Soil pH management [Royaume-Uni]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Tandra Fraser
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2615 - Royaume-Uni
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Tibbett Mark
m.tibbett@reading.ac.uk
University of Reading
Reading RG6 6UA
Royaume-Uni
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
University of Reading (University of Reading) - Royaume-Uni1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
03/05/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

Soil pH management [Royaume-Uni]
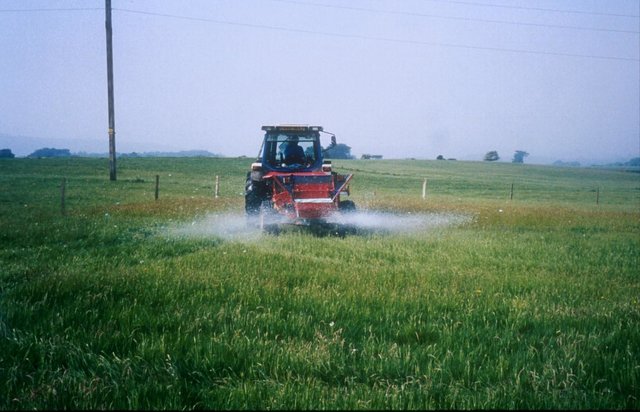
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to a semi-natural state
- Compilateur : Tandra Fraser
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to low-intensity grazing land
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Aims / objectives: To convert the area from intensive pastureland to a semi-natural state with low intensity grazing through alteration of the soil pH. This change in land-use should have a positive effect on both above- and belowground biodiversity.
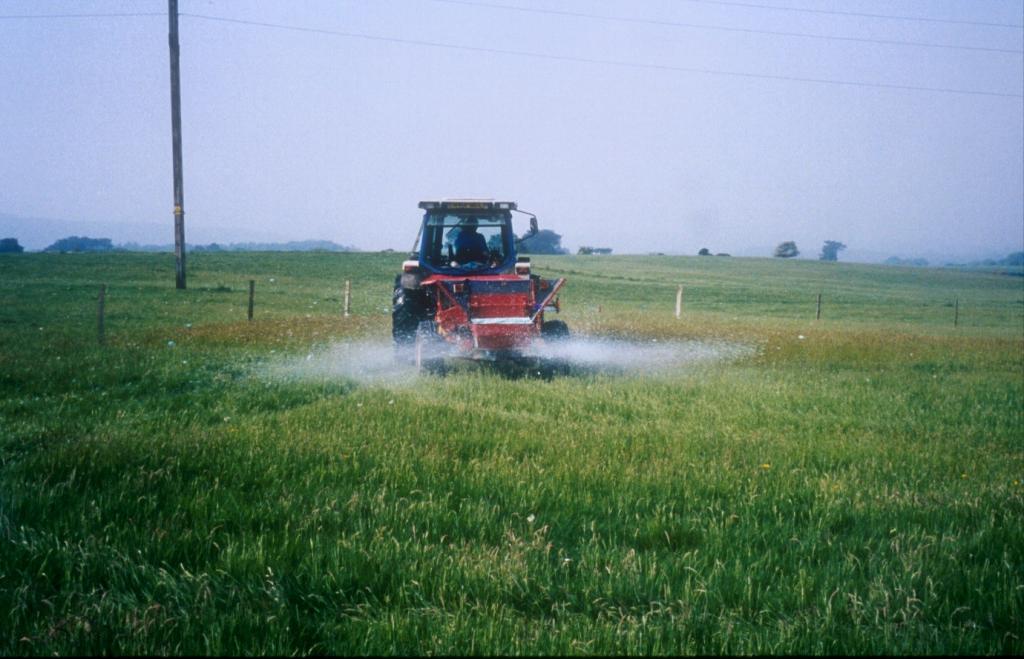
Methods: Plots were established on two adjacent farms owned by National Trust near Wareham, Dorset (Newlines Farm and Hartland Farm). A control and two sulphur amendments were compared on plots on ten fields (five from each farm) on 50 m x 50 m plots. Elemental sulphur (Brimestone 90TM) or ferrous sulphate (Mistrale “Wet Copperas” 50TM) were applied at equal rates of 2000 kg ha-1 in May 2000 and a second application of 1600 kg ha-1 in March 2001.
Stages of implementation: Treatments were applied in 2000 and 2001. Periodic monitoring has been conducted to monitor changes in plant diversity and soil chemical and biological properties.
Role of stakeholders: Stakesholders played an active role in identifying management options and implementing the technology. When the original plots were established, a charitable organisation was the primary stakeholder. For the intent of the current project, other stakeholders became involved, including parish council, landowners, and conservation organisations.
Other important information: Acidification treatments were applied to plots on the Isle of Purbeck that had previously been used for arable production and then high intensity grazing. The site is located on acidic fluvially-deposited soil and was in lowland heath until the middle of the 20th century at which time the land was tilled and treatments of rock phosphate, marl and chalk were added to increase soil pH and nutrient availability and improve the potential of the land for agricultural production.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Royaume-Uni
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Dorset
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Wareham
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
1999
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (soil, pH, below-ground biodiversity, low-intensity grazing)
To manage soil pH change and associated effects on above and below-ground diversity and function
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Management of soil pH and land use change to less intensive system
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Local confusion about land use change
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Public workshop explained reasons to stakeholders
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Loss of earning as less intensive system is less productive
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Ecological benefits balance against economic losses
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The land where the approach was implement was managed by National Trust UK who had a special interest in reclamation and conservation.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
- Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles
- ONG
- organisation internationale
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | soutien extérieur | Land owners who acquired national support |
| planification | soutien extérieur | By specialist |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | By land owner and specialist |
| suivi/ évaluation | soutien extérieur | By Specialist |
| Research | soutien extérieur | By specialist |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les spécialistes de la GDT, après consultation des exploitants des terres
Expliquez:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
Formats de la formation:
- entre agriculteurs (d'exploitants à exploitants)
- réunions publiques
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
- Public meetings
Décrivez/ commentez:
Advisory service was not foreseen for this approach
Advisory service is totally inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; No additional government funding has been acquired.
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- non
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements
area treated aspects were regular monitored through observations
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- écologie
- technologie
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Research on the approach has been carried out by specialists at Bournemouth University and the University of Reading, UK.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 10 000-100 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Department of Environment, Food & Rural Affairs): 50.0%; national non-government (National Trust): 30.0%; other (University): 20.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- intrants agricoles
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental S, Ferrous Sulphate | entièrement financé | |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Conversion to low input system
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Other farms
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Enjoyment of traditional landscape
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- réduire la charge de travail
- paiements/ subventions
- conscience environnementale
- améliorer l'esthétique
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Decreased spending on inputs where the only input in the system in dung from cattle grazing (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue grazing at a low enough density to allow adequate plant regrow) |
| Decreased labour required for management |
| Decreased compaction since regular use of tractors on site is no longer required (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Attempt to minimizing compaction by grazing livestock) |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The conversion in land use from a improved agriculture to a semi- natural low input grazing system should have a positive effect on above- and belowground biodiversity. |
| Considering that the Isle of Purbeck was historically a region of cultural importance, returning the system to a more natural state has important implications for the cultural and recreational value of the land. |
| Low input systems can increase resilience of the system to global change |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Fertilizer application rate too high for one application | Smaller, regular additions over several years |
| Decrease in economic returns | |
| Shrub encroachment (i.e. gorse; Alex europaeus) can be a problem when converting to low input pasture land in this region. | Grazing, mowing, and chemical herbicides are some options for slowing invasions. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Over time nutrients are being drawn down but exporting meat off the land with no inputs | Periodic applications of nutrients may be required to ensure long-term fertility of the system |
| Land use change and restoration are slow process and may result in economic losses on managed lands |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Re-creation of heathland on improved pasture using top soil removal and sulphur amendments: Edaphic drivers and impacts of ericoid mycorrhizas, Diaz, A., Green, I., Tibbett, M., 2008Heathland restoration on former agricultural land: Effects of artificial acidification on the availability and uptake of toxic metal cation, Green, I., Stockdale, J., Tibbett, M., Diaz, I., 2007Are sulphurous amendments an effective tool in the restoration of heathland and acidic grassland after four decades of rock phosphate fertlization, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2005The restoration of heathland and acid grassland at Hartland and Newline Farms, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2001
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Biological Conservation, 141:1628-1635, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006320708001353Water Air Soil Pollution, 178:287-295, http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11270-006-9197-8Restoration Ecology, 13:83-91, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-100X.2005.00010.x/epdfFirst Year Report to National Trust, Purbeck
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Heathland restoration on former agricultural land: Effects of artificial acidification on the availability and uptake of toxic metal cation, Green, I., Stockdale, J., Tibbett, M., Diaz, I., 2007
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Water Air Soil Pollution, 178:287-295, http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11270-006-9197-8
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Are sulphurous amendments an effective tool in the restoration of heathland and acidic grassland after four decades of rock phosphate fertlization, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2005
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Restoration Ecology, 13:83-91, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-100X.2005.00010.x/epdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
The restoration of heathland and acid grassland at Hartland and Newline Farms, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2001
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
First Year Report to National Trust, Purbeck
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Soil pH management [Royaume-Uni]
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to a semi-natural state
- Compilateur : Tandra Fraser
Modules
Aucun module trouvé