Floating Vegetable Garden Using Water Hyacinth as Planting Medium [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Gulayan sa Gakit
technologies_7000 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Perez Mercy
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Philippines
exploitant des terres:
Cutao Arnel
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Philippines
exploitant des terres:
Osigan Marvin
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Philippines
Project Implementer:
Acopiado Ma. Angelita Salome
Agusan del Sur Provincial Environment and Natural Resources Office (PENRO)
Philippines
Project Implementer:
Dumaguit Dennis
LGU of Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
Philippines
Project Implementer:
Asufre Gemma
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
Philippines
Project Implementer:
Tabudlong Richard
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
Philippines
co-compiler:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Plaza Marvin Emmanuel
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Talavera Ana Marie
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Manuel Paquito Jr.
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Barraca Jodel
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Project Implementer:
Amante Romer
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
Philippines
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Integrated Approach in Management of Major Biodiversity Corridors in the Philippines - GEF 6 Project (BD corridor)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
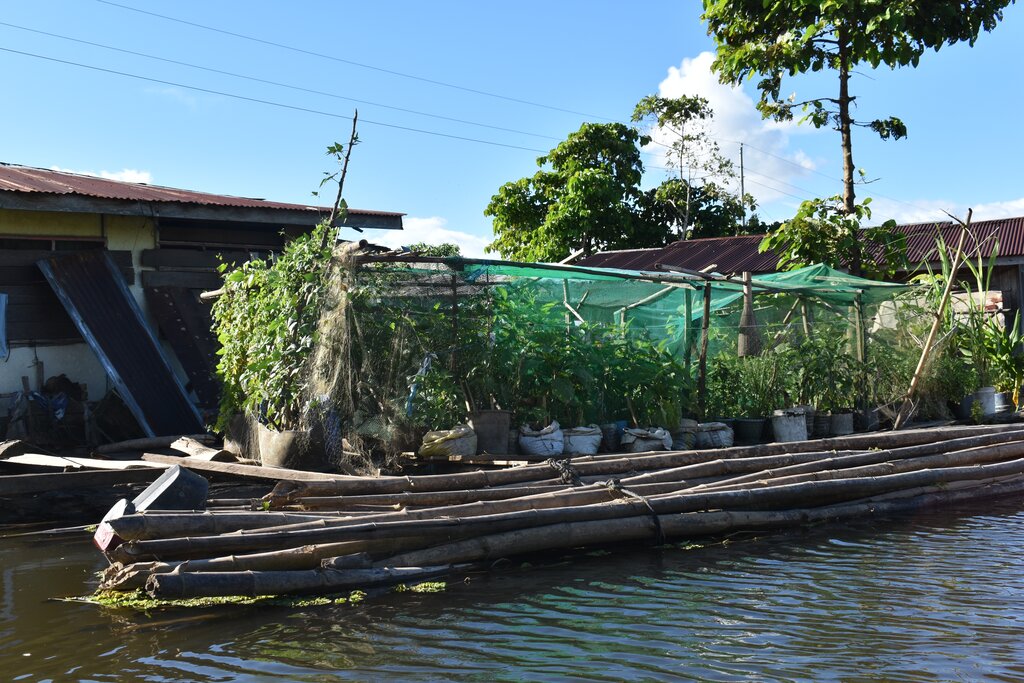
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
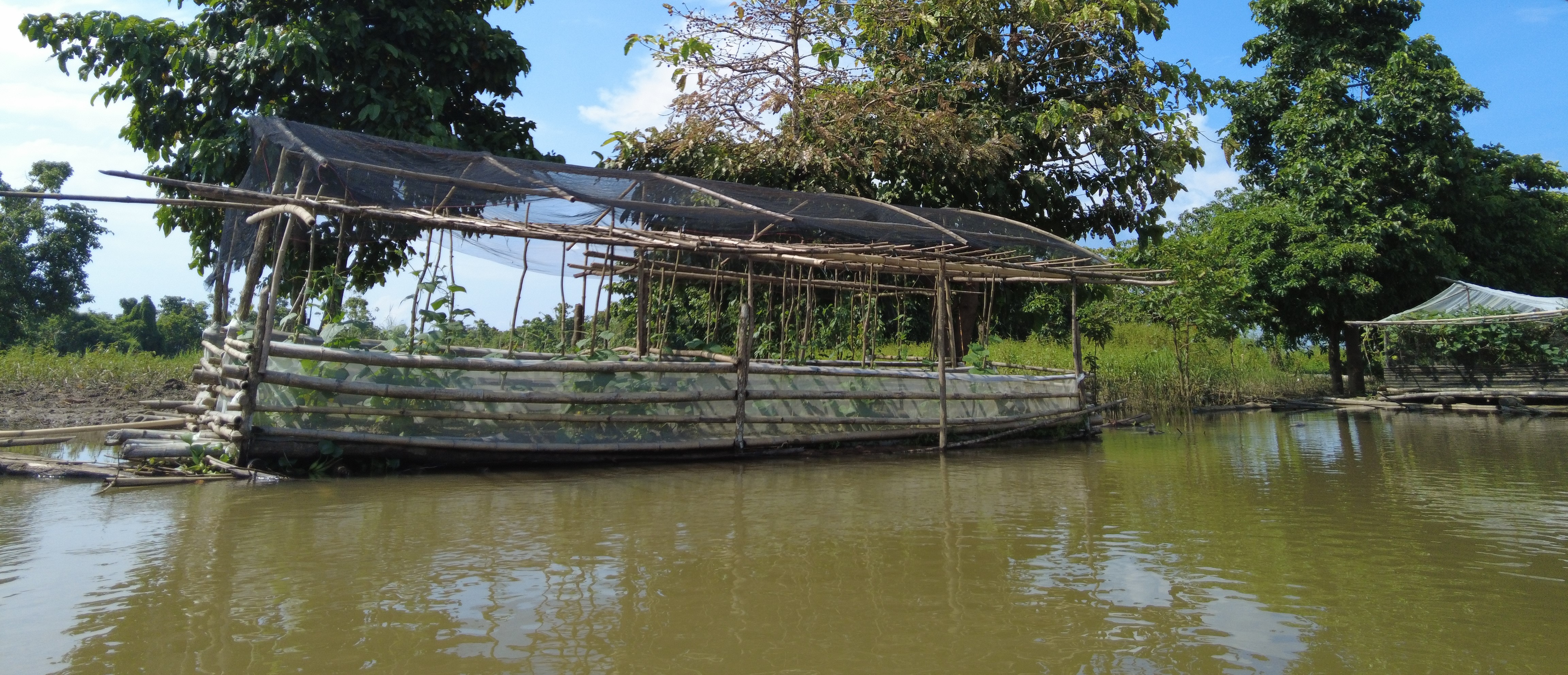
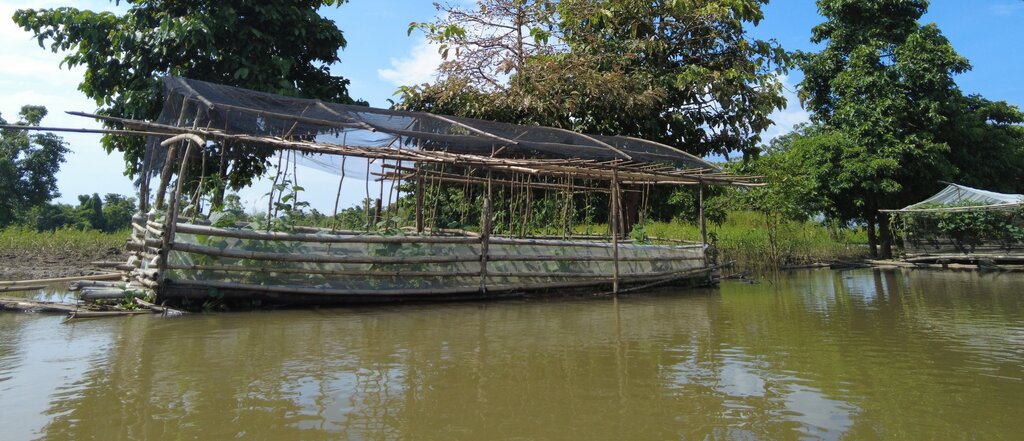
Floating vegetable garden as a climate change adaptation strategy for the indigenous communities living in the wetland of Agusan del Sur to grow vegetables during the flooding season.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Agusan Marsh is considered one of the wetlands in the Philippines that experiences flooding all year round, and most areas are flooded, making it impossible to grow food for the communities living in the area. In order to address this issue, the construction of floating gardens were initiated by the Department of Agriculture CARAGA supported by various government agencies and Non Government Organizations (NGOs).
The floating garden technology and initiative, developed by the Foundation for the Development of Agusanons, Inc. (FDAI), was enhanced by the Department of Agriculture CARAGA and carried out by the Agricultural Program Coordinating Office (APCO) with the aim of establishing a sustainable agricultural system that promotes biodiversity and resilient farming practices. By using decomposed water hyacinth as a medium for growing crops, the technology helps mitigate its negative effects and transforms it into a valuable resource. Water hyacinths have a variety of negative impacts such as clogging waterways hampering boating and fishing, reducing local aquatic biodiversity and obstructing river flows which can aggravate flooding. The technlogy is being adopted by the Adaptation and Mitigation Initiative in Agriculture (AMIA) as a mitigation strategy against the impacts of climate change, enabling communities to better manage and adapt to climate-related risks. It also provides means for communities in flood-prone or coastal areas to engage in sustainable agri-fishery activities, ensuring food security and enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
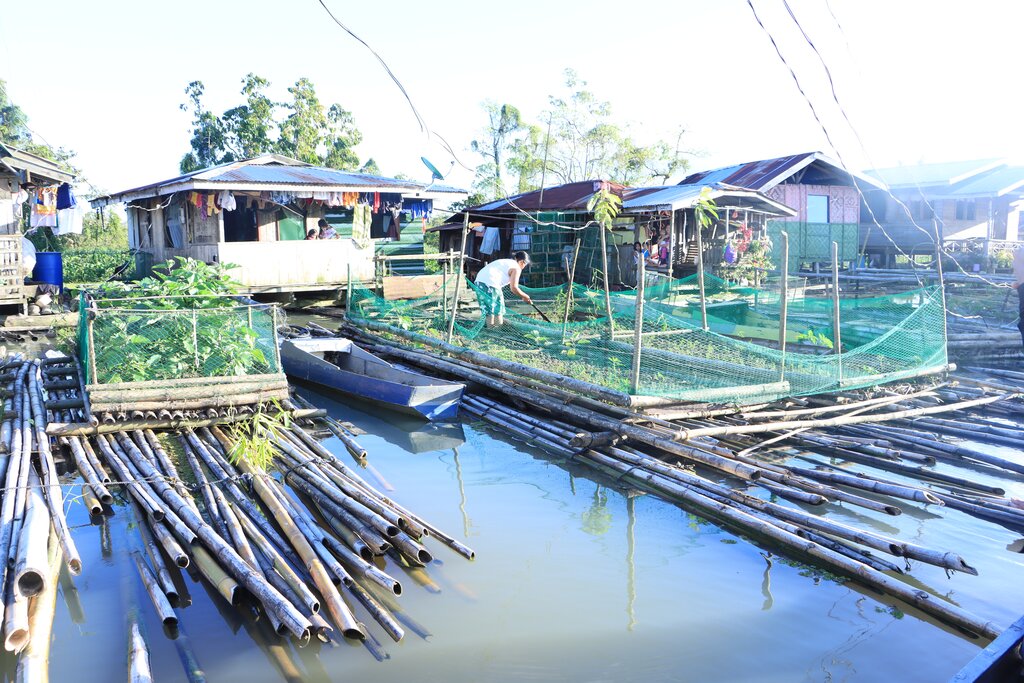
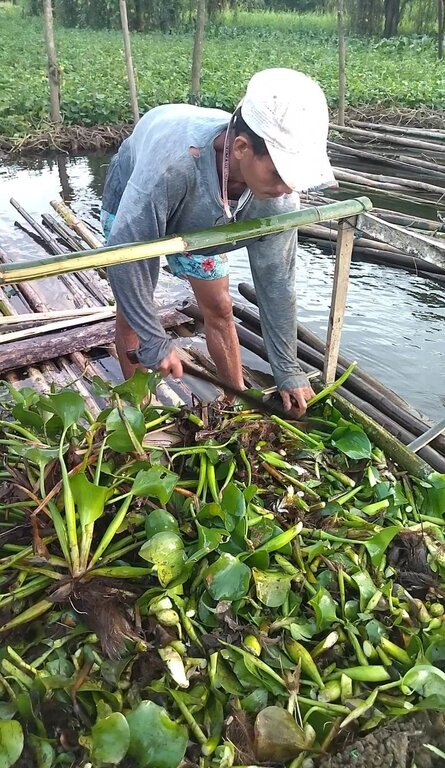
The components of the floating garden include a floater, a base (batangan), flooring (salug), growing substrate composed of layers of water hyacinth and layers of soil. Thewater hyacinths are collected from the river, chopped, and then mixed with the soil for composting before being used as a growing substrate in the floating garden. It is applied in layers as follows: composted hyacinth/soil mix, soil, composted hyacinth/ soil mix, and soil. The use of water hyacinth as substrate for the compost addresses the community’s concern about its proliferation, which causes obstruction in rivers, resulting in the destruction of boats and houses.
The standard dimension of a floating garden is 8 meters (length) by 4 meters (width), but this could be increased depending on the needs and financial capacity of the landusers. Crops planted are high-value vegetables such as pechay (pak choi), string beans, bitter gourd, tomato, bell pepper, cucumber, and eggplant, which were provided by the Department of Agriculture.
The FDAI played a pivotal role in project implementation, overseeing the construction of floating gardens and the provision of supplemental seedlings. The Binus-Ugan Farmers Association (BFA), as the recipient of the project, received 50 units of floating gardens through the Department of Agriculture's Adaptation and Mitigation Initiative in Agriculture (AMIA) Program.
Floating gardens were instrumental to the community in growing crops as their source of food and nutrients during the COVID-19 pandemic, where movement from barangay to barangay was restricted. A barangay is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines. The floating gardens became a source of income as the excess produce was sold to neighbors. The floating garden initiative did not only enhance economic conditions but also attracted local avian species, locally referred to as "pari-pari." Furthermore, it strengthened women's involvement in the community, particularly through their active participation in maintaining the gardens.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Province of Agusan Del Sur
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Talacogon municipality
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The floating garden is within the Agusan marsh which is also considered as wildlife sanctuary.
Talacogon and Bunawan where most of the floating gardens are located. Only the Talacogon floating gardens were visited but during the interview with project implementers, they mentioned that they have also constructed floating garden in Bunawan.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2022
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The construction of floating garden at Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon was funded by the Department of Agriculture in response to the needs of the community for food sources during flooding season when growing crops is not possible because the lands are submerged in water.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Marécages, zones humides
Principaux produits/ services:
Vegetables for own consumption and surplus is being sold
Commentaires:
Floating gardens to grow vegetables are constructed in the wetlands when the area is flooded. For the past years, flooding occurred all year round.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
During rainy seasons, the landusers do not water the crops since the rainwater is already sufficient. When week passed and no rains occur, the landuser will water the crops from the river.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion/ protection des zones humides
- Jardins/ potagers familiaux
- réduction des risques de catastrophe fondée sur les écosystèmes
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S9: Abris pour plantes et animaux

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
Commentaires:
Floating garden structure as shelter for plants
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
- Hp: baisse de la qualité des eaux de surface
Commentaires:
Year round flooding (change in surface water quantity) limited agricultural activities on the land.
This technology address the decline of surface water quality due to the eutrophication of waterbody where water hyacinth is a contributor.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- s'adapter à la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
The community adapted to the state of land degradation in the area by transferring crop production from the year round flooded fields to floating gardens and using the available resource like the water hyacinth as substrate to produce compost used as substrate for plant growth
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
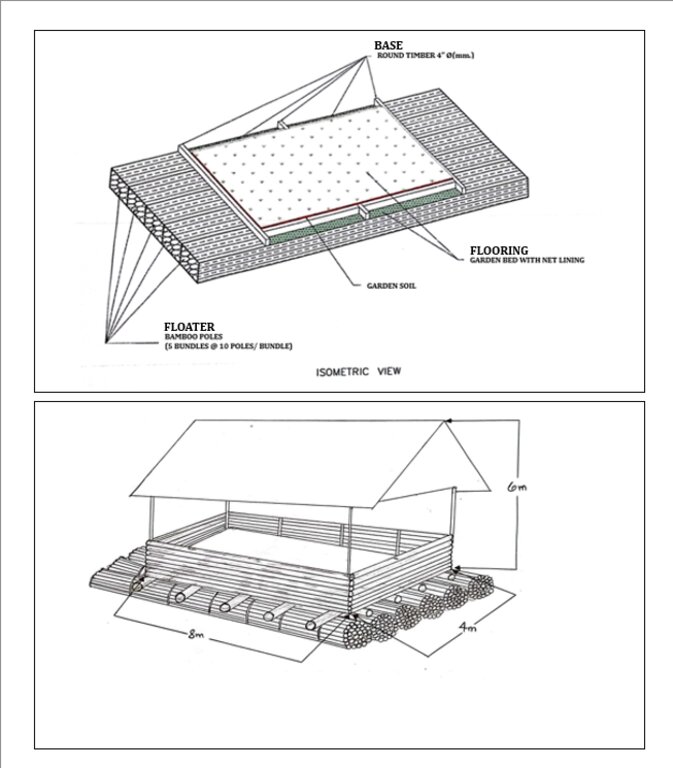
The standard size for the floating garden has a length of 8 meters, width of 4 meters, and height of 6 meters. This could be decreased or increased depending on the the financial capacity and needs of the farmer. It is composed of floater, flooring, and base. The floater is made of bamboo poles (5 bundles at 10 poles/bundle). The flooring is the garden bed with net lining. The base is made up of wood that will act as the crossbeam. Plastic roofing could be added using UV plastic.
Auteur:
Jodel Barraca; Paquito Jr. C. Manuel; and DA CARAGA
Date:
09/01/2024
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
one floating garden unit
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
length-8 meters; width-4meters
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Pesos
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
55,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
350 Pesos
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of the floating garden | All year round |
| 2. | Collection of water hyacinth | All year round |
| 3. | Composting of water hyacinth and mixing with soil | All year round |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of the floating garden | person/day | 16,0 | 350,0 | 5600,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Collection and composting of water hyacinth | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | vegetable seeds | cans | 3,0 | 1500,0 | 4500,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | bamboo as floater | pieces | 200,0 | 40,0 | 8000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | wood for crossbeam | pieces | 4,0 | 200,0 | 800,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | bamboo for floor joist | pieces | 10,0 | 30,0 | 300,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | nails | kilos | 2,0 | 80,0 | 160,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | wood as sidings | board feet (bd.ft) | 4,0 | 20,0 | 80,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | bamboo as pole | pieces | 6,0 | 50,0 | 300,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | rope | pieces | 16,0 | 25,0 | 400,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | carabao rope for anchoring the garden | meters | 20,0 | 28,0 | 560,0 | |
| Autre | UV plastic roofing | roll (12m x 5m) | 1,0 | 6000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 27050,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 491,82 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The cost for the construction of the floating garden was subsidized by the Department of Agriculture
Commentaires:
The materials used for the construction of the floating garden was subsidized by the government. The counterpart of the land user is the labor for the construction.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Change of the bamboo used as floaters | 1 to 2 years |
| 2. | Planting of vegetable seeds | All year round |
| 3. | Fertilizer application | All year round |
| 4. | Application of organic spray | All year round |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Maintenance of the floater | person/day | 3,0 | 350,0 | 1050,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting of vegetable seeds | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Fertilizer application | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Organic Spray application | person/day | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | seeds | cans | 3,0 | 1500,0 | 4500,0 | 50,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Organic Fertilizer | bag | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Organic spray | liter | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | bamboo | pieces | 200,0 | 40,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 16600,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 301,82 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The Department of Agriculture partially subsidized the seeds
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Availability of bamboo in the area which is heavily used as the floater
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
en surface
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau inutilisable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
fréquemment
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
For the past three (3) years, the community has observed that flooding is all year round
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
autre (précisez):
Houses are built with floaters which could be moved depending on the occurrence of floods
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Fishing is the main source of income of the landusers
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Less than 0.5 ha refers to the size of the floating garden itself
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Commentaires:
General characteristics of the situation in the area where the floating gardens are being implemented
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There is an increase in production since floating garden made it possible for the landusers to grow crops in the absence of productive land for cultivation
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The landusers planted other vegetables which were given by the Department of Agriculture.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The production area increased since they could also produce using the floating garden.
Revenus et coûts
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The landuser will not only rely on fishing as source of income but also on vegetable production
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The community does not need to go to the mainland or to the town market to buy vegetables since they could grow their own produce.
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Women's involvement in the community, particularly through their active participation in maintaining the gardens
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Trainings were conducted by the Department of Agriculture on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and vegetable production
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The floating garden provided income to the indigenous people living in the area
Impacts écologiques
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Attracted local bird species, locally referred to as "pari-pari."
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Utilized water hyacinth which is considered as an invasive aquatic weed
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The establishment of the floating gardens reduced the invasive population of the water hyacinth in the Agusan Marsh.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête tropicale | modérément |
| pluie torrentielle locale | très bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | très bien |
| crue éclair | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Serves as an efficient mode of resource utilization on a small productive land area like the Agusan Marsh. |
| Relatively sustainable use of environmental resources. |
| An additional source of sustenance/income from the floating garden's produce. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The floating garden technology could act as an additional tourist spot in Agusan Marsh. |
| There is strong support from various stakeholders, including the Municipal and Provincial Local Government Units, Department of Agriculture and Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) |
| Promote greater engagement within the community. |
| Reduce eutrophication by recycling water hyacinth |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital cost can be a hindrance for the community in Agusan Marsh. | The floating garden could be a project of the Local Government Unit (LGU) where they can subsidize the initial costs. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Erosion on river banks due to bamboo utilization for the construction of the floating garden. (Lack of resource sustainability program). | The community can initiate a bamboo planting program to ensure the sustainability of bamboo production and prevent soil erosion in riverbanks. |
| Some of the floating gardens constructed sunk because of the incorrect proportion of soil and compost ratio | Close monitoring during the land preparation to ensure the stability of floating garden. |
| Lack of monitoring of the technology by concerned government agencies due to the difficult accessibility of the community where the technology is being practiced. It will take three hours using pump boat to reach the barangay. | Government agency involved to look for possible source of funding for procurement of pump boats to be used for monitoring. The Department of Agriculture could train people from the barangay on how to do the monitoring and take measurements. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Number of field visits: 2
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Number of informants: 8
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/12/2024
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Design, User, Experience, and Usability; Aaron Marcus, Elizabeth Rosenzweig, and Marcelo M. Soares (Eds.); 2023; ISBN: 978-3-031-35704-6
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Google Books; Free of charge
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Residents build flood-resilient floating gardens in Agusan Marsh
URL:
https://www.mindanews.com/top-stories/2021/07/residents-build-flood-resilient-floating-gardens-in-agusan-marsh/?fbclid=IwAR2PNh3GmiUKpk8JTWw5kHjcTRz4opsPxJGlWmvzjU33BWyHNR9jUb5ipnw
Titre/ description:
Feature: Vegetable Garden floats in Agusan Marsh
URL:
https://issuu.com/caragainfocus/docs/october_15-21_2022/s/17258517?fbclid=IwAR0tLILkV0qGVCkcLJbMWcn5bAgBKJqxp4bfKKPzXDBBm9Zd3MmQTMlG0Wg
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
The questionnaire, though it's lengthy, has all the relevant information that the interviewee must determine from the site. This incites a comprehensive documentation process, ensuring that all the subject's technology and adjacent information (i.e. community and environmental impacts) are captured.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé