Protection of water resources [ប្រទេសហៃទី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Antoine Kocher
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Eveline Studer
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger, Eveline Studer
technologies_583 - ប្រទេសហៃទី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Focal person EPA HELVETAS
Helvetas
ប្រទេសហៃទី
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Concertation locale pour la protection des ressources [ប្រទេសហៃទី]
La concertation pour la gestion des ressources naturelles implique les communautés, les autorités et l'ensemble des acteurs dans la prise de décision collective pour protéger les ressources en eau notamment, et institutionnaliser leur gestion.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Antoine Kocher
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
The protection of water resources is essential for the supply of drinking water in the rural zones of Haiti, by enabling to preserve the water quality and facilitate the recharge of the resource. Organizing the actors related to the water resource and to the economic, environmental and communal challenges is crucial. This implies, apart from management, the implementation of various technical measures.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The majority of water resources in Haiti is subject to bacterial contamination, which endangers the health of the consumers. The infrastructure for the abstraction and conveyance of water is periodically put to the test by the large variation of discharge, like floods, but also by low flows. The protection of water resources aims to strengthen local actors to better manage water resources. The objective is to take care of the protection of water resources at local level according to rules which are established and accepted by the actors with regard to legal, sociocultural and biophysical aspects.
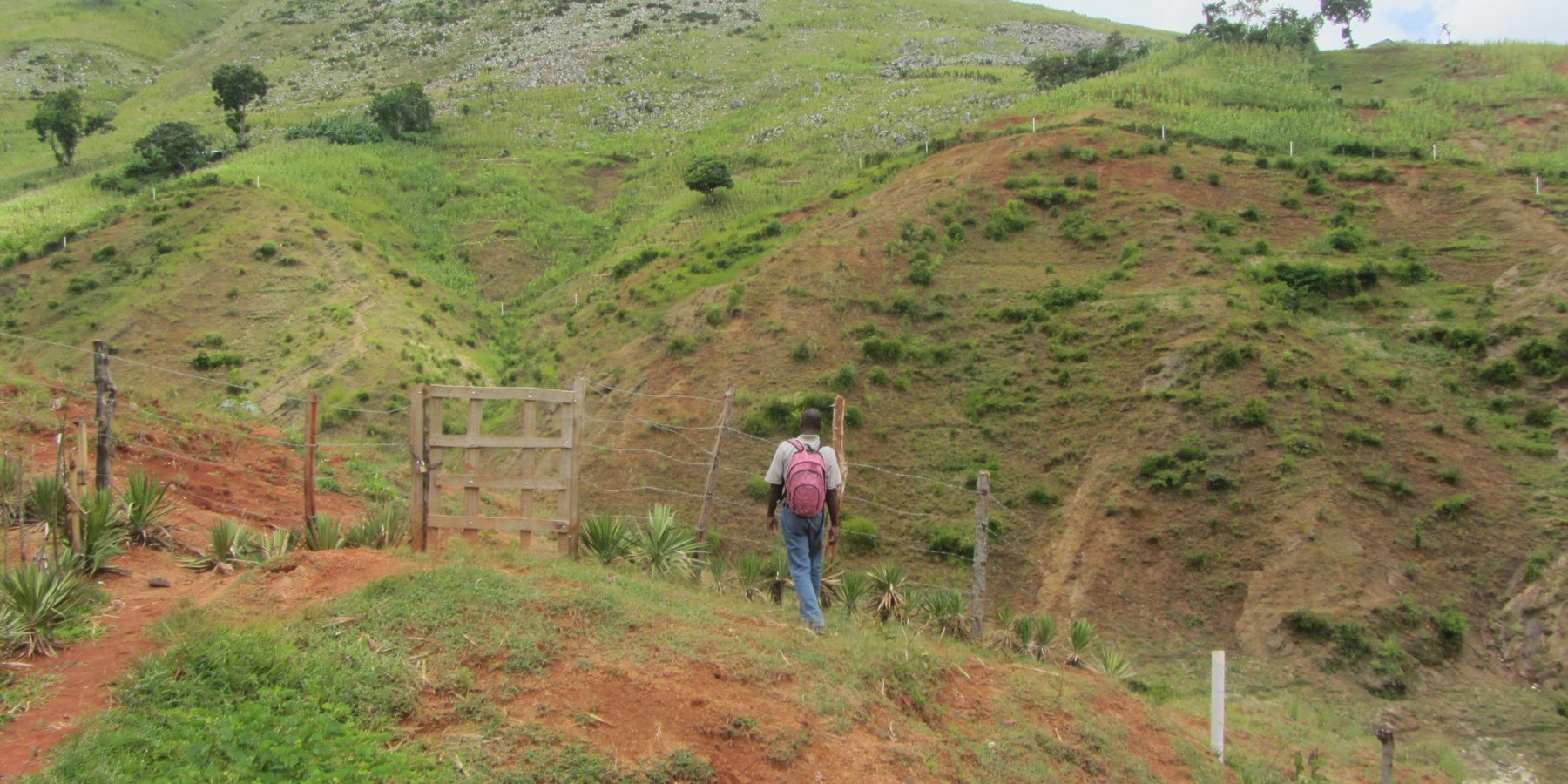
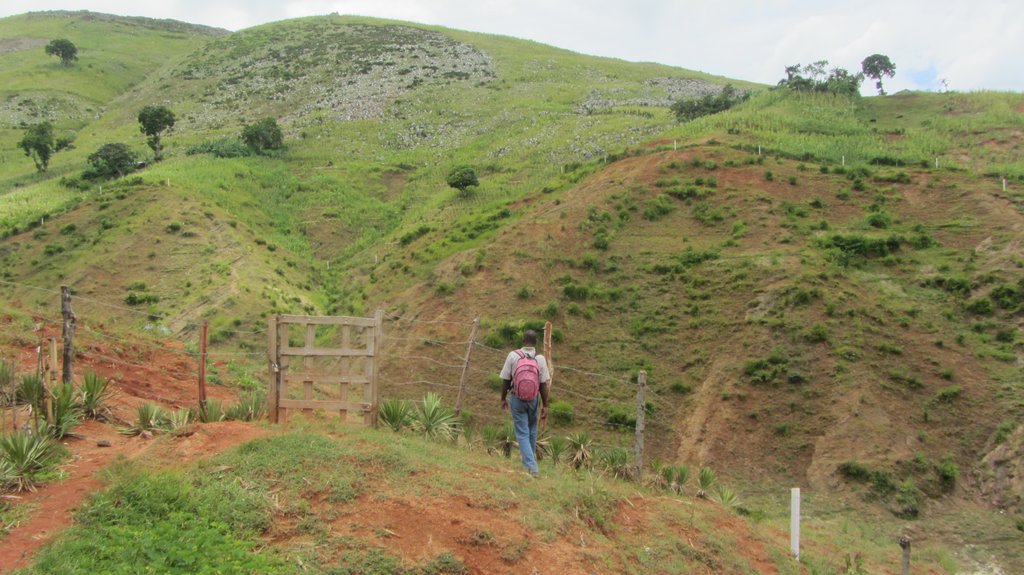
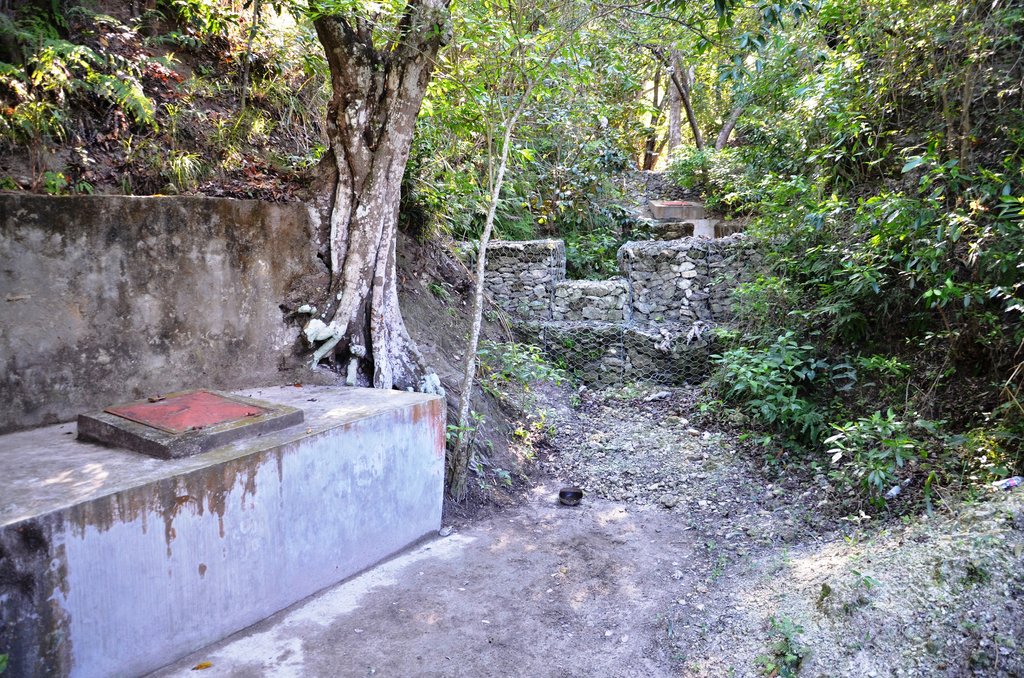
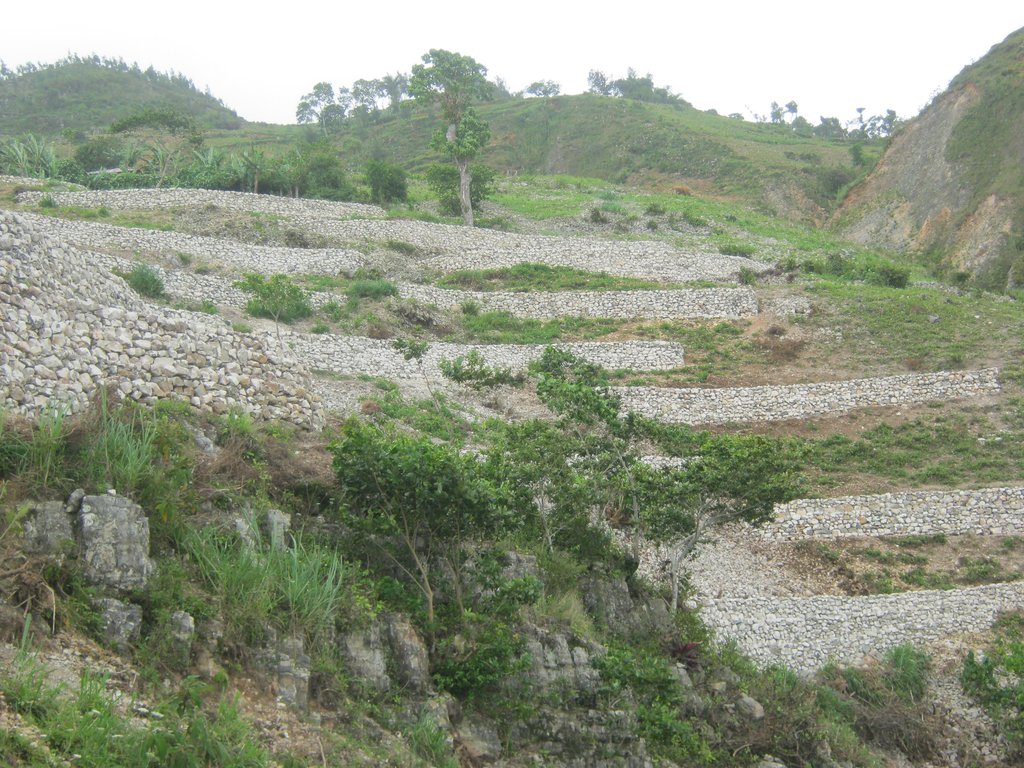
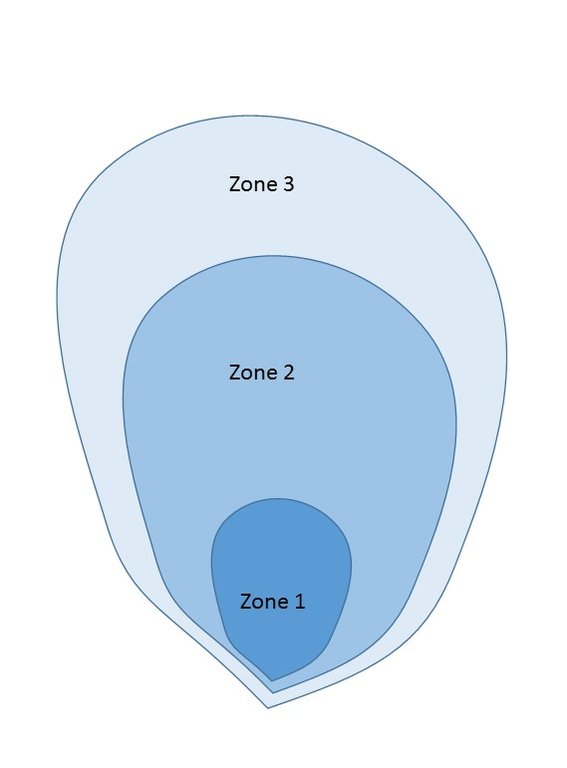
The protection of water resources also implies that technical measures are implemented to conserve and protect catchments, in order to ensure the quality and quantity of the required water and the recharge of groundwater bodies. The technical measures are defined for different zones. Three categories of zones are established with specific restrictions and recommendations, and formalized in a municipal decree which is published by the town councils. A first zone of 1000 m2 directly upstream of the water resource is brought into the domain of the state, fenced, reforested and totally protected from human activities.
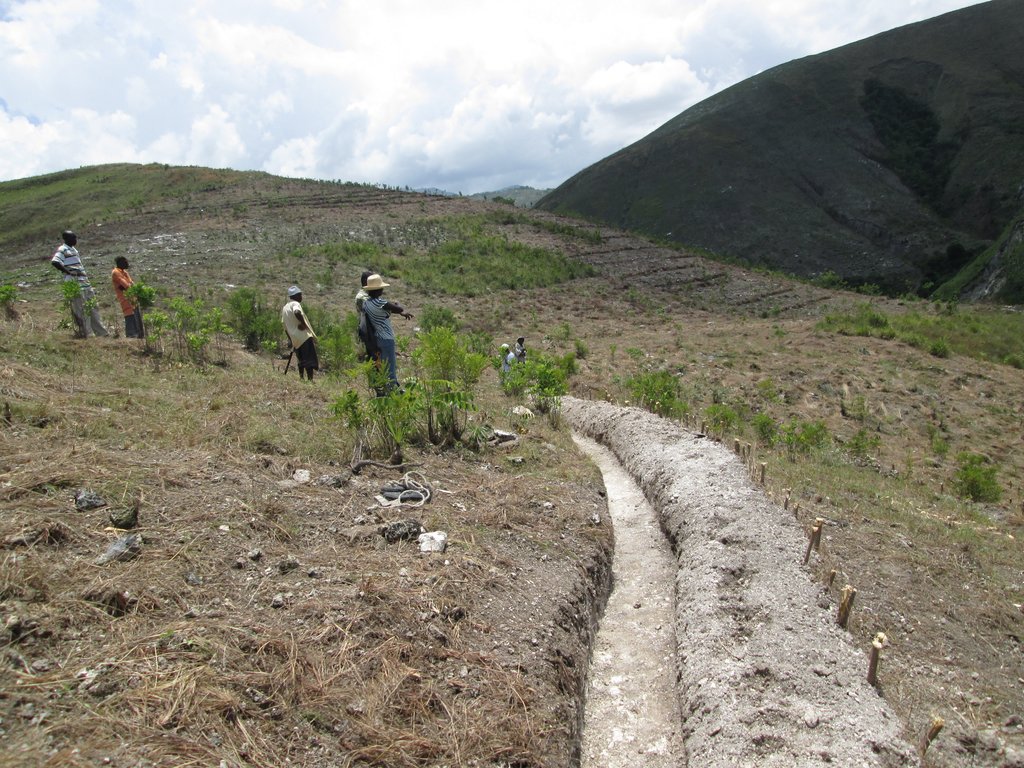
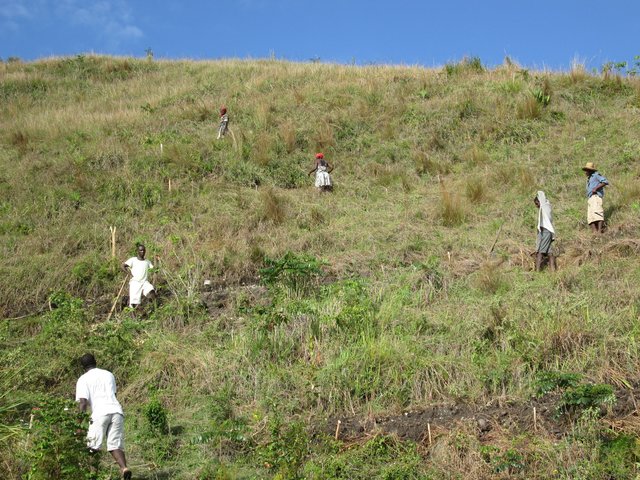
In a second zone of a minimum of 5 ha upstream of the resource, restrictions to the use of the terrain apply, notably with regard to defecation, free-range livestock farming and other harmful human activities, in order to protect the soil and the water quality. The terrain is managed so as to guarantee a good conservation of the soils by reforestation (agroforestry) with different varieties of fruit trees and timber. A third zone can be established if supported by the community, with restrictions on slash-and-burn and free-range grazing, as well as means to preserve the soils and to manage the vegetation cover. This latter zone can cover the whole catchment, and is meant to promote groundwater recharge. The restoration of the catchment through the zoning and the implementation of physical structures includes different techniques such as vegetative barriers and stone walls.
The restrictions on the use of zone 2 are not necessarily in contrast with the interests of the producers. It turns out that the rainfed crops are too much exposed to climatic hazards, and that forestry is a more reliable alternative. Therefore they perceive the development and reforestation of their land as an exploitation of their heritage, and as a profitable investment in the long term, when they will be able to manage the exploitation of the trees and their fruit production. In the first two years, a total maximum grant of 400 USD per ha is paid to the producers in different terms, depending on the success of the conservation activities. These experiences have inspired the setting of national standards on the protection of drinking water resources.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសហៃទី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Artibonite, Central West
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Municipalities of Petit-Goâve, Verrettes, Savanette and Lachapelle
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
The conservation measures are locally applied on the hillslopes, but the restrictions on the use of the protected zones apply uniformly.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Support and incentives through various projects from HELVETAS, in particular projects focused on water services, risk management and support to local governance.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- ដីព្រៃឈើ និងដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វពពែ
- cattle

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ / ដីព្រៃ៖ បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគ្រប់គ្រង:
- កាប់តែមួយចំនួន
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំដើមឈើឡើងវិញ៖ បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទក្នុងតំបន់ និងប្រភេទលុប:
- ពូជបញ្ចូលគ្នា
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ឈើហ៊ុប
- អុស
មតិយោបល់:
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Two agricultural seasons with different crop species
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
មតិយោបល់:
Some zones were cultivated with annual crop varieties, and were subsequently transformed into protected zones, where selective felling is only authorized if natural regeneration is guaranteed, and if the vegetation cover provides an effective soil protection.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកក្រោមដី
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S1: ការធ្វើដីថ្នាក់ៗតាមជម្រាលភ្នំ
- S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង
- S6: ជញ្ជាំង, របាំង, របងឈើខ្ពស់ៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bf: ផលប៉ះពាល់ដែលបណ្តាលមកពីភ្លើងឆេះ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Three protection zones:
Zone 1: 1000 m2, public property, prohibition of any activity;
Zone 2: 50.000 m2, private property destined for agroforestry and protected by soil protection measures. Prohibition on housing, livestock farming, chemical fertilisation, latrines, waste disposal, slash-and-burn, etc.
Zone 3: all areas in the catchment upstream of zone 2, depending on agreements with the land owners and farmers, oriented on agroforestry and protected by sustainable land management measures.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Helvetas Haiti
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
from 0,1 to 5 ha (reference unit 1 ha) - protection of one spring
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
5
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Discussion on legal provisions with the different actors | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 2. | Elaboration of a municipal decree | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 3. | Acquisition of zone 1 | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 4. | Fencing of zone 1 | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 5. | Development of the land plots in zones 1 and 2 | During the dry period (availability of farmers and stability of the slopes) |
| 6. | Treatment of gullies | During the dry period (availability of farmers and absence of surface runoff) |
| 7. | Training of farmers on conservation practices | Before the rainy season |
| 8. | Afforestation | At the start of the rainy season |
| 9. | Maintenance of physical structures | On the long term |
| 10. | Monitoring and inspection | On the long term |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Afforestation, gully correction, land management, fencing | person days | 300,0 | 6,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | shovel, hammer, etc. | None | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seedlings (lump sum for grass and bushes for slope stabilization) | average per site | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 4,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Cement, iron, PVC, piles | average per site | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Acquisition of zone 1 (1000 m2) | lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Rehabilitation and legalization (zone 1) | site | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2680,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 2680,0 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
The supporting project
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of physical structures (dry stone walls, etc.) | after the rainy seasons (two times per year) |
| 2. | Control and monitoring of the zoning regulation (the municipal decree) | Long-term monitoring |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Maintenance of physical structures (1 person-day) | person day | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 25,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 25,0 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The maintenance operations depend on the meteorological conditions (in particular heavy rainfall) and on the type and quantity of structural measures. The topography and geomorphology influence the stability of the structures and hence the maintenance. The maintenance costs are carried by the farmers, or in certain cases by the committee for the provision of drinking water. The control on the restrictions of use of the protected zones is carried out by the local authorities together with the committee for the provision of drinking water. Hence, the costs are distributed over the community funds and financial resources from the water services.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
1500,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Very variable between the regions of the country (from 500 to 3000 mm and above)
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីផត
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
លើស
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Intensive rainfalls lead to temporary excess of water, contributing to superficial erosion.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អខ្លាំង
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
Access to drinking water and irrigation water is arranged by different rules. In general any individual has access to drinking water, but the rights to use water for irrigation are restricted. The capturing of sources for water supply to downstream areas most often causes difficult negotiations between the communities upstream and downstream in the catchment.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកបរិភោគដែលអាចទាញយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
No facility for water extraction
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Water extracted from source
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Extraction and conveyance of water
គុណភាពទឹកបរិភោគ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Contamination by human activities
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Decreasing contamination according to the monitoring of behavior
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Defecation in the open air is practiced by half of the households in the rural areas. The restrictions on access of the protected zones must be accompanied by raising awareness on the hygiene and by improving the availability of sanitation services.
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The zoning and bio-engineering measures improve the water quality, which diminishes problems related to fecal contamination etc.
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The zoning and bio-engineering measures improve the water quality, which diminishes problems related to water rights, considering that water is a limited resource, and is often disputed.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase of infiltration, reduction of runoff and surface erosion, which conserves the soil fertility.
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
High surface runoff
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Improved recharge
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase of infiltration and hence recharge of the groundwater table
ដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduction of erosion by surface runoff
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ដីបាក់/ លំហូរកំទិចកំទី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Better infiltration and controlled deviation of surface runoff, which diminishes the risk of landslides.
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase of soil moisture and recharge of the groundwater table, which diminishes the impact of droughts.
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃព្យុះស៊ីក្លូន/ព្យុះភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The measures diminish the effects of storms and heavy rainfall events by a reduction of surface erosion and a more controlled drainage of water in the gullies, which are stabilized by walls and vegetative barriers.
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
practice of slash-and-burn
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
elimination of slash-and-burn practice
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Certain bio-engineering measures such as dry stone walls or vegetative barriers can limit the propagation of fires.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Surface runoff and discharge upstream reduce the risk of flooding downstream.
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The conservation of soils and woodland in the protected zones reduces and delays the surface runoff, and therefore flood events are less intense. Yet, the area covered by protection measures is still insufficient to manage flood risks.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះស៊ីក្លូនត្រូពិចបន្ថែម | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ដោយទឹកភ្លៀង | ល្អ |
| ដីបាក់ | មធ្យម |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
The measures should be promoted as an investment with an initial cost but a positive return in the medium and long term.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 11-50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
Protection of 34 water resources; 27 ha in zone 1 have been fenced and afforested, 281 ha in zone 2 have been afforested and protected. More than 500 farmers were trained to implement and replicate the various protection measures.
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
The number of replications is low due to the widespread poverty in the region.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The farmers are supported to implement a cost-effective forestry system to replace a very vulnerable rainfed agricultural production system. But it is the population in the downstream part of the catchment who benefits from the protection of the sources, since the quality and quantity of the water is improving. Therefore an equilibrium must be found between the two populations, in order to make both benefit. The water services can be profitable, and hence encourage participation in the efforts of protection upstream in the catchment, by supporting the producers and/or by financing jobs for the protection of land and water. |
| The protection of water resources increases the value of the common heritage and therefore calls for a community-based management. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| On the basis of the vulnerability of the population and the environment in the rural environment of Haiti, the protection of water resources should be established to guarantee a secure and profitable use of water. The participatory methods implemented allow to create a supportive environment, suitable for a community-based effort for local rural development. These mechanisms inspire a culture of citizenship in a local democratic context under development. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The management of state land in zone 1 poses a challenge because this land has to be integrated into the property of the state. The purchase or compensation of these lots can require a long negotiation between the local authorities and the owners. | It is important that the local actors resolve these matters among themselves, and that there is no interference from a project, in order to not distort the negotiation. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The sustainability of the measures and the cost of maintenance are largely dependent on the quality of the measures. | Ensure a good technical instruction and follow-up on-site by trained staff. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
Monitoring of all sites by the actors, during the entire project.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Participatory process of capitalization.
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
Existing document on the capitalization of protecting water resources.
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
20/09/2016
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Boire l’eau et penser à la source (long version)
វេបសាយ:
https://assets.helvetas.org/downloads/capex_hsi_protection_des_source_vlongue.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Boire l’eau et penser à la source (short version)
វេបសាយ:
https://assets.helvetas.org/downloads/capex_hsi_protection_des_sources_vcourte.pdf
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Concertation locale pour la protection des ressources [ប្រទេសហៃទី]
La concertation pour la gestion des ressources naturelles implique les communautés, les autorités et l'ensemble des acteurs dans la prise de décision collective pour protéger les ressources en eau notamment, et institutionnaliser leur gestion.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Antoine Kocher
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល