Joint forest management [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Sumana Datta
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2370 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Varghese Paul
vpaul@teri.res.in
TERI, Habitat Place
Lodhi Road, New Delhi 110 003
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Singh T.P.
11-91-4682111
TERI, Habitat Place
Lodhi Road, New Delhi 110 003, India
Territoire britannique de l'océan Indien
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Vashist Uma Shankar
11-91-4682111
TERI, Habitat Place
Lodhi Road, New Delhi 110 003
Inde
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Tata Energy Research Institute TERI (Tata Energy Research Institute TERI) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

Forest catchment treatment [Inde]
Catchment treatment of degraded forest land including social fencing, infiltration trenches and enrichment planting with trees and grasses for production and dam protection.
- Compilateur : Chetan Kumar
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Government and NGO supported community protection of forested catchments, through village-based Hill Resource Management Societies.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Aims / objectives: Joint forest management (JFM) in India emerged in the 1980s from community initiatives in forest protection. At that time, less than half of the official forest land had good tree cover. Forest protection groups took action, based on 'social fencing' of degraded forest land. JFM was adopted by support agencies - NGOs and Government (State Forest Department) - when its full potential was realised. It is an approach that leads to environmental and production benefits through community co-operation in natural resource management. State-supported JFM in Haryana began on a pilot basis in Sukhomajri village in 1976, and has built on the success of that initiative, spreading to a total of nearly 200 km2, covering 60 villages in Ambala and Yamunagar Districts. The National Joint Forest Management Resolution of 1990 supported the rights of forest communities country-wide. In the same year, the Haryana State Government signed an agreement with The Energy and Resources Institute (formerly TERI: Tata Energy Research Institute) - underpinned by financial support from the Ford Foundation - to help establish Hill Resource Management Societies (HRMS). These state-sponsored, village level societies are key to the success of JFM, and their links to the State Forest Department are crucial.
Methods: The founding principles of HRMS include appropriate social composition, accountability and conflict resolution. They are open to all members of the village communities - regardless of gender or caste - who pay membership fees, and are then officially registered. Management committees are elected, and each must include at least two women. The HRMS oversee forest catchment management activities by villagers, arrange distribution of irrigation water (where applicable) and liase with the State Forest Department and TERI. Hill Resource Management Societies derive income from non-timber forest products - particularly from sales of bhabbar grass (used for rope making) - and from water use charges. This income is managed by the HRMS and used for village development and community welfare. The HRMS plan activities together with the State Forest Department. Under the guidance of the HRMS, communities provide labour (for physical works in the catchment etc), which is partly paid, implement social fencing and share the multiple benefits. Where there is a water harvesting dam all members have the right to claim an equal share of the water, irrespective of whether they have land to irrigate or not.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Ambala amd Yamunanagar Districts
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Haryana State
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
1976
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Forest conservation/ Livelihood enhancement/ institution building)
- develop democratic and powerful Hill Resource Management Societies. - protect the forest land, by means of local participatory governance, and thereby improve the flow of forest products. - boost agricultural productivity through irrigation in village fields from dams in the protected catchments
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - the main basic problem to be confronted was lack of control over the degradation of forest in the Shiwalik Hills which was leading to erosion and siltation of water bodies, and a lack of forest products/grazing. - there was no community organisation established to address these issues on land that was handed over to the village for management by the Forest Department. Clear felling for agriculture, increasing grazing pressure from large herds of cattle coupled with forest fires and reckless felling replaced the dense forests of Shiwaliks by bare hils with thorny bushes. The result was severe erosion on the hills (700T7ha/year) causing serious siltation in lakes/rivers and also affecting agricultural productivity, the primary source of livelihood of the area.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Lack of local institution for natural resource management.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Set up Hill Resource Management Societies.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Inadequate budget from Forest Department for implementation.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Water charges help to provide finance - but the State Government should assist more.
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- entrave
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation Ownership rights affected the approach to a great extent and in a positive way: user rights to forest land are made available equally to all, to reduce potential conflict between unequal 'land owners'.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Inadequate appreciation/understanding of integrated soil and water conservation/production approach within Forest Department.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Build awareness in Forest Department.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Forest dependent families, users of irrigated land
Hill Resource Management Society was formed. There were moderate differences due to social and cultural practices. Women are active in only a few Hill Resource Management Societies, but at least two women must be on each management committee. Although at least one woman from each household is a member of HRMS, presence of women in meetings is found very thin. However, there are few HRMS where women are active.Each family of a village is eligible to become the member of the HRMS irrespective of their caste or economic status. The Executive Committee, who is responsible for the day-to-day functioning also consists of representatives of each caste/hamlets and from landless families (if any in the village). All decisions are taken in the meeting in presence of minimum1/3 of the members.
- Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles
- ONG
From 1990, TERI as facilitator. Ford foundation provided financial support to TERI from 1990
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
Between 1976 and 1990. Haryana forest department, central soil and water conservation institute
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
The Haryana Forest Department and the Central Soil and Water Conservation Research and Training Institute (CSWCRT) of Chandigarh in cooperation with people of Sukhomajri village designed the approach in the beginning. TERI, an NGO has played a role in replicating the approach in other areas (more detail in Annexure).
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Mainly:public meetings; partly: rapid/participatory rural appraisal |
| planification | interactive | Mainly: rapid/participatory rural appraisal; partly: public meetings; Users have been involved in the preparation of 'Microplan' through PRA. |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | Mainly: responsibility for major steps; partly: casual labour; taking responsibility for organisation of casual labour Users have been providing 'social fencing' whereby they stopped taking livestock inside the forests and undertaken other regulatory measures for utilizing forests in a sustainable |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | Mainly: public meetings; partly: interviews/questionnaires; Users participated in vegetation surveys with the forest dept. And TERI to monitor the forest regeneration status. In case of institutional and socio-economic monitoring users were involved in group discussions and as key informant's interv |
| Research | interactive | Land users have tried improved variety of seeds on the land. Provided information/judgement in social science research. |
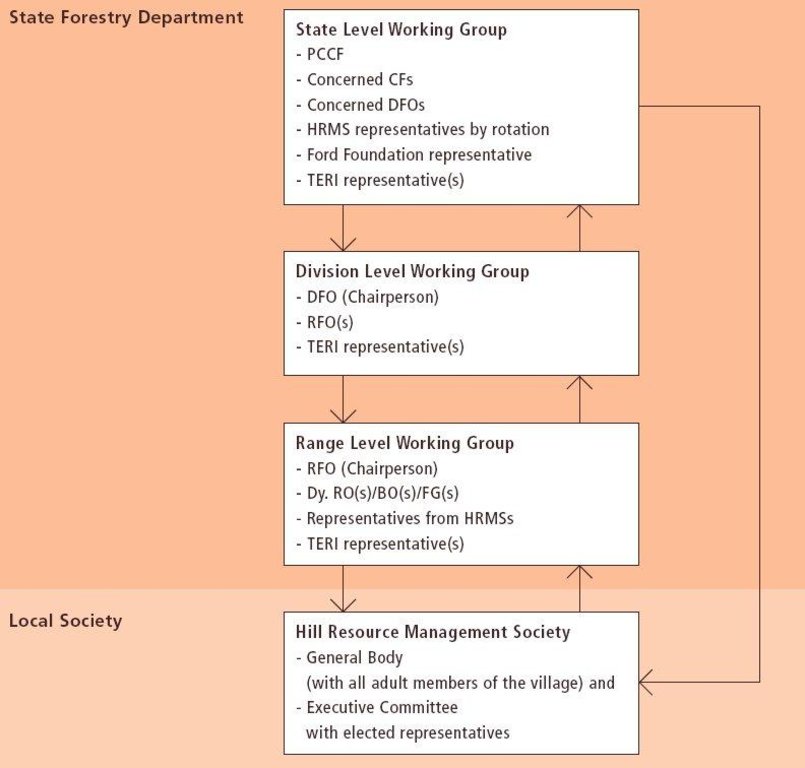
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
Description:
PCCF: Principal Chief Conservator of Forests CF: Conservator of Forests DFO: Divisional Forest Officer RFO: Range Forest Officer HRMS: Hill Resources Management Societies Dy. RO(s): Deputy Range Offic
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les spécialistes de la GDT, après consultation des exploitants des terres
Expliquez:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Mainly made by SWC specialists with consultation of land users in the initial pilot scheme at Sukhomajri, but in other villages, later, land users have taken the lead role with SWC specialists' support.
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- forest dept. Staff (2), politicians/decision makers (3)
Formats de la formation:
- réunions publiques
- cours
Thèmes abordés:
Training given to land users by the Forest Dept in conjunction with TERI on water harvesting structures and their maintenance. There are also workshops and meetings to evolve and maintain water distribution system. Technical information about water harvesting structures and ist maintenance. Workshops and meetings were also held to evolve the distrinution system. A manual has been prepared by TERI
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
Décrivez/ commentez:
Name of method used for advisory service: Formal training to selected group/Group discussion; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: non-governmental agency, Staff of TERI 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: maintenance of SWC structures/management of water distribution/record keeping/management of funds
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Extension, through the Forest Department???s agents, covering forest management and irrigation is given to certain groups amongst the HRMS, but is not yet adequate. More is required from Government.
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, beaucoup
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Précisez le type de soutien:
- renforcement des capacités/ formation
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: change in vegetation
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: erosion status/siltation of water bodies
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: level of participation
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: change in income
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through observations
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Internal reviews are carried out every one or two years: there have been several changes proposed and carried out as a result. These changes were in aspects of sharing water irrigation, and in methods of utilising income derived from forest products - especially bhabbar grass (Eulaliopsis binata).
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- sociologie
- technologie
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Research is carried out by TERI, and covers various aspects (including both technical and social issues). Results are published in handbooks as well as having been compiled in 'The Decade and Beyond' (see references).
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 25.0%; international non-government (-): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 25.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- équipement
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| machines | entièrement financé | bulldozers are used to construct dams etc |
| outils | entièrement financé | |
- infrastructures
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| Buildings | entièrement financé | |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- payée en espèces
Commentaires:
For establishment of dams and infrastructure, labour is rewarded (up to 95%) with cash wages. Over the last few years there have been some contributions from HRMS funds (derived from water user charges etc), which go towards maintenance work.
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
There has been a huge improvement in soil and water management - the forest canopy and its understorey have been restored with all associated benefits. Additionally, in fields below the forest area, levelling of land for irrigation reduces its vulnerability to erosion.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les questions foncières et des droits d'utilisation qui entravent la mise en œuvre des Technologies?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
As it is not in his own land, initially land owners did not own it. However, with time, they realised this helps them utilizing their lands in a far better way.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The original experiment in Sukhomajri has been replicated in 60 other villages within Ambala and Yamunagar Districts - and further afield in Haryana and India generally.
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Land users can continue to maintain what infrastructure has been put in place (dams, irrigation pipelines etc) but technical guidance is required - and at least some budget from the Forestry Department. In terms of managing the forest resources itself, the existence of the HRMS should ensure that this will continue. However, land users might need technical guidance from specialist on maintenance.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Opportunity to earn more from livestock (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Better access to market, and thus value addition, needed.) |
| Opportunity to earn more from agriculture through irrigation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Better access to improved seed and technology required.) |
| Equitable access to benefits (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: New rules and by-laws needed to sustain this.) |
| Integrated approach of natural resource regeneration (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Policy required for encouraging interdepartmental development activities.) |
| Emphasis on training and managerial capacity building (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue emphasis on/targeting of women.) |
| Cost-effective rehabilitation technologies (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Build more capacity amongst land users to implement and manage sustainably.) |
| Creation of strong people's self-help institutions the Hill Resource Management Societies (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Create more awareness among women.) |
| The creation and efficient operation of Hill Resource Management Societies (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continued outside support for HRMS required.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Sustainability of SWC is dependent on regular maintenance | Increased budgetary allocation through Forest Department required. |
| Weak market linkage | Strengthen market linkages for agricultural, livestock and forest products. |
| Moderate participation of women | Build better awareness among women. |
| Lack of credit for investment in agriculture and business | Popularise micro-credit concept under women???s self-help groups. |
| Lack of opportunity/knowledge for value addition to forest products | Training programmes for micro-enterprise development are needed. |
| Average level of literacy | Emphasis on literacy drive and continuous emphasis on cpacity building |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Singh TP and Varalakshmi V (1998) The decade and beyond: evolving community and state partnership. The Energy and Resources
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Varalakshmi V, Hegde ravi, Singh TP. Trends in institutional evolution at the grassroots - A case from the Joint Forest Management Programme, Haryana, India. International journal of sustainable development and world ecology, Sept. 1999
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Singh TP&Datta Sumana(2000) Institutional design for small irrigation system (a case study from JFM area in Haryana) presented in the all India seminar on Environmental and social issues in water resources Development on June 5&6,2000 in Lucknow,UP organized by the Institute of engi
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Datta s, Varalakshmi V. Decentralisation: an effective method of financial management at grassroots (evidence from India) in sustainable development. Vol7No3,August 1999. pp113-120
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Forest catchment treatment [Inde]
Catchment treatment of degraded forest land including social fencing, infiltration trenches and enrichment planting with trees and grasses for production and dam protection.
- Compilateur : Chetan Kumar
Modules
Aucun module trouvé