Floating Vegetable Garden Using Water Hyacinth as Planting Medium [Filipinas]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Gulayan sa Gakit
technologies_7000 - Filipinas
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Perez Mercy
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Filipinas
usuario de la tierra:
Cutao Arnel
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Filipinas
usuario de la tierra:
Osigan Marvin
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Filipinas
Project Implementer:
Acopiado Ma. Angelita Salome
Agusan del Sur Provincial Environment and Natural Resources Office (PENRO)
Filipinas
Project Implementer:
Dumaguit Dennis
LGU of Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Filipinas
Project Implementer:
Asufre Gemma
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
Filipinas
Project Implementer:
Tabudlong Richard
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
Filipinas
co-compiler:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Plaza Marvin Emmanuel
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Talavera Ana Marie
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Manuel Paquito Jr.
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Barraca Jodel
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Project Implementer:
Amante Romer
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
Filipinas
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Integrated Approach in Management of Major Biodiversity Corridors in the Philippines - GEF 6 Project (BD corridor)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - Filipinas1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
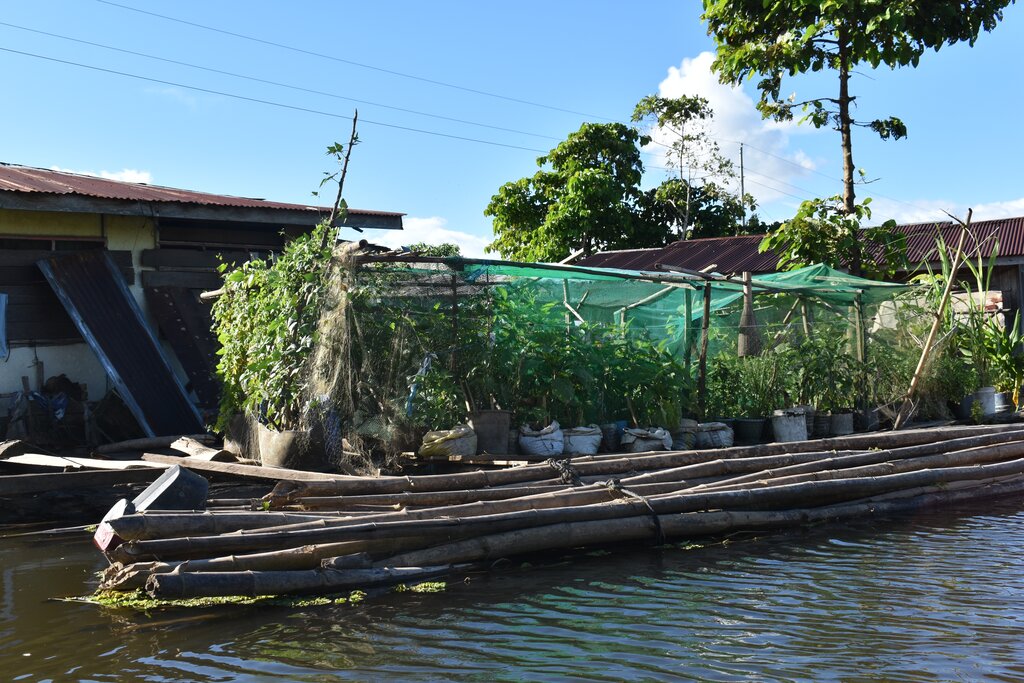
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Floating vegetable garden as a climate change adaptation strategy for the indigenous communities living in the wetland of Agusan del Sur to grow vegetables during the flooding season.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
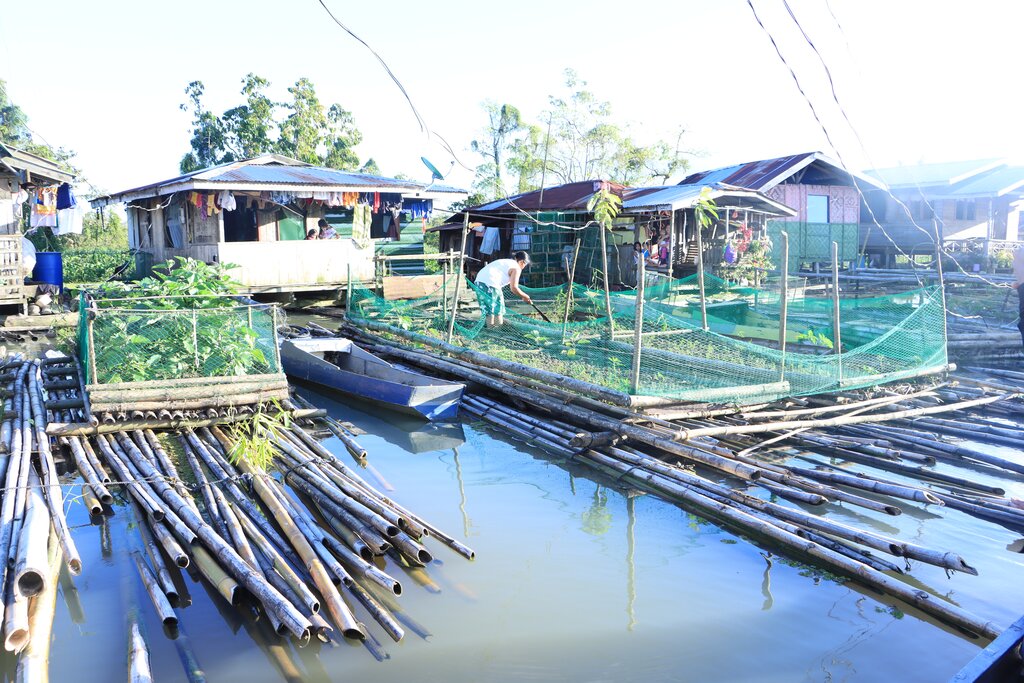
Agusan Marsh is considered one of the wetlands in the Philippines that experiences flooding all year round, and most areas are flooded, making it impossible to grow food for the communities living in the area. In order to address this issue, the construction of floating gardens were initiated by the Department of Agriculture CARAGA supported by various government agencies and Non Government Organizations (NGOs).
The floating garden technology and initiative, developed by the Foundation for the Development of Agusanons, Inc. (FDAI), was enhanced by the Department of Agriculture CARAGA and carried out by the Agricultural Program Coordinating Office (APCO) with the aim of establishing a sustainable agricultural system that promotes biodiversity and resilient farming practices. By using decomposed water hyacinth as a medium for growing crops, the technology helps mitigate its negative effects and transforms it into a valuable resource. Water hyacinths have a variety of negative impacts such as clogging waterways hampering boating and fishing, reducing local aquatic biodiversity and obstructing river flows which can aggravate flooding. The technlogy is being adopted by the Adaptation and Mitigation Initiative in Agriculture (AMIA) as a mitigation strategy against the impacts of climate change, enabling communities to better manage and adapt to climate-related risks. It also provides means for communities in flood-prone or coastal areas to engage in sustainable agri-fishery activities, ensuring food security and enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
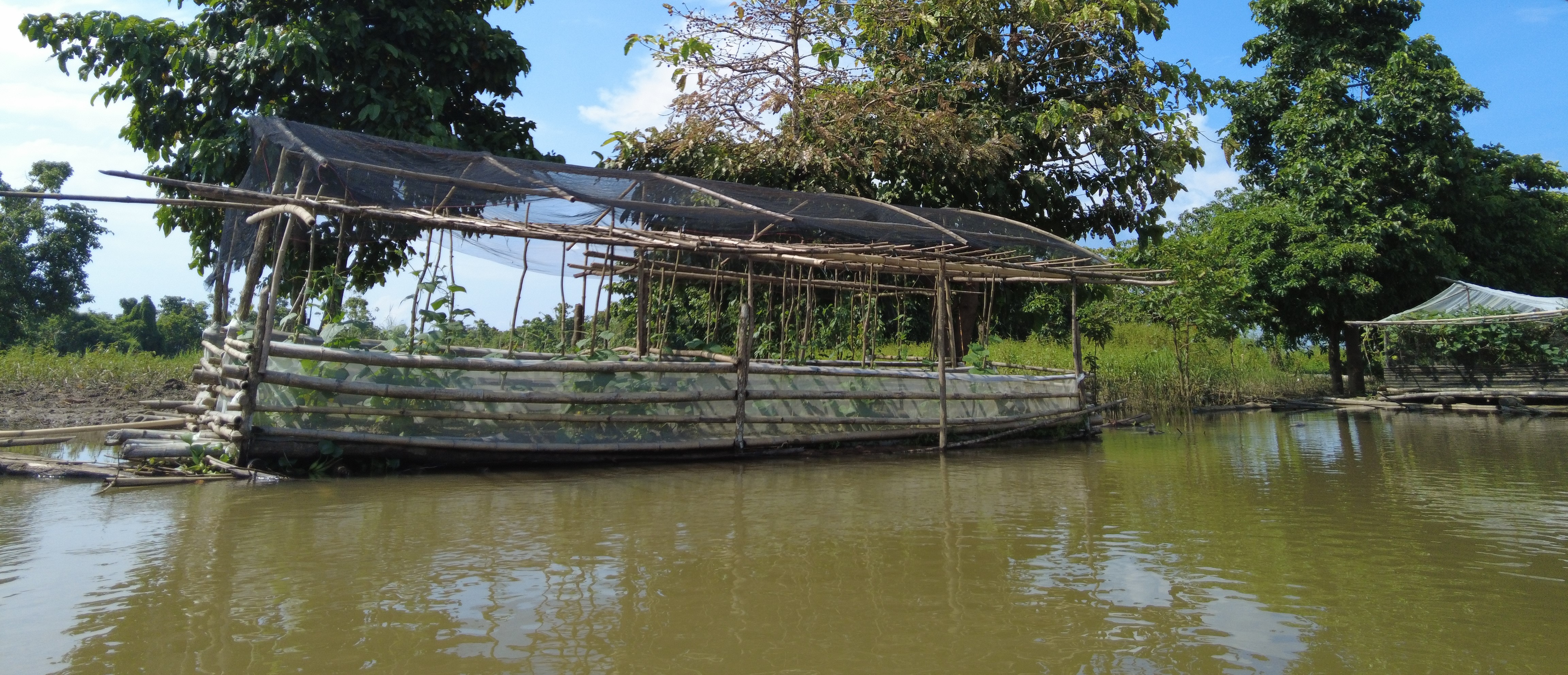
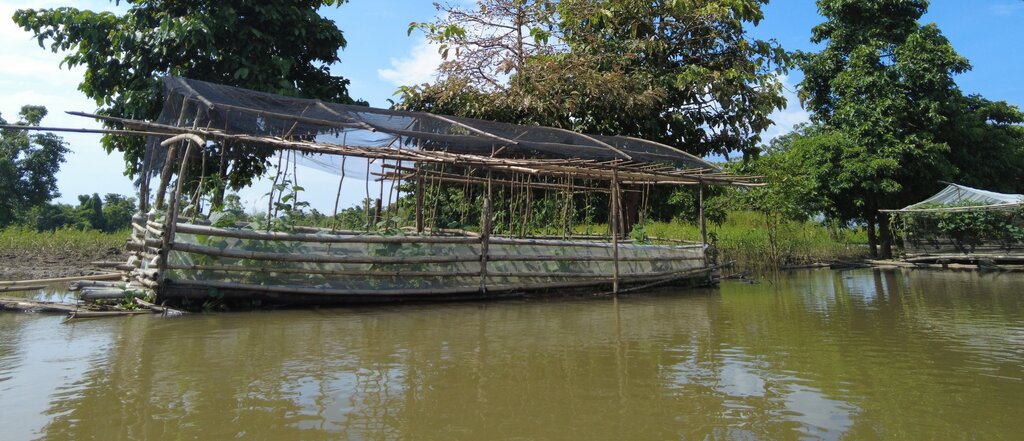
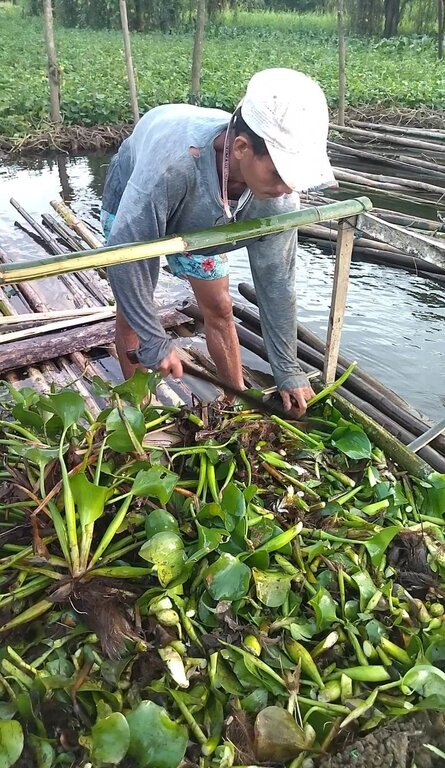
The components of the floating garden include a floater, a base (batangan), flooring (salug), growing substrate composed of layers of water hyacinth and layers of soil. Thewater hyacinths are collected from the river, chopped, and then mixed with the soil for composting before being used as a growing substrate in the floating garden. It is applied in layers as follows: composted hyacinth/soil mix, soil, composted hyacinth/ soil mix, and soil. The use of water hyacinth as substrate for the compost addresses the community’s concern about its proliferation, which causes obstruction in rivers, resulting in the destruction of boats and houses.
The standard dimension of a floating garden is 8 meters (length) by 4 meters (width), but this could be increased depending on the needs and financial capacity of the landusers. Crops planted are high-value vegetables such as pechay (pak choi), string beans, bitter gourd, tomato, bell pepper, cucumber, and eggplant, which were provided by the Department of Agriculture.
The FDAI played a pivotal role in project implementation, overseeing the construction of floating gardens and the provision of supplemental seedlings. The Binus-Ugan Farmers Association (BFA), as the recipient of the project, received 50 units of floating gardens through the Department of Agriculture's Adaptation and Mitigation Initiative in Agriculture (AMIA) Program.
Floating gardens were instrumental to the community in growing crops as their source of food and nutrients during the COVID-19 pandemic, where movement from barangay to barangay was restricted. A barangay is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines. The floating gardens became a source of income as the excess produce was sold to neighbors. The floating garden initiative did not only enhance economic conditions but also attracted local avian species, locally referred to as "pari-pari." Furthermore, it strengthened women's involvement in the community, particularly through their active participation in maintaining the gardens.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Filipinas
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Province of Agusan Del Sur
Especifique más el lugar :
Talacogon municipality
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
The floating garden is within the Agusan marsh which is also considered as wildlife sanctuary.
Talacogon and Bunawan where most of the floating gardens are located. Only the Talacogon floating gardens were visited but during the interview with project implementers, they mentioned that they have also constructed floating garden in Bunawan.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2022
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The construction of floating garden at Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon was funded by the Department of Agriculture in response to the needs of the community for food sources during flooding season when growing crops is not possible because the lands are submerged in water.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Pantanos, humedales
Principales productos/ servicios:
Vegetables for own consumption and surplus is being sold
Comentarios:
Floating gardens to grow vegetables are constructed in the wetlands when the area is flooded. For the past years, flooding occurred all year round.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
During rainy seasons, the landusers do not water the crops since the rainwater is already sufficient. When week passed and no rains occur, the landuser will water the crops from the river.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- protección/manejo de humedales
- jardines domésticos
- reducción de riesgos de desastres basados en el ecosistema
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S9: Refugios para plantas y animales

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Floating garden structure as shelter for plants
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
Comentarios:
Year round flooding (change in surface water quantity) limited agricultural activities on the land.
This technology address the decline of surface water quality due to the eutrophication of waterbody where water hyacinth is a contributor.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
The community adapted to the state of land degradation in the area by transferring crop production from the year round flooded fields to floating gardens and using the available resource like the water hyacinth as substrate to produce compost used as substrate for plant growth
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
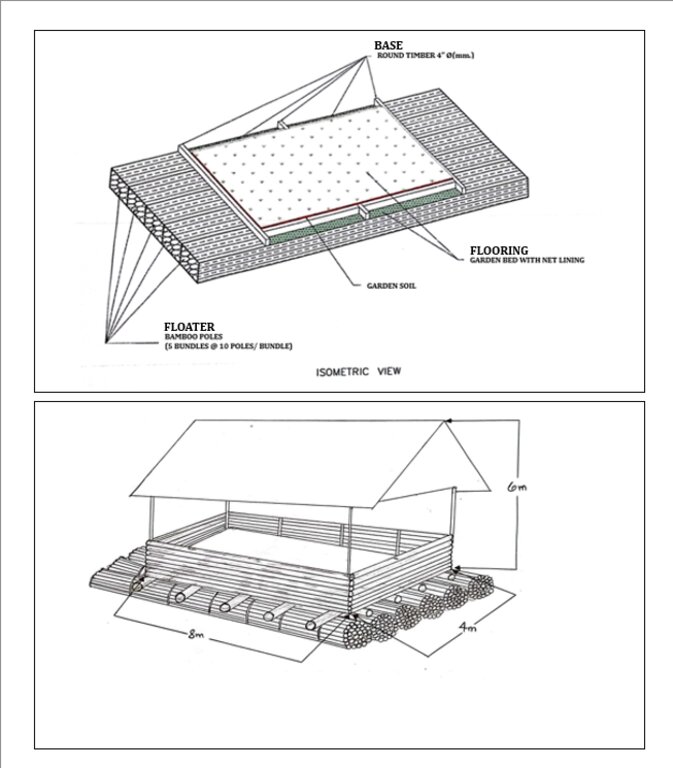
The standard size for the floating garden has a length of 8 meters, width of 4 meters, and height of 6 meters. This could be decreased or increased depending on the the financial capacity and needs of the farmer. It is composed of floater, flooring, and base. The floater is made of bamboo poles (5 bundles at 10 poles/bundle). The flooring is the garden bed with net lining. The base is made up of wood that will act as the crossbeam. Plastic roofing could be added using UV plastic.
Autor:
Jodel Barraca; Paquito Jr. C. Manuel; and DA CARAGA
Fecha:
09/01/2024
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
one floating garden unit
Especifique las dimensiones de la unidad (si fuera relevante):
length-8 meters; width-4meters
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Pesos
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
55,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
350 Pesos
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of the floating garden | All year round |
| 2. | Collection of water hyacinth | All year round |
| 3. | Composting of water hyacinth and mixing with soil | All year round |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Construction of the floating garden | person/day | 16,0 | 350,0 | 5600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Collection and composting of water hyacinth | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | vegetable seeds | cans | 3,0 | 1500,0 | 4500,0 | |
| Material de construcción | bamboo as floater | pieces | 200,0 | 40,0 | 8000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | wood for crossbeam | pieces | 4,0 | 200,0 | 800,0 | |
| Material de construcción | bamboo for floor joist | pieces | 10,0 | 30,0 | 300,0 | |
| Material de construcción | nails | kilos | 2,0 | 80,0 | 160,0 | |
| Material de construcción | wood as sidings | board feet (bd.ft) | 4,0 | 20,0 | 80,0 | |
| Material de construcción | bamboo as pole | pieces | 6,0 | 50,0 | 300,0 | |
| Material de construcción | rope | pieces | 16,0 | 25,0 | 400,0 | |
| Material de construcción | carabao rope for anchoring the garden | meters | 20,0 | 28,0 | 560,0 | |
| Otros | UV plastic roofing | roll (12m x 5m) | 1,0 | 6000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 27050,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 491,82 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The cost for the construction of the floating garden was subsidized by the Department of Agriculture
Comentarios:
The materials used for the construction of the floating garden was subsidized by the government. The counterpart of the land user is the labor for the construction.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Change of the bamboo used as floaters | 1 to 2 years |
| 2. | Planting of vegetable seeds | All year round |
| 3. | Fertilizer application | All year round |
| 4. | Application of organic spray | All year round |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Maintenance of the floater | person/day | 3,0 | 350,0 | 1050,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting of vegetable seeds | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Fertilizer application | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Organic Spray application | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | seeds | cans | 3,0 | 1500,0 | 4500,0 | 50,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Organic Fertilizer | bag | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Organic spray | liter | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | bamboo | pieces | 200,0 | 40,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 16600,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 301,82 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The Department of Agriculture partially subsidized the seeds
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Availability of bamboo in the area which is heavily used as the floater
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
en superficie
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
excesiva
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
inutilizable
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
For the past three (3) years, the community has observed that flooding is all year round
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Diversidad de hábitats:
- elevada
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
otros (especifique):
Houses are built with floaters which could be moved depending on the occurrence of floods
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Fishing is the main source of income of the landusers
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Less than 0.5 ha refers to the size of the floating garden itself
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Comentarios:
General characteristics of the situation in the area where the floating gardens are being implemented
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is an increase in production since floating garden made it possible for the landusers to grow crops in the absence of productive land for cultivation
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
The landusers planted other vegetables which were given by the Department of Agriculture.
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The production area increased since they could also produce using the floating garden.
Ingreso y costos
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
The landuser will not only rely on fishing as source of income but also on vegetable production
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
The community does not need to go to the mainland or to the town market to buy vegetables since they could grow their own produce.
oportunidades culturales
Comentarios/ especifique:
Women's involvement in the community, particularly through their active participation in maintaining the gardens
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Trainings were conducted by the Department of Agriculture on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and vegetable production
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
The floating garden provided income to the indigenous people living in the area
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
Attracted local bird species, locally referred to as "pari-pari."
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
Utilized water hyacinth which is considered as an invasive aquatic weed
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
The establishment of the floating gardens reduced the invasive population of the water hyacinth in the Agusan Marsh.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta tropical | moderadamente |
| tormenta de lluvia local | muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | muy bien |
| inundación repentina | no muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Serves as an efficient mode of resource utilization on a small productive land area like the Agusan Marsh. |
| Relatively sustainable use of environmental resources. |
| An additional source of sustenance/income from the floating garden's produce. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The floating garden technology could act as an additional tourist spot in Agusan Marsh. |
| There is strong support from various stakeholders, including the Municipal and Provincial Local Government Units, Department of Agriculture and Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) |
| Promote greater engagement within the community. |
| Reduce eutrophication by recycling water hyacinth |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital cost can be a hindrance for the community in Agusan Marsh. | The floating garden could be a project of the Local Government Unit (LGU) where they can subsidize the initial costs. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Erosion on river banks due to bamboo utilization for the construction of the floating garden. (Lack of resource sustainability program). | The community can initiate a bamboo planting program to ensure the sustainability of bamboo production and prevent soil erosion in riverbanks. |
| Some of the floating gardens constructed sunk because of the incorrect proportion of soil and compost ratio | Close monitoring during the land preparation to ensure the stability of floating garden. |
| Lack of monitoring of the technology by concerned government agencies due to the difficult accessibility of the community where the technology is being practiced. It will take three hours using pump boat to reach the barangay. | Government agency involved to look for possible source of funding for procurement of pump boats to be used for monitoring. The Department of Agriculture could train people from the barangay on how to do the monitoring and take measurements. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Number of field visits: 2
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Number of informants: 8
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
10/12/2024
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Design, User, Experience, and Usability; Aaron Marcus, Elizabeth Rosenzweig, and Marcelo M. Soares (Eds.); 2023; ISBN: 978-3-031-35704-6
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Google Books; Free of charge
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Residents build flood-resilient floating gardens in Agusan Marsh
URL:
https://www.mindanews.com/top-stories/2021/07/residents-build-flood-resilient-floating-gardens-in-agusan-marsh/?fbclid=IwAR2PNh3GmiUKpk8JTWw5kHjcTRz4opsPxJGlWmvzjU33BWyHNR9jUb5ipnw
Título/ descripción:
Feature: Vegetable Garden floats in Agusan Marsh
URL:
https://issuu.com/caragainfocus/docs/october_15-21_2022/s/17258517?fbclid=IwAR0tLILkV0qGVCkcLJbMWcn5bAgBKJqxp4bfKKPzXDBBm9Zd3MmQTMlG0Wg
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionnaire, though it's lengthy, has all the relevant information that the interviewee must determine from the site. This incites a comprehensive documentation process, ensuring that all the subject's technology and adjacent information (i.e. community and environmental impacts) are captured.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos