Community efforts for improving drinking water quality [Népal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Madhav Dhakal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Piune paani ko gunastar sudhar ka lagi samudayik prayas
approaches_2352 - Népal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Isabelle Provodoli
himcat@icimod.org
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), GPO
Box. 3226, Kathmandu
Népal
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Népal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

Drinking water quality improvement through conservation measures [Népal]
Structural and vegetative measures to improve the quality of drinking water contaminated due to poor sanitation and seepage
- Compilateur : Madhav Dhakal
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
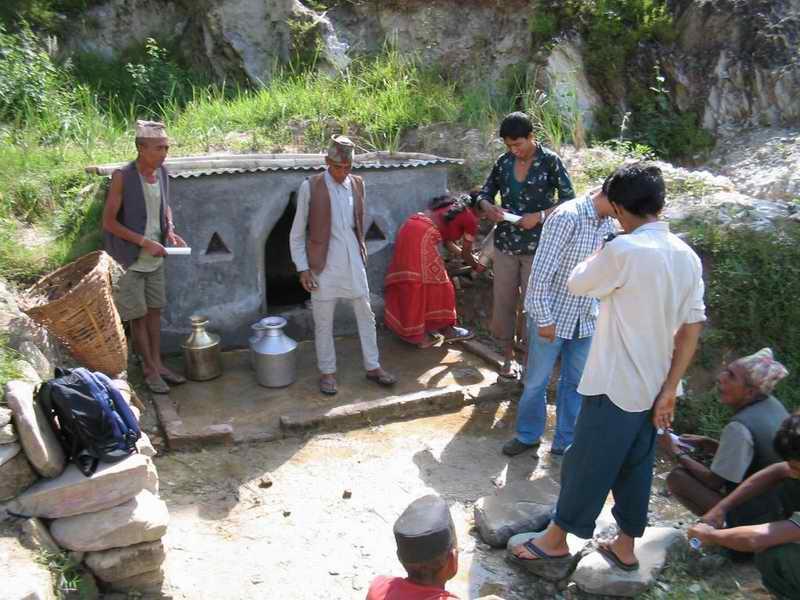
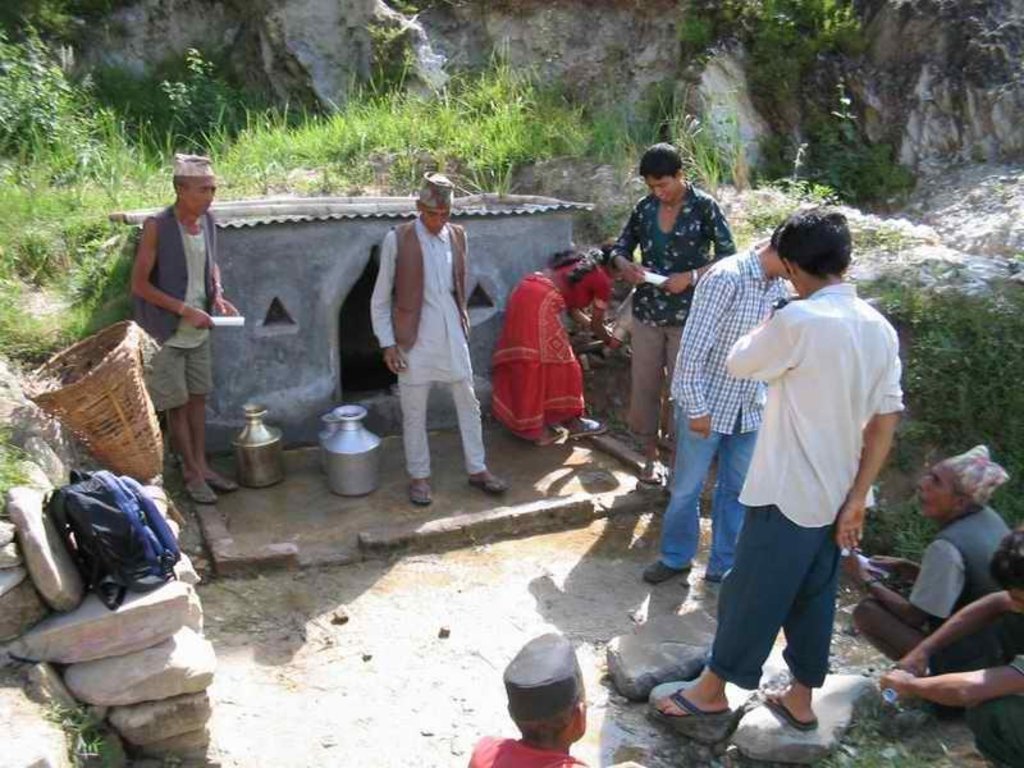
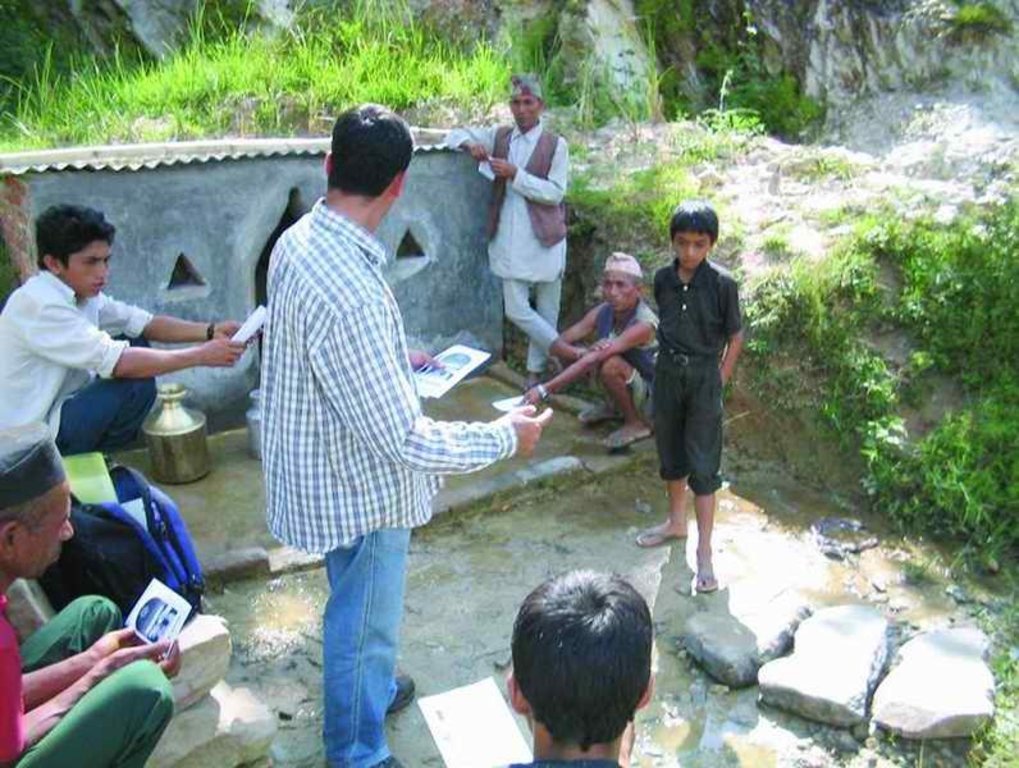
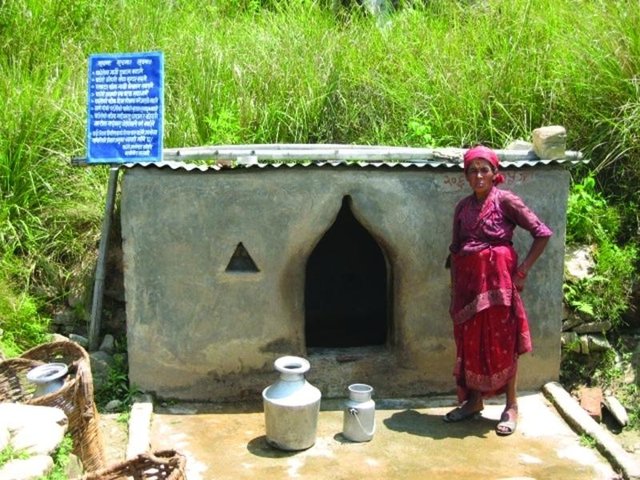
Aims / objectives: The People and Resource Dynamics in Mountain Watersheds of the Hindu Kush- Himalayas Project (PARDYP) implemented this approach with 30 drinking water user households at Barbot in the Jhikhu Khola watershed, Kavre Palanchok. The aim was to improve water quality and availability from an open spring source through participatory planning and implementation. The approach first identified local concerns and observed the sanitary situation of the catchment area. Meetings were held jointly with men and women users from different caste groups (Brahmin, Chhetri, Newar and Kami) to discuss the problems and issues and to identify viable solutions. The advantages and disadvantages of the various options were discussed, after which users selected the following three measures to improve the drinking water supply: 1) building a brick-cement walled structure around the main local spring, 2) establishing check dams across nearby rills and gullies, and 3) planting grass around the spring box and tree saplings within the catchment area. The aim was to prevent direct flow of surface water into the spring and reduce contamination and turbidity of the source. Understanding and support was gained by demonstrating the technology and running an awareness campaign.
Role of stakeholders: The project helped form a users committee made up of 11 women and 1 man and encouraged them to plant grass and tree seedlings across the entire catchment. The project regularly measured the quality of the water and shared the results with the users. Rules and regulations were developed to ensure equitable access to the spring and its sustainable use and management. A notice board with do’s and don’ts was placed near the spring. The users held monthly meetings and established a revolving fund for maintaining the structures. Spring users followed the rules and regulations by washing, cleaning, and bathing at separate sources. Livestock grazing was stopped in the nearby area and the area was regularly cleaned. Furthermore, users were encouraged to treat water for drinking using simple methods like SODIS and the low cost Safa filter to avoid microbiological contamination. They were made more aware of water quality, sanitation, and health issues.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Népal
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Kavrepalanchowk district/ Jhikhu Kholawatershed
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Date (année) de fin de l'Approche (si l'Approche n'est plus appliquée):
2005
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused on SLM only
- To explore and demonstrate appropriate water quality improving technologies and methods in a participatory way. - To increase awareness on water quality, water treatment, and health and hygiene. - To share knowledge gained on the water improvement options with farmers and other stakeholders
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Weak institutional collaboration to develop technological options for improving drinking water quality and availability and to raise awareness on health and hygiene and waterborne diseases.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
For the maintenance of the implemented technology
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Revolving fund collected by users
cadre institutionnel
- entrave
Weak institutional collaboration
Treatment through the SLM Approach: User group formed linking local community organisations
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: mostly state owned land and some private land - which helped implementating the technology as there was no conflict.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Different water treatment methods
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness of structural and vegetative measures; direct water treatment methods including Safa filter, SODIS, chlorination
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Land users worked equally divided between men and women
Improvement of drinking water quality and quantity was the major concern of all spring users.
- ONG
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
- organisation internationale
PARDYP/ICIMOD
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
Concept designed by national specialist and implemented jointly with users
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | public meetings; meetings organised to identify problems and possible options to overcome them. |
| planification | interactive | public meetings; organised regularly to identify implementing steps, and role and responsibility of different stakeholders in overcoming problems |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | responsibility for major steps; the user group responsible for implementation and the project for technical support |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | The quality of the water was measured in each season to monitor the impact of the technology. Detailed progress reports, results, and lessons learned were shared with district level institutions and authorities, water quality reports were shared with spring users at public meetings |
| Research | passive | Water quality and availability recorded before and after technology implemented. Studies on access to water and confl icts among users |
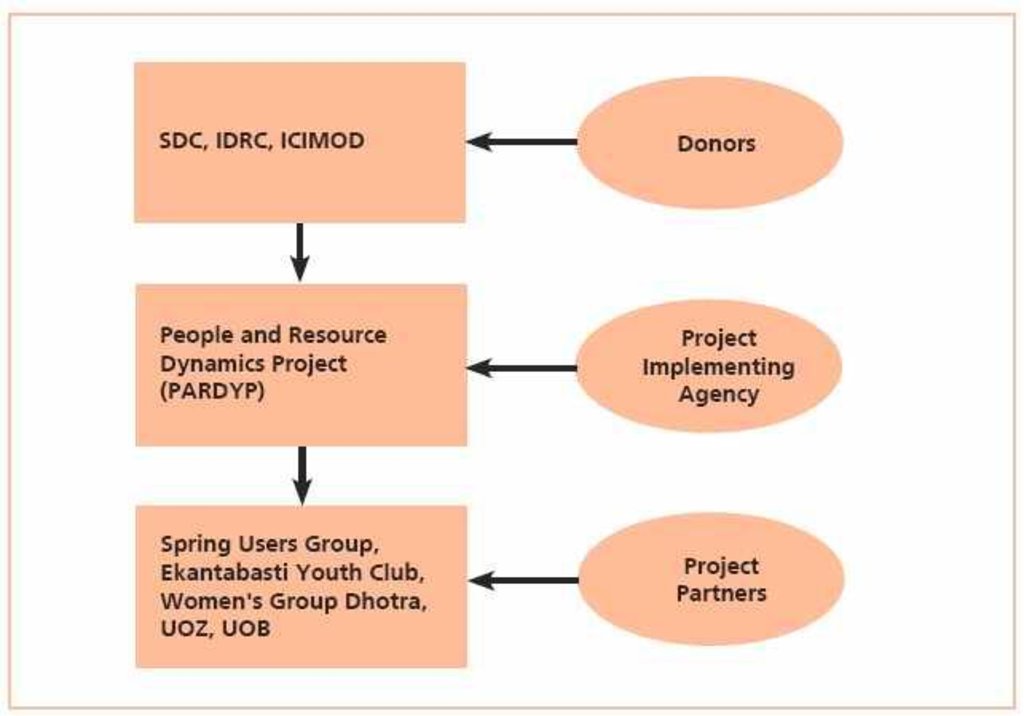
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
Description:
PARDP project donors and implementing partners-- SDC: Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation IDRC: International Development Research Centre ICIMOD: International Centre for Integrated Mo
Auteur:
Madhav Dhakal
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les exploitants des terres soutenus par des spécialistes de la GDT
Expliquez:
Users selected three of the potential conservation options.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. The technology and associated measures were not new to the area and the implementing methods were simple and have been practised for a long time. The project initiated the formation of a users committee and the committee conducted the conservation activities.
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
Formats de la formation:
- réunions publiques
Thèmes abordés:
Concept of conservation measures, and methods of treating contaminated water using SODIS and safa filter.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
Décrivez/ commentez:
Name of method used for advisory service: Sharing information on water quality status, and raising awareness among users.; Key elements: catchment conservation, health hygiene, water treatment methods; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: awareness on health hygiene; catchment conservation activities and water treatment methods were shared during meetings.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, un peu
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Précisez le type de soutien:
- renforcement des capacités/ formation
Donnez plus de détails:
Training on water quality treatment provided to local club
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land use and degradation, sanitary inspection, history of spring, available resources to trap water
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: seasonal water quality and discharge
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: number of spring users, household water requirements, users' issues
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: participation in conservation activities
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The project consulted with the local women's cooperative to solve a conflict over water quantity and access to spring source.
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- sociologie
- technologie
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Access to drinking water, conflicts at water fetching times, water quality and quantity measurement, and effectiveness of water treatment methods.
Research was carried out on station
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- < 2 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (users group): 10.0%
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- autre
| Autre (spécifiez) | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| Planting materials |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
Commentaires:
In implementing the technology and the approach
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Oui
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
To build awareness on SLM and methods of improving drinking water quality. It also helped users to work in a group.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Similar approaches are being followed in other communities across Nepal.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- réduire la charge de travail
due to reduced water fetching time (or distance).
- conscience environnementale
Improved heath due to clean water and better sanitation
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Users are maintaining the implemented technology and also protecting the other nearby spring sources.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Water users committee formed, revolving fund collected, and rules and regulations developed for the sustainable management of the drinking water system (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Maintain links with local community mobilisation groups for continuous guidance and support for the user group and for the proper use of the revolving fund.) |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Users have become more aware of sanitation issues than before (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Awareness campaigns should be organized regularly covering more villages.) |
| Users have become more aware of 1) the quality of their drinking water, 2) its impact on their health, 3) water quality improvement options, and 4) the importance of soil and water conservation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Water quality testing campaigns should be continued and technical know how about different water quality treatment methods for improved health shared at regular meetings) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Water aviallability is still insufficient during dry period (March -May) | Other available nearrer sources should also be used, catchment protection activities should be continued. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Conflicts are visible during the dry season due to insufficient quantity of water. | Good coordination among the group members should minimise conflicts- the strong and balanced role of users committee is vital for the equitable sharing of benefits. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
ICIMOD
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Drinking water quality improvement through conservation measures [Népal]
Structural and vegetative measures to improve the quality of drinking water contaminated due to poor sanitation and seepage
- Compilateur : Madhav Dhakal
Modules
Aucun module trouvé