Community tradition [Afrique du Sud]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : William Critchley
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2625 - Afrique du Sud
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Van der Merwe Rinda
rinda@arc.agric.za
Institute for Soil, Climate and Water
P/Bag x79, 0001 Pretoria, South Africa
Afrique du Sud
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Institute for Soil, Climate & Water - Afrique du Sud1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
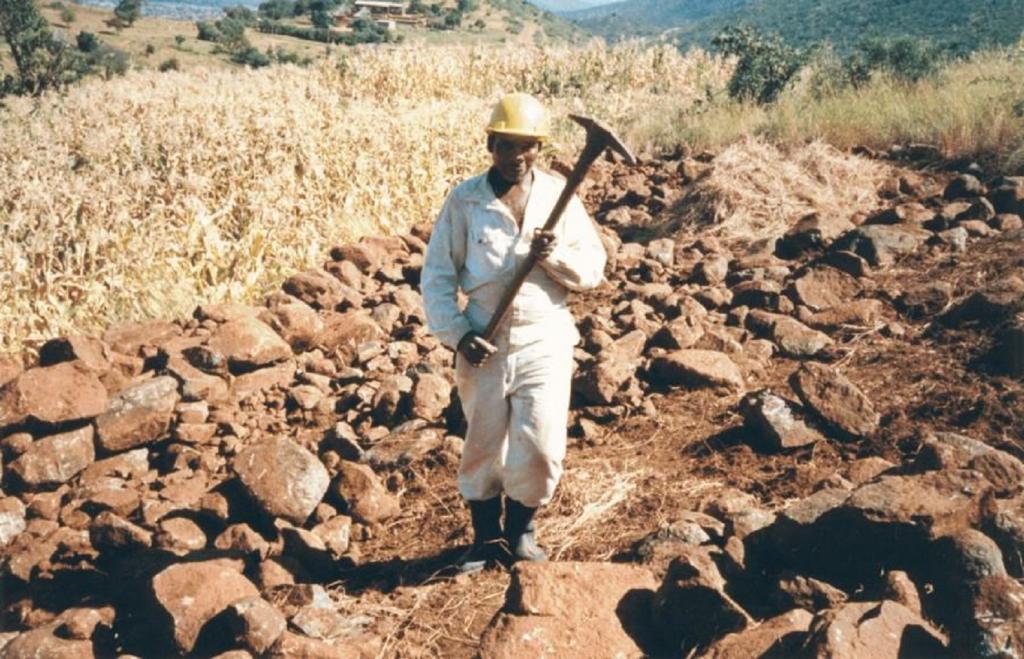
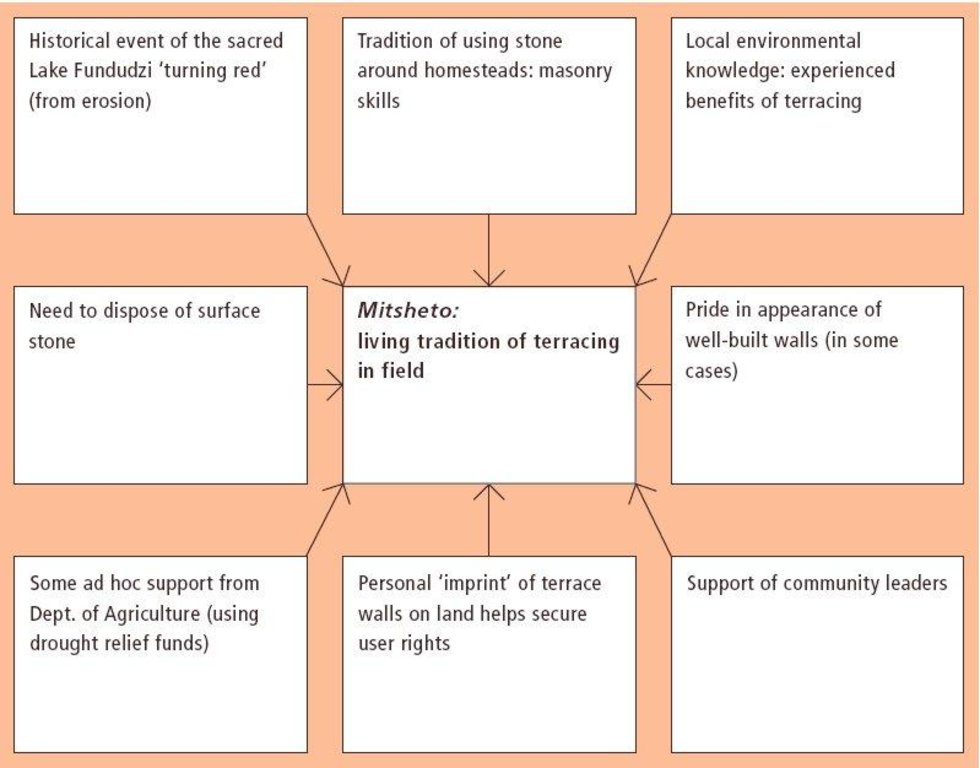
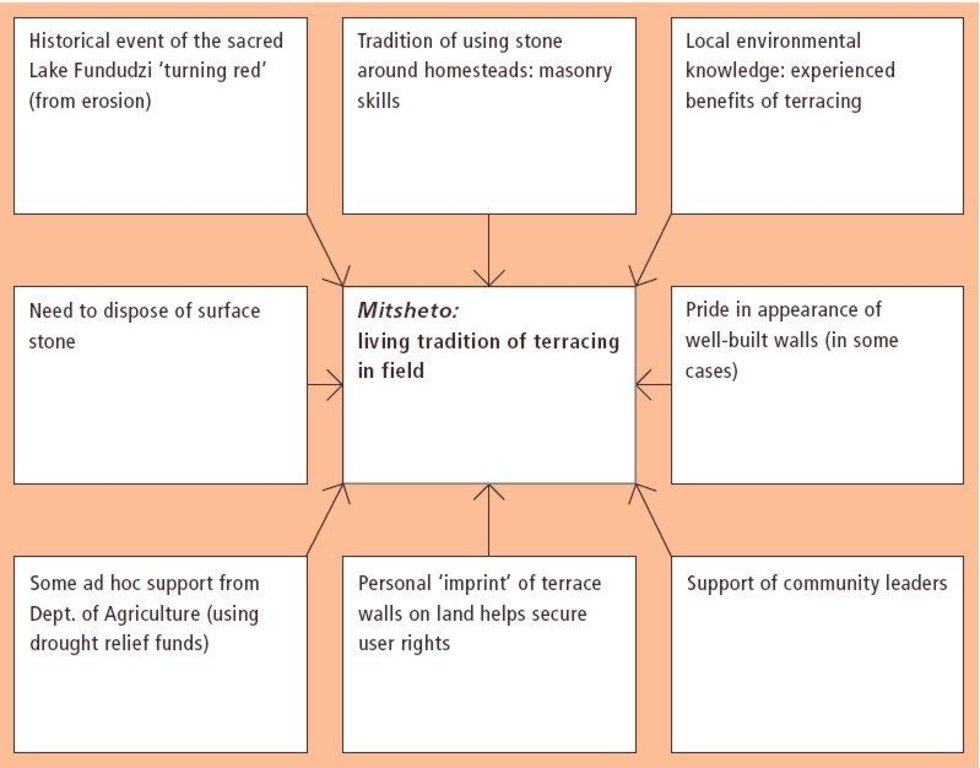
Inherited, and still practiced, tradition of stone terracing - passed down from generation to generation.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
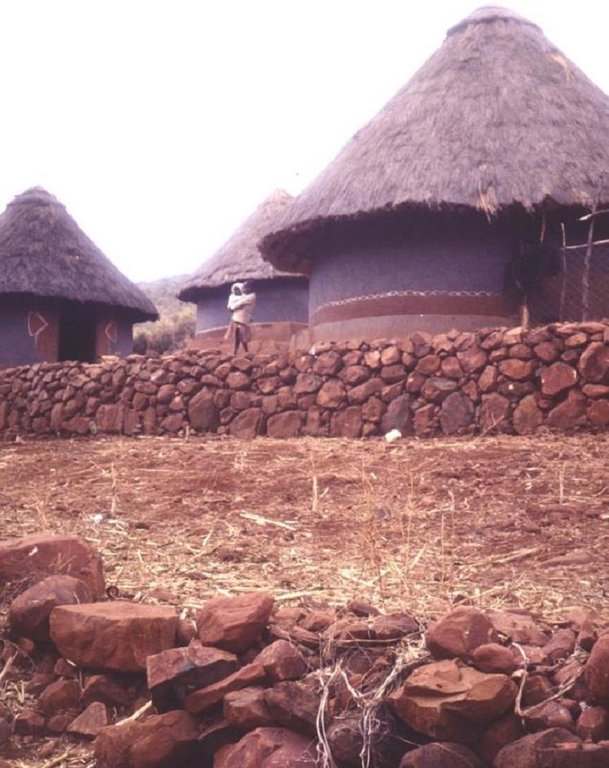
Aims / objectives: The VhaVenda people of Limpopo Province in South Africa have a tradition of building with stone which has been passed down from generation to generation. They construct stone walls around their houses for example, taking a pride in the appearance of their homesteads. There is a historical monument nearby, the stone-built kraal at Dzata, the ruins of which are situated within a few kilometres of the study location. There may even be some evidence that the VhaVenda came originally from the area of the Great Zimbabwe (the famous stone-built fortress in Zimbabwe). It is not surprising therefore that the VhaVenda have used their masonry skills to build terraces in fields to counter erosion and simultaneously to make cultivation - along the contour by oxen - possible. This tradition has been passed down through the ages: it is institutionalised in the community and is practised together by men, women and children on a family basis. It is encouraged by community leaders: a particular example of this was in the 1960s when local chiefs were concerned at the sacred Lake Fundudzi 'turning red' - with sediment eroded from the land - and as a result they launched a conservation campaign to prevent soil wash into the lake. There has been modest and occasional support by the Department of Agriculture, in the form of ad hoc drought relief funds. There is quite a range of technical ability/care taken in terracing. Some walls are meticulously built; others are merely piles of stone across the slope. One of the reasons for this is that work tends to be done on an individual basis. Another result is that fields may take two years or more to be fully terraced. What is evident is that the land users - as well as being experienced masons -appreciate the benefits of the terraces they construct. An investigation of local environmental knowledge and conservation practices has demonstrated this clearly (see reference).
Methods: The causes of erosion were explained by the interviewees as being part natural (rainfall, slope etc) and part anthropogenic (poor road building, up and down ploughing, burning of grassland etc). The main negative impact of erosion was considered to be loss of soil fertility: hence terracing for protection. This indigenous knowledge also extends to soils: eight local soil types and their differences in terms of texture, fertility and erodibility are recognised in the study area.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Afrique du Sud
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Limpopo Province
Map
×2.7 Type d'Approche
- traditionnel/ autochtone
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The objective of the local people is simply to continue making cultivation possible and sustainable, through the local tradition of using stone walls to create terraces and to remove abundant stones from the field.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - the tradition presumably arose as a spontaneous local response to degradation: it remains well entrenched - underlying problems of no flat land to cultivate, soil erosion/fertility decline on sloping fields, and loose stone and rocks impeding animal-draw ploughs
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
autre
- entrave
labour: High labour demand to remove stone from inhibiting cultivation.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Traditional teaching that such stone can be used constructively to improve conservation and yield benefits.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | auto-mobilisation | passing on knowledge; passing on of knowledge from generation to generation |
| planification | auto-mobilisation | |
| mise en œuvre | auto-mobilisation | family-based (or individual) construction |
| suivi/ évaluation | aucun | |
| Research | aucun |
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- les exploitants des terres seuls (auto-initiative)
Expliquez:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Thèmes abordés:
There was/is no formal training - just father to son/mother to daughter.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
Décrivez/ commentez:
Key elements: Some encouragement from Department of Agriculture especially during soil and water conservation campaigns/drought relief periods.
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, un peu
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Donnez plus de détails:
support for SWC campaigns from local leaders
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 5.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 95.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
Commentaires:
Almost entirely voluntary: some small support (approx 5% of the sample monitored) through Government during times of food scarcity with paid relief work.
A (very) small amount of drought relief in recent years from Government
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Great: as part and parcel of the local tradition - for example contour ploughing is facilitated by the fact that the stone lines are on the contour, making this type of ploughing easier.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Only within this small pocket of Thohoyandou District (as far as known).
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
The VhaVenda have built terraces for generations so far, so no reason to think that things will change.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Traditional approaches have the potential to endure (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Acknowledgement and encouragement by the Government and/or NGOs will help this.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| This tradition was largely unrecognised until recently: therefore an opportunity was lost to encourage people and help the approach spread | Publicise widely and carry out farmer-to-farmer/community-to-community visits to further its spread and the spread of local SWC knowledge more generally. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Critchley W and Netshikhovehla E (1998) Conventional views, changing paradigms and a tradition of soil conservation.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé