Protection of water resources [Haití]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Antoine Kocher
- Editor: Eveline Studer
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger, Eveline Studer
technologies_583 - Haití
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Focal person EPA HELVETAS
Helvetas
Haití
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Concertation locale pour la protection des ressources [Haití]
La concertation pour la gestion des ressources naturelles implique les communautés, les autorités et l'ensemble des acteurs dans la prise de décision collective pour protéger les ressources en eau notamment, et institutionnaliser leur gestion.
- Compilador: Antoine Kocher
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
The protection of water resources is essential for the supply of drinking water in the rural zones of Haiti, by enabling to preserve the water quality and facilitate the recharge of the resource. Organizing the actors related to the water resource and to the economic, environmental and communal challenges is crucial. This implies, apart from management, the implementation of various technical measures.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The majority of water resources in Haiti is subject to bacterial contamination, which endangers the health of the consumers. The infrastructure for the abstraction and conveyance of water is periodically put to the test by the large variation of discharge, like floods, but also by low flows. The protection of water resources aims to strengthen local actors to better manage water resources. The objective is to take care of the protection of water resources at local level according to rules which are established and accepted by the actors with regard to legal, sociocultural and biophysical aspects.
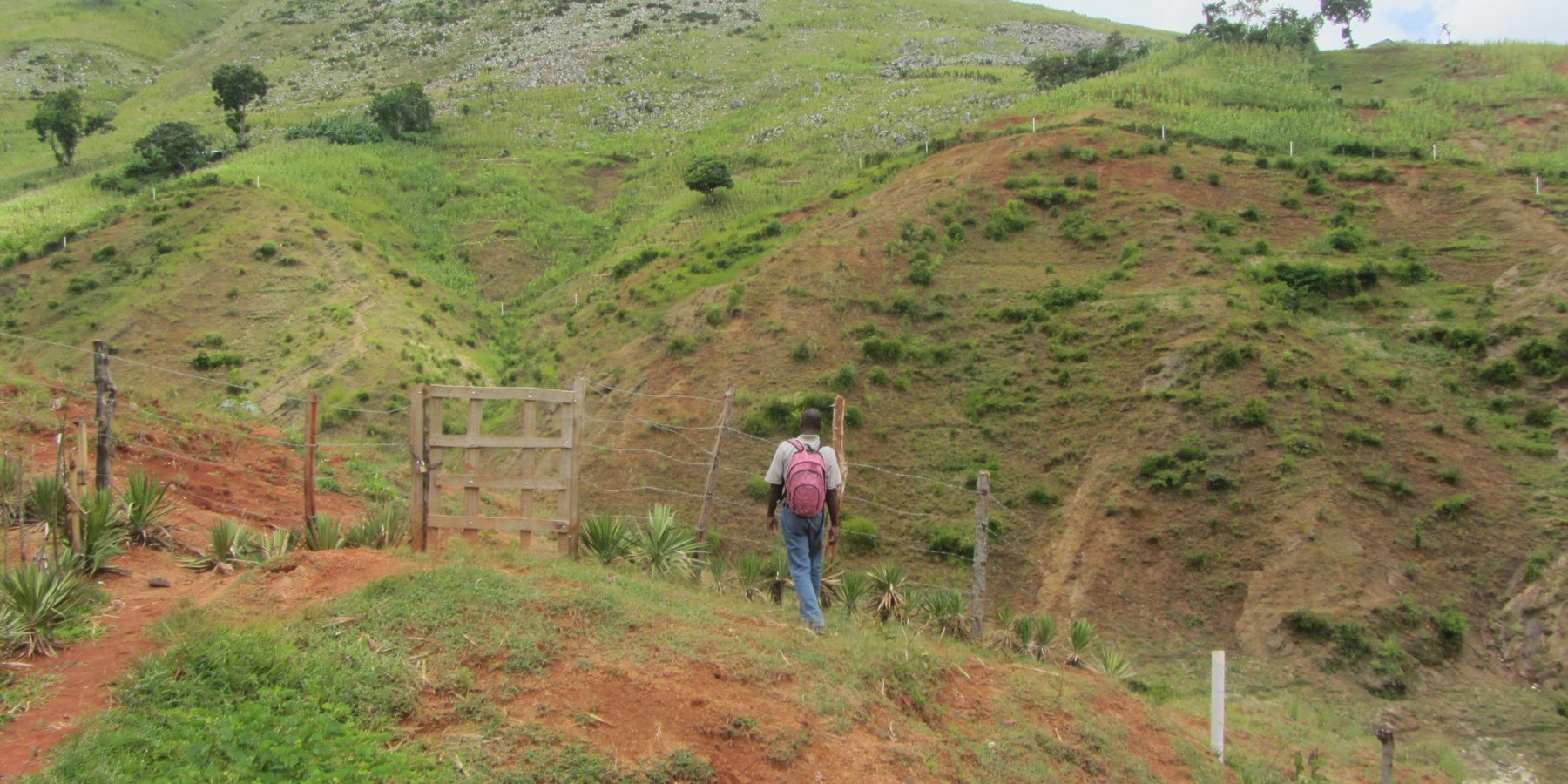
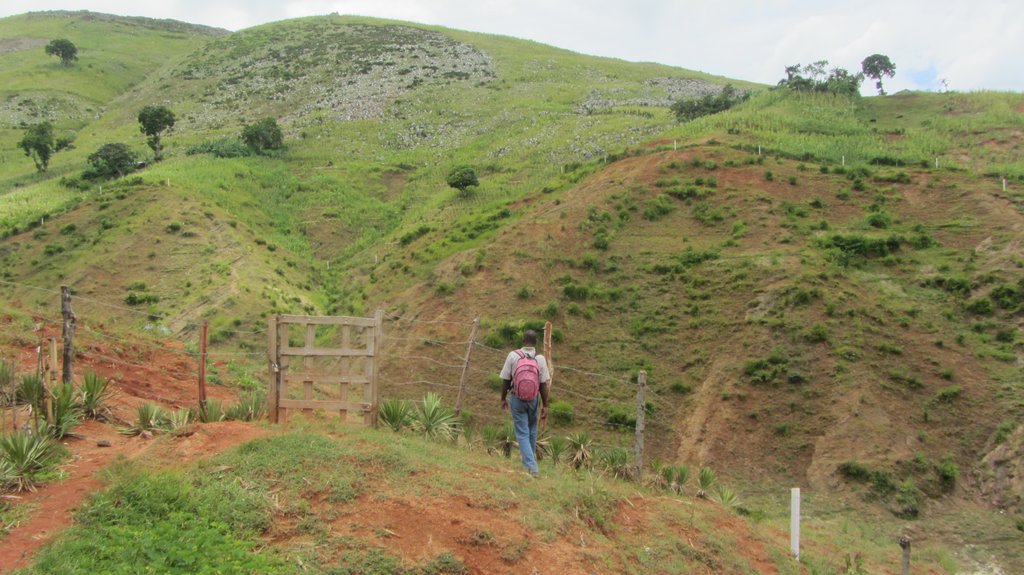
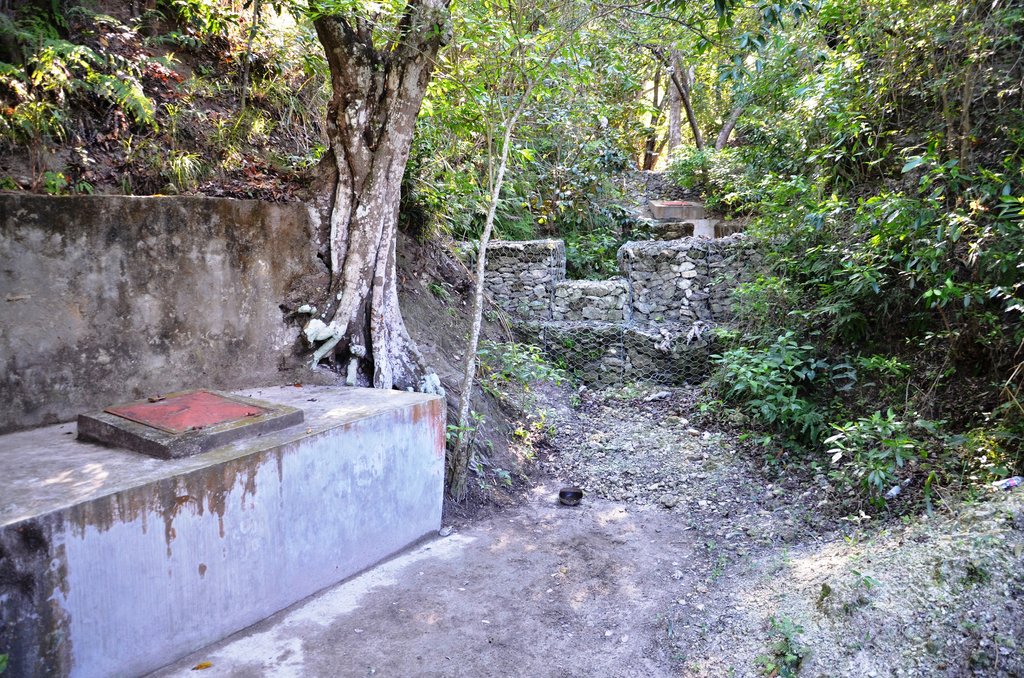
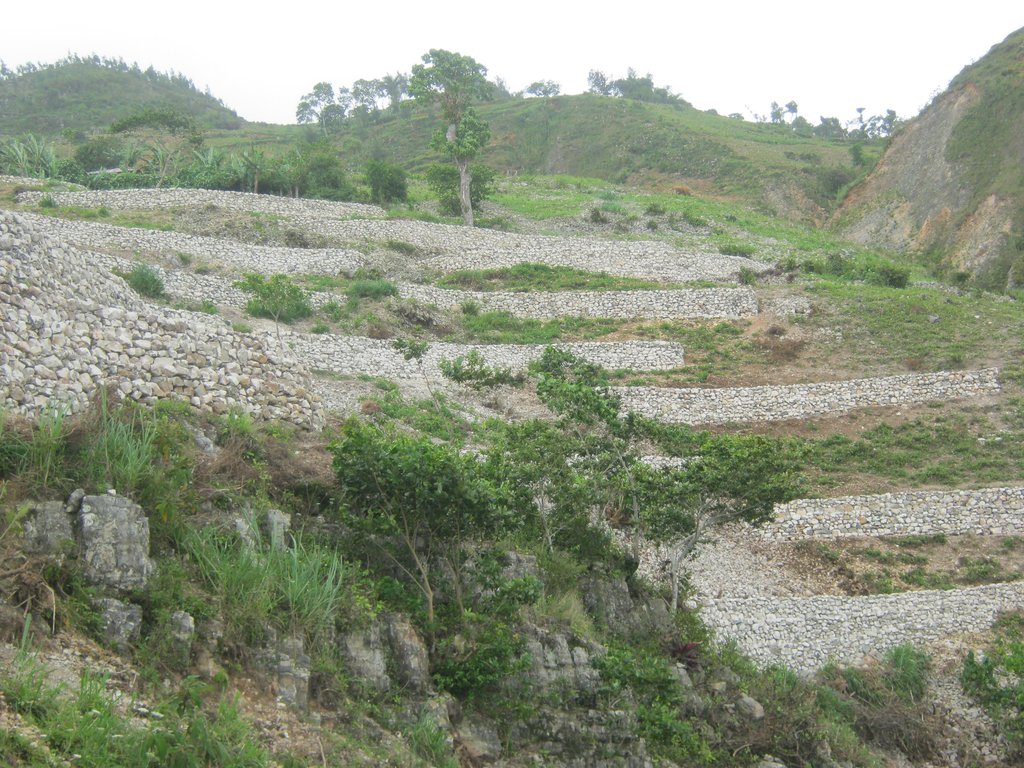
The protection of water resources also implies that technical measures are implemented to conserve and protect catchments, in order to ensure the quality and quantity of the required water and the recharge of groundwater bodies. The technical measures are defined for different zones. Three categories of zones are established with specific restrictions and recommendations, and formalized in a municipal decree which is published by the town councils. A first zone of 1000 m2 directly upstream of the water resource is brought into the domain of the state, fenced, reforested and totally protected from human activities.
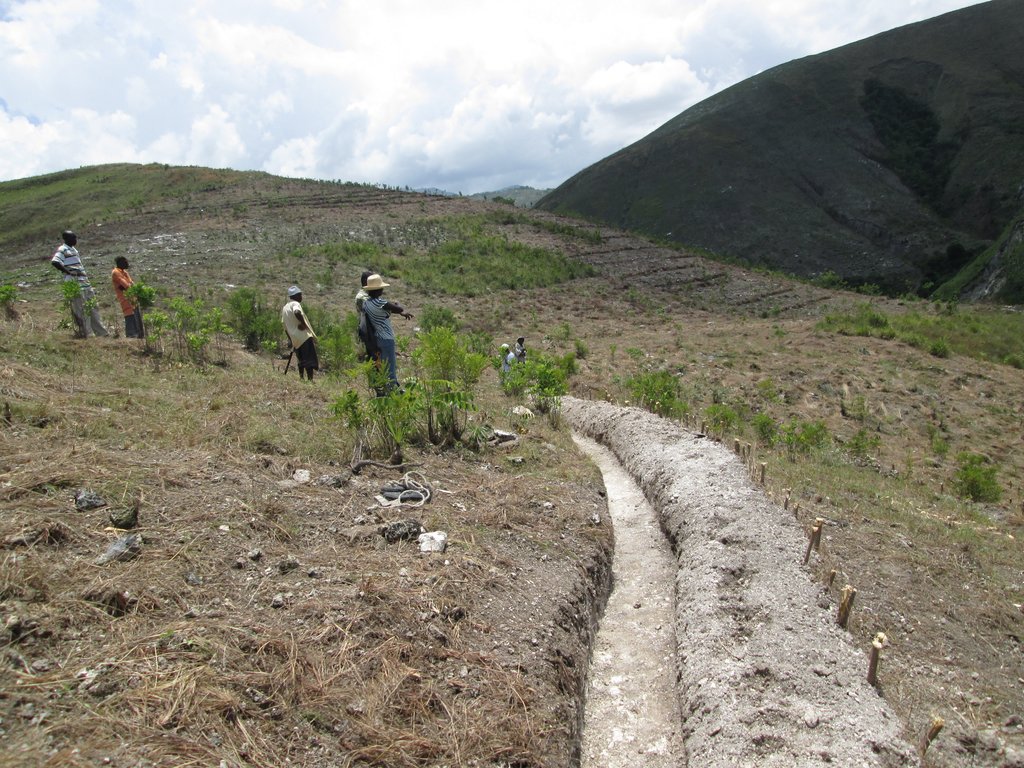
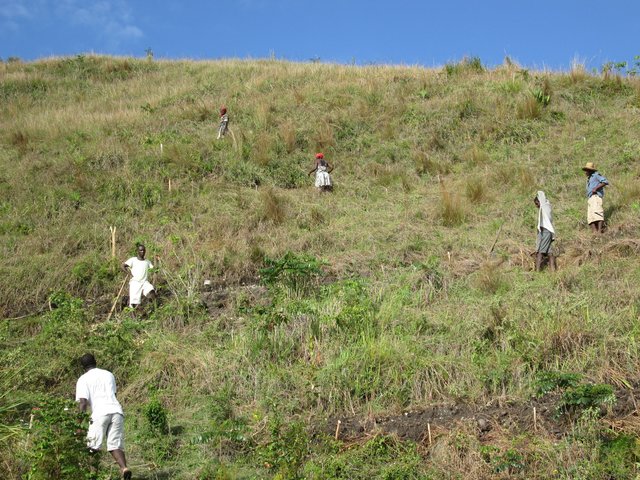
In a second zone of a minimum of 5 ha upstream of the resource, restrictions to the use of the terrain apply, notably with regard to defecation, free-range livestock farming and other harmful human activities, in order to protect the soil and the water quality. The terrain is managed so as to guarantee a good conservation of the soils by reforestation (agroforestry) with different varieties of fruit trees and timber. A third zone can be established if supported by the community, with restrictions on slash-and-burn and free-range grazing, as well as means to preserve the soils and to manage the vegetation cover. This latter zone can cover the whole catchment, and is meant to promote groundwater recharge. The restoration of the catchment through the zoning and the implementation of physical structures includes different techniques such as vegetative barriers and stone walls.
The restrictions on the use of zone 2 are not necessarily in contrast with the interests of the producers. It turns out that the rainfed crops are too much exposed to climatic hazards, and that forestry is a more reliable alternative. Therefore they perceive the development and reforestation of their land as an exploitation of their heritage, and as a profitable investment in the long term, when they will be able to manage the exploitation of the trees and their fruit production. In the first two years, a total maximum grant of 400 USD per ha is paid to the producers in different terms, depending on the success of the conservation activities. These experiences have inspired the setting of national standards on the protection of drinking water resources.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Haití
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Artibonite, Central West
Especifique más el lugar :
Municipalities of Petit-Goâve, Verrettes, Savanette and Lachapelle
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
Comentarios:
The conservation measures are locally applied on the hillslopes, but the restrictions on the use of the protected zones apply uniformly.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Support and incentives through various projects from HELVETAS, in particular projects focused on water services, risk management and support to local governance.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Silvo-pastoralismo

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Ganadería de hacienda
Tipo de animal:
- cabras
- cattle

Bosques
- Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi) naturales
- Plantación de árboles, reforestación
Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi-) naturales: Especifique tipo de manejo:
- Tala selectiva
Plantación de árboles, reforestación: Especifique el origen y la composición de las especies:
- Variedades mixtas
Productos y servicios:
- Madera
- Leña
Comentarios:
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Two agricultural seasons with different crop species
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Comentarios:
Some zones were cultivated with annual crop varieties, and were subsequently transformed into protected zones, where selective felling is only authorized if natural regeneration is guaranteed, and if the vegetation cover provides an effective soil protection.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- medida de pendiente transversal
- manejo de agua subterránea
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas
- S2: Taludes, bancos
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bf: efectos nocivos de los fuegos

degradación del agua
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de aguas subterráneas
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
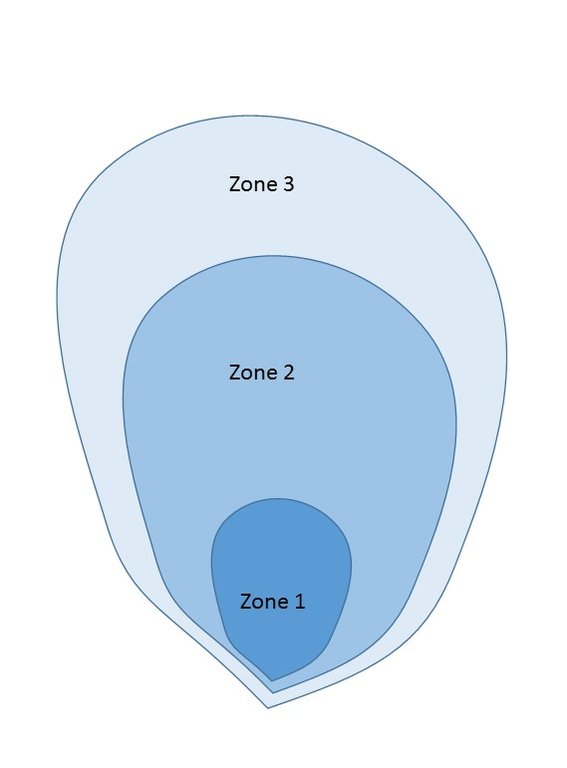
Three protection zones:
Zone 1: 1000 m2, public property, prohibition of any activity;
Zone 2: 50.000 m2, private property destined for agroforestry and protected by soil protection measures. Prohibition on housing, livestock farming, chemical fertilisation, latrines, waste disposal, slash-and-burn, etc.
Zone 3: all areas in the catchment upstream of zone 2, depending on agreements with the land owners and farmers, oriented on agroforestry and protected by sustainable land management measures.
Autor:
Helvetas Haiti
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
from 0,1 to 5 ha (reference unit 1 ha) - protection of one spring
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Discussion on legal provisions with the different actors | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 2. | Elaboration of a municipal decree | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 3. | Acquisition of zone 1 | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 4. | Fencing of zone 1 | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 5. | Development of the land plots in zones 1 and 2 | During the dry period (availability of farmers and stability of the slopes) |
| 6. | Treatment of gullies | During the dry period (availability of farmers and absence of surface runoff) |
| 7. | Training of farmers on conservation practices | Before the rainy season |
| 8. | Afforestation | At the start of the rainy season |
| 9. | Maintenance of physical structures | On the long term |
| 10. | Monitoring and inspection | On the long term |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Afforestation, gully correction, land management, fencing | person days | 300,0 | 6,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | shovel, hammer, etc. | None | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings (lump sum for grass and bushes for slope stabilization) | average per site | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 4,0 |
| Material de construcción | Cement, iron, PVC, piles | average per site | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Otros | Acquisition of zone 1 (1000 m2) | lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Otros | Rehabilitation and legalization (zone 1) | site | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 2680,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 2680,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The supporting project
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of physical structures (dry stone walls, etc.) | after the rainy seasons (two times per year) |
| 2. | Control and monitoring of the zoning regulation (the municipal decree) | Long-term monitoring |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Maintenance of physical structures (1 person-day) | person day | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 25,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 25,0 | |||||
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The maintenance operations depend on the meteorological conditions (in particular heavy rainfall) and on the type and quantity of structural measures. The topography and geomorphology influence the stability of the structures and hence the maintenance. The maintenance costs are carried by the farmers, or in certain cases by the committee for the provision of drinking water. The control on the restrictions of use of the protected zones is carried out by the local authorities together with the committee for the provision of drinking water. Hence, the costs are distributed over the community funds and financial resources from the water services.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1500,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Very variable between the regions of the country (from 500 to 3000 mm and above)
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
excesiva
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Intensive rainfalls lead to temporary excess of water, contributing to superficial erosion.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Access to drinking water and irrigation water is arranged by different rules. In general any individual has access to drinking water, but the rights to use water for irrigation are restricted. The capturing of sources for water supply to downstream areas most often causes difficult negotiations between the communities upstream and downstream in the catchment.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
No facility for water extraction
Cantidad luego de MST:
Water extracted from source
Comentarios/ especifique:
Extraction and conveyance of water
calidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
Contamination by human activities
Cantidad luego de MST:
Decreasing contamination according to the monitoring of behavior
Comentarios/ especifique:
Defecation in the open air is practiced by half of the households in the rural areas. The restrictions on access of the protected zones must be accompanied by raising awareness on the hygiene and by improving the availability of sanitation services.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Impactos socioculturales
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
The zoning and bio-engineering measures improve the water quality, which diminishes problems related to fecal contamination etc.
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
The zoning and bio-engineering measures improve the water quality, which diminishes problems related to water rights, considering that water is a limited resource, and is often disputed.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase of infiltration, reduction of runoff and surface erosion, which conserves the soil fertility.
nivel freático/ acuífero
Cantidad antes de MST:
High surface runoff
Cantidad luego de MST:
Improved recharge
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase of infiltration and hence recharge of the groundwater table
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction of erosion by surface runoff
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
Comentarios/ especifique:
Better infiltration and controlled deviation of surface runoff, which diminishes the risk of landslides.
impactos de sequías
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase of soil moisture and recharge of the groundwater table, which diminishes the impact of droughts.
impactos de ciclones, tormentas de lluvia
Comentarios/ especifique:
The measures diminish the effects of storms and heavy rainfall events by a reduction of surface erosion and a more controlled drainage of water in the gullies, which are stabilized by walls and vegetative barriers.
riesgo de incendio
Cantidad antes de MST:
practice of slash-and-burn
Cantidad luego de MST:
elimination of slash-and-burn practice
Comentarios/ especifique:
Certain bio-engineering measures such as dry stone walls or vegetative barriers can limit the propagation of fires.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Surface runoff and discharge upstream reduce the risk of flooding downstream.
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
The conservation of soils and woodland in the protected zones reduces and delays the surface runoff, and therefore flood events are less intense. Yet, the area covered by protection measures is still insufficient to manage flood risks.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | incrementó | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ciclón extra tropical | moderadamente |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | moderadamente |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación repentina | bien |
| deslizamiento | moderadamente |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The measures should be promoted as an investment with an initial cost but a positive return in the medium and long term.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 11-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Protection of 34 water resources; 27 ha in zone 1 have been fenced and afforested, 281 ha in zone 2 have been afforested and protected. More than 500 farmers were trained to implement and replicate the various protection measures.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
The number of replications is low due to the widespread poverty in the region.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The farmers are supported to implement a cost-effective forestry system to replace a very vulnerable rainfed agricultural production system. But it is the population in the downstream part of the catchment who benefits from the protection of the sources, since the quality and quantity of the water is improving. Therefore an equilibrium must be found between the two populations, in order to make both benefit. The water services can be profitable, and hence encourage participation in the efforts of protection upstream in the catchment, by supporting the producers and/or by financing jobs for the protection of land and water. |
| The protection of water resources increases the value of the common heritage and therefore calls for a community-based management. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| On the basis of the vulnerability of the population and the environment in the rural environment of Haiti, the protection of water resources should be established to guarantee a secure and profitable use of water. The participatory methods implemented allow to create a supportive environment, suitable for a community-based effort for local rural development. These mechanisms inspire a culture of citizenship in a local democratic context under development. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The management of state land in zone 1 poses a challenge because this land has to be integrated into the property of the state. The purchase or compensation of these lots can require a long negotiation between the local authorities and the owners. | It is important that the local actors resolve these matters among themselves, and that there is no interference from a project, in order to not distort the negotiation. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The sustainability of the measures and the cost of maintenance are largely dependent on the quality of the measures. | Ensure a good technical instruction and follow-up on-site by trained staff. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Monitoring of all sites by the actors, during the entire project.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Participatory process of capitalization.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Existing document on the capitalization of protecting water resources.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
20/09/2016
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Boire l’eau et penser à la source (long version)
URL:
https://assets.helvetas.org/downloads/capex_hsi_protection_des_source_vlongue.pdf
Título/ descripción:
Boire l’eau et penser à la source (short version)
URL:
https://assets.helvetas.org/downloads/capex_hsi_protection_des_sources_vcourte.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Concertation locale pour la protection des ressources [Haití]
La concertation pour la gestion des ressources naturelles implique les communautés, les autorités et l'ensemble des acteurs dans la prise de décision collective pour protéger les ressources en eau notamment, et institutionnaliser leur gestion.
- Compilador: Antoine Kocher
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos