Rehabilitation of terraces and diversion construction with gates and channels [Yémen]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Joana Eichenberger
إعادة تأهيل المدرجات والحواجز والبوابات والسواقي
approaches_2635 - Yémen
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Alhadrami Yahya
00967777249274
General Directorate for irrigation
Sanaa
Yémen
Spécialiste GDT:
Sallam Ahmed
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA
Yémen
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority (AREA) - Yémen1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/02/2013
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT
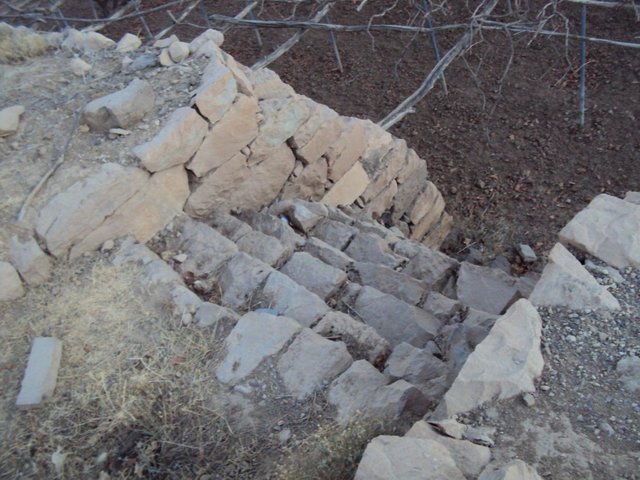

Building Walls's stones to protect lands and building … [Yémen]
use the stones to build walls around agricultural terraces to protect them from erosion and make outlets (Spillway) to discharge excess water and prevent the destruction of the stands
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
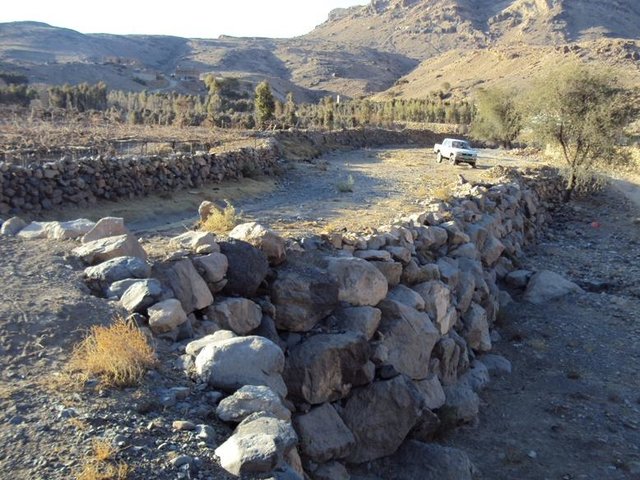

Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels [Yémen]
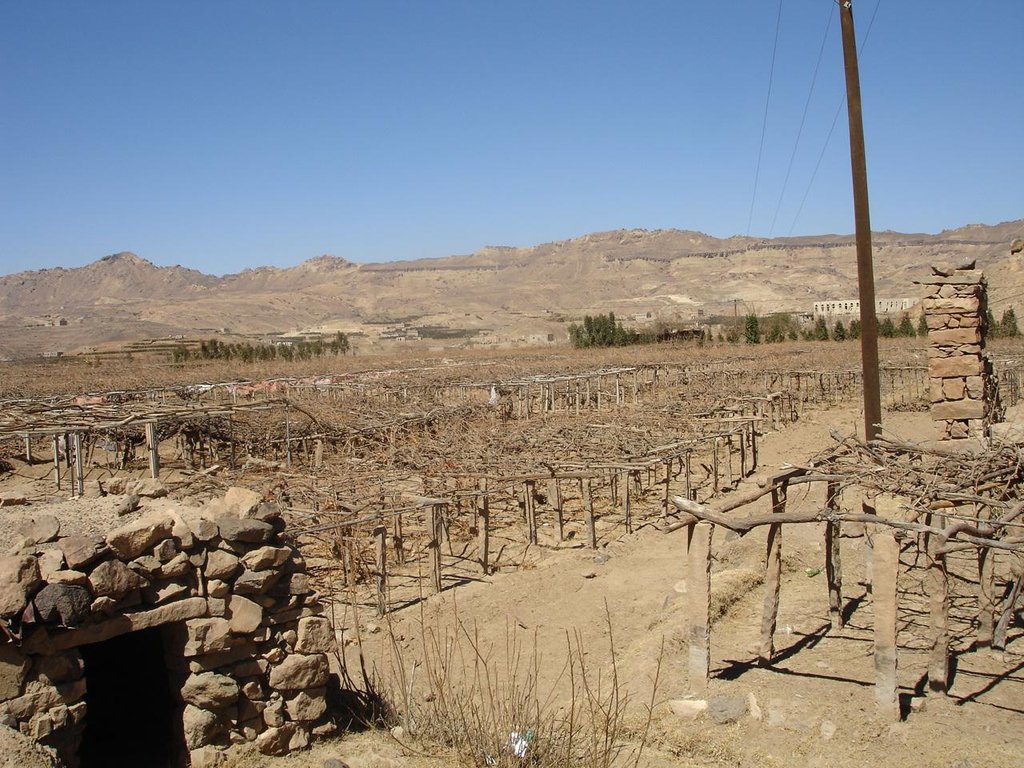
The stone existed in the region are used for building diversion constructions to raise the level of wadi bed to the level of the inlet of the cultivated land that need to be irrigated from water harvesting in addition to distribution channels in the fields
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
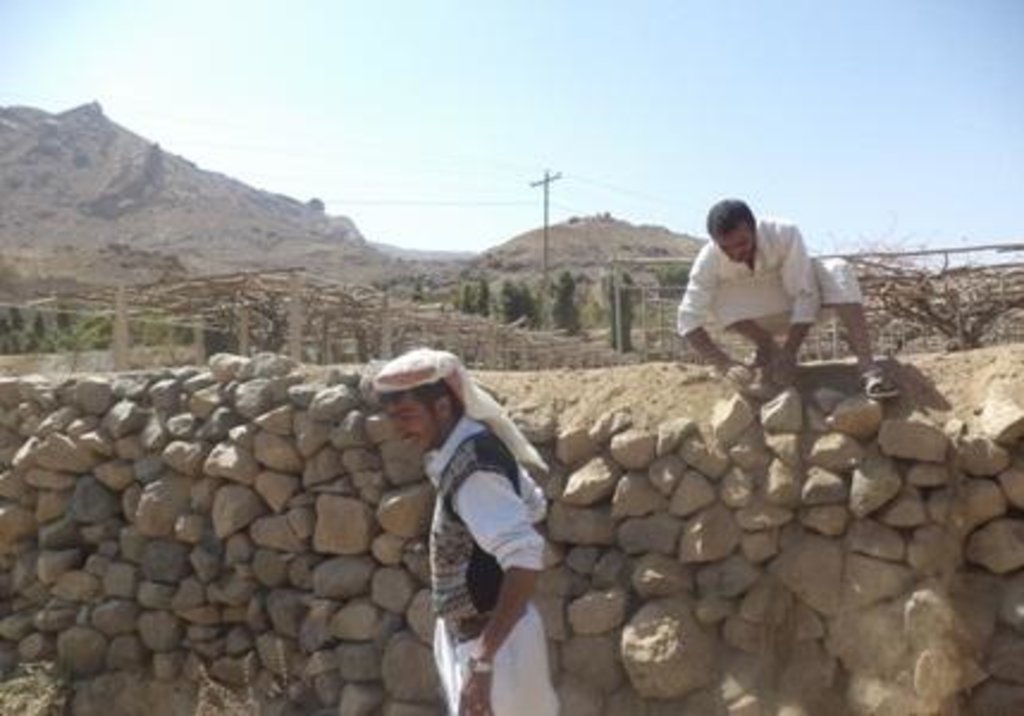
The rehabilitation of walls and outlets of the terraces and diversion construction with accessories from channels and gates are carried out by the local community in a regular way
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Aims / objectives: Before 56 years the cultivated land were stable and sustainable as a result of application the technologies. However, in 1956 a severe flood occurred had let to washed a large area of the cultivated land and people and houses. Then the local community had decided to puts hands together and started to rebuilt all the walls and gates and outlet of the whole terraces that damages from hoods. That was because the cultivated land was the only main source of livelihood at that time. The first step made by the local community are meeting at the invitation of sensible to consult and agree on how to rebuild what has been flashed as a result of floods and determine the priority of work and methods of implementation, it was agreed that the owner where damage event happened should do not pay anything either bring drinking water to the people who attended to assist him. However, first to protect agricultural land prone to erosion In the event of second rainstorm located on the main course Flood water (riparian valley). Then be re-construction of the barrier with accessories.
Key stages
1 - The land users involved in a specific area (position) to collect stones necessary to rebuild the walls of the garrison of land and after processing quantity required by the land users are re-building walls collectively by the community of males, contributing to work both reached 12 years of age male. Were identified on Friday of each week to carry out the construction is completed collecting the required stones.
2 - Settlement of the surface of the soil and filling eroded canyons and remove sediment from agricultural land by land users
3 - grape planting trees in areas affected by erosion
4 - building barriers gradually until they reach the level of agricultural land to be irrigated from the barrier and building gates and canals by the users of the land beneficiaries of the barrier
For agricultural land away from the waterway has been rehabilitated and build by the users of the land due to lack of manpower where everyone is busy their land to address the damage that occurred, and as a result was rebuilt stone walls in places exposed to the risk of erosion and the work of the walls of the soil in places less dangerous .
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Yémen
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Sana'a governorate
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Bani Hushaish district
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
1956
2.7 Type d'Approche
- traditionnel/ autochtone
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Getting benefits from water harvesting in irrigation terraces )
Rehabilitation of terraces and protect it from water damages through or follow the indigenous knowledge that was followed to maintain the terraces. And at the same time harvesting water.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: land degradation and maintain the traditional techniques, improve agricultural production
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Lack of finance
Treatment through the SLM Approach: use available resource in the region
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: all the land was returned to its original borders was interaction in the implementation process in a positive way and did not happen leads boiling obstruct the implementation process
charge de travail, disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre
- entrave
Hard work and lack of labours
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Grouping together to rebuild the break down walls of stone of the terraces (with no money as a help)
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Males over 12 years old
The local community they work collectively and in a positive and self-funded (self-effort) used the available resources available in the region. Approach involves the entire community in all social classes.
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
It came be done through meetings and discussion to select the best method for implementation.
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | aucun | |
| planification | aucun | |
| mise en œuvre | aucun | |
| suivi/ évaluation | aucun | |
| Research | aucun |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- les exploitants des terres seuls (auto-initiative)
Expliquez:
Exchange experiences especially of what concern of indigenous knowledge to activate them because they are practical and most the farmers familiar with them
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Non
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- non
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations
technical aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by other through observations
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Non
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 2 000-10 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (The local community should be responsible for cost of the approaches and technology): 100.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
protect the land from erosion and drought mitigation
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
increased productivity as a result of the availability of irrigation water, reduce maintenance costs and maintain on the ground
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
by increasing the rate of production and hence poverty alleviation
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
Increase the amount of production
- conscience environnementale
- Protect the land from erosion
ِِAs a result of floods
- Drought mitigation
Increase soil moisture
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- non
Si non ou incertain, spécifiez et commentez:
- Find easy ways to do the production process, even at the expense of resources of future generations, the most important ground water that drains a result of drilling wells for the purpose of irrigation, which led to the neglect of maintenance operations may not be great at the present time, but may increase in the future, leading to the extinction of these techniques
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The rehabilitation of degraded agri terraces were carried out by the local farmers who constitute a teamwork (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Development of domestic legislation and to ensure the continued support of collective action) |
| building techniques using the resources available in the region |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Report of traditional knowledge and customs (sallam, et al, 2008)
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Building Walls's stones to protect lands and building … [Yémen]
use the stones to build walls around agricultural terraces to protect them from erosion and make outlets (Spillway) to discharge excess water and prevent the destruction of the stands
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal

Diversion construction with gates and distribution channels [Yémen]
The stone existed in the region are used for building diversion constructions to raise the level of wadi bed to the level of the inlet of the cultivated land that need to be irrigated from water harvesting in addition to distribution channels in the fields
- Compilateur : ahmed algalal
Modules
Aucun module trouvé