Dissemination of Soil Test Results to Farmers through a Participatory Approach [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Santosh Gupta
- Rédacteurs : Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir
- Examinateurs : Udo Höggel, Joana Eichenberger
Mitti ki namuna
approaches_6698 - Inde
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Dissemination of Soil Test Results to Farmers through a Participatory Approach: 18 juin 2023 (inactive)
- Dissemination of Soil Test Results to Farmers through a Participatory Approach: 14 septembre 2023 (inactive)
- Diffusion des résultats d'analyses de sol aux agriculteurs à travers une approche participative: 11 avril 2024 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - KenyaNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
22/02/2023
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
A systematic approach has been developed under the project for collecting soil samples, conducting the soil test results, issuing soil health cards, building the capacity of farmers to interpret the soil health card and apply the required nutrients to the soil based on the soil test result
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
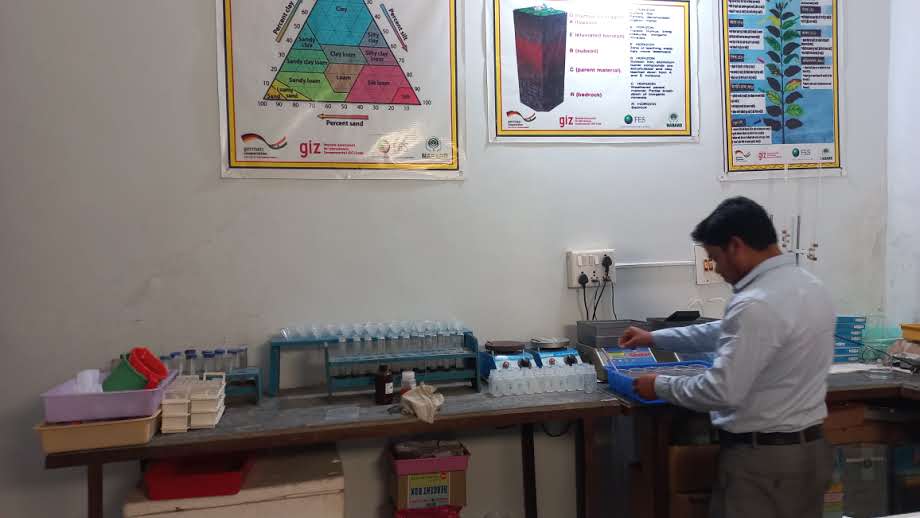
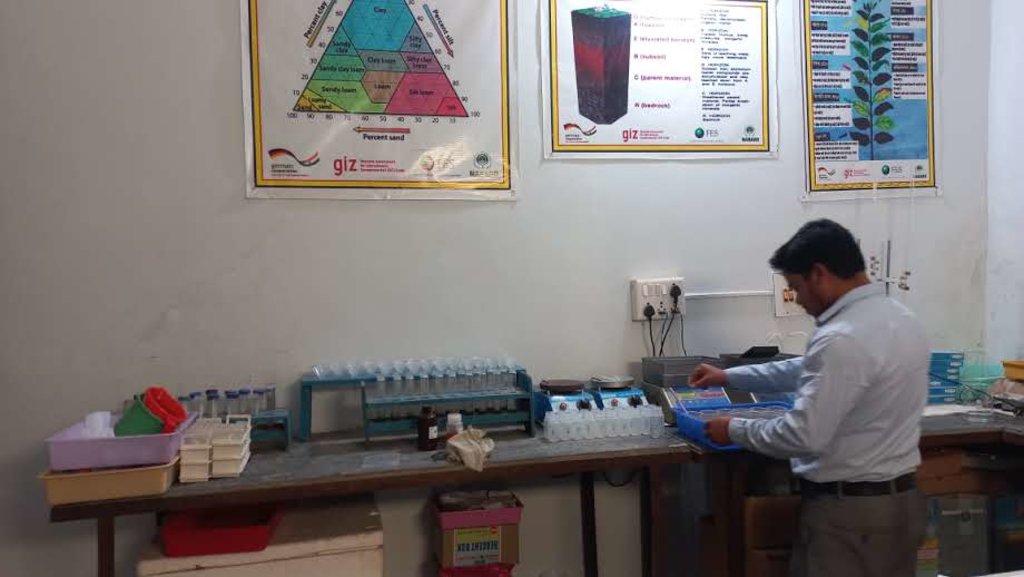
Soil testing is a pre-cultivation activity that gives a good idea about soil structure and mineral composition ratios. The essential nutrients required for various crop growths can be estimated during soil testing. The Foundation for Ecological Security (FES) has established a state-of-the-art soil testing laboratory for testing soil samples in India's Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh. The soil test lab was established in 2016 with a capacity to test 1500-2000 soil samples every year. Based on a soil sampling process, it takes around 2 days to generate the soil test results for 20 soil samples. Collected soil samples are tested for 12 parameters. These parameters include Soil Ph, Soil organic carbon (SoC), electrical conductivity (EC), major nutrients like nitrogen(N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), secondary nutrients like sulphur, magnesium, iron, boron, zinc, manganese, and copper. Based on the soil test report, farmers are issued a soil health card with crop-specific recommendations for additional chemical and organic inputs into the soil.
To ensure the accuracy of the sampling process and proper dissemination of generated results among the farmers, FES has developed a very systematic process which consists of:
•the collection of soil samples
•the analysis of collected soil samples in an FES lab
•the issuance of soil health cards
•the interpretation of soil test results
•noticing of test results to farmers
•farmers are able to implement practices, recommended by the test result
The entire process, from soil sampling to dissemination, is briefly mentioned below:
•Developing the grids for a random collection of soil samples: The first step is to develop a geographical grid for collecting random samples based on predefined parameters. In the irrigated areas, samples are drawn in a grid of 2.5 ha, while in rainfed areas, samples are drawn from a grid of 10 ha. While developing the grid, farmers' fields are categorized into the following parameters. Each of the parameters is assigned a specific score, and based on the obtained score, each farmer’s land is given a specific number for easy identification on soil maps. These include the a) type of soil, b) type of field, e.g., upland, medium land, or low land, c) crop cycle (Single crop, multiple crops) d) The slope of the field. This entire exercise is a soil survey exercise used to develop soil maps for each geographical unit village, block, district.
•Collection of soil samples: From each classified grid, soil samples are collected from 5 different locations between the harvest of one crop and the sowing/planting of another crop when fields are vacant. The soil samples are collected at a depth of 5 to 15 cm. All the collected soil samples are mixed repeatedly, and a portion of the collected soil is kept aside each time. The mixing process is followed 5-6 times to ensure collected soil samples represent the entire area. Finally, around 500 gm of soil is packed in plastic polythene based on the above grid parameters.
•Soil sample analysis: Collected soil samples are transported to the centralized soil test lab in Mandla (MP) for testing and analysis. The samples are analyzed by qualified lab personnel. The analysis process for the above mentioned 12 parameters takes around 2 days (considering 8-9 working hours in a day).
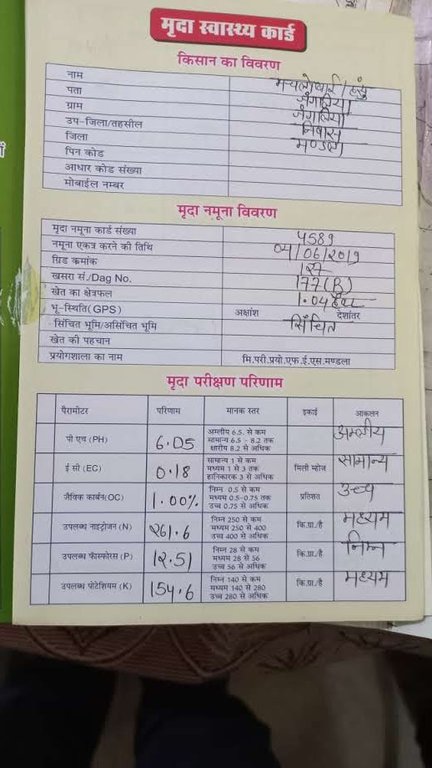
•Issuance of soil health card: Based on the results obtained from the analysis, soil health cards are issued to farmers. The soil health card contains the following information in the local language (Hindi) so that farmers understand the test results and their implications:
a.Basic details of the farmer: name, address, soil grid, GPS coordinates, field identification number, etc.
b.Soil test results for above mentioned 12 parameters: results of the soil test in their respective units, standard numbers, grading of the obtained result (acidic/saline for PH., high, medium, low for other parameters)
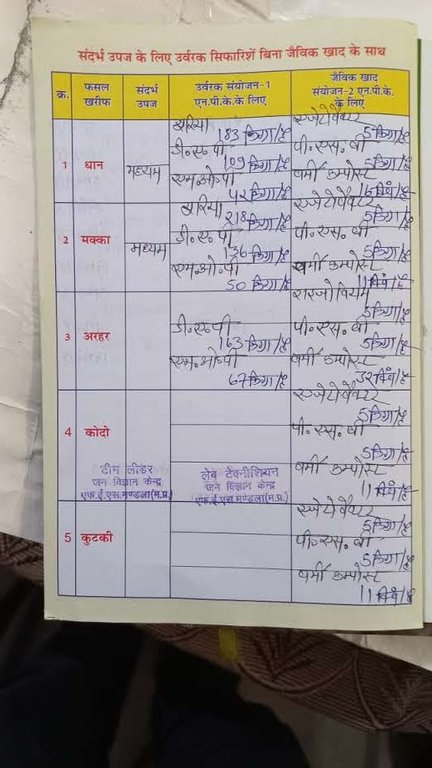
c.Crop-wise soil correction recommendations for major crops: recommendations for synthetic fertilizers, biofertilizers, and compost
d.Pre-printed information with photos for identification of nutrient deficiency in the crops.
•Dissemination of soil health card to farmers: To ensure that farmers understand the results and implement the practices at their field, local community resource persons reach out to every farmer to make them understand the soil test results and closely monitor their farmers’ practices across the crop stages. Farmers are also encouraged to maintain farm diaries for their practices. They are also trained in the preparation of various bio-inputs and compost for application in their field.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
All the photos have been taken at the soil test lab of the FES.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Madhya Pradesh
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Mandla
Commentaires:
Mandla, Madhya Pradesh, India
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2018
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
1. Ensure judicious usage of fertilizers and micronutrients based on the requirement of the soil
2. Ensure quality soil testing and dissemination of results
3. Build farmers' capacity for interpretation of soil health cards
4. Develop soil maps based on the in-house results from the soil test lab
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
cadre institutionnel
- favorise
The entire dissemination methodology is done through community-based organizations
collaboration/ coordination des acteurs
- favorise
Several stakeholders, such as FES, farmers, equipment suppliers, the scientific community, and soil scientists, are involved in the project
cadre politique
- favorise
Soil test results are an excellent input for the agricultural policies around fertilizers, farming practices, and soil health-related policies
gouvernance foncière (prise de décisions, mise en œuvre et application des décisions)
- favorise
A soil health card is an excellent tool for farmers to decide on the usage of fertilizers and the kind of farming practices to implement
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- favorise
Soil health cards inform the farmers and the project management team so to decide on required interventions and farming practices
marchés (pour acheter les intrants, vendre les produits) et prix
- favorise
Very much relevant as soil test results quantify the number of farm inputs to be applied to the farm
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Farmers from the project area
Soil samples were collected from the field of farmers. They have actively participated in the projects for managing the soil samples, participating in the capacity building programs, and implementing the recommended practices.
- organisations communautaires
FES, the implementing NGO, have formed the Villages Environment Committee (VEC) in their project villages as community-based organizations
VECs facilitated the implanting of a project by mobilizing the communities as and when needed. FES reached farmers through the VECs, to collect the soil samples or disseminate the information. VECs also facilitated community-level implementation activities.
- Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles
SLM Specialist
Documentation of the activities
- ONG
Foundation for Ecological Security (FES) is a well-known NGO registered in India. It focuses on ecology-related issues and works closely with farmers and forest-based communities.
FES played an essential role in the project. Primary activities were as follows:
1. Establishment of soil testing laboratory and hiring the technical team to conduct the soil test lab
2. Collection of soil test samples and building the capacity of farmers on soil sample collection
3. Conducting soil test results and issuance of soil health cards to farmers
4. Developing a soil health map for the project areas
5. Capacity building of farmers for the interpretation of soil health cards and ensuring the implementation of recommended practices
- organisation internationale
GIZ, India
Funding of the project
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
Foundation for Ecological Security
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | passive | The FES led the initiation of discussions with its donor organizations. Discussions with communities to understand the challenges and opportunities. |
| planification | interactive | Local community institutions played a significant role in the entire process of planning and execution |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | Farmers and community-based institutions were actively involved in implementing multiple activities under the project, such as collecting soil samples, supplying them to the soil test labs, and Implementing the recommended practices. |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | Community-based institutions played an important role in monitoring individual farmers for implementing the recommendations provided to farmers. They also monitored the results regarding crop progress, crop productivity, and improvement in soil health status. |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- tous les acteurs concernés dans le cadre d'une approche participative
Expliquez:
All actors, including the farmers, CBO, NGO, and soil scientists, mutually discussed and decided on the implementation of technology as all stakeholders were equally crucial for the effective and result-oriented implementation of the technology.
Spécifiez sur quelle base ont été prises les décisions:
- l'évaluation de connaissances bien documentées en matière de GDT (prises de décision fondées sur des preuves tangibles)?
- les résultats de recherches?
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
Si pertinent, spécifiez le genre, l'âge, le statut, l'ethnie, etc.
Both male and female farmers in all age groups were trained under the project. The majority of the farmers were from tribal communities.
Formats de la formation:
- entre agriculteurs (d'exploitants à exploitants)
- zones de démonstration
- réunions publiques
Thèmes abordés:
1. Importance of soil testing for the judicious use of fertilizers
2. Methods for soil sample collection
3. Interpretation of soil health card
4. Dissemination of soil test results and ways and means for implementing the recommended practices following organic and non-organic implementation practices
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
Décrivez/ commentez:
FES has a team of community-based resource persons from the local community and villages to provide advisory services to farmers
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, beaucoup
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Décrivez l'institution, ses rôles et responsabilités, ses membres, etc.
Village-level environment committees were formed to discuss the issues related to environmental concerns, livelihoods, and other social problems at the village level. These committees consist of male and female members representing the entire village.
Précisez le type de soutien:
- financier
- renforcement des capacités/ formation
Donnez plus de détails:
These committees were provided financial support to implement the identified activities based on the provision under the project and proposals submitted by the local committees. FES regularly provides training and handholding support to these committees.
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
The soil health report card is very useful in monitoring of the status of soil health and measuring the impact of various practices and intervention
Si oui, ce document est-il destiné à être utilisé pour le suivi et l'évaluation?
Non
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- écologie
- technologie
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 2 000-10 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Externally funded projects (GIZ)
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Non
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- équipement
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| machines | en partie financé | Different equipment used for testing the soils |
| outils | en partie financé | Different tools are used for collecting soil samples and for soil testing |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
5.5 Autres incitations ou instruments
D'autres incitations ou instruments ont-ils été utilisés pour promouvoir la mise en œuvre des Technologies de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a permis la prise de décisions fondées sur des données probantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Soil health card-based changes in soil management and developing the evidence for soil health monitoring
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré la coordination et la mise en œuvre de la GDT selon un bon rapport coût-efficacité?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Reduced the cost of applying fertilizers and other inputs through a result-based application
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Training and handholding by the team of implementing partners have helped land users to interpret the result of soil health card, collection of soil samples and following the recommended practices
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des autres parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Other stakeholders such as implementing team got information about the outcome of their practices. More importantly, the soil health card was helpful in providing precise information on the application of fertilisers and bio-inputs.
Est-ce que l'Approche a encouragé les jeunes/ la prochaine génération d'exploitants des terres à s'engager dans la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Youths were greatly involved in collection of soil samples
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la rentabilité/ bénéfice, rapport coûts-bénéfices
With soil test results, land users now need to apply only the required nutrients in a specific quantity. This reduced the cost of soil management and fertilisers.
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Soil test results were helpful in preventing and reducing the non-judicious usage of synthetic fertilisers, which was among the major reasons for land degradation in the project area. Also recommendations for both organic and synthetic fertilisers based on the soil health cards helped farmers in replacing synthetic fertilisers with organic fertilisers.
- conscience environnementale
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Yes. The benefit in both reduced cost and improved soil health are the triggers to sustaining the practices. Also, the involvement of local community institutions will also ensure the sustainability of interventions.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Judicious use of fertilizers and pesticides based on the nutrient requirement of soil, as mentioned under the soil health report |
| Separate recommendations for both chemical and organic (bio-inputs) are a good way for land users to make informed decisions |
| Tracing the improvement in soil health status based on the land users' agricultural practices |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Developing the soil maps for the entire area to design appropriate interventions for the project |
| Instead of general recommendations for input application, the soil health card helped develop farmer/village-centric extension services for the farmers |
| Understand the impact of various interventions through periodic soil testing to document what has worked and what has not. Even this evidence can be used to monitor the soil organic carbon content for designing carbon-based projects and/or to access national or international carbon reduction credits. |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Farmers are still unaware of the soil test facility and its benefits | Regular awareness programs along with a demonstration of soil sample collection |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Farmers' strong belief in the application of a certain quantity of fertilizers to ensure better production | This requires specific behavior change campaigns through local demonstration and documentation |
| Government authorities also conduct the soil test and issue the soil health card. However the farmers' experience with such system has not been outstanding. | Put efforts into conveying the difference between both approaches by promptly issuing the soil health card |
| The soil test lab is in the District capital, so farmers in far-away areas may face difficulties in accessing the facility | Explore the option of establishing soil test labs near farmers' locations |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
1
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
5
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
2
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
3
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Operational Guidelines for implementation of CENTRALLY SPONSORED SCHEME SOIL HEALTH CARD
URL:
https://agricoop.nic.in/sites/default/files/GSHC3.pdf
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé