Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar [Afganistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Ahmad Khalid Wiyar
- Editores: Megha bajaj, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy, Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
د ځنګل رغونی او کرنیزی ځنګلداری لپاره د پمپ په واسطه د ابه خور سیستم
technologies_7473 - Afganistán
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 5 de marzo de 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 24 de marzo de 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 18 de mayo de 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 9 de julio de 2025 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Safi Sharifullah
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Afganistán
usuario de la tierra:
Safi Mohammad Afzal
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
Afganistán
usuario de la tierra:
Safi Qiamuddin
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
Afganistán
usuario de la tierra:
Safi Farhad
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
Afganistán
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in AfghanistanNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Afganistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
No, the technology described here is not problematic with regard to land degradation. In fact, it promotes sustainable land management by enhancing soil health, preventing erosion, and supporting afforestation efforts. This technology contributes to the restoration and conservation of forest ecosystems.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
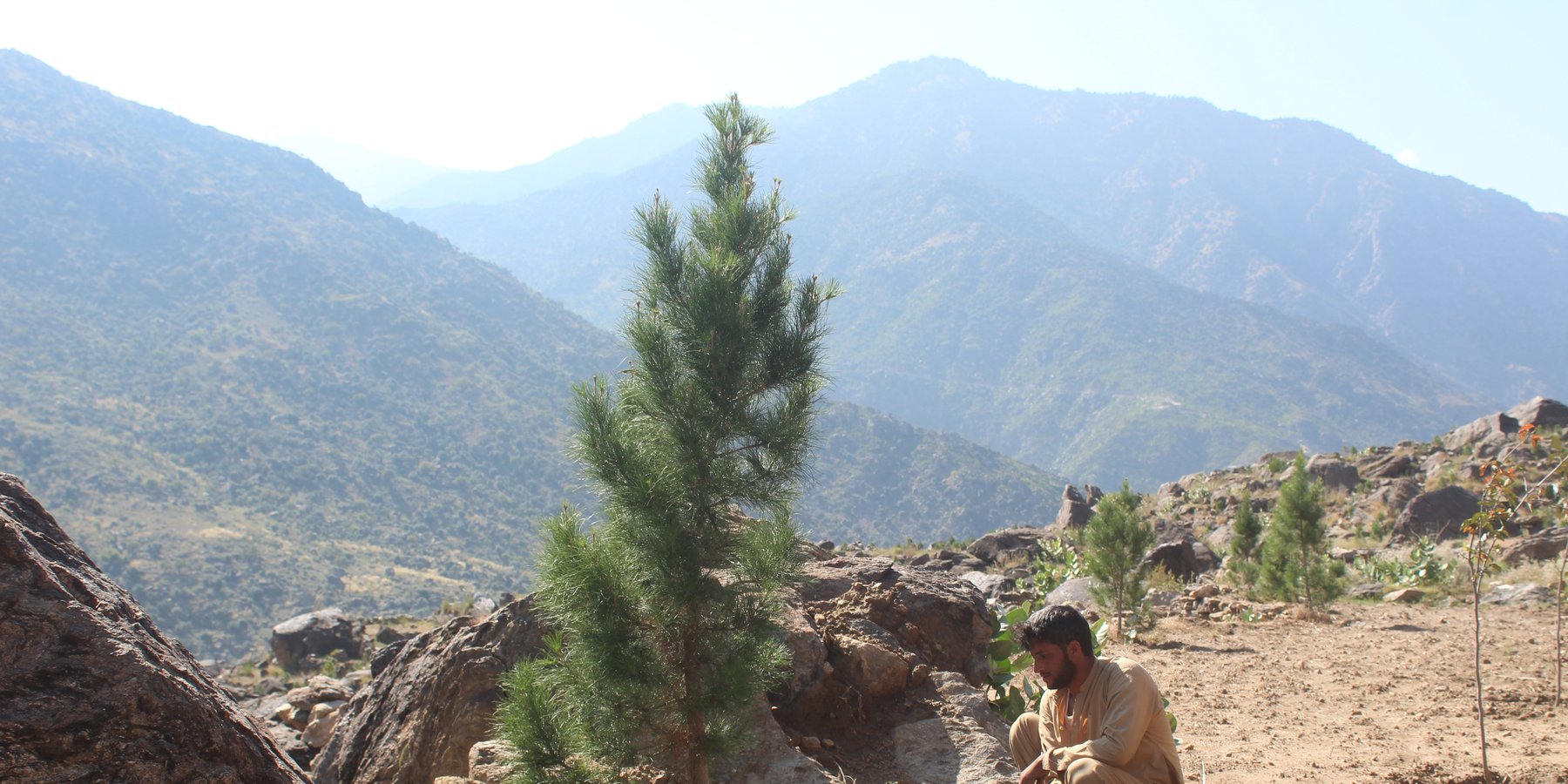
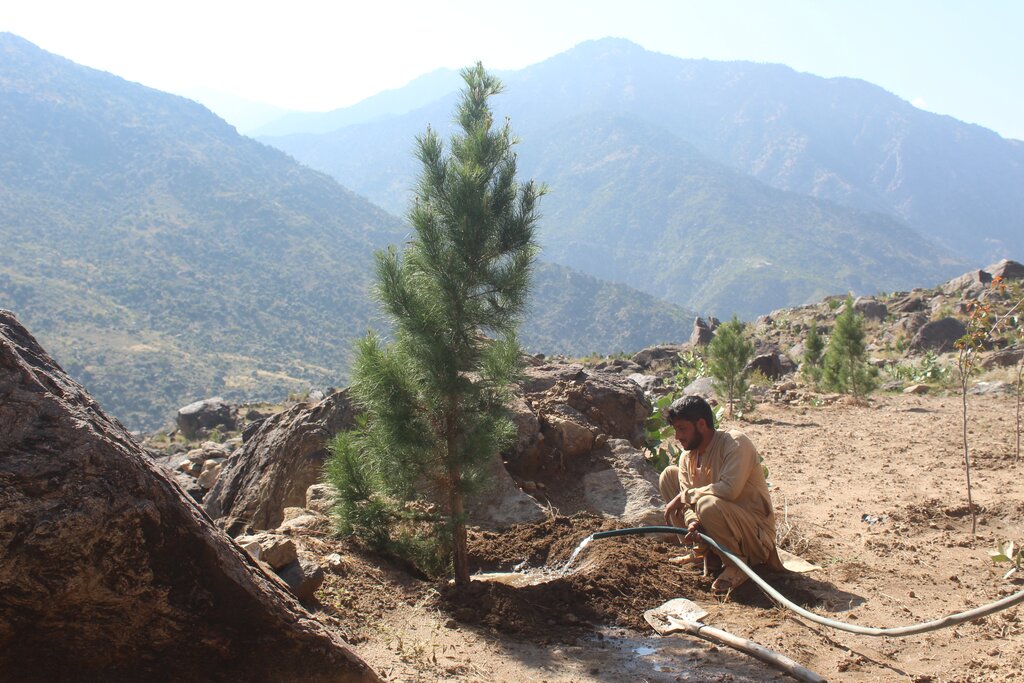
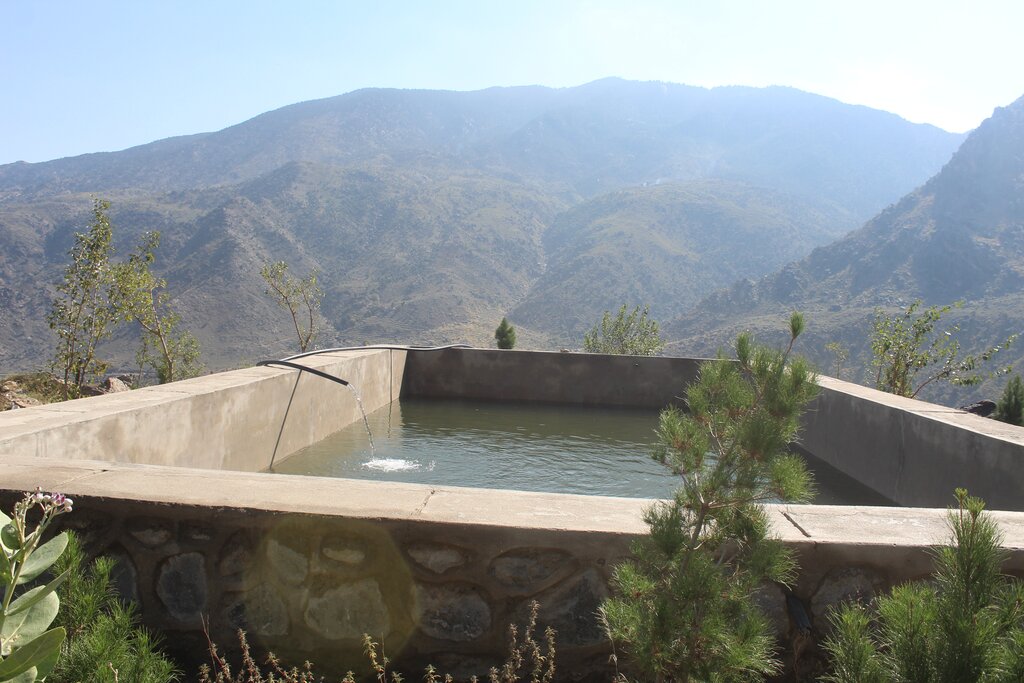
Water exploitation is a major issue in Afghanistan. The lift irrigation technology helps to irrigate an afforestation/agroforestry area (demonstration plot) using surface water (rivers) and solar-powered submersible pump. The construction of reservoirs at the demo plot ensures efficient water storage and use for irrigation purposes without relying on groundwater. A well-designed pipe irrigation scheme is implemented to distribute water evenly across the site, supporting plant irrigation and growth.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
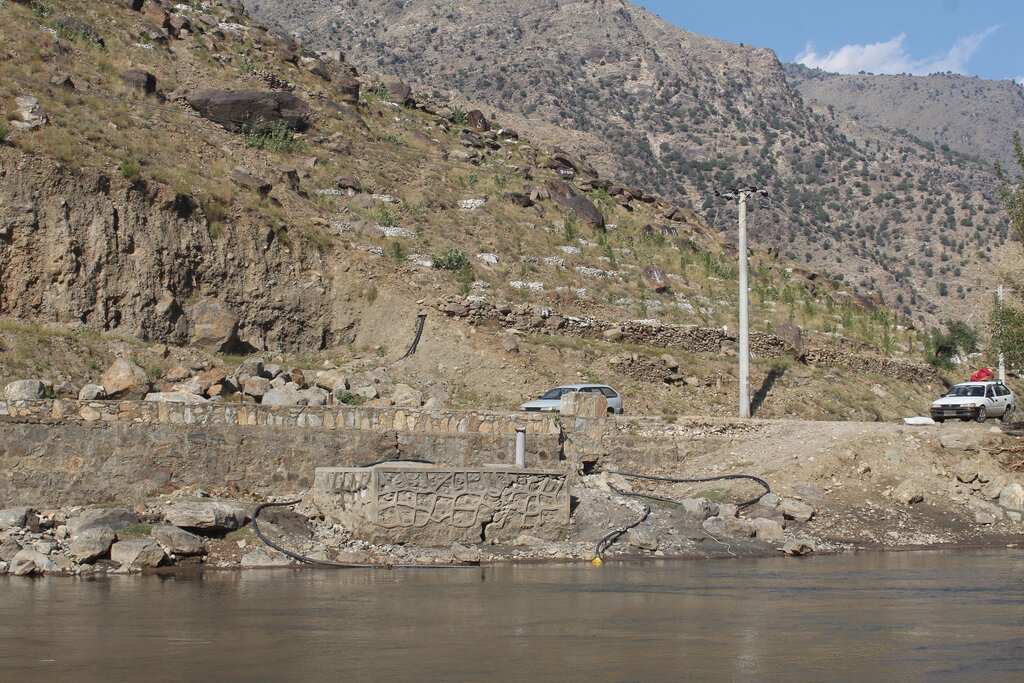
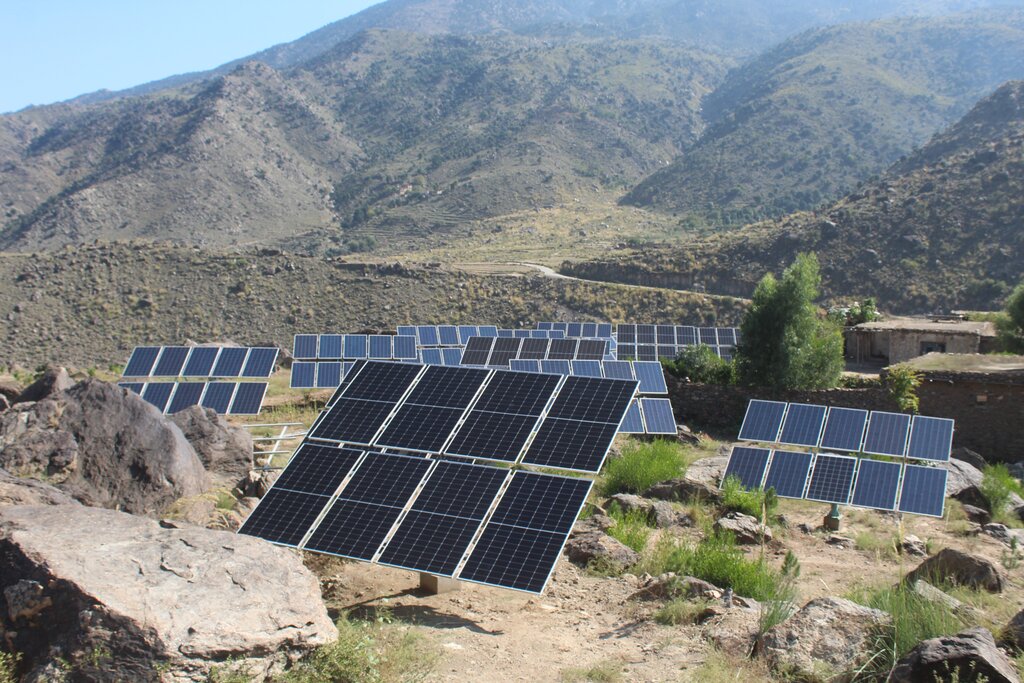
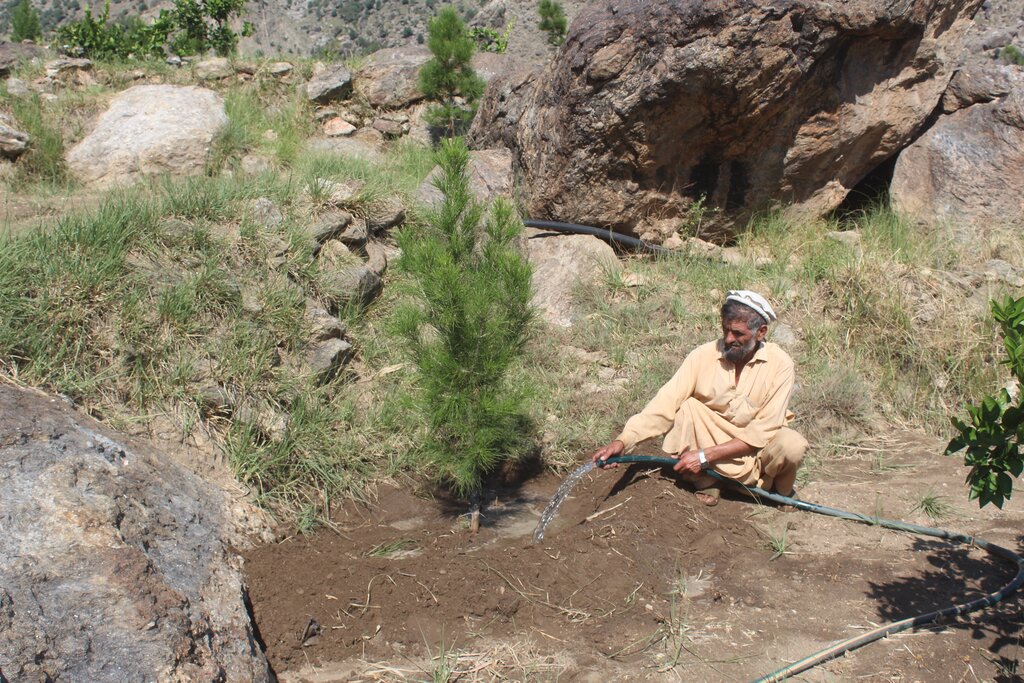
Water exploitation is a critical issue in Afghanistan, and the project aims to address this challenge through innovative and sustainable technology. The technology involves the use of solar panels and submersible water pumps to efficiently lift water from a nearby river to reservoirs constructed uphill, which is then distributed by gravity with the help of a pipe system to irrigate planted saplings in the afforested and agroforestry area. For afforestation, Pinus eldarica (Afghan pine) was planted due to its adaptability and soil stabilization properties. Additionally, citrus and persimmon trees are introduced for agroforestry, combining tree cultivation with agricultural benefits. This integrated technology promotes biodiversity, soil health, and sustainable land use, making the site a model/ demonstration site for afforestation and agroforestry practices. This is a significant advancement in the local area, utilizing clean energy to promote sustainable land and forest management and environmental restoration. The project is implemented on communal land, covering 50.25 hectares of land.
The primary purpose of this technology is to create an efficient irrigation system that extracts and transports water to support afforestation and agroforestry activities. By doing so, it aims to restore forest cover, mitigate environmental challenges such as land degradation, and promote long-term ecological and socio-economic sustainability. The technology includes key components such as solar panels, water pumps (submersible), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, water reservoirs, and saplings. Additionally, it requires labor, technical assistance, capacity-building programs, and construction materials for its establishment and maintenance.
The benefits of this technology are substantial. It has successfully irrigated previously barren land, achieving an impressive 85% survival rate for the saplings that were planted in the plot, while preventing land degradation and improving soil health. Without this technology, survival rates would drop to zero due to the arid conditions. Furthermore, the project has enhanced the capacities of local farmers/community members, enabling them to replicate and demonstrate the technology within their community. This has fostered a sense of ownership and empowerment among land users.
Land users have expressed both appreciation and concerns regarding the technology. On the positive side, they value its efficiency and reliability, as the solar panels provide a consistent water supply, especially during the hot/sunny season, leading to increased greenery and healthier trees. The cost-effectiveness of solar energy, with its low operational costs compared to traditional diesel pumps, has also been a significant advantage. Additionally, the environmentally friendly nature of the technology aligns with their desire for sustainable practices. The capacity-building programs provided by organizations like FAO have further empowered users to manage the system effectively.
However, some challenges have been noted. The initial investment costs for purchasing, installing and construction of the technology are high, making it difficult for smallholder farmers to replicate. Technical issues, such as inverter failures or battery malfunctions during extreme weather conditions (e.g., cloudy weather), can disrupt operations. Additionally, not all community members are equally informed about the technology’s benefits, highlighting the need for increased outreach and engagement efforts to ensure broader adoption and understanding.
In summary, this solar-powered irrigation technology represents a groundbreaking innovation in the area, combining clean energy with sustainable land management practices. While it has demonstrated significant environmental and agricultural benefits, addressing the challenges of initial costs, technical reliability, and community engagement will be crucial for its long-term success and scalability.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Lugar:
N/A
Nombre del videógrafo:
N/A
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Afganistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
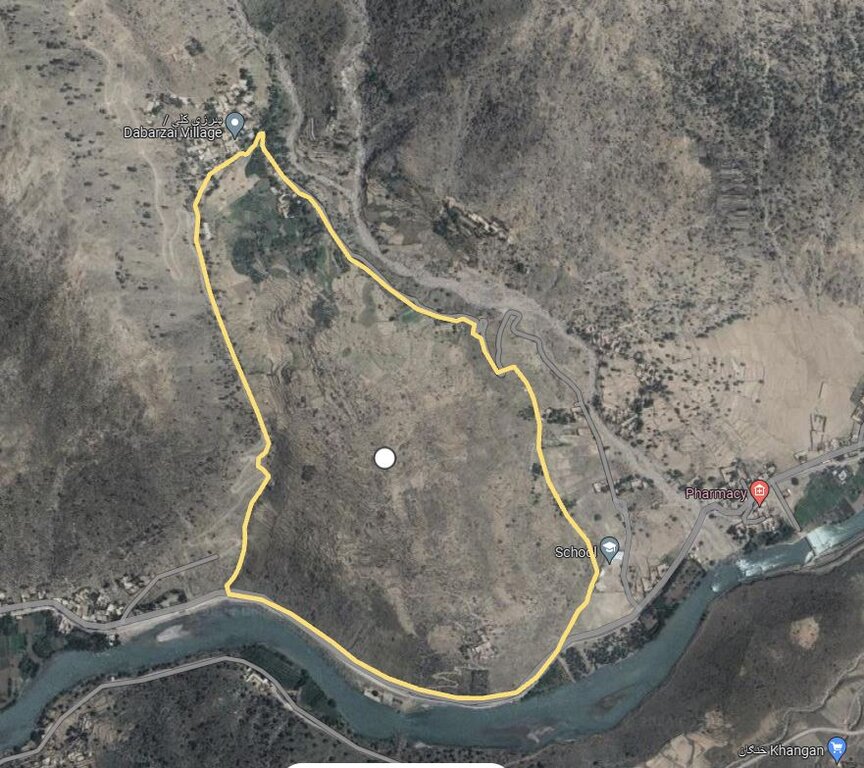
Kunar
Especifique más el lugar :
Managi village of Manogi district
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
The area is about 50.25 ha, and the coordinate has been taken from the center of the site, where technology has been implemented:
34.9419930°N71.0119714°E
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2022
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
GEF-06 Community based Sustainable Land and Forest Management in Afghanistan
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- cítricos
- Persimmon
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No

Bosques
- Plantación de árboles, reforestación
Plantación de árboles, reforestación: Especifique el origen y la composición de las especies:
- Monocultivo variedad local
tipo de plantación de árboles, reforestación:
- plantación de bosque subtropical seco - Pinus spp.
Tipo de árbol:
- Especies de Pinus (pino)
¿Los árboles especificados son deciduos o imperecederos?
- imperecedero
Productos y servicios:
- Conservación/ Protección de la naturaleza
- Recreación/ turismo
- Protección contra desastres naturales
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierra no productiva
Especifique:
5 decades ago, the area was a forest area, but due to war, smuggling and drought the area become barren land.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
The saplings planted in the area have been supplementary irrigated. Prior to the implementation of this technology, the land was barren, and seasonal rains led to soil erosion.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de plantación forestal
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- tecnologías de eficiencia energética
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
- S7: Equipo para cosechar agua / provisión de agua/ irrigación
- S10: Medidas de ahorro de energía

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M3: disposición de acuerdo al entorno natural y humano
Comentarios:
The project has successfully implemented afforestation by planting trees and promoting agroforestry through the cultivation of fruit trees. To improve irrigation management, the project installed a 1-inch underground pipeline system with connected taps, enabling the attachment of flexible hoses. This efficient setup ensures optimal watering of saplings while significantly reducing water waste. By implementing this approach, the project has enhanced vegetative cover and successfully planted approximately 32,000 saplings. Additionally, the project constructed 14 rotating mounting structures for solar panels, installed 134 solar panels, established pipe schemes for manual irrigation of saplings, and constructed 6 water reservoirs with different capacities. The integration of trees at optimal spacing, combined with regular cultural practices, has further supported the project's goals.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
Comentarios:
The planting pits are specially designed for planting of saplings. Additionally, farmers construct small barriers near plants (eye-brows and trenches), known as micro-catchments, to collect and retain water. It is important to note that these micro-catchments are distinct structures, separate from pits and reservoirs, and are specifically built to support water retention for plants. The enhanced vegetation cover and the establishment of micro-catchments for water collection significantly reduce soil erosion. Soil improvement and enrichment, as well as habitat enhancement, are supported through these practices. Additionally, they contribute to groundwater recharge and help control runoff.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The human-induced causes of land degradation include deforestation, overgrazing of livestock, and unsustainable agricultural practices. In response, following the implementation of a specific technology, local communities established regulations rooted in their customs and traditions to protect the site, which is quarantined for five years. These regulations prohibit herders from grazing animals, cutting trees, engaging in unsustainable agricultural practices, and uprooting bushes for fuelwood. Additionally, the community has constructed rainwater harvesting structures, such as eyebrows and trenches, across the site to address natural causes of land degradation through runoff by enhancing water infiltration. As a result, the site is now effectively protected from both human-induced and natural land degradation.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
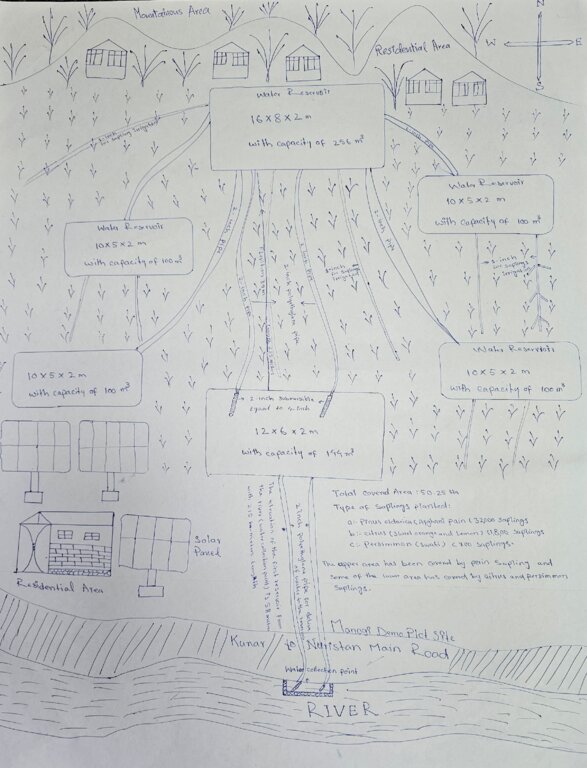
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
According to the technical specifications from the project engineer, 6 reservoirs have been constructed with varying dimensions and water holding capacities as follows:
1.First reservoir: Dimension of 12x6x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 144 m³.
2.Central reservoir: Dimensions of 16x8x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 256 m³.
3.Four additional reservoirs: Each measuring 10x5x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 100 m³
In total, the reservoirs will hold 800 m³ of water, ensuring a reliable water supply for irrigation of the area. Two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs by gravity.
Furthermore, excavation and backfilling for 2-inch polyethylene pipes should be done to a depth of 80 cm with a width of 50 cm. For 1.5-inch pipes, excavation and backfilling should be 40 cm deep. The installation of 1.5-inch polyethylene pipes, including all elbows, joints, connectors, and valves, should be carried out every 30 meters on both sides, connecting to 1-inch pipes, in accordance with specifications and to satisfaction.
Additionally, 32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghan Pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings were planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. The saplings are spaced 5 meters apart, both plant-to-plant and row-to-row, as part of afforestation and agroforestry initiatives. This effort aims to restore ecosystems, enhance biodiversity, and improve soil conservation.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Fecha:
01/03/2022
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
50.25 Hectares
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5 USD
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Awareness and mobilization of the community | Aug-2021 |
| 2. | Survey and site selection followed by feasibility study | Sep to Oct-2021 |
| 3. | Stakeholder consultation | Aug-2021 till Sep-2022 |
| 4. | Preparation of technical design, drawings, and Bill of Quantities (BoQ). | Nov to Dec-2021 |
| 5. | Initiation of procurement process for required tools and equipment | Jan to Feb-2022 |
| 6. | Excavation and construction of water reservoirs, setting up pipe system and installation of solar panels for irrigation. | Mar to Sep-2022 |
| 7. | Capacity building of the target communities | Aug- 2021 till date |
| 8. | Practical interventions: production or purchase of saplings, digging planting pits, transplatation and irrigation of saplings and establishment of micro-catchments | Feb to Mar-2023 |
Comentarios:
The awareness-raising session on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) was successfully held to improve understanding of land and forest management practices and conservation efforts. Community members were actively mobilized to support the project, aiding in the completion of construction and installation work.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Unskilled labor for planting of saplings | Man/day | 450,0 | 5,0 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Skilled labor for installation of irrigation system and constuction of reservoirs | Man/day | 50,0 | 10,0 | 500,0 | |
| Equipo | Water Pump 2 inch - 10HP/7500w | Number | 4,0 | 450,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Equipo | Solar Panel minimum size 400W and 270W | Number | 132,0 | 82,0 | 10824,0 | |
| Equipo | DC to AC Inverter 7.5-11KW | Number | 4,0 | 450,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Equipo | Polyethylene Pipes 2 Inch and 1.5 Inch with all elbows, joints, connectors and valves after 30 meter for both sides to connect pipes. | Meter | 4300,0 | 2,75 | 11825,0 | |
| Equipo | Rotating PV panels mounting structure (manual) | Number | 28,0 | 270,0 | 7560,0 | |
| Equipo | DC and AC current wire | Meter | 1800,0 | 2,5 | 4500,0 | |
| Equipo | Distribution board | Number | 2,0 | 70,0 | 140,0 | |
| Equipo | Flexon 1 inch rubberize pipes | Meter | 5500,0 | 1,4 | 7700,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Saplings procured & transported | Sapling | 32000,0 | 0,775 | 24800,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Planting tools | lump sum | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Organic fertilizers for transplanted saplings added through community | Kg | 16000,0 | 0,1 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | 6 reservoirs constructed by a construction company (cement, stone, sand excavation, etc.. | lump sum | 1,0 | 35000,0 | 35000,0 | |
| Otros | Patrolling, irrigating and quarantine of the site | lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 111799,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 111799,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The remining cost were covered by the project.
Comentarios:
The first two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs through gravity.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Patrolling | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump (submersible) | Ad hoc /Annually |
| 4. | Plot maintenance (Pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding,). | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacement of failed saplings | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing micro-catchments | Spring/annually |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labor for cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Man/day | 60,0 | 5,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Labor for patrolling | Man/day | 360,0 | 5,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Labor for repairing micro-catchments | Man/day | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Manage the solar system operations | Man/day | 360,0 | 2,77 | 997,2 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Labor for weeding and mulching | Man/day | 30,0 | 5,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Pump submersible, PVC pipe, fittings | lumpsum | 3,0 | 500,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Shovels | lumpsum | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | saplings | Sapling | 2000,0 | 0,6 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Organic fertilizers (cows dungs) | Kg | 16000,0 | 0,1 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 7787,2 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 7787,2 | |||||
Comentarios:
The community has hired an individual to manage the solar system operations. This person is responsible for both operating the solar system for lifting water and overseeing the distribution of water for irrigation purposes among community members.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
All equipment are imported and has resulted into higher cost.
Natural hazards, floods and windstorms will increase the costs of repairs and replacement
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
300,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Most of rain occur in the months of Feb, Mar, Apr, July and Aug.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
The data has been collected based on the farmers observation and local practices.
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
The area where the technology is applied covers 50.25 hectares and is managed by 112 land users.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
In Afghanistan, the traditional land use system involves the equitable distribution of deserts and barren land among the local residents. The decisions made by the elders are respected and adhered to by all members of the community.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
fruit production (citrus and persimmon)
Comentarios/ especifique:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as part of the agroforestry system and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people. Based on the production, the socio-economic status of the community members is expected to improve.
producción de madera
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
A total of 32,000 forest saplings (Pinus species) were successfully planted
Comentarios/ especifique:
32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghani pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. Following agronomic practices, the four Ds—dead, diseased, damaged, and dying—branches will be pruned and utilized for shelter and fuel.
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
0 fruit trees
Cantidad luego de MST:
Approximately 1,200 fruit trees, including sweet orange and persimmon species, have been planted
Comentarios/ especifique:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as a agroforestry and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people.
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
The area was once barren and occasionally used for rainfed cultivation, where most farmers grew wheat. Now, with the introduction and implementation of the technology farmers can also intercrop beans, mung beans, and others. Farmers who have more than 1 hectare of land hire labor for agronomical practices.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
100%
Comentarios/ especifique:
With the adoption of this technology, irrigation for planted saplings is now available 100% throughout all seasons of the year.
Ingreso y costos
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Timber Production, Non-Timber Forest Products, Ecotourism, Agroforestry, Wildlife Conservation and Fuelwood and Biomass
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Recreational opportunities that benefit both local communities and visitors such as nature trails allowed individuals to engage with nature, promoting physical activity and wellness. The reforestation efforts have led to the restoration of habitats for various wildlife species, this provides opportunities for wildlife observation and photography, and contributing to local ecotourism.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved due to workshops and on job trainings
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better soil coverage by plantation of saplings and micro-catchment structures
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the availability of irrigation water and the establishment of micro-catchments to harvest water and enhance water infiltaration soil moisture for sapling growth has increased
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to natural regeneration and plantation of saplings and intercrops
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better soil coverage and less water runoff
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Comentarios/ especifique:
better soil cover reduced water runoff and ultimately flooding
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil erosion was reduced and has been better controlled
impacto de gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to plantation
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia estacional | primavera | incrementó | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de viento | moderadamente |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
The community economic condition is not good. So, without receiving incentives they are not able to adopt such technology easily.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Improved water availability with minimized fuel cost and decreased pollution as well as minimum operational cost |
| Opportunities/ potential for upscaling of the technology |
| Use of clean energy to contribute to mitigate climate change |
| Reduce greenhouse emission through carbon sequestration |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The technology is highly efficient and suitable for adoption by land users. It promotes clean energy, reduces greenhouse gas emissions through carbon sequestration, and contributes to climate change adaptation. |
| The area has been successfully afforested, restoring its natural beauty and original landscape. |
| The vegetation cover on the previously degraded land has been significantly enhanced. |
| This technology with its approach for implementation represents an effective solution for the restoration of degraded soils. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Inadequate maintenance and repair services of the technology | Linkage to the service provider and maintenance services. Nation wide technology transfer |
| Solar water lifting relies on fully sunny days for operation, which can sometimes be a limitation, especially when weather conditions are cloudy or during periods of low sunlight. This can result in insufficient water being lifted to meet the irrigation needs of the site. | Backup charging system/battery system |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Solar water lifting depends on sunny days for operation, which can sometimes fall short of meeting irrigation needs during cloudy periods. | Combining solar power with backup energy (like batteries or grid connection) |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
10
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
15
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
2
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
28/11/2024
Comentarios:
The data has been collected during Oct and Nov 2024
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos