



This case describes how a group approach can facilitate and encourage improved dairy production with better sheds, more productive breeds, environmental sustainability and marketing. Upgraded dairy production is described in detail under the technology “Improved dairy sheds” (T6898).
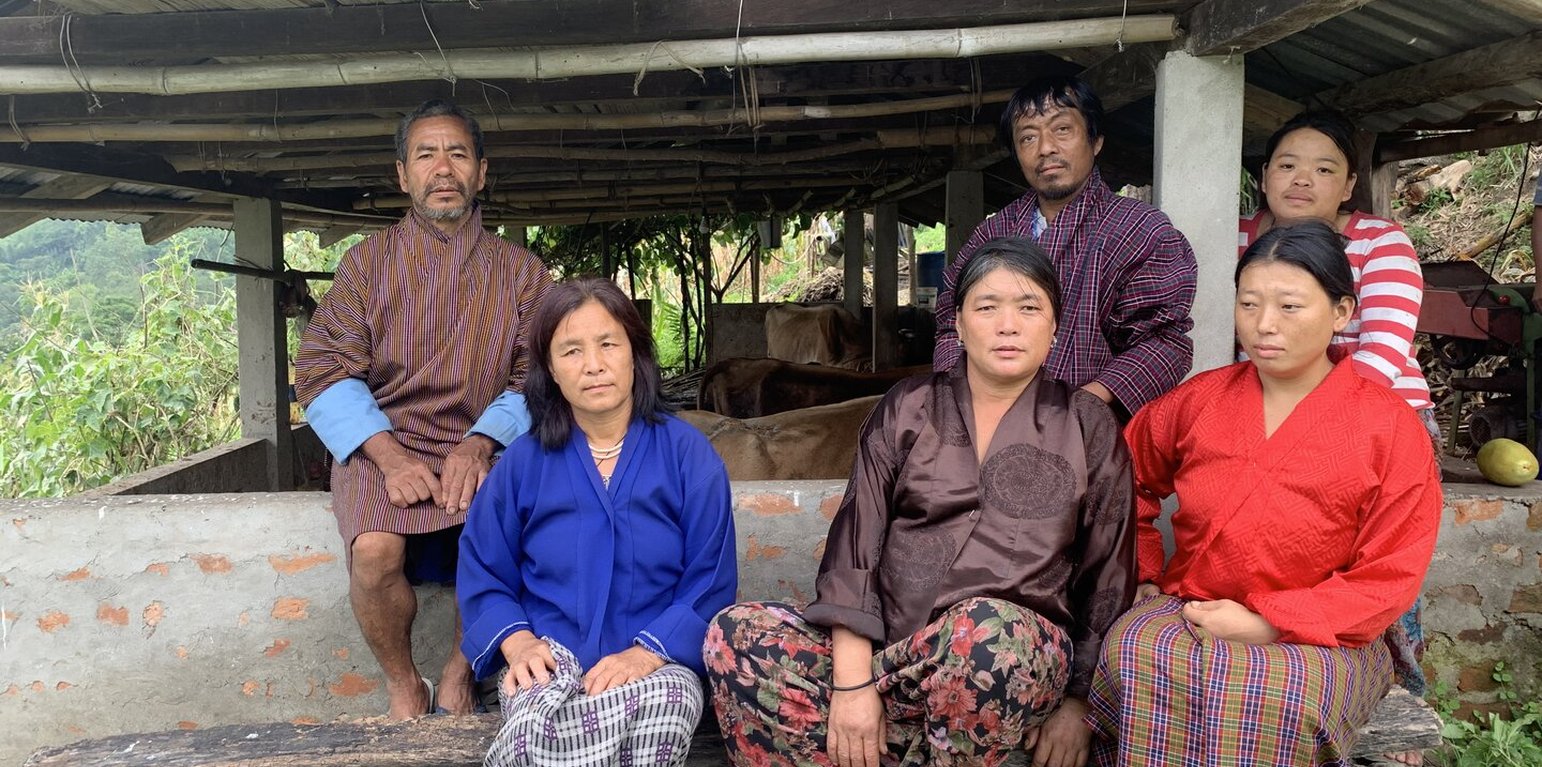
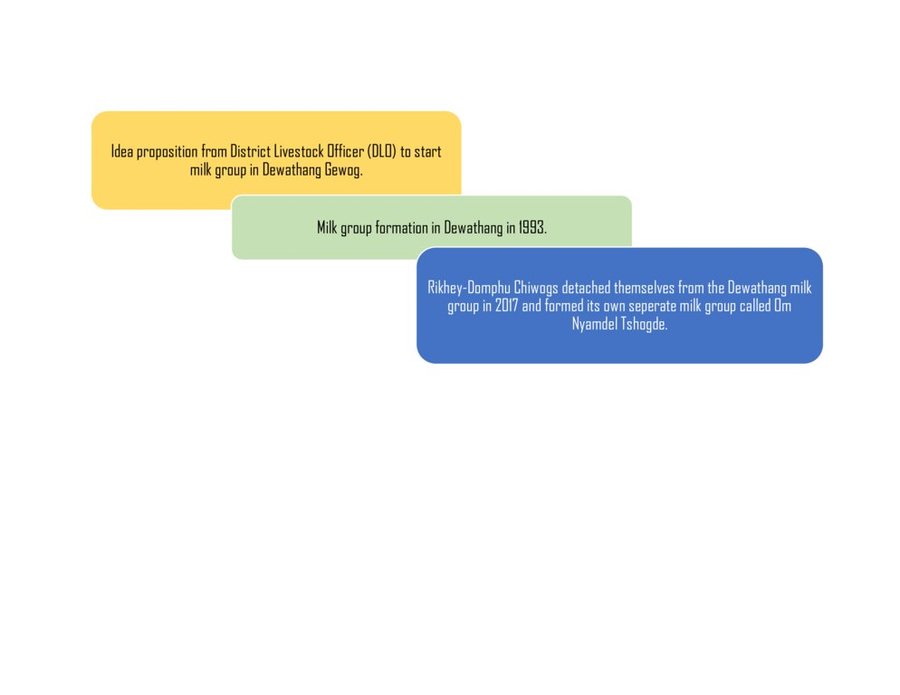
Initially, the land users were a part of a bigger milk group established in 1993. In 2017, some detached themselves and formed “Om Nyamdel Tshogde” which is a group composed of 67 members from Rikhey and Domphu chiwogs, led by a Chairperson, Mrs. Yangzom. The group also has a treasurer, Drungchen, and a driver. The main objective of forming the milk group was to improve the livelihoods of land users through higher yields via better livestock farming. The group formation process was assisted by the livestock extension officer. The funding was mobilized from the community itself.
The group members, with some support from the government, constructed improved dairy sheds, and biogas plants, and received training on fodder plantations. The stakeholders involved were land users, livestock extension officers, and the private cooperative B-COOP. The land users' role is to coordinate and conduct activities related to livestock farming. The extension officer's role is to provide veterinary and technical services. B-COOP's role is to buy dairy products from the group, especially milk.
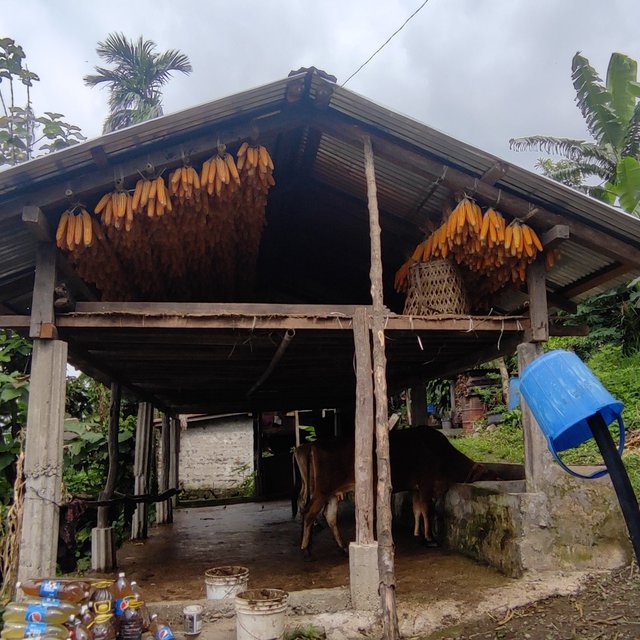
The group members have installed improved dairy sheds with cemented floors, feeding troughs, corrugated galvanised iron (CGI) roofing, and a continuous water supply. Also, cattle have access to timely veterinary services. Cow dung and urine are used as fertilizers and also in biogas plants. Biogas plants generate renewable energy (methane), thereby cutting down the use of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) gas which is derived from fossil fuel.
Under improved dairy sheds, stall-feeding is practised which bars the cattle from going to forests to feed. This prevents the degradation of land by cattle movement through trampling. For better nutrition and feeding, grass fodder species including Super Napier (pakchung), Napier, and Guatemala are grown, cut and and fed to cattle. In addition, other feeds provided included banana stems, maize stems, maize powder, mustard cake, and processed feeds. The group delivers at least 300 litres of milk per day to B-COOP, and some milk goes to India.
Improved breeds have replaced numerous low-yielding local cattle thereby making more efficient use of cattle feed. Also, fewer, more productive animals help reduce environmental degradation and methane losses to the atmosphere. The majority of cattle reared have been bred through artificial insemination. Most cattle are 50:50 hybrids between local breeds and improved breeds such as Jersey. Improving the breeds helps to increase milk production (e.g Holstein Friesian) and or percentage butter fat (e.g. Jersey). To feed and sustain productive, improved breeds, various fodder species are cultivated in large areas. This helps in carbon sequestration and preventing soil erosion.
What the land users like about the approach is that improved livestock farming results in a continuous source of income, as milk production is not seasonal like vegetable production, it provides organic fertilizers for fields, improves livelihoods, makes use of waste such as cow dung in biogas plants which means reduced dependency on LPG gas which is quite expensive. Also access to credit is increased. Government support has increased after the milk group formation. Furthermore, the workload is shared among the land users, especially during the making of biogas plants, thus easing the workload per person.
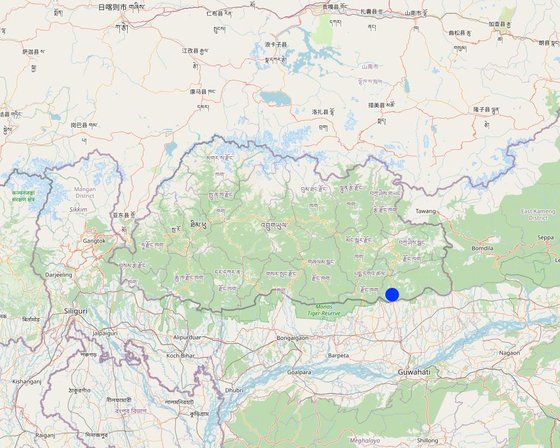
Lieu: Kheripam village, Domphu chiwog, Dewathang gewog, Samdrup Jongkhar Dzongkhag, Bhoutan
Date de démarrage: 2017
Année de fin de l'Approche: sans objet
Type d'Approche

| Quels acteurs/ organismes d'exécution ont été impliqués dans l'Approche? | Spécifiez les parties prenantes | Décrivez le rôle des parties prenantes |
| exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales | The land users of Rikhey-Domphu chiwogs. | Collectively produce milk (at least 300 L/day). |
| Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles | Livestock extension officer. | Provide technical support to land users. |
| secteur privé | Bhutan Cooperative (B-COOP) | Buy milk from the group. |
Les décisions ont été prises par
Les décisions ont été prises sur la base de
-Biogas plant construction
-Fodder grass plantation
Deep freezers
Cement bags CGI sheets Pipes Metals A part of these materials was financed by the government.
La main d'oeuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était
Improved livestock farming system has promoted technologies such as improved dairy sheds and biogas plants.
The land users have adopted technologies such as improved dairy sheds and biogas plants.
The land users have been able to sell milk and other dairy products to B-COOP and India and this has helped the land users generate income. Also, B-COOP and India have benefitted from the continuous milk supply from the milk group. The milk group has helped in forming a partnership between the land users and the buyers.
The land users have developed pasture land of Super Napier, Napier, and Guatemala grasses for stall feeding of cattle. This has minimized the issue of cattle entering other land users' fields and foraging on the crops.
Land users from different backgrounds are now part of the milk group.
Land users in the milk group are a mix of males and females. There is no gender discrimination.
Land users have assured monthly income due to the sale of milk and other dairy products. This has led to better household income. Also, stall feeding under an improved dairy shed has promoted the cultivation of fodder of good quality and variety leading to increased and quality milk production.
Land users now sell milk and other dairy products to B-COOP and India.
Biogas plants have reduced the use of LPG in some households.
Group marketing has helped land users earn better.