Contour Grass Hedgerows on Steep Slopes [Bután]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: ONGPO LEPCHA
- Editor: Kuenzang Nima
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Tsayi Gaytshig (ཙྭའི་རྒད་ཚིག།)
technologies_6854 - Bután
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Daza Khemo
Boucholing village
Bután
usuario de la tierra:
Dorji Ugyen
Boucholing village
Bután
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Bután1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology described is not problematic with regard to land degradation.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
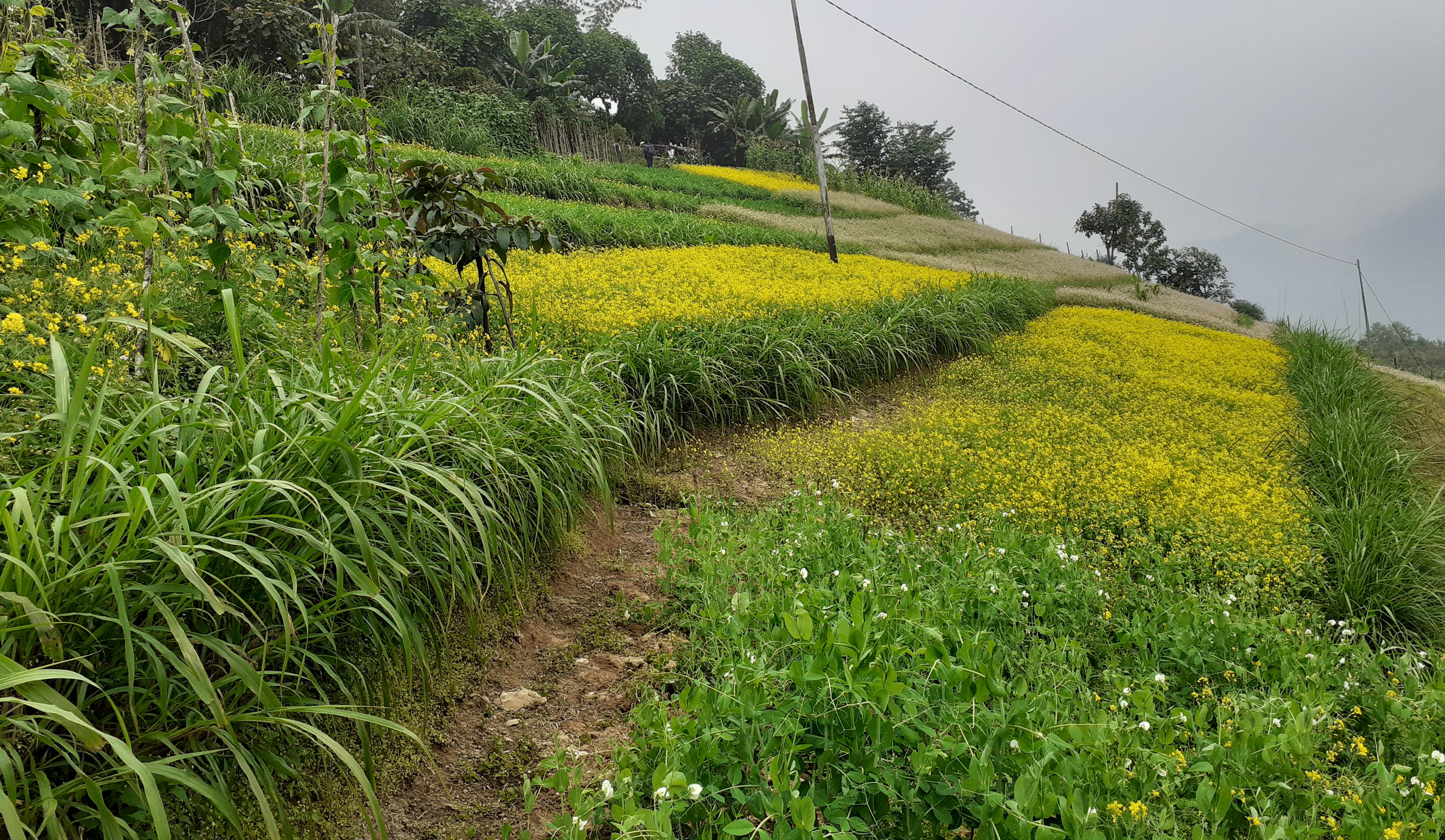
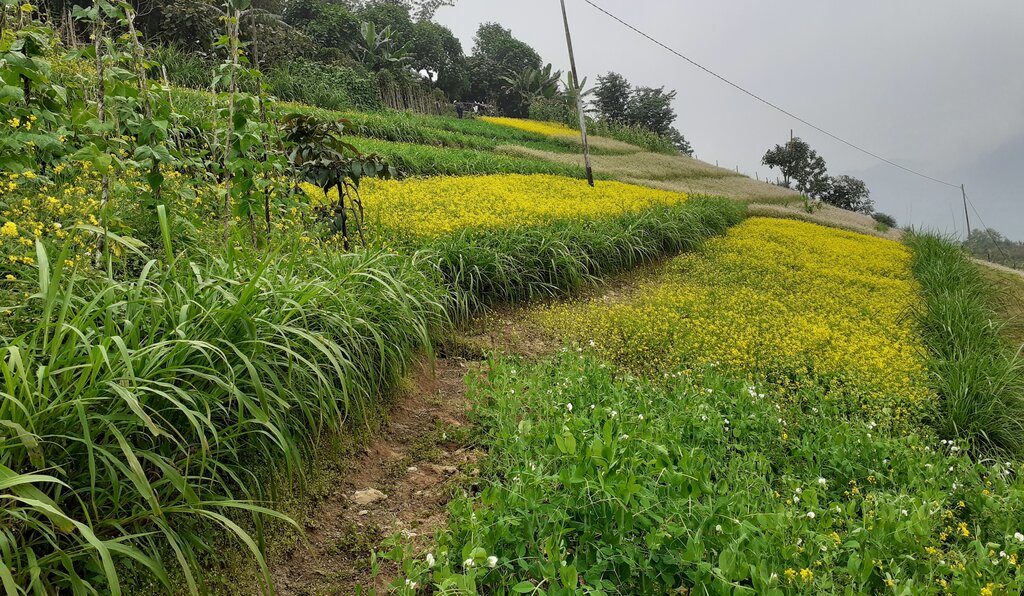
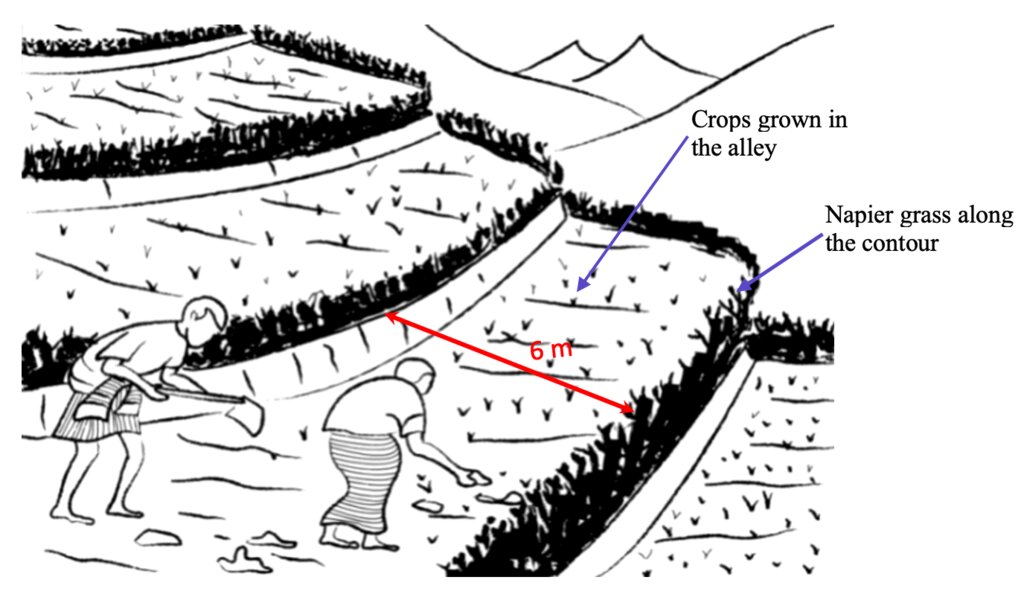
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involve planting of Napier grass cuttings along contour lines on the slope at a horizontal distance of 6 m. The area between the contour hedgerows is used for crop cultivation.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involves planting Napier stem cuttings along contour lines on slopes. They are planted at a horizontal distance of 6 meters between rows and 15-20 centimeters between cuttings within lines. On average it requires 3500-4000 Napier slips to cover one acre (0.4 ha). Hedgerows form living barriers that trap sediment and reduce surface runoff. With time, as the sediment builds up behind the hedges, the area between the hedgerows develops into flat alleys or “terrace beds”. This technology is effective in reducing soil erosion and conserving water. The hedgerows also boost crop productivity. The contour hedgerow system is widely used in hilly terrain in Bhutan and elsewhere.
The main purposes of the technology are to 1) serve as a barrier to check the movement of soil and water down the slope, 2) effectively utilize sloping areas for agricultural purposes, and 3) increase crop and fodder production.
The major activities/ inputs needed to establish/ maintain contour hedgerows are: 1) surveying of the area by an SLM specialist (planning and site assessment), 2) selecting suitable hedgerow planting materials, 3) registration of interested farmers, 4) training of farmers, 5) layout of contour lines using A-frames, 6) distribution of planting materials and establishment of hedgerows in farmland, 7) monitoring and evaluation of hedgerows, and 8) maintenance of hedgerows. Maintenance includes replacement of cuttings in gaps - either damaged by cattle or natural mortality and trimming of grass back to 15 centimeters after reaching 1 meter. Inputs required include: 1) planting materials (Napier grass), 2) A-Frame for contour lines, 3) spades, pickaxes, shovels, crowbars, etc., and 4) human resource input by SLM specialists.
Contour hedgerows have many benefits/ impacts on the livelihood of the land users including 1) soil and water conservation, 2) use of the sloping areas for crop or fodder production, 3) effective conservation through using local materials with a 90% survival rate, 4) habitat for natural predators, pollinators, insect-eating birds, and rodent predators, 5) groundwater recharge, and 6) they beautify the overall agricultural landscape. Another important benefit of the hedgerows is the availability of fodder grass for livestock, which otherwise would have to be collected from the forest. The disadvantages include the need for regular maintenance and gapping up. At times, conflicts arise within the community due to grazing of hedges by neighbors’ cattle.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Bután
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Mongar
Especifique más el lugar :
Boucholing village, Thangrong gewog (block), Mongar Dzongkhag (district)
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 10-100 km2
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2014
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The project was funded by UNDP and technical support was provided by the SLM Specialists from the National Soil Service Center and the agriculture extension agent of Thangrong gewog.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas dulces, ñame, taro/cocoy am, otro
- vegetales - verdura de hojas verdes (ensaladas, repollo, espinaca, otros)
- chilli
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Vegetables are grown for two times in a year but the cereal crops are grown for only one time.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
Maize and legumes
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Maize followed by vegetables
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water is a major constraint and land users mostly depend on rain for irrigation.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes
Comentarios:
Napier grass were planted on the bunds if the already constructed terrace.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
Comentarios:
The technology addresses the issue of soil erosion through rain and prevented the degradation the top soil.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
The main goal of the technology is to combat farm land degradation and prevent soil erosion.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Technical drawing as per the specification given in the SLM Guidelines 2021. See steps for the establishment of hedgerows below:
a)Determine the hedgerow interval for each landform based on the gradient (but based on farmers feedback, the interval is generally set at 6 meters) and then lay out the contour lines. Along the contours, prepare a strip of land with a width of about 40-50cm wide to plant the grass slips or broadcast fodder grass seeds. Napier (Pennisetum spp.) and Pakchong grass spp. is recommended as hedgerow plants for areas that are below 1600 m. However, for areas above 1600 m, temperate grass mixture should be considered;
b)A row of fodder grass slips or seedlings should be planted with a spacing of 15-20 cm. If grass slips are used, at least two nodes should be inserted into the soil for proper establishment/rooting. On the other hand, if grass seeds are used, the seed rate should be 25g per square metre;
c)Mulching should be done right after the grass slip planting or grass seeding to reduce surface erosion, conserve soil moisture, and aid proper germination;
d)Gap filling and trimming of hedgerows should be done as and when required. The trimmed materials can either be used as fodder or mulching materials; and
e)If desired, improved fruit trees suitable at the proposed site can be planted along the hedges at 5 x 5 m spacing. Fruit trees in two adjacent hedgerows should be planted in staggered position to avoid competition for sunlight, water, and soil nutrients.
Autor:
NSSC
Fecha:
10/09/2021
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
Ha
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
0.4
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Ngultrum
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
82,08
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
250
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planning | done between the stakeholders several times |
| 2. | Community meeting and member agreement | twice |
| 3. | Training and workshop | for almost a week |
| 4. | Demonstration | once |
| 5. | Implementation (Planting of napier in the field in groups) | based on the land users convenience and season of plantation |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labours | person-days | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Napier | bundle | 35,0 | 200,0 | 7000,0 | |
| Otros | Payment for resource persons | No of days | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 15500,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 188,84 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The funding was provided by UNDP, with technical support from the National Soil Services Center and the Dzongkhag.
Comentarios:
The cost breakdown of the technology establishment was for one acre of land.
The total grant amount was Nu. 2,834,416, however, the total budget for Boucholing specifically was not available.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting, cutting of napier and maintaining the height of the plant | when the napier reaches a height of one meter |
| 2. | Replacing of missing and damaged hills | whenever possible |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | person-days | 2,0 | 250,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Napier slips | Bundle | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 2500,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 30,46 | |||||
Comentarios:
Minimal cost go into the maintenance of the hedgerows.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Labour cost and cost of the planting materials.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The data used was from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Dry subtropical zone
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Contour hedgerows can be applied in both concave and convex situations, so not relevant
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
The flooding of the area occurs mostly due to heavy rainfall and some surface water.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Diversidad de hábitats:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Higher diversity because Napier grass adds to diversity to already existing crops.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
There are a total of 130 acres of land with an average area of around 2.3 acres for each household.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the land act and rules and regulations which dictate the land use in the country.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop production is higher than in the past since the contour hedgerows have helped control soil erosion and allowed for proper land utilization. The land user reported about a 25% increase compared to the past.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The crop quality is also relatively better now compared to the past when the technology was not applied. The land users reported that crops near the hedgerows were found more greener.
producción de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
No fodder was produced
Cantidad luego de MST:
After napier plantation, napier are harvested as fodder for cattle.
Comentarios/ especifique:
Napier grass was not planted in the past. It was introduced by the National Soil Services Center as part of this technology. The Napier grass planted along the contour has helped not only with soil erosion control but also provided fodder grass for the cattle. The land user reported that there was a 100% increase in fodder because unlike in the past now they don't have to send their cow for grazing in the forest.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Compared to normal grass that the cattle would graze on, napier is nutrient-rich and of better quality than the normal grass.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The napier plantation has helped prevent soil erosion that would normally occur in the farm lands thereby preventing crop failure due to soil fertility and moisture conservation.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
With the help of the project, the land users were able to utilise the sloping land. This enabled land users to grow crops other than maize.
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The contour hedgerows have allowed for the sloping and degraded lands to be revitalised into usable cultivable lands.
manejo de tierras
Cantidad antes de MST:
Hard manual land management
Cantidad luego de MST:
mechanization of the agriculture in the community
Comentarios/ especifique:
With the help of the project, farm lands in the community were made into terraces and made land management easier compared to the past.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
The expenses on agricultural inputs have stayed relatively the same, however, has made working on the farm land easier.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
With fodder availability, land users can now focus more on agriculture instead of herding cattle for grazing. The project has also allowed for land users to diversify their products.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Workload has decreased due to farm mechanization through use of power tillers, which was not possible prior to the SLM intervention.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Prior to hedgerow establishemt, there was serious surface erosion, which is not the case now.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Cantidad antes de MST:
primarily maize was cultivated
Cantidad luego de MST:
maize, cole crops, tubers and chilies are cultivated
Comentarios/ especifique:
In the past, the community members would normally cultivate maize and small amounts of vegetables for self consumption, but now a diverse variety of crops are cultivated.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
Cantidad antes de MST:
More prominent in the summer season
Cantidad luego de MST:
occurrence is very minimal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The presence of a terrace and hedgerows in the bunds of the terrace has prevented the erosion of the soil in the farm lands of the farmers.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Downstream flooding is relatively less, since the hedgerows has prevented or reduced surface eorsion which would otherwise impact the downstream settlements and water bodies.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien | |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta local | muy bien |
| granizada local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| deslizamiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Since the project was fully funded and minimal cost went into its establishment by the land users, the benefits are higher.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
40 households
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
Since the program was supported by project, the labor were contributed by the land user while the inputs in all sites were provided by the project at every household level.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Hedgerow requires less management |
| Napier are also used as fodder for livestock |
| Prevents the land from erosion due to heavy rain |
| Helps in build up of terraces and facilitates in mechanization of farm |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Additional income opportunities through the production of marketable products from hedgerow vegetation. |
| Improved livelihoods for communities through long-term agricultural productivity. |
| Support for sustainable agricultural practices and resilient farming systems. |
| Preservation of fertile land and protection of agricultural resources. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Grazing of hedges by free cattle in absence of fences in farm land | Establish community byelaws not to let their cattle free in the fields or install fencing aroung the field. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Shading and potential competition with crops for soil nutrients by hedges | Maintaining height and width of hedges |
| The establishment and maintenance of contour hedgerows require time, effort, and financial resources | The funding for the establishment of technology has already been provided and for maintenance, the expenditure is minimal. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
1 household
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
2 individuals
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
ICIMOD. (1999). Manual on Contour Hedgerow Inter-cropping Technology. ICIMOD.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://lib.icimod.org/record/31840/files/manual_on_contour_hedgerow_inter-cropping_technology.pdf
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Pellek, R. (1992). Contour hedgerows and other soil conservation interventions for hilly terrain. Agroforestry Systems, 17, 135-152.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00053118
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Kaushal, R., Mandal, D., Panwar, P., Rajkumar, Kumar, P., Tomar, J. M. S. & Mehta, H. (2021). Chapter 20 - Soil and water conservation benefits of agroforestry.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128229316000204
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Sustainable Land Management for improved land productivity and community livelihood in Thangrong, Mongar
URL:
https://sgp.undp.org/spacial-itemid-projects-landing-page/spacial-itemid-project-search-results/spacial-itemid-project-detailpage.html?view=projectdetail&id=27647
Título/ descripción:
Soil erosion control with contour planting
URL:
https://apps.worldagroforestry.org/Units/Library/Books/Book%2082/imperata%20grassland/html/4.1_soil.htm?n=20
Título/ descripción:
Sustainable Land Management: Guidelines and Best Practices 2021
URL:
https://www.nssc.gov.bt
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos