Hydraulic Ram Pump assisted river water lifting and application of stored water through drip irrigation for alley cropping [巴基斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Hydram Pump
technologies_5740 - 巴基斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Maqsood Muhammad Mudassar
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Shrestha Arun Bhakta
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Raza Haider
WWF-Pakistan
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Dhakal Madhav
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Ali Ajaz
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Hassan Faizan-ul-
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Karim Fazal
WWF-Pakistan
巴基斯坦
Consultant:
Azeem-ullah
Azeemullah & Company Chartered Accountants
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Kundi Rehmat-ullah
GetGreen Tech
巴基斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Shah Ghulam Muhammad
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
巴基斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Agricultural Water, Energy, and Hazard Management for Improved Livelihood in the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan (UIB, Pakistan)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
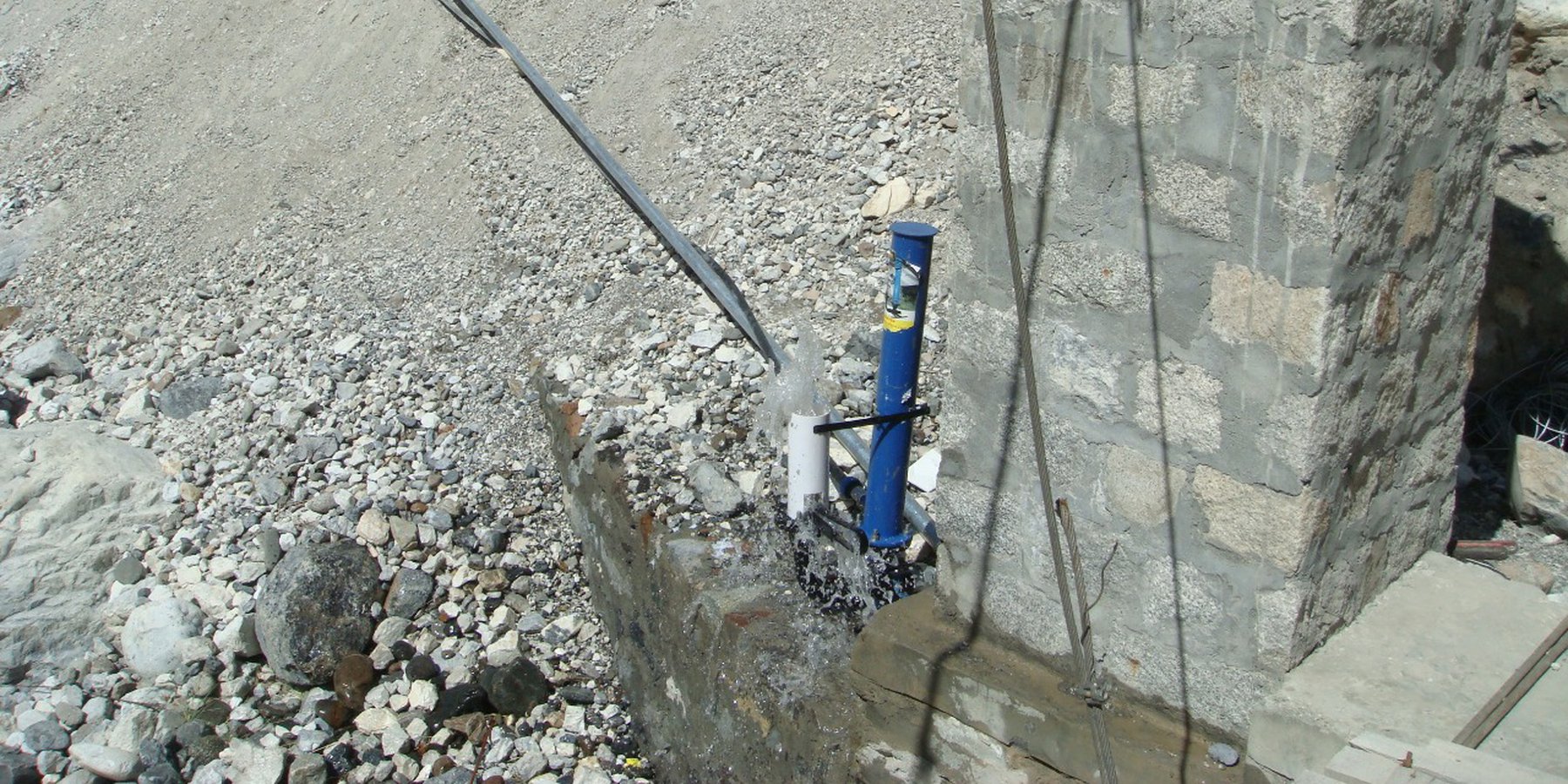
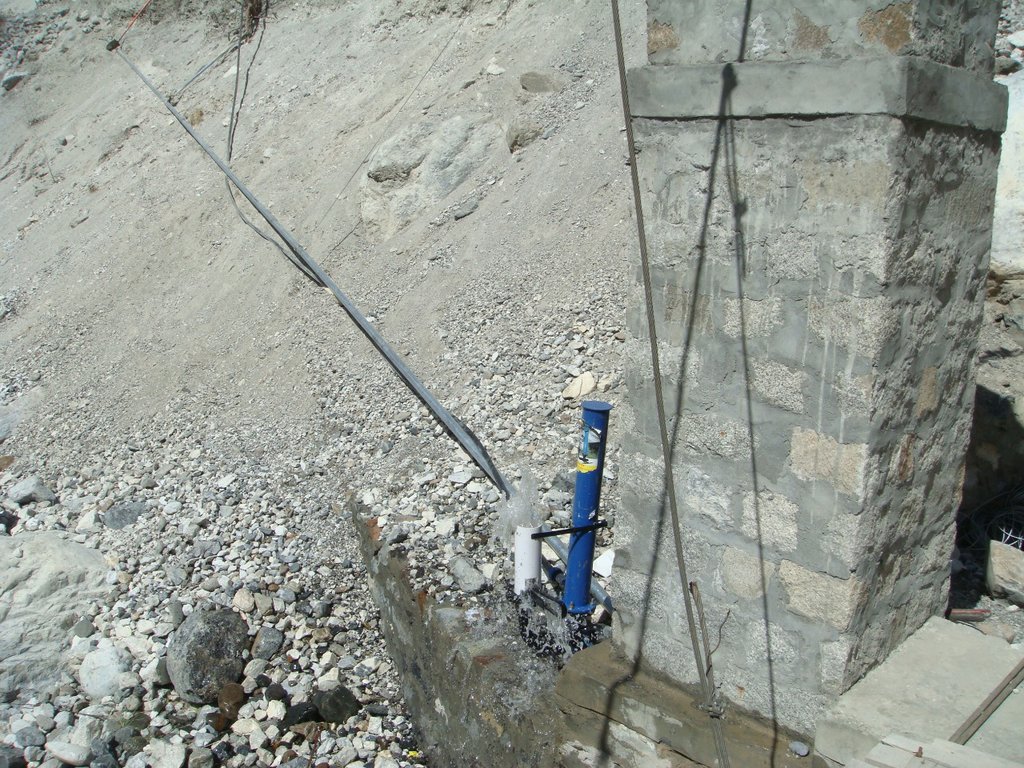
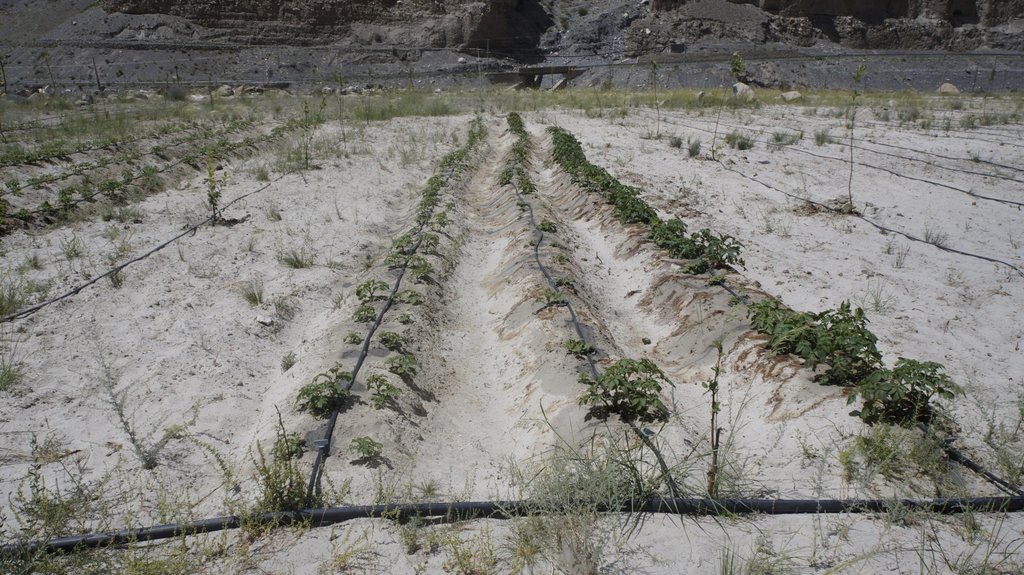
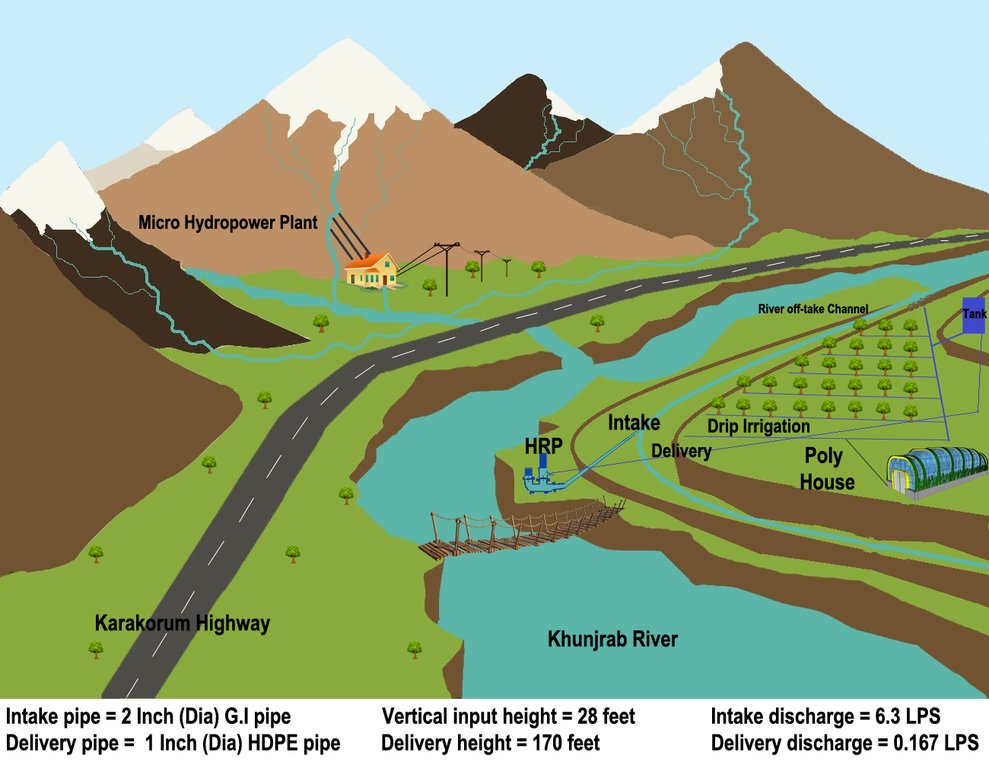
The water from a contour canal (off-taking from Khunjrab River) was lifted through hydro ram pump to uphill plastic storage and distributed to alley cropping (newly established orchard and vegetable rows) through drip irrigation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Agriculture, livestock herding and tourism are the major contributors to Gilgit Baltistan economy. The arable land in this region is limited (only 2%) and more than half of which is still barren due to unavailability of irrigation water supplies. The reported dependency of irrigated areas on glacier fed irrigation is more than 90 percent, which now have been fluctuating due to changing climate. This region has been experiencing drastic changes in climate which resulting into lowering of glacier and water related disasters leading towards discontinuity of irrigation water supplies. The electrical power energy options are limited as well as unreliable and in situ replacements are very expensive.
The technological package was applied in arid climate at an elevation ranging from 2340m to 4877 m above sea level. Khyber is located at 36.56o N latitude and 74.79o E longitude. The area receives 150-200 mm annual rain-fall. The population of Khyber village is 1200 residing in 150 houses. Almost 46 percent of population is salaried, 20 percent own business and roughly 19 percent engaged with farming to earn bread and butter for families. The average landholding per household is 3.8 acres out of which 1.25 acre is cultivable waste due to insufficient water supplies and local labor.
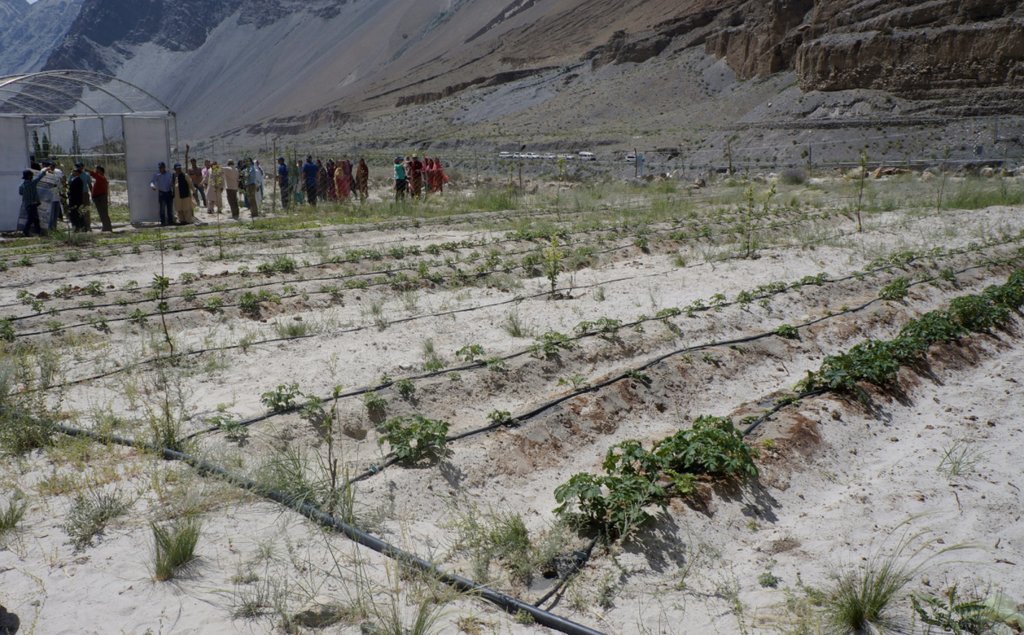
To address the above issues, the Indus Basin Initiative (IBI) of International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) through its a consortium of local partners including Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Mountain Agriculture Research Centre (MARC) and WWF-Pakistan has been demonstrating the alternative agricultural water management package of practices in lifting water for irrigation using Hydro ram pump. This study also presents the findings based on the experiment/demonstration and testing conducted in the pilot. The pilot site is located in Khyber village of Hunza, Gilgit Baltistan.
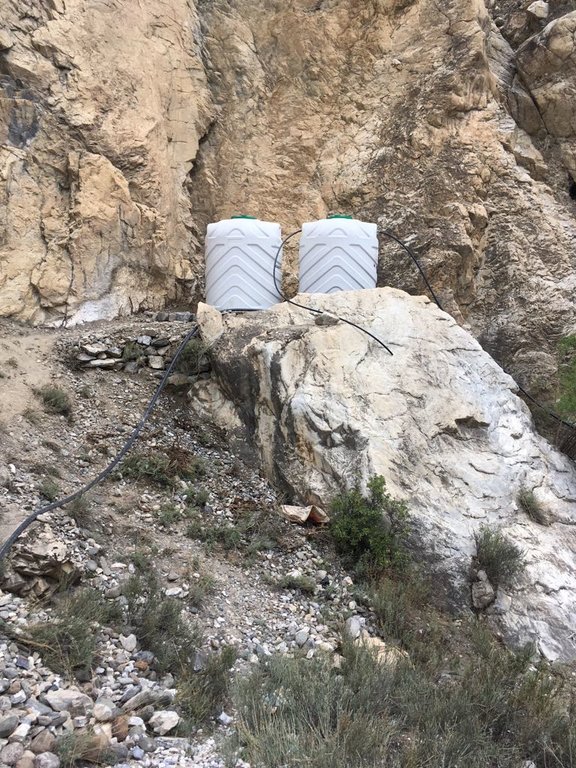
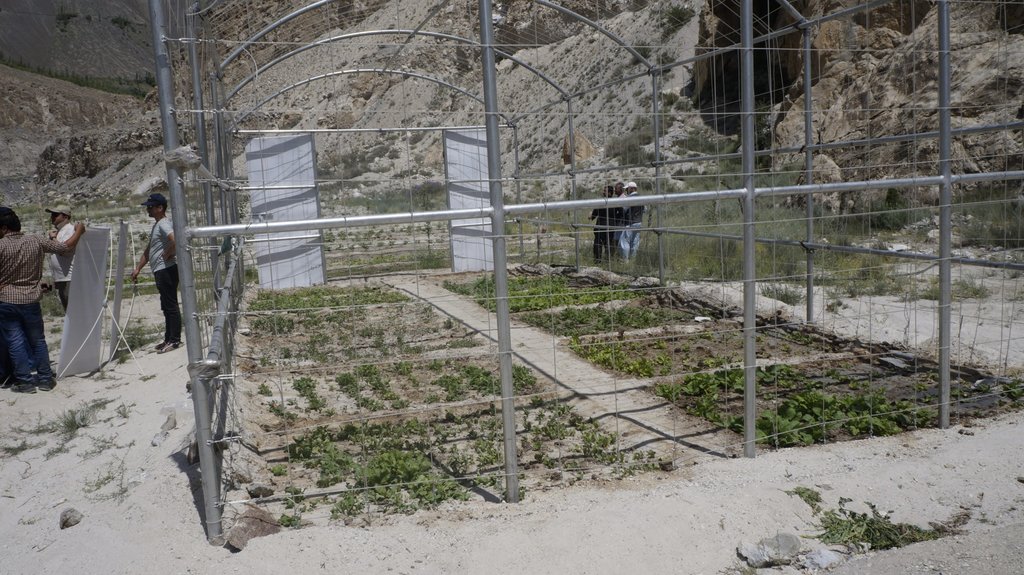
The pumping unit comprises a hydro ram pump (which is a zero carbon emission technology and needs no electricty to run, and it is locally customized having 1 inch/25mm out-take pipe) to lift water from a contour channel originating from the Khunjrab River and to carry the water to storage tanks (4000 liters) made up of plastic that has been placed upslope at 175 feet (53,3 m) vertical height from the river. The water from the storage tanks was supplied to alley cropping (apple sapling rows and vegetables rows) through pressure compensating drip irrigation system. The pumping capacity of the pump is 10.2 liters/minute, which is irrigating around 350 apple plants and vegetable rows at 2.5 acre (1ha). The storage tank was kept 45 feet (13,5 m) vertical height from the orchard field. Plan to plant distance and row to row distance of apple was maintained at 15 feet (4,6 m) and 20 (6 m) feet respectively. Drip irrigation system was established for each apple plant, as well as vegetables rows. Pits were constructed for planting apples and later they served also as water harvesting pits /check basins. Gilgit Baltistan chapter of WWF-Pakistan mobilized the local community, while PCRWR and MARC provided technical support to the Khyber Community in establishment of this pilot site. The community youth provided voluntary support during the land preparation, plantation and installation of hydro ram pump as well as drip irrigation system and the uphill storage tanks.
The cost of a complete package including hydro ram pump with accessories, storage tanks, intake and distribution systems, drip irrigation, apple plants and operational expenses for the site was US$ 25, 865 for 2.5 acre (1ha) of land. Women Organization of Khyber village takes care of the maintenance of technological package (fortnightly desilting of drip irrigation and storage tanks and annual repair of hydraulic ram pump). The fruit production has not yet started as it is a newly established farming site. However, seasonal vegetable farming has just started. The produce is small as soil fertility is still building up. Currently, the grown vegetables are being sold or used in the village at household level. However, with higher yield in future, the total income from the farm produce (currenty vegetables only) would be divided equally among the participating 150 households of Khyber Village. A comprehensive cost benefit analysis study has been conducted. It has been envisioned that apple orchard would mature in 4 to 5 years in cold climate of Gojal. By the 6th year, the farm would produce enough to the reach break-event point. The vegetable production has started now and the envisioned annual income is 15,000 PKR (almost 111 USD, if 1 USD=135 PKR).
The community welcomed the new technology and is now planning to outscale it in other areas to bring more land under cultivation. The women organization in the pilot site are positive about the less labourous agricultural activities and foresee to extend the alley cropping under drip irrigation to the rest of 7.5 acres, too. This technology is being dessiminated to different stakeholders including practitioners, policy and decision makers, academia, researchers and local farming communities. For this purpose, exposure field visits and farmers' field days have been arranged by the implementation partners.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
巴基斯坦
区域/州/省:
Gilgit Baltistan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khyber Village, Hunza District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The community has protected the site with barbed wire with wooden posts.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2018
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The Indus Basin Initiative of ICIMOD, with support of Government of Australia under Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio (SDIP), has been developing capacity (resilience to climate change) of vulnerable communities of Gilgit Baltistan through pioneer introduction of contextually new innovative technologies.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Only one crop is grown owing to the climate of this area
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
The seasonal vegetables are grown in between two successive apple orchard rows meaning Alley Cropping.
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

不毛之地
具体说明:
Barren land
注释:
Due to unavailability of glacial-melt water, 50% of arable land in Gilgit Baltistan could never be cultivated. Before the interventions were implemented, this land was left barren.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
注释:
River water is being lifted throuh hydro ram pump, stored in elevated storage tanks and distributed through drip irrigation
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- 节能技术
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal, due to water related disasters.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Due to water access cultivation of before barren land was possible and vegetation cover improved.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Hydro Ram Pump: Locally manufactured with pumping capacity of the pump: 10.2 litres/minute. The intake G.I pipe (2 inch/50mm diameter) of 83 feet (25 m) long is connected to water channel. The vertical difference between hydro ram pump and water channel is 28 feet (25m). The out-take HDPE pipe of (1 inch/25mm diameter) of 200 feet (61m) carries water from hydro ram pump to plastic storages. The vertical distance between hydro ram pump and plastic storage tanks is 175 feet (53 m).
The capacity of storage tank: 4000 litres, location of storage tank: 175 feet height (53m, vertical) from the river and 45 feet height (14m, vertical) from the orchard field.
Drip Irrigation: Surface and pressure compensating. The spacing of dripping points: 15 feet (4.6m). Plant to plant and row to row distance of apple 15 feet (4.6m) and 20 feet (6m) respectively.
作者:
Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood
日期:
25/03/2020
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Technological package at pilot site covering 2.5 acre (1 ha)
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
US$ 14.5 for skilled person and US$ 7.5 for unskilled person
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site identification in consultation with the communities | March 2017 |
| 2. | Detailed feasibility surveys of the site | May 2017 |
| 3. | Implementation agreement with the community | January 2018 |
| 4. | Installation of hydro ram pump | June 2018 |
| 5. | Installation of storage (plastic tank) with a line filter attached to it for the operation of the drip system and avoid sediment entry into the tank | June 2018 |
| 6. | Digging of pits for plantation of the apple orchard | June 2018 |
| 7. | Laying of drip irrigation systems | June 2018 |
| 8. | Plantation of tubed apple (Kala Kolu variety) it is bought from the local nursery | June 2018 |
| 9. | Training to selected farmers as caretakers of the technologies for its days to day repair and maintenance | August 2018 |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Plumbing and technical workers | 1 | 1.0 | 775.0 | 775.0 | 33.0 |
| 劳动力 | Installation charges | 1 | 1.0 | 968.0 | 968.0 | |
| 设备 | Ram Pump & Accessories | 1 | 1.0 | 8526.0 | 8526.0 | |
| 设备 | Drip Irrigation | 1 | 1.0 | 5813.0 | 5813.0 | |
| 设备 | Off-seasonal vegetable tunnel | 1 | 1.0 | 4715.0 | 4715.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Apple tree saplings (lumb sum) | 1 | 1.0 | 3165.0 | 3165.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost (250 kg) | 1 | 250.0 | 0.12 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Feasibility study | 1 | 1.0 | 1873.0 | 1873.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 25865.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 25865.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
ICIMOD through fundings from Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade under Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio
注释:
The USD to PKR exchange rate while time of budget transfer was 1 USD=104.50 PKR
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of hydro ram pump | twice an year |
| 2. | Desiltation of plastic tanks | twice an year |
| 3. | Desiltation of drip irrigation system | once an year |
| 4. | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | once in 2 years |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Repair of hydro ram pump | 1 | 2.0 | 3.75 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Desiltation of plastic tanks | 1 | 2.0 | 7.5 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Desiltation of drip irrigation system | 1 | 1.0 | 37.0 | 37.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | 1 | 0.5 | 37.0 | 18.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Repair of hydro ram pump | 1 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | 1 | 0.5 | 100.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Vegetable seeds | 1 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Diammonium phosphate (DAP) | 1 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost (250 kg) | 1 | 1.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 245.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 245.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Since the most of the material (drip irrigation etc) is imported thus cost varies with foreign currency exchange rates. Moreover, the costs are also higher in Gilgit Baltistan comparing to plains of Pakistan owning to expensive transportation.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
150.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
it varies from 150 mm to 200 mm
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Passu ghar
农业气候带
- 干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water is available in the river but fields are higher up than river
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
This pilot site has been handed over to women organization of Khyber village, so women are managing all agricultural activities at this site.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
注释:
Most of the uncultivated land is communal, community decides uses of the land
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The fruit production has not yet started as it is a newly established farming site. However, seasonal vegetable farming has just started. The produce is small as the soil nutrition building is still in process. Currently, the grown vegetables are being sold or used in the village at household level.
生产区域
SLM之后的数量:
2.5 acres/1ha
注释/具体说明:
Production area increased as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
14,688 litres per day
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation water availability increased with innovative technological packages to previously barren land
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Automized irrigation has decreased labour
其它社会经济效应
Organic vegetables for household consumption
社会文化影响
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
Women have been allocated 10 acre arable land (pilot area) for their agricultural area. Out of this 10 acres, ICIMOD with its partners and community organization has brought 2.5 acres under cultivation.
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Community institution (village development organizations) strengthened due to the approach of farming in a group.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil moisture as a result of water harvesting pits, mulching and efficient drip irrigation.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Soil cover improved due to vegetation
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Reduced soil loss ( from wind and water erosion) due to application of mulch and also due to vegetation cover and above-ground biomass.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
The intervention has introduced block orchard technology which will help to reduce the impacts of CO2 emmissions from vehicles along the China Pakistan Economic Corridor. Moreover, the water management interventions being used are also climate smart.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地雪暴 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 寒潮 | 好 |
| 极端冬季条件 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
| 山洪暴发 | 好 |
| 滑坡 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
A comprehensive cost benefit analysis study has been conducted. It has been envisioned that apple orchard would mature in 4 to 5 years in cold climate of Gojal. By the 6th year, the farm would enough produce the reach break-event point. The vegetable production has started now and the envisioned annual income is 15,000 PKR (almost 111 USD,, if 1 USD=135 PKR).
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
ICIMOD and its consortium of partners piloted the technology in this region at one village only in District Hunza, which was further out-scaled by WWF under UNDP project to six other districts (one site per district) and now federal government has awarded a project to Government of Gilgit Baltistan (National Programme for Enhancing Command Area of Small and Mini Dams in Barani Areas of Pakistan, Gilgit Baltistan Component) to upscale the piloted technology to all districts (atleast 5 sites per districts) which means 50 hydro ram pump cum drip irrigation models. This project will cost 2.6 million USD.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The hydro ram pump assisted river water lifting integrated with drip irrigation is the first of its kind in the upper Indus basin. The system is simple and anyone once trained can operate it. It will contribute to nearly 40% of the additional income of the Khyber Village |
| The technological package is environmentally friendly and are effective adaptation measures in the context of climate change. |
| Women are involved in agricultural activities and this intervention has provided them relief. Women are now generating seasonal income from growing seasonal and off-seasonal vegetables. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The first innovative technological package in Gilgit Baltistan that is climate-resilient as compare to traditional practices. |
| Water application through drip irrigation is very efficient as compared to flood irrigation. |
| The technological package can last more than 20 years. Maintenance cost is nominal. |
| As women are predominantly responsible for farming activities, improved water access and application through drip reduces their work-load and frees up time for other activities |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Drip irrigation and parts of solar panel may not be available locally. | A spare parts should be made available locally for immediate replacement as and when required. |
| The investment cost is high. | Explain cost-benefit analysis to aware farmers that the benefit is high in the long run. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Field visits was done several times as this was a part of the project activity. Cost benefit analysis was done in 2020.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Collaboration Strengthens Climate Resiliency of Upper Gojal Gilgit Mountain Villages in The Upper Indus Basin, CIMOD, 2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.icimod.org/collaboration-strengthens-climate-resiliency-of-upper-gojal-gilgit-mountain-villages-in-the-upper-indus-basin/
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Zero-carbon water pumps turn Pak barren mountains green, Syed Abu Bakar, 2020
URL:
https://www.thenews.com.pk/print/636825-zero-carbon-water-pumps-turn-pak-barren-mountains-green
7.4 一般注释
The questionannaire is very comprehensive.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块