost varies with foreign currency exchange rates. Moreover, the costs are also higher in Gilgit Baltistan comparing to plains of Pakistan owning to expensive transportation.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
150,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
it varies from 150 mm to 200 mm
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Passu ghar
Zona agroclimática
- árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water is available in the river but fields are higher up than river
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
This pilot site has been handed over to women organization of Khyber village, so women are managing all agricultural activities at this site.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Comentarios:
Most of the uncultivated land is communal, community decides uses of the land
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The fruit production has not yet started as it is a newly established farming site. However, seasonal vegetable farming has just started. The produce is small as the soil nutrition building is still in process. Currently, the grown vegetables are being sold or used in the village at household level.
área de producción
Cantidad luego de MST:
2.5 acres/1ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
Production area increased as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
14,688 litres per day
Comentarios/ especifique:
Irrigation water availability increased with innovative technological packages to previously barren land
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Automized irrigation has decreased labour
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Organic vegetables for household consumption
Impactos socioculturales
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Women have been allocated 10 acre arable land (pilot area) for their agricultural area. Out of this 10 acres, ICIMOD with its partners and community organization has brought 2.5 acres under cultivation.
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
Community institution (village development organizations) strengthened due to the approach of farming in a group.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved soil moisture as a result of water harvesting pits, mulching and efficient drip irrigation.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil cover improved due to vegetation
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced soil loss ( from wind and water erosion) due to application of mulch and also due to vegetation cover and above-ground biomass.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
impacto de gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
The intervention has introduced block orchard technology which will help to reduce the impacts of CO2 emmissions from vehicles along the China Pakistan Economic Corridor. Moreover, the water management interventions being used are also climate smart.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de nieve local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de frío | bien |
| condiciones extremas de invierno | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
| inundación repentina | bien |
| deslizamiento | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| período extendido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
A comprehensive cost benefit analysis study has been conducted. It has been envisioned that apple orchard would mature in 4 to 5 years in cold climate of Gojal. By the 6th year, the farm would enough produce the reach break-event point. The vegetable production has started now and the envisioned annual income is 15,000 PKR (almost 111 USD,, if 1 USD=135 PKR).
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
ICIMOD and its consortium of partners piloted the technology in this region at one village only in District Hunza, which was further out-scaled by WWF under UNDP project to six other districts (one site per district) and now federal government has awarded a project to Government of Gilgit Baltistan (National Programme for Enhancing Command Area of Small and Mini Dams in Barani Areas of Pakistan, Gilgit Baltistan Component) to upscale the piloted technology to all districts (atleast 5 sites per districts) which means 50 hydro ram pump cum drip irrigation models. This project will cost 2.6 million USD.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The hydro ram pump assisted river water lifting integrated with drip irrigation is the first of its kind in the upper Indus basin. The system is simple and anyone once trained can operate it. It will contribute to nearly 40% of the additional income of the Khyber Village |
| The technological package is environmentally friendly and are effective adaptation measures in the context of climate change. |
| Women are involved in agricultural activities and this intervention has provided them relief. Women are now generating seasonal income from growing seasonal and off-seasonal vegetables. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The first innovative technological package in Gilgit Baltistan that is climate-resilient as compare to traditional practices. |
| Water application through drip irrigation is very efficient as compared to flood irrigation. |
| The technological package can last more than 20 years. Maintenance cost is nominal. |
| As women are predominantly responsible for farming activities, improved water access and application through drip reduces their work-load and frees up time for other activities |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Drip irrigation and parts of solar panel may not be available locally. | A spare parts should be made available locally for immediate replacement as and when required. |
| The investment cost is high. | Explain cost-benefit analysis to aware farmers that the benefit is high in the long run. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Field visits was done several times as this was a part of the project activity. Cost benefit analysis was done in 2020.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Collaboration Strengthens Climate Resiliency of Upper Gojal Gilgit Mountain Villages in The Upper Indus Basin, CIMOD, 2017
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.icimod.org/collaboration-strengthens-climate-resiliency-of-upper-gojal-gilgit-mountain-villages-in-the-upper-indus-basin/
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Zero-carbon water pumps turn Pak barren mountains green, Syed Abu Bakar, 2020
URL:
https://www.thenews.com.pk/print/636825-zero-carbon-water-pumps-turn-pak-barren-mountains-green
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionannaire is very comprehensive.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos