Pre-Monsoon Dry Sowing (PMDS) [India]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Santosh Gupta
- Editores: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Kim Arora, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: Udo Höggel, Sally Bunning
technologies_6697 - India
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
GIZ India (GIZ India) - IndiaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - KeniaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - India1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology described here is related to sustainable land and other resource management systems.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
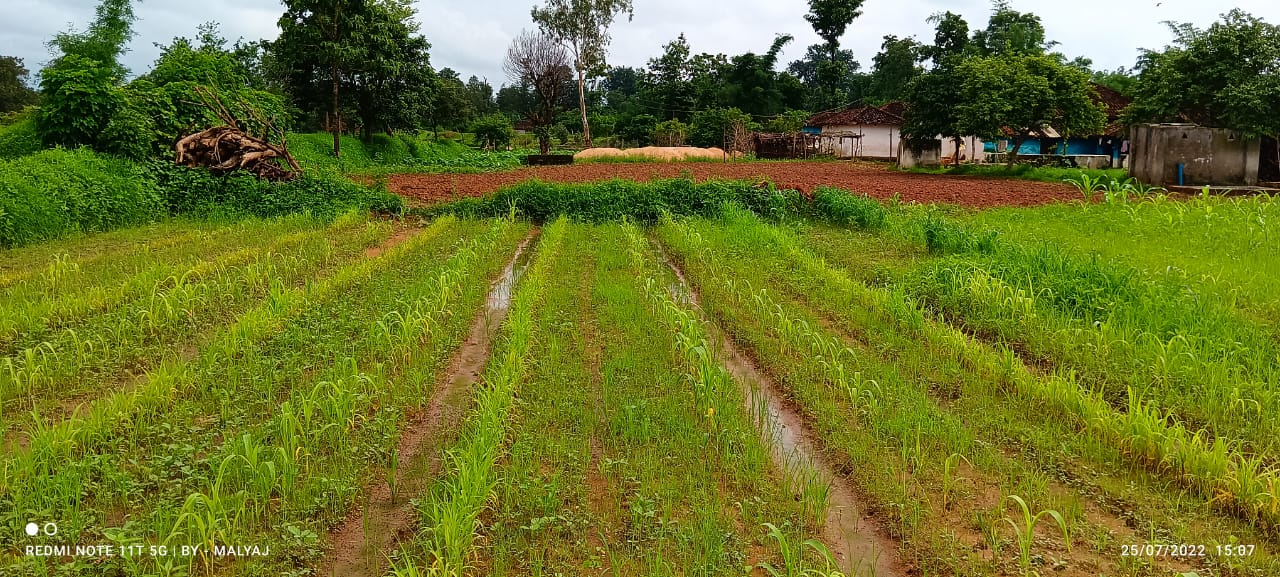
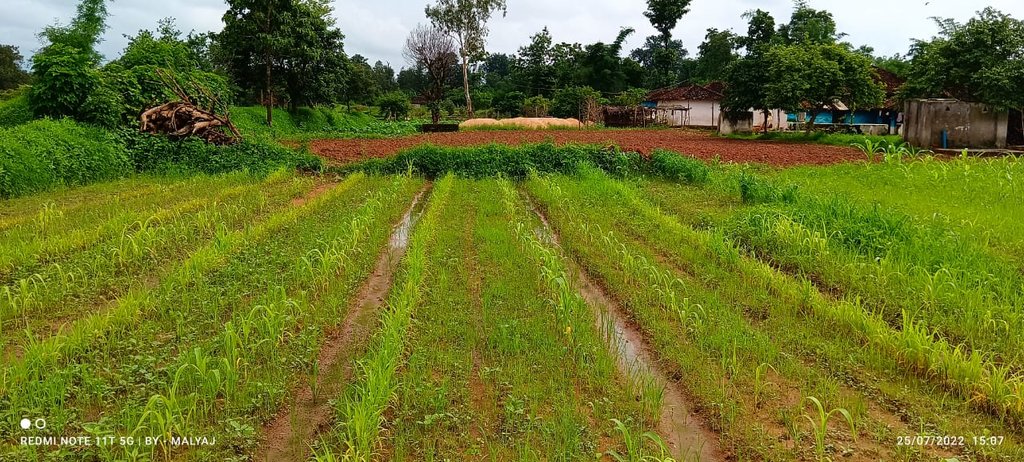
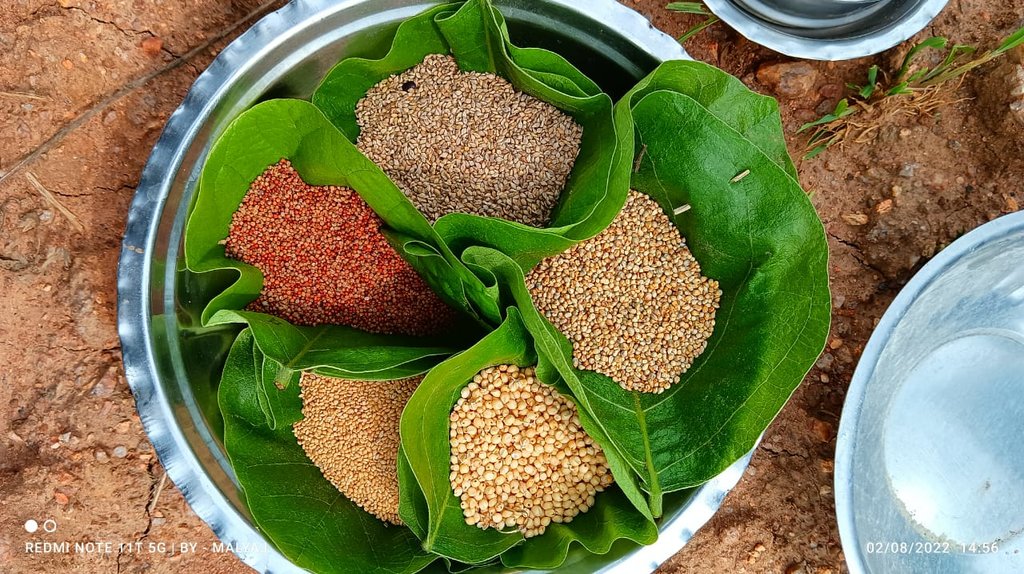
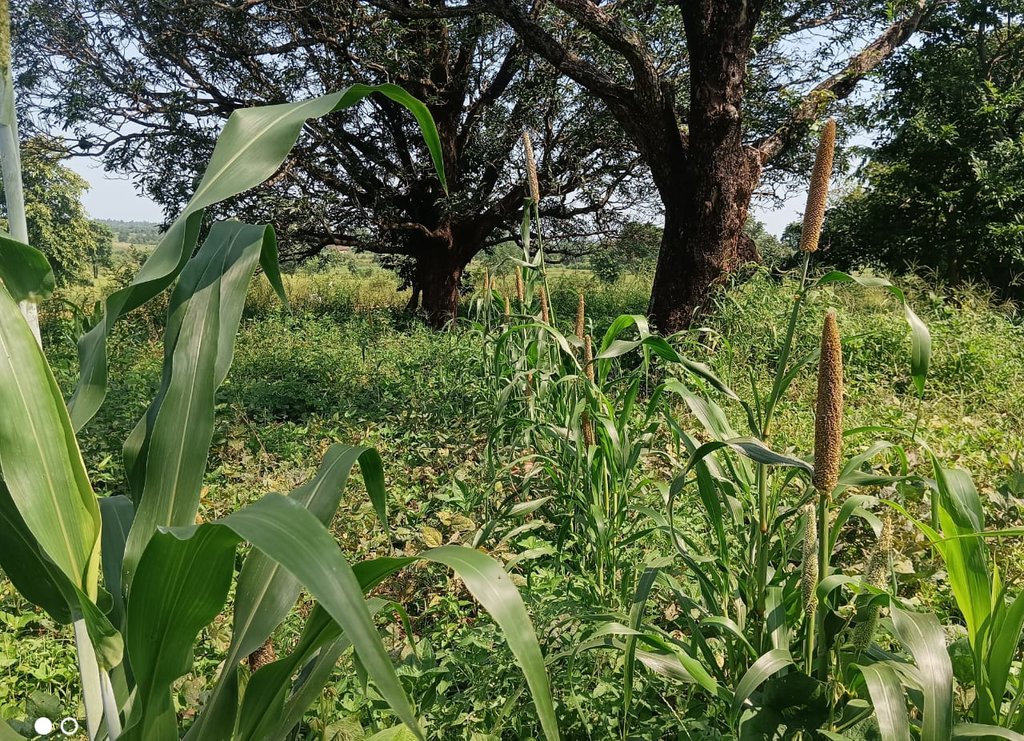
The Pre-Monsoon Dry Sowing Technology aims to sow 12 to 15 different crop varieties in April without waiting for rain. To achieve this the seeds are pelletized with a mixture of clay soils, bio-inoculants like dried Ghanjeevamruth and Dravajeevamrit, and ash. The main objective of this technology is to empower rainfed farmers by utilizing the initial rainfall in April and May for crop cultivation. By using pelettized seeds, they can maximize the effectiveness of rainfall showers before the arrival of the monsoon season. Such seeds can also survive, if there are delay in the rainfall as the pellets around the seed help it in maintaining the moisture.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Pre-monsoon dry sowing (PMDS) is a system of sowing, tilling and tending the land wherein the farmer grows crops in non-farming seasons or whenever there is no crop cover on the land. This can be practised before the advent of monsoon, during summer (April-May), after Kharif and before the beginning of the Rabi season (September and October). PMDS harnesses the water vapor from air that gets settled in the form of early morning dew. The dew supplies the required moisture to the soil. (Reference:-https://apcnf.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/IDS-2020-2021-APCNF-PMDS-Report.pdf)
In the study where PMDS was practised before the onset of the monsoon season, typically during the dry month of April. The seeds are pelletized with a mixture of clay soils, bio-inoculants, and ash, which creates a protective coating around the seed and helps it to germinate even in the case of delayed rains or very little rainfall. The coating around the seed, helps it to maintain moisture and support its germination. As the name suggests, the technology is good for utilising the pre-monsoon season by advancing the sowing cycles, using the usually dry months of summer and utilising the pre-monsoon rains.
This technology benefits rainfed areas where farmers rely solely on rainfall for irrigation. PMDS aims to promote an extended duration of crop cover under rainfed conditions, allowing farmers to cultivate crops with a reduced risk of crop failure in the cases of delayed or lower rainfall. Since seeds are germinated before the arrival of monsoon, there are times when they can also survive the heavy rains. This technology is useful in utilising moisture to the best extent possible as seeds are covered with the outer layer of clay and other stuff. In the Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh, farmers utilized seeds from their homes, comprising 12 to 15 crops, including cereals, pulses, and spices. These collected seeds were pelletized, dried for 24 hours, and broadcasted into minimally tilled soil. The diversified crop combination was grown until July and mixed with the soil before paddy transplanting. This process improves the soil's microbial activity, resulting in increased yields in crops grown before paddy and in the paddy crop itself. Therefore, the farmers benefit from increased production and yields through this technique of PMDS.
PMDS not only improves the economics of farmers but it also improves soil health. The covering of the soil with different crops protects it from heat, pounding rain, and wind. It also improves diversity in soil microorganisms, beneficial insects and other species. Covering soil for 365 days with plant diversity is also critical to protect soil health and balance climate change. PMDS can facilitate all these functions.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
India
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Madhya Pradesh
Especifique más el lugar :
Bichhiya block
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
The technology is applied by rainfed farmers in the Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2022
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The modified PMDS technology used in another program, the Andhra Pradesh Natural Farming Program, has been adopted here.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - arroz (humedal)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Generally, Paddy is transplanted in July Month in the Mandla District and harvested around November. This region is majorly rainfed, and only 9% of the area has some irrigation source.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cereales - sorgo
- legumes and pulses - lentils
- Lentils include - Black gram, Cowpea, Green Gram, Red Gram and Oil seeds including sesame and Coriander.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
The above mention crops are generally mixed together and grown on the same patches of land in April.
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
Comentarios:
The PMDS technology has enabled crop diversification in the Mandla District from April to July.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- perturbación mínima del suelo
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A6: Manejo de residuos
A6: Especifique manejo de residuos:
A 6.4: retenido

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
The PMDS (pre-monsoon dry sowing) technique involves crop diversification and the utilization of rainfed land from April to July, typically left unused, to improve soil health. This is achieved by planting green crops that are later harvested, leaving the crop biomass in the soil to retain moisture, and subsequently growing paddy crops on the same land. This approach has the added benefit of increasing yields, improving crop quality, and reducing farmers' reliance on only one single crop.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación
- Pu: pérdida de la función bioproductiva a causa de otras actividades

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
Comentarios:
Mandla district receives rainfall of around 1500mm, and soil is highly susceptible to erosion. Covering the soil with different crops reduces the erosion potential, and mixing the soil with biomass improves soil health.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Land degradation by water erosion is reduced by covering the topsoil with crops for an extended duration. The addition of crop biomass improves soil health.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
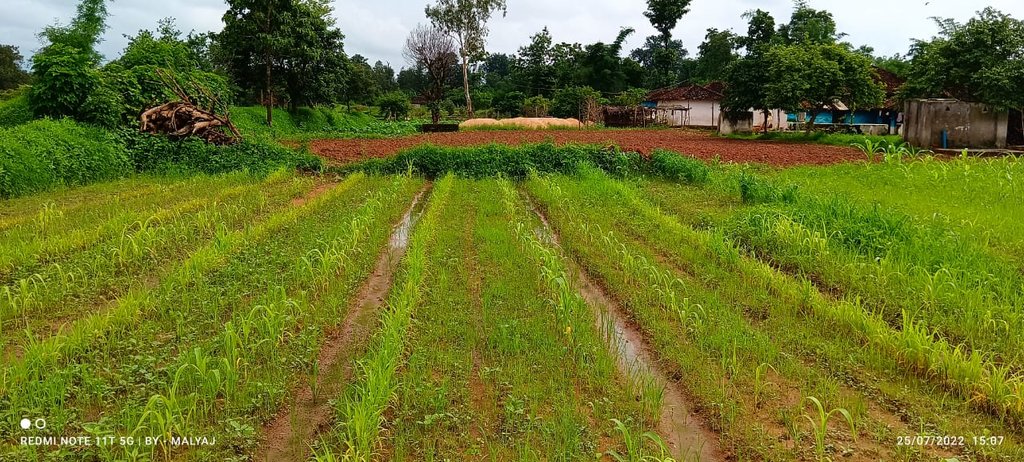
PMDS was undertaken at various sizes of plots based on the availability of land with farmers. Some farmers did at 0.10 acres of land while others did at 2 acres. Also, there was no fixed pattern that was followed for the quantity and variety of seeds. Whatever seeds were available were sown. In the image above, it can be seen that the field where PMDS was undertaken has multiple crops at different stages of their growth while the area with no PMDS has no crop and fallow red soil can be seen.
Autor:
Santosh
Fecha:
22/02/2023
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1 acre
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
INR (March, 2023)
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
82,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
204 INR
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
Comentarios:
There are no establishment activities under the PMDS.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Comentarios:
There are no establishment costs required for PMDS as it's only a sowing activity. Farmers do hire agriculture equipments to undertake the activity.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
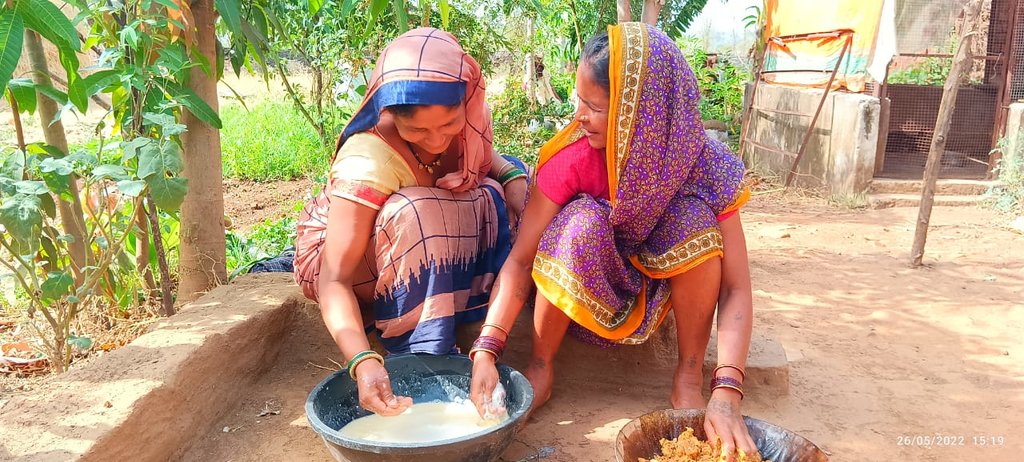
| 1. | Collection of seeds | 1 month before the onset of Monsoon (mid May in project area) |
| 2. | Seed treatment and preparation of seed balls | End of May in project area |
| 3. | Broadcasting of the seed balls | End of May in project area |
| 4. | Soil rotation | 2-3 days after the broadcasting of seed balls |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fodder and other produces | Mid of June to mid of July |
| 6. | Mixing the green manure in soils | End of July or before transplantation of rice |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Seed treatment, preparation of seed balls | Person days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Broadcasting of seeds | Person days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Harvesting of the crops | Person days | 2,0 | 150,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Agriculture equipment for soil rotation | Hour | 0,5 | 600,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Cultivator | Hour | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds of different crops | kg | 6,0 | 75,0 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Bio-inputs | LS | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 2450,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 29,7 | |||||
Comentarios:
Technical inputs were provided from the project around the seed treatment, sowing, and monitoring of the crops.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Availability of seeds, bio-inputs, and rainfall pattern. Usually, there are rains during the pre-monsoon season in the project area, however, in case of no rains at all during the entire summer, farmers may not be in a position to achieve the desired results.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1427,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Monsoon season is from June-September, which has the majority of the rainfall.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
District at glance report of Ministry of Water Resources, Central Groundwater Board, North Central Region BHOPAL, 2013
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
- semi-árida
The National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning (NBSS&LUP) developed twenty agroecological zones based on the growing period as an integrated criterion of adequate rainfall, and soil groups. It delineated boundaries adjusted to district boundaries with a minimal number of regions. Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh lies in a Hot subhumid ecoregion with red and black soil. Precepitation - 1000–1500mm; Potential evapotranspiration -1300–1500 mm; Length of growing period-150–180days.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Bichhiya is a block in the Mandla district characterized by diverse topography. The block is located in the southern part of the District and is situated in the foothills of the Satpura range.
The topography of the Bichhiya block is hilly. The block has an average elevation of around 550 meters above sea level. The hills are covered with forests and are rich in flora and fauna.
The region has several small streams and tributaries that flow through it, which are mostly seasonal and originate in the hills.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
The region has several small streams and tributaries that flow through it, primarily seasonal and originating in the hills. The area is also known for its waterfalls, including the Patalpani waterfall, a popular tourist destination.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Diversidad de hábitats:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The area is surrounded by Kasha National Park and Phen Wildlife Sanctuary, with a good presence of forest area. Thus biodiversity is outstanding.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Bichhiya block has a significant tribal population. According to the 2011 Census of India, the block has a total population of around 47,000, of which approximately 41% are classified as Scheduled Tribes (STs). The powerful tribes inhabiting the region include the Gonds, Baigas, and Korkus.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Based on the discussion with land users and implanting agency, production of the main crop (Paddy) increased by 20-25%. (The crop combination under PMDS has some nitrogen-fixing crops and the crop biomass improves the nutrient availability for the next crop which is paddy, also the better moisture helped the improvement in productivity of paddy crop as well.). Additional production from crops sown in April month was generated. An impact assessment study to document the quantifiable results has not been conducted so far.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Risk of of production failure reduced due to crop diversification
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop diversification by sowing multi crops of cereals, millets, pulses, and oilseeds in otherwise paddy predominant area
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The gross sown area increased as the land was brought under cultivation from April to July
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Through this technology crop biomass was added to improve soil to improve its organic content and structure
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase in farm income due to additional crop production and increase in yield of the main crop
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
12 to 15 different crops are grown in PMDS, reducing the crop failure chances and improvements in soil structure, therefore storing the soil moisture for an extended duration
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Diversity in crops will reflect in increased and more diverse food availability
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction in evaporation loss from April to July and effective utilization of soil moisture and rainfall in this duration
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved soil structure due to the addition of crop biomass in the soil leads to the retention of soil moisture. The extended duration of crop cover also reduces evaporation losses.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Extended duration of crop cover from April - July
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction in soil loss due to crop cover
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop biomass increases organic carbon in the soil improving the availability of nutrient in the soil
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Extended duration of vegetation cover of the soil
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase in biomass above ground by using pre-monsoon rainfall
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
12-15 different crops are sown togehter
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
micro-clima
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
All the impacts indicated here are based on the discussions with land users and implementing agency. The reported outcomes are based on eye observations and estimations. Some of the impacts are also based on the reports and secondary documents published on the PMDS.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
PMDS method is farmland-specific technology wherein effective utilization of natural resources (land and rainfall) is done. Therefore no direct off site impact of the technology is observed.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Otro cambio climático gradual | Adaptation to climate vulnerabilities by crop diversification and effective utilization of natural resources | incrementó | muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Otros extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
| otros (especifique) | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? |
|---|---|
| Adaptation to climate change | muy bien |
Comentarios:
The technology adapts well to climate change, as crop diversification sustains rainfall variability. An increase in soil biomass improves soil health. Making the system more resilient to climate variability.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The PMDS technology does not require any higher establishment cost, as most of the material is locally available. The maintenance of technology is also limited as once the pelleted seeds are sown there is hardly any maintenance required. The returns on the use of technology are very positive as an additional source of income is available.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Approximately 100 farmers have adopted the newly introduce PMDS technology in 2020-21.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
Comentarios:
Approximately 100 farmers have adopted the newly introduce PMDS technology in 2020-21, supported by capacity building and training programs
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
otros (especifique):
Diversified Combination
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
The crop combination is diversified based on the seeds available and household nutrition requirements
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Increase PMDS crop productivity and yield 20-25% subsequent crops, especially paddy crops |
| Soil structure is improved |
| Crop Diversification: 12 - 15 different crops are grown on the same piece of land |
| Fodder availability to animals during the summer season |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Ensuring a crop cover for 365 days leads to reduced soil erosion and improved soil health |
| Maintaining the soil moisture for the subsequent crops, which are cultivated in the rain-fed conditions |
| Regular practice of PMDS can increase the soil's organic carbon as a lot of green manure is incorporated in the soil resulting in higher carbon content |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Open grazing of cattle during summer is a common practice. As there are no standing crops in the field, farmers tend to allow their animals for open grazing. However, the cultivation of crops using the PMDS method tends to attract cattle as other fields in the project areas do not have any green cover. | Village-level community institutions can develop a system to minimize the grazing in the fields having crops or the higher adoption of PMDS by the farmers will gradually reduce this risk as PMDS can be a good source of green fodder as well. |
| Farmers are putting in extra quantities of seeds for various crops for sowing during the PMDS. In normal cases, they will sow the seeds only after the onset of the monsoon and when the field is ready for sowing. Thus in PMDS, they may feel like losing their seeds if there is no germination due to delays in monsoon or other reasons. | Farmers can be supported by providing seeds for the first year to mitigate the risk and exchanging weather-related information in advance. So that they can make an informed decision. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Very low to no awareness of the PMDS methodology and benefits among the project farmers. | Regular handholding and demonstrations along with good audio-video documentation for dissemination. |
| Possible delay in sowing and harvesting of the Kharif and Rabi crops due to delayed monsoon or appropriate soil conditions. | Scheduling the crops based on a crop calendar is one solution; another solution is to explore the seed varieties suitable for delayed sowing. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
4
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
3
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
1
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
2
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
22/02/2023
Comentarios:
During the field visit, interviews were conducted with land users and the project implementation team to understand the process, impact, and challenges in the adoption and implementation of PMDS technology.
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Assessing the Impact of Andhra Pradesh Community Managed Natural Farming: A comprehensive Approach Using Crop Cutting Experiments Pre-Monsoon Dry Sowing Farming in Andhra Pradesh
URL:
https://apcnf.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/IDS-2020-2021-APCNF-PMDS-Report.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos